13 July 2020
10695
0
5 out of 5
Painful sensations in the lower back are no less typical for women than for men. They can occur against the background of various factors, including quite dangerous diseases and physiological causes. Therefore, it is important to be able to distinguish manifestations of banal fatigue and overwork from signs of pathological changes, and if you suspect the occurrence of the latter, seek qualified medical help. After all, one of the consequences of non-intervention in the presence of certain diseases accompanied by back pain can be disability.
Physiological causes of low back pain in women
One of the main natural causes of back discomfort in women is hormonal fluctuations throughout life. They occur during adolescence, every month during the reproductive period, during pregnancy and at the onset of menopause. In each of these cases, the level of some hormones in the body increases and others decrease. Against the background of complete health, such processes are physiological and do not cause any dangerous changes in the functioning of individual organs and entire systems. But with existing disorders, fluctuations in hormone levels can cause a number of diseases, some of which may be accompanied by lower back pain.
The appearance of aching, weak pain more than 2 times a month in non-pregnant women of reproductive age is a sign of abnormalities and requires consultation with a specialist.
Thus, the physiological causes of low back pain in women are:
- menses;
- pregnancy;
- menopause
Also, discomfort of varying severity in the lumbar region can occur after a hard day at work or active work in the gym or on the ground. It is caused by overstrain of the back muscles and goes away on its own. Sometimes too much stress on the lower back can cause muscle and ligament strains. In such cases, the pain is more acute, which requires consultation with a specialist and the creation of the most gentle conditions for the lower back in order to avoid rupture of muscles and ligaments.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy is a difficult period for every woman’s body. Over the 40 weeks from conception to birth, a lot of changes occur in it, ranging from hormonal changes to a sharp increase in weight, a shift in the center of gravity and an increase in the natural deflection in the spine. This leads to the almost inevitable occurrence of lower back pain of varying degrees of intensity. If they are not accompanied by bloody vaginal discharge and are not acute in nature, they are regarded as a variant of the norm.
But at the same time, physiological changes for pregnancy contribute to the exacerbation of chronic diseases and the manifestation of those that were previously hidden. They also create the preconditions for the development of new disorders, especially in the spine. Therefore, kidney pathologies, osteochondrosis, protrusions and intervertebral hernias are often diagnosed during pregnancy. All this can also be signaled by lower back pain.
Climax
The decline of a woman’s reproductive function is accompanied by a decrease in estrogen production and an increase in the production of other hormones. This leads to so-called hot flashes, mood swings, as well as pressure surges and sometimes lower back pain.
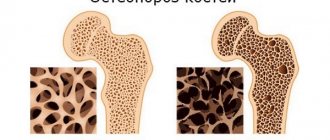
But back discomfort during menopause often does not indicate menopausal changes themselves, but the development of osteoporosis, i.e., a decrease in bone density. This, in turn, can lead to disruption of the integrity of the vertebral bodies and the occurrence of compression fractures of the spine.
What accompanying symptoms may accompany pain?
For acute pain in the lower abdomen and lower back, the doctor suggests a diagnosis based on the patient’s gender. Women with acute pain most often suffer from cystitis.
This is a bacterial infection, and the description of the symptoms also includes frequent and painful urination, a general deterioration in the body’s condition, including an increase in body temperature to 37-38 ° C, and cloudy urine.
If there are no signs of cystitis, the woman is examined for intestinal problems, which may be accompanied by bloating and aching pain in the abdomen and lower back. In the absence of these symptoms, the girl is sent for an ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
Often the causes of pain in the lower back are caused by the formation of an ovarian cyst. Such cases are accompanied by sharp pain in the left or right lower abdomen.
In addition to the cyst, gynecological problems with accompanying pain in the abdomen and lower back include adnexitis, or inflammation of the appendages. In most cases, the pain radiates to the thigh, is noticed in the mammary glands, and is not associated with the menstrual cycle. With this disease, a woman notices purulent-bloody vaginal discharge.
Endometriosis gives a similar clinical picture. The direct diagnosis is made by a gynecologist.
It is worth noting that severe nagging pain in women does not always indicate serious pathologies. In most patients, these symptoms appear in the middle or end of the menstrual cycle, on days 10-15 or 25-32 of the cycle.
Such pain is associated with the period of ovulation and premenstrual syndrome, respectively. The presence or absence of these signs is purely individual and can manifest itself differently in each woman.
If the critical days are delayed by 7 days or more, accompanied by nagging pain in the lower abdomen and lower back, there is a high probability of pregnancy. In this case, you should do a rapid test at home and contact a gynecologist.
