Although the thoracic spine is considered the most stable, young people are increasingly complaining of pain in this area.
A sharp decrease in the age when patients first feel pain in the thoracic spine, and the increased incidence of complaints are due to an unhealthy lifestyle.
Often, the pain syndrome is completely unrelated to the spine, and the lack of timely medical assistance is fraught with serious consequences.
What does the thoracic spine consist of?
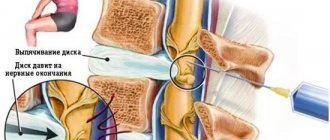
When considering the issue of pain in the thoracic spine, first you need to pay attention to the structure of this section. It consists of 12 vertebrae. The shape of the thoracic spine is similar to the letter “C” in a mirror image. The thoracic spine is directly connected to the posterior wall of the chest. The ribs are attached to the thoracic vertebrae through joints. With the help of the spine, the ribs are connected into a strong frame that forms the chest. The mobility of the thoracic vertebrae is limited.
Is the spine to blame?
Pain can be a consequence of local degenerative changes in the spine, as well as atherosclerosis and diabetes mellitus, which impairs the blood circulation of cartilage and muscles.
Thoracic osteochondrosis occurs due to irrational stress on the body, prolonged sitting at the computer, and lack of sports in a person’s life.
Aortic spasm
A reason that deserves special attention, because it may turn out to be key. The largest artery is connected to the ligament that covers the vertebrae and maintains their position.
From a tense aorta, the longitudinal ligament also comes into tone, which contracts along its length and forces a person to adopt a posture that requires a lot of energy. To compensate for slouching, the muscles that hold the upper spine tighten. The person is aligned, but suffers from pain in the area between the shoulder blades.
Chest pain may also be caused by more complex deformities, such as:
- scoliosis;
- kyphosis;
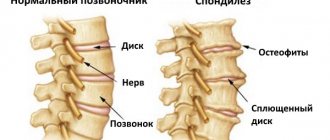
- spondylosis;
- degenerative-dystrophic pathologies of the spine.
The diseases listed above provoke radicular pain, which can lead a person to an orthopedist, chiropractor, vertebrologist or neurologist.
The main manifestations of radicular syndrome are:
aching pain that intensifies with reflex exhalation through the mouth or nose;
girdling pain or localized in a specific part of the body;
pain radiating along the nerves with lumbago;
parasthesia with numbness;
a state of muscular defence, when the muscle fibers in this part of the spine become very tense;
breathing problems and other disorders.
If the lesion touches the intercostal nerves, as well as the thoracic roots of the spinal cord, then the condition is accompanied by intense and prolonged radiating pain of a burning nature with short shooting pains. It intensifies at night and when moving.
Tietze syndrome
A rare condition. It is based on swelling that affects the area of the second or third costal cartilage. The pain has a clear localization, but sometimes radiates to the neck and shoulder area.
The condition is not accompanied by hyperthermia and redness of the skin. Spontaneous regression of pain is observed after 2-3 weeks, but it may continue for a longer period. The syndrome most often affects children and young adults.
Torso twisting can lead to a condition called anterior rib syndrome. It is accompanied by severe pain in the area of the cartilages of 8-10 ribs.
Pain can be a consequence of spinal overload, which occurs with prolonged sitting and weakness of the muscle corset. It also occurs with spinal instability.
Among other reasons:
- tumor process;
- stomach pathologies;
- pancreatic diseases;
- disturbances in the functioning of the small and large intestines.
In older people, pain in the thoracic region can be caused by: osteoporosis, myocardial infarction and atherosclerosis.
Classification of pain syndrome
Pain in the thoracic spine can have a different nature, and the correct diagnosis of the disease and further successful treatment depend on the accompanying symptoms. Experts combine the following into the main group of syndromes (irritative muscular-tonic):
- Pectoralis minor syndrome. A person feels pain at the level of 3–5 ribs, as well as in the forearm. The pain is aching, with a possible burning sensation. It gets worse at night or with movement (for example, if you move your arm away).
- Interscapular pain syndrome. There is a feeling of heaviness of the load. The pain can be aching, boring or aching and localized in the interscapular area. In this case, there may be no pain when palpating the thoracic spine. Pain increases when bending over, lying on your back for a long time, and in some other cases.
- Serratus posterior superior syndrome. This syndrome appears with osteochondrosis of the upper thoracic intervertebral discs. The pain in this case is dull and deep, it is localized in the area under the scapula.
