To coordinate the work of the peripheral nervous system, several large plexuses are formed, consisting of individual branches of the radicular nerves. In the region of the spinal column there are the cervical, brachial, lumbosacral plexuses and the cauda equina. Each of them breaks down into sections, trunks and branches. Their axons are responsible for the innervation of individual parts of the body.
Plexopathy is a pathological condition in which the structure of a particular nerve plexus is affected. Depending on the location, it is divided into cervical, brachial and lumbosacral. Compression of the cauda equina is classified as a separate category and is called a syndrome. It occurs mainly against the background of osteochondrosis.
Other types of plexopathy can be triggered by injuries, compression due to the development of infiltrate or tumor, compression by a displaced intervertebral disc or vertebral body. A common cause is cicatricial deformation of the ligamentous and tendon apparatus that occurs after traumatic exposure. Scar tissue puts pressure on the nerve fiber structures and plexopathy develops.
The long course of this disease leads to muscle paralysis and the person loses working capacity. If the nerve plexus atrophies, it will be very difficult to restore its functionality. In the early stages, complete recovery is possible through the use of manual therapy methods.
If you have signs of plexopathy in one area or another, we recommend that you make an appointment with a neurologist as soon as possible. This specialist will be able to prescribe tests that will allow you to make an accurate diagnosis. A treatment plan will then be developed.
In Moscow, you can make an appointment for a free appointment with a neurologist at our manual therapy clinic. After making a diagnosis, the doctor will talk about the prospects for using the techniques in your individual case. To make an appointment for a free appointment, just call the clinic administrator and agree on a time convenient for your visit.
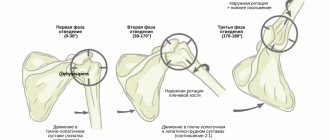
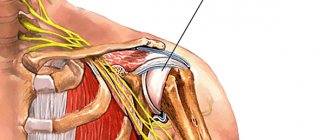
Brachial plexus plexopathy of the upper limb
Brachial plexopathy is the most common form of the disease, since the nerve ganglion is located in a place that is constantly at risk of traumatic injury.
Very often, brachial plexus plexopathy is the result of an obstetric error - the baby comes out incorrectly during birth, and the doctor retracts his arm, damaging the node. Erb's syndrome subsequently develops, which consists of paralysis of the deltoid muscle. It becomes impossible to perform actions to move the direct body away from the body.
Plexopathy of the shoulder joint develops when the C5-C6 radicular nerves are damaged, resulting in paresis of the biceps brachii muscle. Concomitant paralysis of the supinator may occur, which also entails the inability to flex the upper limb at the shoulder joint.
Partial plexopathy of the hand develops when the C3 radicular nerve is damaged. In this case, insufficiency of the functions of the supraspinatus and infraspinatus muscles develops. Circular rotation of the shoulder joint and rotational movements of the arm become difficult.
Dejerine-Klumpke syndrome with cervicobrachial plexopathy develops in case of damage to the C8 root. Such upper plexopathy leads to the fact that a person cannot move the hand and its fingers, and fine motor skills of the hand on the affected side are completely lost.
With injuries, total plexopathy of the upper limb often develops, in which tendon reflexes are absent and it is impossible to make any movements with the fingers, hand, forearm and shoulder.
In some cases, plexopathy of the shoulder is a sign of the development of lateral amyotrophic dystonia. This is a serious disease that leads to gradual paralysis of all muscles of the body and death. Therefore, if the first clinical symptoms of brachial plexopathy appear, we recommend that you immediately consult a neurologist. The doctor will conduct all the necessary examinations and prescribe effective treatment that will stop pathological changes in the body.
Causes
Plexopathy has a neurological origin. Its development is determined by the following factors:
- Mechanical injuries, wounds, sudden pulling out of an arm or leg. Post-traumatic destruction of nerve fibers is the most common cause of plexitis. Neuronal clusters can be damaged by a fracture of the clavicle bone, sprain, dislocation of the joint area, a strong blow to the shoulder, rupture of ligaments, or penetrating wounds. Pathology can also develop with constant minor injuries - for example, with constant use of crutches or working with certain tools.
- Birth injuries.
- Compression by neoplasms - tumors, hematomas, aneurysms , etc. In bedridden patients, the cause of the disease may be a prolonged stay of the limb in an uncomfortable position.
- Poisoning with various toxins .
