Joints often present unpleasant “surprises” in the form of swelling, pain, crunching or limited mobility. For example, yesterday you easily set your own bench press record in the gym or enjoyed playing beach volleyball, but today, due to severe pain, you cannot pick up a small cup of morning coffee. Or you noticed a suspicious lump near the wrist joint, which does not particularly bother you, but is noticeably increasing in size every day. What is it and where did it come from? Which doctor should I make an appointment with? How to treat the disease? You shouldn’t worry too much ahead of time, but you definitely need to make an appointment with an orthopedic traumatologist. You may have a relatively harmless hygroma.
What is hygroma
Hygroma (synovial cyst) is a synovial bursa of a joint filled with exudate, which has increased in size and has become similar to subcutaneous dropsy. The synovial bursa (sometimes called bursa from the Latin bursa synovialis) is a cavity located in the joint area and filled with synovial fluid. It separates the bones of the joint and soft tissues, protects the joint from mechanical shock, softens the friction of bones against tense muscle fibers and tendons in places of constant flexion and extension.
With hygroma, the synovial bursa is filled with lymphoid infiltrate, serous or hemorrhagic exudate. In this case, the walls of the superficial synovial bursae (located close to the surface of the skin) often become compacted and thickened, and can adhere to soft tissues.
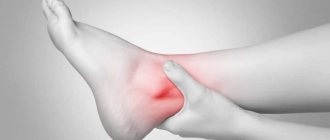
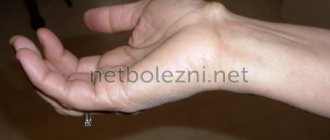
Hygroma can form in the area of any joints, but most often appears on the wrist.
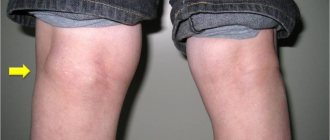
The figure shows a hygroma of the wrist and elbow joint:
Features of the hygroma removal procedure
This type of surgical treatment is performed using local anesthesia. In rare cases, general anesthesia may be used if a longer operation is required. In most cases, surgery lasts no more than half an hour.
At the initial stage, a rubber tourniquet is applied to the damaged limb and anesthetic is infiltrated in the area of the incision, as well as along the edges of the tumor.
Subsequently, a small incision is made in the skin over the formation and a puncture is performed to remove the contents.
At the next stage, the hygroma is isolated from adjacent tissues to its base, after which the protrusion is excised.
At the final stage of the surgical intervention, the synovial bursa in the area of excision is sutured and the resulting wound is sutured. As a result, a tight bandage is applied and the joint is fixed with a plaster splint.
Symptoms
At first, the hygroma has the size of a large pea (approx. 0.5-1 cm), which gradually increases in size. The maximum diameter of the hygroma does not exceed 6 cm. Moreover, the smaller the synovial cyst, the thicker its contents. Large formations usually contain more liquid exudate.
On palpation, an elastic capsule filled with liquid is felt under the skin. If there are no adhesions with soft tissues, then it has limited mobility and moves when pressed, as if moving to the side. The exception is cases when the walls of the synovial bursa are pathologically changed (thickened, compacted, for example, during proliferative processes, hyperkeratosis). In these cases, it is impossible to feel the contents of the bag; it feels like a dense lump.
If the synovial cyst is accompanied by an inflammatory process or has reached a large size, then painful sensations appear on palpation. It compresses all surrounding soft tissues and can pinch nerve endings.
Main indications and contraindications for surgical intervention
The most effective method of treating these formations is considered to be surgical treatment.
There are a number of main indications for surgical intervention:
- rapid growth of education;
- the presence of intense and systematic pain;
- problem of tissue innervation due to compression of nerves;
- loss of motor functions of the joint;
- risk of spontaneous rupture of formation;
- manifestation of inflammatory and purulent processes;
- unaesthetic appearance.
There are also a number of contraindications to surgery, including:
- infectious diseases in acute stages;
- diseases in the stage of decompensation;
- blood clotting problems;
- period of pregnancy and lactation.