- Serratus posterior inferior syndrome. A person feels a dull, obsessive pain in the back at the level of the chest. There is some limitation in the flexion movements of the torso. With palpation, the pain becomes stronger.
- There are other syndromes: radicular, radicular-vascular, irritative-reflex.
Classification
Depending on the source of pain in the thoracic spine, doctors distinguish:
- radicular pain - occurs due to compression of the spinal nerves due to diseases of the spine;
- referred - the pain is only localized in the spine, but the source is other organs;
- specific - characteristic of oncology, tuberculosis and other serious diseases;
- nonspecific - most often occurs due to curvature of the spine, often accompanied by radicular syndrome.
Pain in the thoracic spine: causes
When a patient has pain in the thoracic spine - during movement or at rest, it is important to understand why the pain occurred. The reasons can be very different, as well as other symptoms and the nature of the pain itself.
Diseases of internal organs
Infectious, viral and other diseases of internal organs can provoke pain in the spine. In other words, pain in the spine is a concomitant symptom of an underlying disease not related to the musculoskeletal system. Such diseases include:
- tuberculosis;
- polio;
- herpes or shingles;
- diseases of the liver, gall bladder, stomach and other elements of the gastrointestinal tract;
- pneumonia;
- kidney diseases;
- inflammation of the appendix, etc.
Diseases of the musculoskeletal system
Diseases of the musculoskeletal system affect the structure and condition of the spine and can cause back pain in the thoracic region. Such diseases include:
- scoliosis, kyphosis and other diseases that result in poor posture. The pain appears due to the fact that there is constant muscle strain in the cervicothoracic region;
- osteochondrosis in various forms;
- intervertebral hernia;
- radiculitis.
Injuries
Mechanical damage to the spine can cause back pain in the thoracic spine, i.e. injuries of various types: bruises, dislocations, fractures. Complex fractures in the spine lead to serious mobility impairments, including complete paralysis.
Sympathetic nerve disorders
The nervous system is directly related to the musculoskeletal system. Disorders of the sympathetic nerves can lead to pain in the spine at the chest level.
Features of treatment
Treatment of diseases of the spine and joints should be comprehensive. If you eliminate the symptoms, but do not treat the underlying disease, it may worsen and soon lead to a new exacerbation.
First, if the back pain in the thoracic region is very severe, intensive therapy methods are used to quickly relieve acute symptoms. In this case, the patient can undergo therapeutic blockades - injections of painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs into the center of the localization of the pathological process. They provide almost immediate pain relief.
During the first examination of the patient, the doctor also learns his complaints and studies the medical history. In some cases, the data obtained in this way is sufficient to make a diagnosis.
The subsequent therapy program is drawn up by the doctor individually, taking into account the main diagnosis, concomitant pathologies and other factors.
Treatment of protrusions, herniated intervertebral discs and scoliosis of 1-2 degrees in most cases is carried out using conservative methods and does not require surgical intervention.
Treatment of radiculitis should include therapy not only for this syndrome, but also for the underlying disease. Radiculopathy does not develop independently, but in the presence of other spinal pathology.
Thoracic osteochondrosis also needs to be treated non-symptomatically. Thanks to the right approach, you can reduce the severity of pain and ensure restoration of the structure and functionality of the spine.
For the treatment of diseases of the spine and joints the following is used:
- medications;
- massotherapy;
- spinal correction;
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- therapeutic exercises.
Each technique has its own mechanism of action and ensures the achievement of a specific result. The best effect is achieved with complex treatment, when all parts of the pathological process are affected.
Sometimes, after completing the main treatment, the patient may need to undergo a rehabilitation course. Its purpose may be to eliminate residual neurological symptoms and restore normal mobility of the spine and joints.
You can find out about the cost of treatment in the “Prices” section.
How to relieve pain. First aid
Often patients, when they first feel pain in the spine, try to help themselves, resorting to various folk remedies or even advice from the Internet. This is not worth doing - you need to go to a neurologist
. But you should know a few first aid recommendations for pain in the spine that will help reduce pain before the doctor arrives, or before your first independent visit to a medical facility.
- If the pain increases with movement (walking, running, etc.), it is logical to assume that the person needs to be at rest more.
- Some ointments and gels, which are available in a wide range of pharmacies today, have an analgesic effect. Sometimes, when pain significantly complicates life, it makes sense to resort to the help of these remedies. In this case, you need to carefully study the instructions for a specific ointment or gel.
