Types of back pain
The diagnosis can be assumed taking into account the nature of the pain in the back.
For example, if the pain is aching and worsens with heavy lifting, physical overexertion, hypothermia or prolonged immobility, then the cause may be myositis, lumbago or intervertebral hernia.
Acute pain radiating to the legs or arms may indicate radiculitis, intervertebral hernia or osteochondrosis. The discomfort intensifies when walking, bending or coughing, and weakness is felt in the limbs.
The same intervertebral hernia, lumbago and osteochondrosis, as well as spondylosis can also cause throbbing pain. This is confirmed when the pain does not subside even after analgesics.
If bursting or pressing pain occurs in the chest area, this is a sign of pulmonary embolism or myocardial infarction. Discomfort in the spine indicates spondyloarthrosis, and in the lumbar region - intestinal obstruction. The cause of pressing pain in the neck may be atherosclerosis.
Back pain after sleep
In the morning, your back can hurt not only because of an incorrectly selected mattress or incorrect posture during sleep. Hypothermia, stress, or heavy lifting the day before can cause stiffness and pain below the shoulder blades, in the lower back, or in the right or left side.
There may be other reasons: curvature of the spine, osteochondrosis, intervertebral hernia or obesity. Additionally, your back may hurt in the morning during pregnancy.
Pathologies of the spine and joints
Discomfort in the spine may be associated with diseases of the musculoskeletal system:
- Ankylosing spondylitis. Due to muscle spasm, the patient leans forward to reduce discomfort. Subsequently, the inflamed vertebrae become woody and grow together, causing the spine to become less flexible.
- Rheumatoid arthritis. The disease begins in the knees, hips or shoulders, subsequently moving to the cervical spine. In the morning, patients experience shooting sensations and stiffness: the affected vertebrae put undue pressure on the nerves.
- Spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis. The patient feels discomfort in the lower back: the vertebrae are displaced and compress the nerve endings.
- Osteomyelitis. Acute muscle pain occurs due to infection in the bone tissue of the spine.
- Osteochondrosis. With this disease, the depreciation of the spine becomes worse. The discs between the vertebrae are damaged, and the fibrous ring is torn: the core of the disc comes out through cracks and is pinched.
- Intervertebral hernia. The protrusion between the vertebrae is compressed during movement, resulting in pinching.
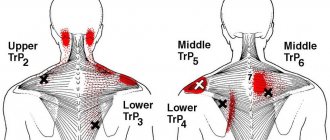
Muscle-related diseases
The source of discomfort can be spasms and tightness in the muscular corset that supports the spine:
- Fibromyalgia. With this disease, the back hurts from the neck to the lower back, and the discomfort worsens when pressing on certain places.
- Dermatomyositis. The skin around the striated and smooth muscles becomes inflamed.
- Polymyositis. The disease occurs due to overexertion or hypothermia: it hurts to turn, and the muscles feel weak.
- Polymyalgia rheumatica. It is difficult for the patient to get to his feet without someone’s help, and asymmetry is clearly noticeable in his back.
- Charcot's disease. Peripheral nerves along the spine become inflamed. Sensitivity becomes worse, muscles become weaker, and the patient’s gait changes.
Spinal cord diseases.
Unpleasant sensations may occur due to the fact that any part of the spinal cord is pinched or inflamed.
Sources of pain in this case:
- compression of the spinal membranes as a result of a fracture, hematoma or abscess;
- inflammation of nearby muscles;
- circulatory disorders;
- hemorrhage;
- lack of vitamins;
- complication of HIV or syphilis;
- back tumor of various etiologies;
- multiple sclerosis.
Psychosomatics
The back can also hurt due to psychological factors: depression, nervous strain, chronic stress or sexual dissatisfaction.
Muscle diseases
Muscle diseases are also often accompanied by diseases of the lower back and overlying areas:
- Myositis is inflammation of the lumbar muscles. Accompanied by aching pain. Usually occurs after hypothermia.
- With injury or heavy physical activity, pain in the lower back often occurs, ranging from mild to cutting. Staying in one position for a long time is also often the cause of this unpleasant phenomenon.
- Overexertion and muscle spasms are a consequence of sedentary work and a sedentary lifestyle.
