- Hygroma of the knee joint
- Hygroma of the wrist joint
- Hygroma of the ankle joint
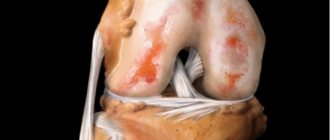
Hygroma is a volumetric formation in the joint cavity filled with mucous, serous, hemorrhagic or fibrinous secretion. Depending on where exactly in the joint capsule the joint hygroma is diagnosed, it can be classified as:
- Superficial hygroma, in which the walls are thickened, uneven and can be equal in density to cartilage, fusing with the underlying tissues.
- Deep, in this case it is located in isolation, since its walls do not reach the walls of the joint capsule.
There are several phases of development of hygroma:
- Serous inflammation, during which lymphoid and lymphocytic infiltrates predominate in the exudate. Overgrowth of connective tissue may also occur. Sometimes areas of necrosis and hemorrhage form.
- Proliferative inflammation, in which granulation appears on the inner surface of the synovial bursa, which forms cords and pockets like a bunch of grapes.
If the hygroma is small, then, as a rule, there is a thick mass inside it. In the case of the formation of a large hygroma, the exudate is often serous and hemorrhagic and contains cholesterol crystals. Such hygromas are also called rice bodies.
Hygromas can develop in all age groups, including children.
What is joint bursitis
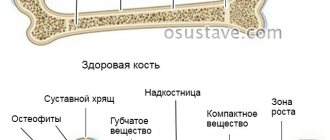
The bursa or joint capsule is located in those parts of the body where there is movement and shock absorption is needed. The joint capsule is a kind of pocket made of a durable outer shell and mucous tissue inside. Its task is to protect the joint from injury, increased friction of moving elements against each other and nourish the cartilage tissue of the joint, which does not have its own blood vessels. To do this, the cells of the inner layer of the bursa produce a special synovial fluid. It contains all the microelements necessary to nourish and moisturize cartilage.
The hip joint has several bursae located on the lateral side of the thigh (trochanteric) and deep within the joint are the iliopsoas and sciatic. Bursitis most often occurs in the trochanteric, ischial, or iliopsoas bursae of the hip joint.
With inflammation, the amount and composition of the lubricating fluid changes. Calcium salts appear in it, the amount of protein increases, there may be traces of blood and inflammatory elements. The fluid itself becomes larger, the joint capsule swells, causes pain and causes limited mobility in the joint.
Traditional methods
Traditional methods of therapy are often used for single-chamber hygroma. With multiple forms of pathology, the use of recipes from the people is dangerous due to the growth of education. For the treatment of the pathology in question, the following folk remedies are used:
- Baths;
- compresses;
- lotions.
There are many safe, effective traditional medicines.
Honey + aloe (compress)
More often people use products made from honey and aloe. These components are taken in equal parts and mixed. Rye flour is added to the finished mass. A cake is formed from the formed mass, which is then applied to the formation in the evening. In order for the therapeutic effect to be more pronounced, you should cover the knee with polyethylene and wrap a warm cloth over it. Remove the application in the morning. This should be done until the cyst disappears.
Cabbage juice
It is taken orally. The juice should only be freshly squeezed. It should be taken before meals. You should drink 200 ml per day. juice
Cabbage leaf + honey (compress)
In the evening you can apply compresses. Use a whole sheet. A small amount of honey is placed on it. The sheet is applied to the affected area. To fix the sheet, use a tight bandage. The compress should be removed in the morning.
Alcohol lotions
This method is often used for hygroma. The patient should apply natural fabric and gauze to the painful area at night (they are moistened with alcohol in advance). After establishing an alcohol compress, wrap the knee with a warm cloth.
Types of bursitis
Depending on the location where the inflammation occurs, there are:
- Trochanteric bursitis of the hip joint is a pathology in the area of the outer protrusion of the pelvic bones, where pain will be felt.
- Ischial - inflammation occurs near the ischial tuberosity. Pain occurs when straightening the leg from a bent position.
- Iliopectineal - this inflammation is characterized by pain and noticeable swelling on the front surface of the thigh.
The most common form is trochanteric bursitis of the thigh (occurs up to two times more often than other types). It can bother women more often due to the anatomical features of the female pelvis - a wider pelvis leads to more intense muscle friction.
Trochanteric bursitis is often familiar to those who are professionally or actively involved in running or cycling at an amateur level, work that requires constant standing.
Depending on the nature and duration of bursitis, it can be:
- Acute - develops over several days, often as a consequence of injury. So acute trochanteric bursitis can be a consequence of falling on one side or a sharp collision (for example, hitting a table with your hip). The acute phase lasts about a month, after which, if not cured, it will become chronic.