- If a person has previously been diagnosed with gastritis
,
cholecystitis
and other pathologies of internal organs, pain in the spine can be caused by a violation of the therapeutic diet. Strict adherence to the prescribed diet will help get rid of pain.
Prevention of osteochondrosis of the thoracic region
To avoid relapses, create comfortable conditions for sleeping and working. Watch your weight and eat right. Keep up your physical activity. But the main thing is not to neglect your health and not to skimp on it. Don't let things take their course. After recovery, try to do at least one maintenance session of gentle manual therapy once every three to six months - this will reduce risk factors. Don’t forget, advanced osteochondrosis leads to complications - protrusion and disc herniation. Remember: your health comes first!
Advanced osteochondrosis leads to complications - protrusion and disc herniation.
Diagnostics
There are three main types of diagnostics that allow you to accurately determine the disease:
- Detailed examination of the anamnesis. In other words, at the first appointment, the doctor finds out from the patient what symptoms are bothering him, conducts a visual examination, palpates the desired area, and prescribes initial tests.
- Manual diagnostics, that is, a targeted examination of the patient’s body to localize the pathology.
- X-ray
,
MRI
, ultrasound,
ECG
and other hardware techniques that allow you to assess the condition, structure, location of internal organs and human bone tissue.
Chest pain caused by changes in the central nervous system
Chest pain can also occur with other diseases. One of the most common diseases that causes frequent and prolonged pain in the chest is cardioneurosis, which develops against the background of a temporary functional disorder of the central nervous system. Neuroses are the body’s response to various mental shocks (intense, short-term or less intense, but long-lasting).
Pain due to cardioneurosis can have a different character, but most often it is constant, aching and is felt in the area of the apex of the heart (in the lower part of the left half of the chest). Sometimes pain due to cardioneurosis may resemble pain due to angina pectoris (short-term acute), but taking nitroglycerin does not relieve it. Often attacks of pain are accompanied by reactions from the autonomic nervous system in the form of facial flushing, moderate heartbeat, and a slight increase in blood pressure. With cardioneurosis, other signs of neuroses are almost always present - increased anxiety, irritable weakness, etc. Helps with cardioneurosis are the elimination of traumatic circumstances, the correct daily routine, sedatives, and for sleep disorders - sleeping pills.
Sometimes cardioneurosis is difficult to distinguish from coronary heart disease (CHD); the diagnosis is usually made based on careful observation of the patient, since there may be no changes on the ECG in either case.
A similar picture can be caused by changes in the heart during menopause. These disorders are caused by changes in hormonal levels, resulting in neurosis and metabolic disorders in the heart muscle (menopausal myocardiopathy). Pain in the heart is combined with the characteristic manifestations of menopause: flushing of the face, bouts of sweating, chills and various sensory disturbances in the form of “goosebumps”, insensitivity of certain areas of the skin, etc. Just as with cardioneurosis, heart pain is not relieved by nitroglycerin; sedatives and hormone replacement therapy help.
Which doctor should I contact?
If severe pain appears in the thoracic spine, when it is difficult to breathe, you should immediately seek qualified medical help. To begin with, you can make an appointment with a therapist, who, after studying the symptoms, will give a referral to a specialist: a neurologist
,
surgeon
,
orthopedist-traumatologist
, oncologist,
gastroenterologist
, etc. To reduce the time spent searching for the right specialist, quickly find out your diagnosis and begin treatment, contact the Energo clinic. Highly qualified doctors of all major specialties work here, who will certainly help you cope with the disease.
Treatment of osteochondrosis of the thoracic region
As you understand, osteochondrosis is a real “tangle” of symptoms, which, by unraveling, the doctor will relieve you of pain and torment. But it is not possible to eliminate changes in the vertebrae and discs. Therefore, the words “treatment of osteochondrosis” must be understood correctly. If you are interested in eliminating pain and other suffering, then yes, it is quite possible. And if you conduct an academic discussion on the topic of returning the vertebrae and discs to their original appearance, “like a newborn child,” then no, the past cannot be returned. You need to be realistic, and then you will not fall for scammers.
Don't fall for scammers!
It is impossible to return the vertebrae and discs to their original appearance!
What method of treatment is considered the main one?
Gentle manual therapy is the main type of treatment for osteochondrosis of the thoracic region. It’s like an antibiotic for pneumonia—you can’t do without it. The remaining types - massage, medications, physiotherapy and exercise therapy - are auxiliary.
How does gentle manual therapy work?