Symptoms of pulling the lower back and lower back in men may indicate developing diseases of the genitourinary system. These include cystitis (less common than in women), vesiculitis, prostate adenoma, testicular torsion, urolithiasis, etc.
The listed diseases may be accompanied by weakness, nausea, increased or decreased body temperature, and pressure surges. Problems with the gastrointestinal tract can also be accompanied by pain in the lower lumbar region. These include colitis, cholecystitis and other diseases that can occur in men of any age.
Sometimes prostatitis is also a cause of sharp pain in the lower abdomen and lower back. The symptoms of this disease are similar to cystitis and affect erectile functions, so only a urologist can make an accurate diagnosis.
Diseases that cause lower back pain in women
Very often, lower back pain in women is a consequence of the development of various diseases. There are quite a few different pathologies for which back discomfort is one of the first signs. This is typical for gynecological diseases and kidney diseases. But more often, lower back pain is the result of the onset and progression of pathologies of the lumbar spine, including:
- osteochondrosis;
- protrusions and intervertebral hernias;
- scoliosis;
- in rare cases, tumors of benign and malignant nature;
- spinal fractures, etc.
Predispose to the development of such disorders:
- excessive physical activity;
- passive lifestyle;
- obesity;
- large breast size;
- habit of slouching;
- wearing the wrong shoes;
- heredity, etc.
Gynecological diseases
Inflammatory and non-inflammatory diseases of the ovaries, fallopian tubes and uterus can be accompanied by pain of varying intensity in the back. They are often accompanied by painful sensations in the lower abdomen, and sometimes by the appearance of various types of vaginal discharge.
Therefore, lower back pain can occur against the background of:
- cystic formations in the ovaries;
- uterine polyps;
- endometriosis.
Kidney diseases
Pyelonephritis, renal failure, glomerulonephritis are almost always accompanied by pain in the lumbar region. Most often, they are observed only on one side and are accompanied by pain, increased frequency of urination, and a change in the color of urine.
Also, lower back pain in women can be caused by urolithiasis and the movement of stones through the ureters. This is accompanied by sharp, severe pain and the appearance of traces of blood in the urine.
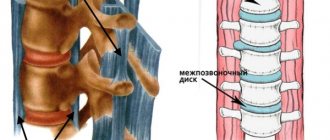
Osteochondrosis
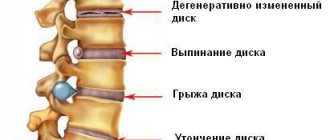
Osteochondrosis is the name given to degenerative-dystrophic changes in the intervertebral discs, which are located between the vertebral bodies. They are cartilaginous formations, the shape of which can be roughly called round. Inside each disc there is a nucleus pulposus, which has a gelatinous consistency. It is surrounded by a dense fibrous ring, ensuring the constancy of the disc shape.
Under the influence of high loads, a sedentary lifestyle, pregnancy and other factors, they begin to actively wear out and dehydrate. This leads to a decrease in their height, which is accompanied by lower back pain in women.
If treatment is not started in a timely manner, under the influence of pressure from the vertebral bodies, the nucleus pulposus will flatten more strongly and put pressure on the fibrous ring. Since its fibers lose elasticity during degenerative processes, they gradually rupture, which creates the preconditions for the formation of protrusions and intervertebral hernias.
Protrusions and intervertebral hernias
Protrusion is the protrusion of a disc into the spinal canal, where the spinal roots and the spinal cord itself pass. It is formed as a result of tearing of part of the fibers of the fibrous ring and its deformation, but while maintaining the integrity of the outer part. Protrusions can compress the nerves passing at the level of the discs of the lumbar spine and provoke radicular syndrome, i.e. pain will be present in the lower back and radiate to the legs.
Back discomfort usually occurs after prolonged standing, sitting, or physical activity. In the absence of rest, it tends to intensify and sometimes become unbearable.
In the absence of competent, comprehensive treatment, the fibrous ring eventually ruptures, and the nucleus pulposus is able to partially leak into the spinal canal. This is how a herniated disc forms. At the moment of rupture of the fibrous ring, a woman may feel a sharp pain, which gradually passes and relief occurs. As the pressure inside the disc equalizes, the pain temporarily subsides, which is often mistakenly perceived as an improvement. But soon they resume and become more pronounced, since the hernia puts stronger pressure on all structures passing inside the spinal canal at the level of the lesion.
Additionally, there are sensory disturbances in areas innervated by the affected nerves. More or less pronounced limitations in mobility are observed.
Scoliosis
Scoliotic deformity of the spine often occurs in adolescence, but if it is not noticed and corrected, the disease can progress and cause discomfort in adult women. Pregnancy especially contributes to its aggravation.