- Chronic – a less intense and protracted inflammatory process.
There is also a difference in the reason why bursitis developed. There are:
- Specific inflammations - due to non-infectious factors - joint injuries, heavy and constant load with monotonous movements.
- Nonspecific - it is caused by infectious damage to the joint due to tuberculosis, soft tissue infections and other causes.
The composition of synovial fluid is also important for understanding the cause of the disease and principles of treatment. Based on this criterion, bursitis is divided into:
- Serous.
- Hemorrhagic - the presence of blood in the fluid.
- Purulent is the most dangerous form of acute bursitis with severe pain, rapid development and risk of complications.
Complications.
It is not recommended to open the lump at home due to the high risk of complications. Since when a cyst is injured, fluid can be pressed into the joint cavity and surrounding tissues. After this, the ganglion sheath fuses and it fills up again. Sometimes, in place of one crushed one, several hygromas are formed at once. There is also the possibility of inflammation, as well as suppuration and infection. It is highly not recommended to carry out this operation yourself, due to very negative consequences.
Symptoms
An inflammatory process in the joint - bursitis of the hip joint is manifested by the following symptoms:
- Pain in the thigh when walking, flexing/extending the joint, lying down (especially on the sore side). The most acute pain is at the very beginning of inflammation, and as trochanteric bursitis of the hip joint becomes chronic, the symptoms gradually become less pronounced. With purulent bursitis, everything is different - as the amount of pus in the joint capsule increases, the pain becomes more severe.
- Edema - swelling (diameter can reach up to 10 cm) will be noticeable with bursitis of the trochanteric bursa or anterior. When the internal bags are inflamed, swelling is not visible.
- Impaired joint mobility due to swelling or pain.
- Redness of the skin and an increase in its temperature are not always noticeable signs.
- Symptoms of general intoxication of the body - weakness, fever.
- Inflammation of the inguinal lymph nodes.
The symptoms of hip bursitis in women and men are the same, although the disease itself occurs more often in women (especially with active running). The very moment of injury (with post-traumatic bursitis) occurs with acute and sudden pain and a click. In the future, it hurts to squat, climb stairs, or make rotational movements with your foot.
The course of the disease varies depending on the form of bursitis:
- In the acute form, there is obvious pain, a burning sensation in the joint, and an increase in temperature.
- In chronic cases, there may be no characteristic signs or the symptoms will be mild.
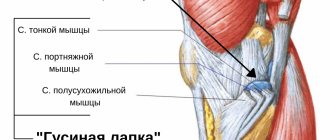
How do hygromas and ganglia appear?
A bulge forms on the wrist joint, which is best visible when the arm is flexed. The skin over the tumor moves quite easily, but the formation itself cannot be moved away. If the hygroma is of an impressive size, then movements in the articular part are significantly limited. Also, the “bump” puts pressure on the tendons and nerves, which will cause pain. In some cases, hygromas go away on their own and do not require treatment. Ganglia grow from tendons and are a rather dense growth, which mainly grows at the base of one of the fingers. However, they are very small and rarely larger than a grain of rice. However, when clenching a fist and other movements, they can cause severe pain. The shape of the nail plate changes. As a rule, this type of synovial cyst occurs in old age as a consequence of arthrosis.
Causes
The main causes of hip bursitis:
- Injuries and damage to the joint and femur due to falls and impacts. The most dangerous cases of purulent and infectious bursitis are injuries with violations of the integrity of the skin.
- Heavy physical activity - standing work, running on uneven terrain, cycling and some other sports.
- Diseases of the spine and joints - arthritis, scoliosis, arthrosis and others.
- Allergies or autoimmune diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, scleroderma and others), when inflammation occurs due to the reaction of one's own immune cells.
- Deposits of calcium or uric acid salts in the joints, for example, with gout.
- Diseases and conditions in which metabolism is disrupted: diabetes mellitus, kidney disease, long-term treatment with steroid hormones.
- Performed operations on the hip joint.
Risk factors for bursitis include:
- Overweight.
- Postural disorders and body asymmetry.
- Flat feet.
- Congenital joint dysplasia.
Features of a child
The causes of the disease, clinical manifestations and complications in children are the same as in adults. The only difference is that in children this disease is extremely rarely associated with joint pathology, more often with genetics, injuries and excessive physical activity. Children's hygromas heal themselves much more often than adults (40% of cases). To do this, limit sports activities and monitor the tumor. For the treatment of children, mud therapy, ultraviolet light, electrophoresis, paraffin baths are used; it is undesirable to use massage, laser therapy, puncture, shock wave procedures, and the introduction of sclerosing and enzymatic agents. If necessary, children undergo surgical removal of the tumor. Up to 10 years of age under general anesthesia, and after that under local anesthesia, just like for adults.