- The influence of infection in the development of infectious diseases ( herpes , tuberculosis , syphilis ).
- Metabolic disorders due to diabetes and other endocrine disorders.
- Autoimmune disorders.
- Diseases of the cervical spine. Due to protrusion , displacement of the vertebrae or intervertebral herniation of the cervical discs, compression of the roots and an inflammatory reaction occur. Osteochondrosis can also lead to plexitis .
- Hypothermia, too much physical exertion.
- Hyperabduction syndrome is a pinched nerve bundle during sudden abduction of the shoulder joint.
- Costoclavicular syndrome is the formation of additional cervical ribs.
Cervical plexopathy
The cervical nerve plexus is located at the level of the C2-C3 vertebrae. It is responsible for the muscles of the back of the neck and shoulder girdle, the skin of the scalp and part of the face. A large branch of this plexus extends inside the chest to the diaphragm. That's what it's called - diaphragmatic. Regulates the functioning of the muscle fibers of the diaphragm and participates in the breathing process.
Cervical plexopathy is relatively rare in neurologist practice. During its development, the following clinical signs are noted:
- paralysis of the muscles of the neck and collar area, which entails the inability to make certain movements of the head;
- soreness in the back of the head;
- the appearance of a burning sensation and tingling sensation in the scalp;
- disruption of the process of swallowing solid food and liquids, since this node is responsible for the innervation of the supraglottic muscle;
- soreness in the area of the auricle and mastoid processes;
- attacks of hiccups that do not go away;
- disruption of the abdominal breathing process (the patient breathes mainly due to the expansion of the chest volume).
When symptoms of cervical plexopathy appear, it is necessary to begin treatment in a timely manner, since there is a high probability of developing serious complications associated with ischemic processes in the structures of the brain and myocardium.
Prevention
To prevent elbow tendinitis, do not overload the joints, avoid repeated monotonous movements, group correctly when lifting weights, do not make sudden movements, warm up your muscles before training.
To increase the strength and elasticity of tendons, include beef, beef liver, eggs, vegetable oils, dairy products, fish, bell peppers, and nuts in your diet.
Fatty foods, black tea, coffee, chocolate, sorrel, radish, as well as hormonal contraceptives block the absorption of calcium, which is necessary for the functioning of muscles, ligaments, and tendons.
Important! A drug based on long-acting hyaluronic acid “HYAL-IN PROLONG” stimulates the metabolism of connective tissue structures, accelerates regeneration in case of microtrauma, and prevents inflammation. Indicated for long-term preventive use by athletes during professional activities with a high risk of tendinitis.
Timely initiation of comprehensive treatment of tendinitis will avoid surgical intervention. Elbow pain indicates the need for medical examination and treatment. The earlier therapy is started, the more effective the treatment and the more favorable the prognosis.
Lumbosacral plexopathy
At the bottom of the spine there are three plexuses (lumbar, sacral and cauda equina). The lumbar nerve plexus is formed by the branches of the Th12 and L1-L3 radicular nerves. The sacral plexus includes branches of the roots S1-S4.
In most cases, lumbosacral plexopathy develops against the background of degenerative dystrophic disease of the intervertebral discs with their pronounced protrusion and hernia. Protrusion of the annulus fibrosus or nucleus pulposus puts significant pressure on the plexus structure. This provokes the development of dystrophy and disruption of innervation function.
Lumbar plexopathy develops due to the negative effects of the following reasons:
- injuries (bruises, sprains of tendon and ligamentous tissue, compression fractures of the vertebral bodies and their spinous processes, dislocations and subluxations);
- infectious inflammatory processes in the abdominal cavity;
- pregnancy in violation of the recommendations of the attending physician and significant discrepancy of the pelvic bones;
- aortic aneurysm and other vascular pathologies that have a compressive effect on the plexus tissue;
- systemic vasculitis, lupus erythematosus, scleroderma, ankylosing spondylitis and other rheumatoid processes;
- tumors in the pelvic cavity, abdominal cavity and paravertebral space;
- abscesses and hematomas, lipomas and atheromas;
- toxic effects of heavy metal salts, certain types of pharmacological drugs, arsenic, etc.
Lumbar and sacral plexopathy at the initial stage of its development manifests itself in the form of severe pain, localized in this area and spreading along the anterior and posterior surface of the thigh. It is not uncommon for pain to radiate to the groin area. As the disease progresses, gait changes and intermittent claudication appears. A person begins to avoid serious physical activity on the lower limbs.