The pathology is accompanied by back pain of varying severity, which directly depends on the degree of scoliosis. Its presence can be suspected by the asymmetrical position of the pelvic bones, legs, and waist triangles. Also, the curvature of the ridge is noticeable when bending forward along the shoulder blade protruding on one side and the back is distorted. If left untreated, scoliosis will progress, pain will intensify, and internal organs will also suffer, as they will shift from their natural positions.
Tumors
Spinal tumors are not as rare as they might seem. Quite often, benign formations are found, in particular vertebral hemangiomas (vascular tumors). Also, the spine and surrounding tissues can become the site of metastases of malignant tumors of other organs.
Regardless of their nature, neoplasms tend to grow and compress nerves, muscles, blood vessels and gradually destroy the vertebrae. If they are located in the lumbar spine, lower back pain of varying intensity occurs. This is accompanied by increased fatigue, and the pain syndrome is difficult to eliminate or cannot be eliminated with traditional painkillers.
Spinal fractures
Spinal fractures are most common in older women who have already entered menopause. They can even appear from a sudden movement or lifting a heavy object, and at a younger age they are more often the result of impacts, accidents and falls.
In older women, spinal fractures may not be accompanied by severe pain. Often there is only mild discomfort, which causes such a dangerous pathology to be diagnosed untimely. In other cases, a spinal fracture causes severe pain and provokes serious impairment of motor functions.
Kidney diseases
The condition of the lumbar region is affected not only by the female genital organs. Such pain is characteristic of kidney diseases.
After all, they are located on the sides of the first two lumbar vertebrae.
| Disease | Features of the disease | Symptoms |
| Urolithiasis disease | Stones form in the urinary system | Lower back spasms, nausea, vomiting, blood in urine |
| Pyelonephritis | An inflammatory process occurs in the kidneys | Attacks of lower back pain from a diseased kidney, urination problems, fever, nausea, vomiting, weakness |
Blood and urine tests help diagnose diseases.
Types of lower back pain in women
Pain in the lower back can have a different character and manifest itself with different severity in different conditions. These criteria allow doctors to make a correct assessment of the situation and suggest where to look for the cause of back pain.
A signal that a woman needs to consult a specialist as soon as possible and begin treatment is acute pain in the lower back. Its appearance is a protective reaction of the body to a developing degenerative-dystrophic or inflammatory process. After all, pain becomes a consequence of irritation of the nerves by altered tissues. This leads to spasm of the back muscles, which further increases the discomfort.
The pain can be nagging, aching, dull or pressing. They can be a consequence of overstrain of the back muscles, hormonal changes, and if they persist for a long time - chronic inflammatory or degenerative processes. Therefore, if such lower back pain occurs in women more often than 1-2 times a month and persists for more than a few days, you should also make an appointment with a doctor.
Often, women with back pain begin to use painkillers and ointments or gels on their own. Such remedies do not help eliminate the causes of discomfort, but only temporarily relieve pain, while the pathology continues to progress and cause complications.
Physical exercise
Have you overestimated yourself? Did you work out hard in the gym the day before? Or did you decide in one day to fence off your dacha plot from all the weeds at once? Then it’s clear why the next day you can’t get up, and when you get up, you can’t bend over.
Advertising:
This type of pain is characterized by:
- appears only while moving;
- absence of weakness, fever and signs of inflammation;
- no irradiation to other areas of the body.
After 2-3 days, the muscle pain in the lower back will disappear.
Diagnosis of the causes of pain syndrome
In order to determine the causes of lower back pain, women are advised to consult a neurologist, vertebrologist, urologist or gynecologist. If you have doubts about what disease provoked the disorder, you can make an appointment with a therapist, who will refer the patient for a consultation with the right specialist.
To diagnose diseases that cause back pain, the following are used:
- UAC and OAM;
- blood chemistry;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys and pelvic organs;
- X-ray of the spine;
- CT;
- MRI;
- electroneuromyography.
To diagnose spinal pathologies, it is most preferable to use MRI, since this method, while absolutely safe for human health, can provide the most accurate information about the condition of the intervertebral discs, spinal cord, nerves and other structures. This will allow you to detect even minor protrusions and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Malignant neoplasms
The body of spongy bones, which make up the vertebrae, is most vulnerable to cancer cells. Sometimes the tumor does not form in the lumbar vertebrae at all, but above or in nearby organs. Metastases reach the vertebrae with tentacles.
Advertising:
Lumbar pain, the etiology of which is not determined from time to time, may be a symptom of the appearance of a malignant formation both in the bones and in the internal organs.
