Pain is one of the symptoms of a disease, an unpleasant sensation with which the body signals the development of a pathological process. When pain appears in the left shoulder joint, there can be various reasons - pain can occur immediately after an injury or some time after it, as a result of the development of an infectious lesion of organs or tissues, or an inflammatory process. The pain can be aching, sharp, constant or intermittent. Depending on the pain syndrome, certain symptoms, changes in blood counts, the disease is diagnosed based on ultrasound, CT, and MRI studies.
In the therapeutic department of the Yusupov Hospital, joint diseases are diagnosed using modern medical equipment. Rheumatologists use modern techniques and innovative drugs to restore joint function. Treatment of diseases of the right and left shoulder joint is carried out with the help of hormonal therapy, physiotherapeutic procedures, massage, drug therapy, and in severe cases, surgical assistance is provided. Rehabilitation of patients is carried out in the rehabilitation center of the hospital.
Causes of pain: from tumors to injuries
As in most other cases of painful sensations in various organs of the musculoskeletal system, only a specialist can answer the question of why the arm hurts from the shoulder to the elbow. Causes include various diseases and injuries. Discomfort may occur due to the following reasons:
- Organ damage due to trauma.
- Diseases of the shoulder joint of various origins.
- Abnormalities of the spinal column.
- Accumulation of anaerobic metabolism products in muscle tissue.
- Osteoporosis and its consequences.
- Neuralgia of the brachial and other nerves.
- Connective tissue diseases.
- Tumor diseases.
- Consequences of infections.
Injuries are often a consequence of athletes' passion for sports or professional activities. Also, many traumatic situations arise due to extreme entertainment.
The inability to raise your arm is a fairly common problem. Shoulder pain can be one of the most debilitating and painful conditions. Many of you just wake up one day with this pain. The pain can be localized in the upper part or along the lateral surface of the shoulder joint. In some patients, the pain is most pronounced in the evening and at night, while in others it occurs only when raising the arm up. Most of you will not remember any shoulder injury. Most did not change their training regimens or make them more aggressive. In most cases you are 40-60 years old and it can be your dominant or non-dominant hand. Let's look at the most common causes:
- Upper shoulder pain
- Pain in the shoulder joint when raising the arm
- Limitation of movements in the shoulder joint.
There are many problems that limit movement in the shoulder joint or cause pain when lifting or moving the arm. Most often these are problems with the rotator cuff.
The rotator cuff is the most common cause of pain along the outer shoulder joint in adults. This is also the main reason why you cannot lift your arm up or experience pain when moving.
Shoulder pain can be caused by injury. Believe it or not, shoulder injury is a less common cause of pain.
Rotator cuff injuries often occur due to repetitive stress, such as lifting weights or throwing sports equipment. Rotator cuff injuries can also occur from falls and from prolonged work with raised arms (such as trimming trees or painting a house).
The rotator cuff is formed by four muscles located under the deltoid muscle. Together, these muscles control movement in the shoulder joint, ensuring normal function.
If the rotator cuff becomes damaged, inflamed, or torn, you lose the ability to lift your arm up. The most common rotator cuff problems are:
- Rotator cuff tendonitis
- Rotator cuff tendinosis
- Rotator cuff tears
- Partial rotator cuff tears
- Calcific tendinitis
- Adhesive capsulitis or frozen shoulder
The causes of shoulder pain vary depending on age. Some problems are more common in certain age groups. Tendonitis is more common in athletes at a younger age. In middle age - tendinosis, calcific tendonitis, arthrosis of the acromioclavicular joint (ACJ) and frozen shoulder. Let's take a brief look at each of the most common causes of pain and limitation of movement in the shoulder joint.
Arm pain: similarities and differences
Patients presenting with pain in the arm may describe completely different symptoms due to differences in the causes of the disease. But at the same time, there are often similarities in complaints. So, the muscles of the arm from the shoulder to the elbow hurt, combined with numbness due to nerve compression, and this, in turn, can be a consequence of both inflammation of the joints and dislocation. Referral of pain to the arm is observed with angina pectoris, colic, cholecystitis, and stomach ulcers.
So, based on the nature of the pain, they distinguish:
- acute, starting abruptly, which cannot be tolerated without medication - characteristic of injuries, damage to joints, nerves;
- having a baking character - together with shortness of breath and bluish discoloration of the skin, they are often a companion to myocardial infarction, in which case an ECG is required;
- dull, without strong expression, when the arm aches from shoulder to elbow - characteristic of a bruise, closed fracture, arthrosis, tear of muscles, ligaments and tendons.
Sensory disturbances can cause numbness in the hand, causing painful discomfort. Patients in this case also describe a symptom such as “crawling goosebumps.” Both signs are evidence of the onset of osteochondrosis, which must be treated promptly.
How and with what to treat
Treatment of the disease is aimed at eliminating the cause of the pain syndrome, destroying pathogenic microflora and eliminating the symptom complex of the disease.
- Drug systemic treatment . Therapeutic measures for arthritis and arthrosis consist of the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - Meloxicam, Indomethacin, Ketoprofen, anesthetics and chondroprotectors. If there is no therapeutic effect, patients are prescribed hormonal drugs - Prednisolone, Hydrocortisone and narcotic analgesics. Medicines are taken orally, administered intravenously and intra-articularly. So, for arthrosis, intra-articular injections of hyaluronic acid preparations are effective.
- Medicinal local treatment . To reduce pain in the elbow joint, arm and shoulder, use anti-inflammatory ointments - Dolgit, Amelotex, Diclofenac. If the pain is caused by spasms of the muscles of the shoulder girdle and neck, anti-inflammatory ointments based on muscle relaxants should be used. For injuries and bruises accompanied by ruptured ligaments and tendons, apply ice to the sore spot, and make a vinegar compress at night.