The nutrition of the discs is directly related to the muscles surrounding the spine. In addition, the back muscles themselves are one of the constituent causes of pain in osteochondrosis of the thoracic region. Gentle manual therapy is a special method that allows you to return muscles to their natural physiology, eliminate spasms, muscle tension and improve nutrition of the discs.
Intervertebral discs are the only part of the body that does not have blood vessels and is nourished by the proper functioning of the muscles.
In addition, when performing treatment using hands, the chiropractor:
- will relieve the load from the affected vertebrae and discs and distribute it correctly;
- relaxes the muscles and helps them return to normal;
Thereby:
- relieves the patient of clamps;
- improve disk power supply;
- will restore the motor functions of the body;
- normalizes blood circulation.
Manual influence mobilizes the internal forces of the body and triggers self-healing mechanisms.
The treatment is absolutely safe.
Treatment at home
If you don’t have time or don’t have enough financial resources for treatment in a clinic or sanatorium, you can achieve impressive results in getting rid of osteochondrosis at home. The recommendations below will help you cope with the disease.
Nutrition
It is necessary to introduce into the diet foods that help accelerate metabolism in case of excess weight and the regeneration of cartilage tissue. It is important that the food you eat is rich in nutrients, microelements, antioxidants, polyunsaturated fatty acids, vitamins and is easily digestible.
You need to eat 4-5 times a day every 2.5-3 hours, preferably at the same time. Portions should be no more than 300 g, so as not to overload the stomach and liver. Three meals should contain 26-30 g of protein. Protein is essential for building muscle tissue. Thus, metabolism will speed up, the body will stop accumulating fat, and the cells will receive constant nutrition.
The first breakfast and dinner should be predominantly protein. For example, egg white and cucumber. The main principle of the first and last meals is the absence of insulin spikes, which is achieved by eliminating carbohydrates. Cucumber, although a carbohydrate, has a low glycemic index. Protein without a small amount of fat and carbohydrates is not digestible.
Recommended Products:
- legumes as a protein substitute for meat (beans, including green beans, lentils, peas);
- vegetables in large quantities (with the exception of starchy ones, which should be consumed with caution);
- jelly and jelly (contain natural collagen, necessary for joints);
- chicken wings (the bones must be gnawed, it is their contents that are most valuable);
- poultry, red meat in limited quantities;
- salmon fish, caviar and milt;
- squid, seaweed (no more than 100 g at a time);
- olive oil, camelina oil, flaxseed oil (if there are no liver problems), sesame oil; adults should avoid sunflower oil;
- fruits in limited quantities with low sugar content
It is advisable to boil, steam, stew or eat all dishes fresh.
The drinking regime is mandatory, since the required amount of water provides relief from dehydration, cellular nutrition and promotes weight loss. The daily water intake is calculated using a simple formula: 30 x weight. Tea, coffee, herbal infusions, juices, and fruit drinks are not considered water.
Physical exercise
Physical exercise is an integral part of the treatment of osteochondrosis of any part of the spine. The following techniques may be included:
- Gymnastics developed by Russian scientist Yuri Gushcho. It includes elements of dynamic and static yoga. He also advises carrying out hardening procedures. If you are interested, you can read his book “12 Keys to the Longevity Safe,” in which he talks about what to do to live as long as possible while being active. It makes sense to trust him, because Yuri independently lifted himself out of a wheelchair and recovered from coxarthrosis. He has many awards, gratitude from the President of the Russian Federation.
- Gymnastics using the technologies of Dr. Bubnovsky. His technique is quite effective and can be done at home. A set of exercises can be found on the Internet in video format, and books with full instructions are also available.
- Pool. Swimming not only helps you lose weight, but also strengthens your heart, lungs and develops your back muscles.
- Isometric gymnastics. This type of exercise was first developed for astronauts returning home. Exercises allow, without damaging the joints, to restore weakened muscles, restore flexibility and ease of movement. Gymnastics is indicated for many pathologies of the musculoskeletal system, including osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine.
- Walks in the open air. It is advisable to spend an hour every day for intense walks, preferably in park areas or along the coast. The goal is to improve cerebral circulation, muscle nutrition, and mood.
- Exercises to correct posture.
Complete rest
It is imperative to develop the habit of going to bed and waking up at the same time. Ideally, go to bed at 21 o'clock and wake up at 5-6 am. During this time, the brain manages to restore the functioning of the internal systems of the body, the psyche and process all the information that it received the day before. This is especially important for spinal health.
To sleep, you need to choose the right mattress and pillow. It is better to forget about too soft or hard options.