During the paralysis stage, there is first a feeling of severe muscle weakness in the legs. Then there is a feeling of impaired skin sensitivity with the concomitant appearance of paresthesia. The color of the skin changes to pale. They become dry and peeling appears (this sign indicates a violation of tissue trophism).
If timely treatment is not started, complete paralysis of the lower extremities develops very quickly, and large joints of the legs begin to collapse. It is very difficult to restore the functionality of the sacral and lumbar plexus. There is a high probability of death due to paralysis of the small and large intestines and bladder.
General information
Plexitis is a pathological condition of the branches of the nerve plexus, which has a nonspecific inflammatory nature. The disease can affect different nerve plexuses, depending on which plexitis of the cervical, brachial, and lumbosacral plexuses is diagnosed. In addition, plexitis includes solaritis - damage to the solar plexus.
The code for MBK-10 is G54 (damage to the nerve roots and plexuses G54). Unilateral lesions develop more often; bilateral lesions are less common. The bilateral form is more difficult to treat, since longer rehabilitation is required and the patient feels worse, suffering from weakness and severe pain. The disease most often affects people of working age – from 20 to 60 years. This disease is often confused with neuralgia . However, the main difference is that with plexitis, the nerve plexus and its parts become inflamed, and with neuralgia, the tissues surrounding the nerve become inflamed.
As a rule, brachial plexopathy is a secondary or concomitant pathology. How exactly the disease manifests itself, why it develops and how to treat it will be discussed in this article.
Gymnastics
Exercises for recovery:
- - initial position - standing or sitting. Raise your shoulders up and down. Perform 8-10 times;
- - initial stance - similar. Bring your shoulder blades together and then return to the original position. Do this 8-10 times;
- - the starting position is similar, hands are lowered. Raise them, hands to shoulders, spread elbows to the sides, then lean them back against the body. Circular movements of the arm bent at the elbow clockwise and counterclockwise. Perform 6-8 times;
- - starting position is the same as in previous exercises. Bend the injured arm, straighten it, move it to the side (straight or bent at the elbow), return to its original position. Do 6-8 times;
- - starting position is similar, bending towards the injured limb. Circular movements with a straight arm clockwise and counterclockwise. Perform 6-8 times;
- - initial stance - similar. Throw your hand back and forth. Do 6-8 times;
- - the initial pose is similar. Swing forward and backward with both hands and cross in front of you. Do 6-8 times;
- - initial position - similar. Lean forward. Bend the injured limb at the elbow and straighten it using the healthy one. Do 5-6 times;
- - starting position is similar. Circular rotations in the elbow joint in both directions. The uninjured part of the body must be supported by the sick one. Perform 6-8 times;
- - initial stance - similar. Turn your forearm and hand with your palm towards you and away from you. Do this 6-8 times.
Medical physical education classes are carried out 6-8 times a day.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
Physiotherapy plays an important role in recovery. Its use allows you to quickly restore tissue, relieve inflammation, tone muscles, and reduce pain.
The most commonly used treatments are ultrasound, currents, paraffin therapy, cold therapy, and the introduction of subcutaneous medicinal solutions through electrophoresis. Mud applications and laser therapy are also popular.
After the acute symptoms of the pathology disappear, patients are prescribed a course of therapeutic exercises in order to restore the normal functioning of the muscular system. The standard complex looks like this:
- Reduction and dilation of the shoulder blades in a standing position. The pose should be as relaxed as possible. Repeat up to 10 times.
- Raising and swinging your arms above your head, imitating the movements of trees during strong winds. Repeat at least 7 times.
- Circular rotation of the shoulders in different directions in a standing position. Repeat for 30 seconds.
- Raise your arms perpendicular to the floor and perform “scissors” for 20 seconds.
- In a standing position, raise your shoulders towards your neck and head. Repeat the exercise 10-15 times.
The entire complex should not last more than 10-15 minutes. All movements must be performed slowly. During the process, cramps may occur in the affected limb, which disappear by the 3-4th session.
Diagnosis of plexitis
The first stage of diagnosis is palpation and questioning of the patient.
This problem is usually addressed to a neurologist. To make a diagnosis, the following steps must be taken:
- Palpation of the sore spot to differentiate the diagnosis from neuralgia.