- Physiotherapeutic treatment . Electrophoresis, magnetic therapy, as well as osteopathic treatment, massage, therapeutic exercises, and yoga are indicated only after the patient’s condition has been stabilized and the acute stage of the disease has been eliminated.
- Surgery . If conservative treatment of arthrosis of the shoulder joint does not give a positive result, then proceed to surgical treatment of the pathology - endoprosthetics of the affected joint.
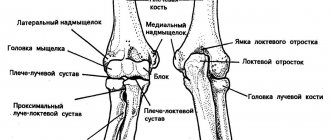
Diagnostic methods for pain in the ulnohumeral region of the arm
A patient who complains of discomfort and pain in the arm from shoulder to elbow is examined. The doctor details the complaints, examines the damage, visually assesses the color scheme and tone of the skin in the area where the pain is localized. By comparing the condition of the joints and studying motor activity, we can make the first assumptions about the presence or absence of damage. In cases where the arm is pulled from the shoulder to the elbow, a flexion resistance test helps.
But, as a rule, an examination cannot give an objective picture of the disease. Therefore, to make an accurate diagnosis, the following research methods are used:
- general (clinical) blood test (CBC);
- blood test for biochemistry;
- X-ray examination;
- CT;
- MRI;
- densitometric study.
The CBC diagnoses inflammation in the body, and a biochemical study clarifies the presence of specific pathological abnormalities. Thus, osteoporosis is characterized by changes in calcium levels.
An x-ray is needed to determine the condition of the bones. Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging help to assess the condition of tissues and skeletal components. Densitometry reveals deviations from bone density standards, which is especially important for osteoporosis.
Diagnostics
Patients with forearm pain are examined by orthopedic traumatologists. In case of purulent lesions, patients are referred to surgeons, in case of pain syndrome of neurological etiology - to neurologists. The diagnostic program includes a survey and physical examination, during which the condition and functions of the limb are assessed, deformity, pathological mobility, swelling and other symptoms are identified. The following procedures may be prescribed:
- X-ray of the forearm.
Performed for severe traumatic injuries, suspected osteomyelitis, periostitis, benign and malignant tumors. In other conditions, it is often performed to exclude changes in bone tissue. Detects violations of bone integrity, areas of compaction, rarefaction, etc. - CT scan of bone. Effective when examining solid structures. It is carried out when the results of radiography are ambiguous. Allows you to clarify the size and location of the pathological focus, detect even minor changes, and build a three-dimensional model of the affected area.
- MRI
. Like computed tomography, it is used in the final stages of the examination. On MRI of the bone, changes in the periosteum are clearly visible. Soft tissue MRI shows signs of inflammation or degeneration in the muscles and tendons. - Electrophysiological studies
. EMG, ENG and ENMG are indicated if a neurological etiology of the pain syndrome is suspected. They make it possible to determine the level of nerve damage, assess nerve conduction, and the condition of the innervated muscles. - Lab tests
. In case of purulent lesions, it is possible to assess the severity of inflammation. In rheumatoid arthritis, specific markers are identified. In oncological processes, they are prescribed to assess the general condition of the body and the degree of dysfunction of various organs.
How to treat arm pain from shoulder to elbow
First of all, you need to remember the dangers of self-medication and not to make the disease worse. Only accurate diagnostics carried out in laboratory and outpatient conditions by specialists can identify methods of subsequent therapy. At the initial stage, medications will be prescribed to help relieve pain symptoms. Further, drug and physiotherapeutic treatment of pain in the shoulder and arm is carried out in a complex. Sometimes it is supplemented with herbal medicine.
The following types of medications are usually prescribed:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - to relieve inflammation, bleeding and pain.
- Hormonal and anti-inflammatory - to support immune resistance.
- Painkillers.
- Chondroprotective - for the treatment and restoration of joint functions.
- Calcium-containing - to accelerate bone healing and relieve osteoporosis symptoms.
Vitamin D is also used to activate healing procedures. A number of drugs have a whole range of side effects. Therefore, when prescribing, specialists are guided by the dynamics of the body’s condition and expediency.
How to avoid pain in the humeroulnar area?
Prevention is the best alternative to treatment. This simple truth also applies to cases where the arm hurts above the elbow. Strong, but regular exercise will help strengthen joints and muscles. Atherosclerosis loves people with excess body weight, so you should eat right and move more. Of course, you need to avoid traumatic situations, not get involved in fights and not look for extreme sports where it is unnecessary. Regular medical examinations and timely diagnosis will help to avoid a situation where the arm hurts between the shoulder and elbow.
Traditional medicine
Along with traditional treatment with medications, you can also try folk remedies. Using self-prepared potions will help speed up your recovery from illness:
- Compresses with vinegar: dilute a tablespoon of vinegar in 0.5 liters of water. Moisten a cloth with liquid, wring it out and apply to the sore spot overnight. Cover with a warm blanket or scarf on top. In the morning, remove the compress.
- Compresses with propolis: leave a clean rag in the bee hive in the fall, and remove it from there in the spring. The canvas will be covered with a layer of propolis. Apply the cloth to the sore joints for a while.
- Using alcohol tincture: 3 soup spoons of lilac flowers, 1 spoon of burdock root and 2-3 pods of chopped hot pepper, pour 1 liter of alcohol and keep in a dark place for 3 days. Rub the affected area before going to bed.
Many people, even with very severe ailments and pain in the shoulder joints, prefer to treat themselves with improvised means using well-known ointments and compresses. But if the pain does not subside within a week, you should definitely visit a doctor to avoid further complications.