Causes of hygroma formation
Hygromas can be congenital or acquired. They can appear at any age in both sexes (children, adolescents, women and men).
The most likely causes of fluid accumulation in the synovial bursa of a joint are the following factors:
- excessive physical activity, especially when working out in the gym without warming up
- joint injuries, recurrent (habitual) dislocations
- performing monotonous, monotonous movements (for example, related to professional activities). This could be the work of a typist on a keyboard, an assembler or packer on a conveyor belt, etc.
- inflammatory, infectious diseases, systemic, autoimmune diseases, metabolic disorders and any other diseases affecting the joints (arthrosis of various etiologies)
Sometimes the reason for the appearance of hygroma is known to the patient, for example, if the “bump” began to grow after an injury with tendon rupture. And in some cases, it is not possible to establish the cause of the pathology because there were no provoking factors. Therefore, we can say with confidence that no one is safe from hygroma. Prevention methods, although not very reliable, are protection from injuries and timely treatment of any diseases that can cause joint pathology.
Unpleasant diagnosis
A benign lump forms on the toe, sole, ankle (above the ankle), shin, foot and knee joint (on the knee and below the knee). Hygroma occurs on the thigh (left and right), in the area of the patella, wrist, calf muscle and other areas. Regardless of the location of formation, the cyst is treated. Let's look at the most common varieties.
Knee-joint
Hygroma of the knee joint, or Baker's cyst, develops in size up to ten centimeters and is formed against the background of complications of rheumatoid arthritis, hemarthrosis, deforming arthrosis. The location below the knee makes it difficult to identify the tumor (among the ligaments and muscles). The neoplasm creates discomfort for the patient when bending the knee. A tingling sensation is felt, turning into intense pain, the source of the sensation is a swelling of the popliteal fossa on the knee joint.
On the ankle
A cyst on the ankle is formed due to joint dislocations, sprains and tendon ruptures. If a lump develops in areas of nerve compression, you will notice a decrease in the tactility of the specified area and a decrease in its activity. Difficulties arise when wearing shoes. The lump on the ankle will have to be removed and the pain will be relieved.
No time for a pedicure
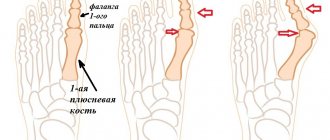
The tumor develops on the toes and can even occur on the little finger. The tumor on the big toe occurs mainly in women. The finger begins to become very bothersome when a hygroma develops on the joint. The reason is wearing narrow shoes with heels and neglecting preventive measures in the form of massages and the use of medications. A sore toe makes it difficult to wear shoes.
On the sole
People with flat feet are at greater risk than others of developing a benign cyst on the sole of their foot. Due to the weakened shock-absorbing function of the arch of the right or left foot, the joint capsules are injured under the condition of constant load on them. The compaction develops immobile and resembles a bone growth. During diagnosis, the neoplasm is confused with a malignant tumor, so the study is carried out carefully.
How dangerous is hygroma? Is it a tumor?
Hygroma is a neoplasm, but does not contain mutated defective cells and cannot degenerate into a malignant tumor. But if the cyst is accompanied by an inflammatory process, then the synovial bursa may become filled with serous,
fibrinous or hemorrhagic exudate. As its quantity increases, unpleasant sensations appear due to the stretched bag and compression of soft tissues, blood vessels and nerves; the process of venous stagnation and neurological pain may begin.
Also, do not forget that a “harmless hygroma” may be a symptom of bursitis or actually be a tumor. Therefore, it is imperative to consult a traumatologist-orthopedic surgeon.
Treatment of hygroma on the leg
Hygroma is treated in a variety of ways.
Methods:
- Conservative,
- Ethnoscience,
- Surgical intervention.
Conservative techniques
Treatment with these methods is used in the initial stages of the disease on the leg, when the patient refuses surgical removal. Unfortunately, conservative therapy often causes relapse of the disease.
Methods:
- Crushing. This method is used very rarely due to its danger and pain. The cyst is crushed, the contents spread inside.