- Determining the affected area using trigger points.
- Electroneurography is a hardware method for studying the passage of impulses along nerve fibers.
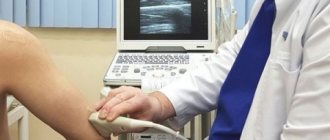
- Ultrasound of the shoulder joint to check for soft tissue damage.
- Complete X-ray of the affected arm, as well as fluorography of the lungs to rule out a growing tumor.
- Blood tests - general and biochemical, including sugar.
- MRI or CT.
The most effective way to confirm plexopathy is an MRI. It is prescribed when other data do not confirm damage to the nerve plexus, but also do not refute it.
Treatment methods
The medications are prescribed by the doctor based on the cause of the disease.
Brachial plexopathy is treated depending on the cause that caused it:
- If a tumor is detected, surgery is prescribed. When nerve fibers are damaged, plastic surgery is performed.
- Infectious plexitis is treated with antibiotics as well as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to relieve pain and swelling.
- Plexopathy of viral etiology can be eliminated by taking vitamins, antiviral drugs, and immunostimulants of plant origin.
- Post-traumatic plexitis varies in severity. In case of a fracture, the arm is fixed in a cast and bandage, immobilized to create rest for the muscles of the shoulder girdle.
- If there is a metabolic disorder, it is necessary to consult an endocrinologist and prescribe a treatment regimen for the underlying disease.
Birth injuries must be treated immediately, since the recovery potential in childhood is much higher.
For severe pain, a drug blockade is prescribed, which lasts from several hours to several days.
Physiotherapy, exercise therapy, massage
You need to start developing the joint under the supervision of a specialist.
Restoring the lost functions of the brachial nerve plexus can begin after the pain has been relieved. This may take a whole week if the cause of the pain is an ordinary bruise or a minor accident.
To improve blood circulation, massage and lymphatic drainage procedures are prescribed (the massage is done from the fingertips to the shoulder). After 3-4 days, the swelling disappears and the pain goes away.
Therapeutic exercise is indicated for improving metabolic processes in tissues after surgery, eliminating hematomas, suturing an open wound, and eliminating infections. With prolonged immobilization after an injury, the arm needs to be developed.
When nerve fibers are completely destroyed, exercise therapy is needed in order to learn to feel the hand. It takes time for other fibers to take over the functions of the lost nerves.
In addition to exercise therapy, you can engage in swimming - it provides moderate physical activity and tones the entire body.
Physiotherapy helps to quickly restore normal function to the muscles for which the damaged nerves were responsible. Magnetic therapy, UHF, electrophoresis, wraps, mud therapy are available methods that complement drug treatment.
ethnoscience
As part of complex therapy, you can use compresses from cabbage leaves or burdock.
Traditional medicine methods are not prohibited as auxiliary measures to strengthen the body and stimulate the immune system to fight against infection. In some cases, it is not recommended to use only traditional recipes:
- with post-traumatic plexitis, as a result of which the nerve plexus is completely destroyed;
- for systemic specific infections - traditional methods are powerless in this case;
- If a tumor is detected, the malignant neoplasm must be removed surgically.
In other cases, auxiliary measures will not cause harm to health.
Recommended for use:
- anti-inflammatory ointments based on herbs and pork fat - hops, sweet clover, St. John's wort, 10 g each, grind into powder, mix with petroleum jelly or fat;
- vitamin cocktails from greens, teas, salads from sprouted grains to increase the level of immune protection - nettle, spinach, clover, vetch, young peas are suitable;
- warming compresses - from steamed oatmeal, hot boiled potatoes;
- absorbable compresses, for example, from cabbage leaves.
Fresh berries contain vitamins and minerals. If possible, you need to make fresh juices, smoothies, and lemonades.
If there is no open wound, it is recommended to make a 10% solution of table salt, wet a napkin and apply it to the sore spot. Salt stimulates tissue to recover, relieves inflammation, kills infections, even very deep ones.
How to prevent pathology?
To prevent the development of plexopathy, the following recommendations must be followed:
Rational nutrition is one of the preventive measures that prevent the development of the disease.
- maintain the correct load regime;
- do not overload your arms and spine;
- avoid situations that could cause injury;
- suppress infectious inflammation completely;
- carry out health-improving physical exercises;
- eat rationally;
- choose adequate obstetric care.