To understand whether the pain is temporary or is it a serious inflammation, it is necessary to undergo a diagnosis.
Localization of back pain
Unpleasant sensations in different points of the back are caused by different factors.
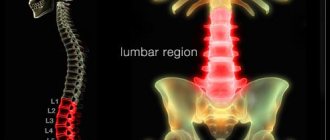
For example, pain in the right side occurs due to lordosis, scoliosis, kyphosis or displaced intervertebral disc. The left side hurts due to splenitis, pinched spine or duodenitis, and the source of pain in the lower back can be radiculitis, osteochondrosis or intervertebral hernia.
If it hurts just above the lower back on the right, it could be myositis, on the left it could be osteochondrosis.
Discomfort throughout the spine signals protrusion, which can develop into osteochondrosis.
Arthrosis and osteochondrosis
Arthrosis is a joint disease that manifests itself most intensely in the morning. In the early stages, after a short warm-up, the unpleasant sensation subsides. But in an advanced stage, pain can become a constant companion, intensifying every day. Arthrosis is usually attributed to age-related changes when metabolism in cartilage tissues is disrupted. Existing osteochondrosis aggravates the course of the disease. Thoracic osteochondrosis is a fairly rare occurrence. It can occur for various reasons:
- As a result of injury or surgery.
- With a sedentary lifestyle.
- As a consequence of arthritis or spondylitis.
- With existing osteochondrosis of other parts of the spine.
Arthrosis also gives a persistent feeling of discomfort and is characterized by periodic pain radiating to the thoracic region and lateral areas.
When do you need to see a doctor as quickly as possible?
If the cause of back pain is overexertion or stress, it will subside after a few days. However, in cases where the pain only increases, urgent medical attention is needed.
Immediate consultation with a doctor is necessary in the following situations:
- it is not possible to find a body position in which the pain becomes weaker;
- recently had a back injury or bruise;
- the condition worsens at night;
- the patient's gait has changed;
- the patient has a fever;
- limbs weaken, go numb, tingling is felt;
- Painkillers don't help.
Liver and gallbladder diseases
Biliary colic rightfully bears the title of one of the most severe types of pain associated with diseases of the internal organs.
It occurs with cholelithiasis, when a stone causes blockage and spasm of the bile ducts. In chronic cholecystitis, pain occurs under the right rib, in the pit of the stomach, and can radiate under the right shoulder blade. It is dull in nature, bothers some patients constantly, while in others it occurs in the form of rare attacks. Usually, the deterioration of the condition is provoked by errors in the diet.
Also, pain under the right rib can be a manifestation of hepatitis, cirrhosis, or liver cancer.
Our expert in this field:
Allahverdyan Alexander Sergeevich
Surgeon-oncologist, professor, MD. Head of the ROH expert group. International expert
Call the doctor Reviews about the doctor
Diagnosis of back pain
To determine the cause of discomfort in the back, you need to make an appointment with a neurologist. If necessary, blood tests may be required to determine infection or inflammation. Examinations may also be required, which will be prescribed by a specialist.
Duplex and triplex ultrasound scanning of the vessels of the neck and brain is needed to diagnose the causes of headaches, dizziness or high blood pressure.
MRI allows you to see tumors on the vertebrae, compression of the spinal nerves and spinal cord, herniated intervertebral discs, and narrowing of the spinal canal. CT scan is needed to detect vertebral fractures.
X-rays help evaluate the condition of bone structures to diagnose fractures, spondylolisthesis, arthritis and degrees of postural impairment.
Electromyography reveals nerve compression due to spinal stenosis or herniated disc.
Gynecological diseases in women
In women, the cause of pain in the lower abdomen on the right is often inflammatory processes in the uterine appendages (adnexitis), ovarian cysts. The intensity of the pain varies; it can spread to the groin or leg.
More serious conditions that require immediate medical attention are also possible. For example, tubal pregnancy, in which the fertilized egg is implanted not in the uterus, but in the fallopian tube. Worrying is aching, cutting or cramping pain on the side where the embryo is attached, prolonged scanty uterine bleeding. Tubal pregnancy threatens to rupture the fallopian tube, a life-threatening condition.
How to relieve back pain?