Becker's cyst in a child occurs most often among similar diseases, usually at 6–10 years of age, but can appear in the first year of life, and even during intrauterine development.
Diagnostics
Treatment of hip bursitis begins with diagnosis. The doctor must make sure that it is bursitis and not another disease with similar symptoms. It is also necessary to understand the nature of inflammation - depending on the cause, different treatment will be required. Post-traumatic bursitis requires a mandatory reduction in the load on the joint, and infectious bursitis requires the use of antibiotics.
During the consultation, the doctor conducts an examination and learns in detail about the existing complaints and the characteristics of their occurrence. In addition, more accurate diagnostic methods are needed:
- Blood and synovial fluid analysis.
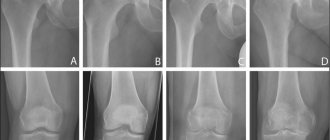
- X-ray to evaluate pathologies in the joint - osteophyte deposits or others.
- Ultrasound or MRI are studies that allow you to evaluate soft tissues, the processes occurring in them and blood circulation in the joint area.
Clinical picture
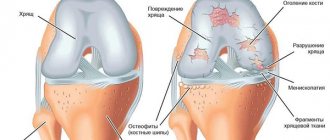
Often a person is not aware of the presence of a hygroma in the knee joint: the compaction does not cause any inconvenience other than an aesthetic one. Hygroma is not capable of degenerating into a malignant tumor, but there is a possibility of it increasing in size up to 6 cm in diameter. In this case, the asymptomatic course is replaced by a clinical picture of inflammation.
The first sign of pathology is the formation of a small localized tumor, clearly visible under the skin. In most cases, only one hygroma is formed, but sometimes a person is diagnosed with several lumps in different joints. Unlike synovitis, bursitis, and malignant neoplasms, hygroma has clear boundaries.
It can be soft, elastic or hard. The seal is not interconnected with the epidermis, so upon palpation the skin easily moves. As the disease progresses, patients complain of the following symptoms:
- pain and discomfort that occurs when trying to bend and straighten the knee;
- decreased range of motion in the joint;
- increase in pain intensity with increased physical activity;
- irradiation of pain to the ankle area after physical activity.
The severity of pain depends on the location of the hygroma and its size. As the compaction increases, it begins to irritate sensitive nerve endings and compress muscle fibers. Therefore, as the pathology progresses, the pain gradually intensifies.
Usually the condition of the skin over the lump does not change. But people with dry, irritation-prone epidermis may experience flaking. The skin becomes rough, red, and cracks. Another feature of hygroma is that after increased physical activity it increases, and after a few hours its size decreases.
Treatment
Complex conservative therapy is used, which may include:
- Drug treatment of hip bursitis - depending on the symptoms, painkillers, anti-inflammatory drugs, glucocorticosteroids and antibiotics are prescribed (for purulent and infectious inflammation). Medicines can be in different forms of release, administered by injection, and their effect will be enhanced by physiotherapeutic procedures.
- Physiotherapy using various methods: laser, magnetic and ultrasound therapy, electrophoresis, galvanization, darsonvalization, procedures with interference currents and other physiotherapeutic methods at the discretion of the doctor. They improve blood circulation and lymphatic drainage in the area of inflammation, provide pain relief, reduce inflammation, relax muscles and enhance the penetration and effect of drugs.
- Taping, wearing an orthosis and other methods to reduce the load and support the joint, ensure its immobility - this is especially effective for new-onset acute bursitis.
- Acupuncture (acupuncture, acupuncture) – effects on biological active points on the body.
- Therapeutic massage and manual therapy are procedures that effectively reduce pain, swelling and serve for the treatment and prevention of a wide variety of joint diseases.
- Physical therapy is a set of exercises that will speed up the healing process. They activate blood circulation and lymph flow, reduce pain and inflammation. Treatment with movement is especially important for the chronic form of the disease and prevention of relapses. Measurement is important - not every exercise will help. With bursitis that appears due to heavy physical activity, on the contrary, you need to provide rest to the joint and reduce stress. What exercises will the exercise therapy doctor recommend, and the training itself in the exercise therapy room with an instructor will be more effective and safe than independent exercise at home.
- Surgical intervention - drainage of pus from the bursa and washing of the capsule with antiseptic drugs, antibiotics, removal of the bursa in case of acute inflammation with the risk of rupture of the bursa membrane and spillage of pus into adjacent periarticular tissues. Thus, surgical treatment of trochanteric bursitis of the hip joint allows a person to return to physical activity without restrictions several months after treatment.