At the same time the following are observed:
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- bone fractures;
- weight loss;
- lack of appetite;
- exhaustion.
So lower back pain should make a woman seek treatment right away. Usually it hides illnesses that require immediate treatment.
Conservative treatment of low back pain
Treatment tactics are developed for each patient separately. First of all, it depends on the diagnosis and the presence of concomitant diseases. Since lower back pain in women is most often caused by diseases of the spine, we will dwell on them in more detail.
Patients are always prescribed comprehensive treatment aimed at both reducing pain and eliminating the causes that caused it. The nature of therapy is selected strictly individually. It often includes:
- drug therapy;
- physiotherapy and massage;
- Exercise therapy.
It is important for patients to make changes to their own lifestyle and diet. If you are overweight, you should take measures to reduce it, as well as rationalize physical activity. In other words, it is important to avoid overstraining the lower back, stop carrying heavy objects, but also not lead a sedentary lifestyle. Office workers, seamstresses and representatives of other “sedentary” professions are recommended to take daily walks, as well as leave the workplace every hour for at least a few minutes. Swimming will also greatly benefit your spine.
Conservative therapy is effective only in the early stages of the development of pathological changes in the spine. At later stages, the situation can only be corrected through surgery.
Drug therapy
For most spinal diseases, the drug treatment of low back pain in women is based on drugs from the following groups:
- NSAIDs;
- corticosteroids;
- muscle relaxants;
- B vitamins.
Other medications may also be prescribed, which the doctor selects for a particular patient, based on her state of health. For severe pain, blockades can be performed. The procedures involve the injection of an anesthetic solution with a corticosteroid directly into the area where the nerves pass. Blockades are effective only for neurological pain and can only be performed by highly qualified medical personnel in medical institutions, otherwise there is a high risk of complications.
Physiotherapy and massage
For vertebrogenic pain, procedures are prescribed that produce an anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antispasmodic effect. Additionally, physiotherapy and massage improve blood circulation and tissue trophism, which contributes to their speedy recovery. Therefore, the courses most often used are:
- electrophoresis;
- magnetic therapy;
- UHF;
- laser therapy.
Exercise therapy
Therapeutic physical education plays a serious role in the fight against pain and diseases of the spine. With the help of an individually selected set of exercises and its daily implementation, it is possible to strengthen weakened back muscles and activate blood circulation. This will help the reparative processes proceed faster and create additional support for the spine.
Prevention of pain when the lower back and lower back are pulled
Prevention of pain when the lower back and lower back are pulled include:
- Distribution of daily physical activity regimen. They include morning exercises and exercises aimed at stretching muscles, joints and bones, especially the spine. In addition, it is necessary to strengthen the muscular skeleton - functional training and swimming or athletics training will help with this.
- Regularly undergoing massage courses - classical or cupping, spa treatments, visiting bath complexes in order to relax and soften muscles and joints.
- Proper nutrition to eliminate the risk of damage to the gastrointestinal tract. It is necessary to maintain a balance between nutrients, proteins, fats and carbohydrates, consume plant fiber, and do not neglect vitamin complexes. In addition, you should exclude alcohol, smoked foods and fast food from your diet. To prevent dehydration, it is recommended to consume 1.5-2 liters of fluid per day.
By following these simple recommendations, you can reduce the occurrence of lower back problems to a minimum.
First aid for burning in the back
A burning sensation in the lower back can occur at any time, so you need to know how to alleviate the condition of a person facing a similar problem. Before doctors arrive or contact specialized specialists, you can try to understand why your lower back is burning, but you still shouldn’t take drastic actions. To get started you need:
- Take the most comfortable position when pain is minimal and the back muscles are relaxed. One option is to straddle a chair and rest your chin on your arms crossed on the back. The fetal position also helps relieve pain. In any case, you need to choose the option that will be as comfortable as possible.
- You can take painkillers, which, of course, will not solve the problem, but will partially relieve the burning sensation and relieve acute pain.
- Sometimes, when the lower back pulls and burns, massage is an effective remedy. But there is no need to be zealous, since in case of problems with the musculoskeletal system, intense impact on the problem area can only worsen the situation. Light stroking and patting will be enough to relieve the burning and itching.
First aid in such a situation is aimed at alleviating the person’s condition to such an extent that he can independently get to a medical facility. If there is no improvement, the burning sensation and pain intensify, you should call an ambulance. You need to remember that you shouldn’t put off talking to your doctor until later, because you can’t figure out for sure why your lower back is burning on your own. The unpleasant itching may hide serious problems that sometimes require surgical intervention.