First of all, you need to relax. To do this, lie on your stomach on a flat, hard surface, preferably the floor. After a few minutes, roll over onto your back and raise your legs so that they are at a 90-degree angle. This will reduce the load on the spine.
Anti-inflammatory ointments and creams will also come in handy. When the pain subsides, you need to carefully get up and bandage the painful area with a scarf or towel.
If there are no painkillers, a cold compress - an ice pack or a product from the freezer - will help relieve severe pain. It will not be possible to completely get rid of discomfort, but it can alleviate the condition. The diametrically opposite option will also help - a heating pad or a heating compress.
A light workout or a leisurely walk will help get rid of discomfort.
Causes that most often lead to spinal myositis
- Infectious diseases. As a rule, this is the flu or acute respiratory infections caused by other viruses.
- Less common is bacterial myositis. It is more severe, leading to severe pain, severe deterioration of the condition, and increased body temperature. An abscess appears in the muscle tissue.
- Poisoning with various substances. These may be certain medications (for example, statins), alcohol, toxins.
- Constant stress on the back muscles. They may be related to the nature of the profession, improper sports training. Chronic trauma leads to the development of an inflammatory process.
- Injuries. They are caused not only by mechanical damage, but also by frequent seizures and other conditions.
- Parasitic diseases. Also sometimes act as a cause of myositis of the spinal muscles, although much less frequently compared to other factors.
Treatment of back pain
After examination and diagnosis, the doctor prescribes treatment. To relieve discomfort, the specialist prescribes painkillers, B vitamins and muscle relaxants. Sometimes bed rest and wearing a special corset are recommended.
An important stage of treatment is physiotherapy. These are electrophoresis with drugs, laser therapy, phonophoresis and magnetic therapy. Electrical nerve stimulation and acupuncture also help.
For back pain, massage, manual therapy, osteopathy and exercise therapy are effective. They also help with rehabilitation after injuries.
Treatment of pelvic pain in men
Treatment methods directly depend on the cause that caused them. In any case, it is carried out comprehensively. Thus, for prostate tuberculosis, anti-tuberculosis medications “Salyuzida”, “Metazid” are prescribed, and therapeutic methods are used. If there are indications, they resort to surgery - cavernotomy.
In prostate fibrosis, efforts are directed toward eliminating prostate sclerosis, for which surgical intervention is used to eliminate the affected areas and restore patency of the urinary tract. In addition, treatment of pelvic pain in men
may include physiotherapeutic and local procedures, exercise therapy aimed at stimulating blood flow in the legs. Drinking alcohol, smoking tobacco, and consuming spicy foods is not recommended.
What is chronic myalgia?
Myalgia, like any other pain, has its own time frame, when it passes from an acute and subacute state to a chronic course.
The medical community generally considers pain that lasts more than 12 weeks to be chronic. What is the main difference between acute pain and chronic pain? This question lies in the plane of neurophysiology. In case of acute pain, from the site of conditioned tissue damage, nerve impulses are transmitted along the nerves to the spinal cord, where the simplest reflexes are carried out, for example, withdrawing a hand when touching a hot object. Next, these nerve impulses along the conductors of the spinal cord enter the responsible areas of the brain, where the processing of incoming impulses occurs, their emotional coloring, where the idea of the localization and nature of the irritation is subsequently synthesized. Based on the information received and processed in the brain, a person takes one or another action in response to irritation, i.e. a higher reflex (conditioned) is formed based on existing experience. It can be concluded that acute pain, by its nature, is a protective mechanism to survive in a harsh and dangerous environment.
The situation is different with chronic pain. If nerve impulses continue to enter the central nervous system for a long time and irritate it (the spinal cord and brain), then the neurons at the level of this segment of the spinal cord become hyperexcitable, the pain threshold decreases, i.e. a slight touch is enough to cause severe pain. At the same time, a similar situation occurs in the brain: a secondary focus of pathological impulses is formed, which affects the psycho-emotional sphere of a person, which is manifested by depression. This whole process is called central sensitization. The formed secondary focus itself begins to generate impulses that are perceived as pain, that is, the sensation of pain will already be there, despite the presence or absence of a primary focus on the body. This is the main difference between acute pain and chronic pain, which is inherently an independent disease and requires a completely different approach to treatment.