- Puncture. A thick needle is inserted into the body of the cyst, with the help of which the contents are sucked out. Sclerosing agents are injected inside and secured with a pressure bandage. Relapse after such removal occurs quite often.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed by a specialist. May include mud therapy, electrophoresis, ultraviolet irradiation, paraffin therapy.
- Drug treatment. Includes the use of various ointments and lotions. Before use, you must carefully study the instructions for use and consult a specialist.
These techniques allow you to cope with the disease without surgery.
Folk remedies
Treatment with folk remedies for hygroma cannot be considered as the main one. However, additional use of folk recipes will help to cope with the disease faster. How to treat the disease in this way?
Methods:
- A copper coin should be applied to the tumor, secured with a bandage and left for a couple of days. At the initial stage of hygroma on a toe or other part of a limb, this method helps quite quickly.
- Drinking freshly squeezed cabbage juice daily for a month will help get rid of swelling on the ankle or knee joint.
- Before going to bed, place a cabbage leaf smeared with honey on the sore spot.
- Mix equal amounts of honey and aloe juice with the same amount of flour. You need to make a cake from the dough, which is applied to the affected area and fixed with a cellophane bandage.
- Red clay is mixed with a solution of sea salt to form a paste. The resulting ointment is applied to the hygroma and carefully bandaged. When the bandage dries, it is periodically moistened with water throughout the day. Remove for a couple of hours, then reapply.
There are quite a few recipes for folk remedies that can help treat the disease. Care should be taken when using this method to avoid allergic reactions and irritation of the skin.
Surgical intervention
Removing a hygroma on a toe or other area of a limb through surgery is the most effective way to get rid of the disease. This technique is prescribed for certain factors.
Factors:
- Rapid tumor growth
- Advanced stage of the disease
- Compression by the formation of blood vessels and nerves,
- Inflammatory processes, suppuration,
- Severe pain,
- The formation causes severe discomfort when walking and is unaesthetic.
The surgical operation is divided into three stages.
Stages:
- Preparation. Includes various studies - computed tomography, x-ray, biopsy, visual examination, general blood and urine tests.
- Operation. It is performed in a medical facility under local anesthesia. General anesthesia is used in severe cases and when removing tumors in young children. A tourniquet is applied to the limb, the specialist makes an incision in the cyst and removes the contents. The cavity of the formation is sutured, then the wound is sutured and a tight bandage is applied.
- The recovery period includes daily dressings and wearing an orthosis. The sutures are removed approximately ten days after surgery. Full recovery occurs after a couple of months.
Hygroma can be removed using a laser. The operation is performed in the same way as described above, but is less traumatic. Any intervention does not exclude infection from entering the wound or incomplete removal of the hygroma. However, relapses after surgery are quite rare.
Is it necessary to treat hygroma?
A small synovial cyst that does not bother the patient does not need to be treated. If it is caused by overstrain or excessive physical activity, then you just need to create resting conditions for the joint for a while. For this purpose, an immobilizing orthopedic orthosis is used.
For discomfort and moderate pain, conservative treatment is recommended. An orthopedic traumatologist usually prescribes physiotherapeutic procedures that improve blood circulation and lymph outflow in this area, help reduce inflammation and tissue regeneration.
For severe pain, in cases where treatment is ineffective and the cyst continues to increase in size, surgical treatment is prescribed. There are several methods:
- aspiration - removal of the contents of the hygroma through a puncture and synovial membrane
- surgical excision – open abdominal surgery
- laser removal of hygroma
It is not difficult to remove a hygroma, but there is a risk of relapse. Therefore, you first need to find the cause of the fluid accumulation so that the cyst does not grow again after some time. If the hygroma contains purulent exudate, then it is necessary to sanitize the cavity and install drainage and rinse. In any case, you must definitely consult a doctor, and not be treated with dubious traditional methods or wait until it “goes away on its own.”
Causes of hygroma in children
A benign tumor of this type occurs in children, even in newborns and infants. Most cases occur between the ages of 6 and 10 years. The causes of illness in a child are due to physical exertion, pathology of joint development, decreased activity and injuries. The risk of hygroma in an infant is minimal. Neoplasms appear on the knees when the baby crawls and transfers body weight to them.