In general, the prognosis for the treatment of bursitis is positive - inflammation can be relieved by various methods and complications such as tissue sepsis, the formation of fistulas, the development of arthritis and osteomyelitis and other pathologies can be avoided. But much depends on the patient himself - how quickly he sought help, how he adheres to the doctor’s recommendations.
Therapy is aimed not only at relieving inflammation and improving mobility in the joint, but also at treating the cause of inflammation so that there are no relapses. It determines which doctor treats hip bursitis - only an orthopedic traumatologist or will require the participation of an immunologist and other doctors.
Operation
When treatment of hygroma of the knee joint without surgery does not give the desired effect, surgical types of therapy are used. Surgery for hygroma is prescribed due to the likelihood of complications. The tumor is benign in nature, reaching a certain size, and puts pressure on the nerves and blood vessels. In this case, the blood supply to the affected area deteriorates, and various complications are possible.
Therapy without surgery
Sometimes after non-surgical therapy, there are no results. In such cases, surgery is necessary. For hygroma of the knee joint, surgery is prescribed by specialists only if there are certain indications:
- Rapid growth of formation;
- the size of the tumor is too large;
- the presence of pain that cannot be tolerated.
For hygroma of the knee joint, surgery is performed using one of the following methods:
- Bursectomy. The surgeon makes the incision using a scalpel. Through the created access, he deletes the formation. The efficiency of this method is quite high. This is explained by the fact that at the same time the specialist removes the tumor and its base. But there is a minus. This is a complex rehabilitation, because it will require measures aimed at healing the wound;
- laser therapy. A special feature of this method is the evaporation of the formation using laser beams. In this case, the patient does not need rehabilitation. This method is often used because of its safety. Laser therapy can be used to treat a wide range of patients. There are no scars after the procedure.
- Any surgical intervention is performed using anesthesia. After removing the hygroma, a fixing bandage is applied to the knee area. An orthosis may be used. This device is necessary to immobilize the joint and speed up the rehabilitation process.
- The use of endoscopic excision of the cyst is considered effective. This approach significantly reduces the rehabilitation period.
Prevention
You can reduce the risk of inflammation of the joint capsule or the development of relapses using preventive measures. Effective:
- Moderate physical activity.
- A balanced diet so that the cartilage tissue receives all the necessary nutrients.
- Maintaining a normal weight - every extra kilogram increases the load on the spine and joints.
- Maintaining immunity by such methods as a daily routine, adequate sleep and rest, a balanced diet, walks in the fresh air and other measures.
- Wearing comfortable orthopedic shoes, maintaining posture.
Who is diagnosed with the disease more often by doctors?
Doctors detect this pathology in workers of the following professions: loaders, postmen, teachers. Cases of development of pathology in women are more common. Hygroma of the knee joint in children is often caused by a knee injury.
Often the disease in question manifests itself with the development of an existing joint disease (deforming type of arthrosis, rheumatoid arthritis ). Hygroma of the knee joint can develop in children and adults under the influence of various factors ( arthrosis , increased loads on the joint). Therefore, experts draw attention to the fact that people should be more attentive to their health.
Treatment of bursitis at the Kuntsevo Diagnostic and Treatment Center
Specialists from the Kuntsevo Multidisciplinary Medical Center are ready to help in the diagnosis and treatment of a wide variety of diseases. We work according to the principles of personalized medicine, using innovative techniques with proven effectiveness.
The clinic has high-tech diagnostic, treatment and rehabilitation facilities. We are confident in the accuracy of the diagnoses and the effectiveness of the prescribed treatment and its results.
We work daily at the address: Moscow, st. Partizanskaya, 41. Phone for appointments and consultations: +7 (495) 480-75-77.
Diagnostic measures
If there is a suspicion that the pathology in question has developed in an adult or child, an examination in a clinic is required. Research will help in making an accurate diagnosis.
At the very beginning, the surgeon examines the person seeking help. At the same time, he studies the anamnesis. The data obtained already make it possible to make a preliminary diagnosis. To confirm or refute it, the doctor refers the patient to a number of additional diagnostic measures:
- Radiography. This diagnostic method is prescribed in most cases;
- ultrasonography. This diagnostic method is considered very informative. It allows for a complete examination of the tumor. The doctor can evaluate the structure of the hygroma;
- Magnetic resonance imaging. This diagnostic method is necessary when the doctor suspects a nodular structure of the formation. Diagnostics makes it possible to accurately determine the contents of the tumor;
- neoplasm puncture.
Differential diagnosis of the pathology in question may also be necessary. The doctor may prescribe a differential diagnosis with other benign tumors, as well as with tumor-like formations of soft tissue:
- Traumatic cysts (epithelial);
- atheromas;
- lipomas.
After the doctor examines the results of all the studies performed, he selects the appropriate method of therapy.