Many women are frightened by such a diagnosis as “mastopathy”. Concerns are caused by lumps in the chest and the threat of their growth. Lumps are benign formations of the mammary gland, consisting of connective tissue. Degeneration into a tumor is possible only if the doctor’s recommendations are not followed and the lifestyle is incorrect, so patients with this diagnosis need to know what factors can cause complications.
Why is thoracic osteochondrosis called a “chameleon”?
The thoracic spine has a special feature - the ribs are attached to it. Thanks to this, it is less mobile than the neck and lower back. Consequently, osteochondrosis in the thoracic region develops less frequently, according to the principle: “less mobility - less wear.” But it develops less often - this does not mean it proceeds easier. And indeed it is. After all, among other things, osteochondrosis of the thoracic region gives a person a lot of worry and anxiety. We are talking about chest pain. Since the pain zone of the thoracic spine coincides with the zone of the heart, the symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis are often confused with angina pectoris or myocardial infarction. It is not for nothing that they say about thoracic osteochondrosis that it is a “chameleon”. After all, he can pretend not only to have a heart disease, but also a disease of the lungs, liver, stomach, gallbladder or pancreas. And here you can’t make a mistake and overlook a heart attack or other serious disease, for example, pathology of the mammary glands in women. Such mistakes are costly, even if everything works out in the end. After all, this can “drive” a person into severe stress. That is why it is very important to find an experienced and knowledgeable doctor who will understand everything and distinguish the symptoms of osteochondrosis of the thoracic region from other pathologies.
It is very important to find an experienced and knowledgeable doctor.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis of the thoracic region are usually divided into two categories - radicular and reflex.
Types of disease
The likelihood of complications depends on the type of mastopathy: in some forms the risk of negative consequences is minimal, in others it increases significantly. There are three forms of the disease:
- Fibrous mastopathy. An option that indicates the initial stage of the disease. The gland lobules increase in size, connective tissue begins to grow, and small compactions form. If the patient does not comply with the health program, the pathology progresses to the next form.
- Cystic mastopathy. Borderline precancerous condition. The gland contains neoplasms with an altered cellular structure, called cysts. When this form of the disease is detected, the doctor prescribes treatment for the patient and gives recommendations that must be strictly followed.
- Fibrocystic or mixed mastopathy. An intermediate option that also requires therapy and preventive measures.
Complications can be prevented by strictly observing contraindications. Here is a list of what not to do if you have mastopathy of the mammary gland.
Radicular symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis
They occur due to the impact on the nerves leaving the spine.
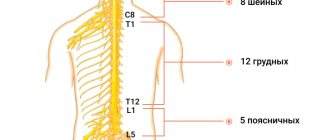
Spinal nerves
There are many nerves coming out of the spine. They are called spinal nerves. Each such nerve gradually branches and follows a specific area of the body with clearly defined boundaries. This area is called the zone of segmental innervation. Each vertebra, disc, nerve and zone are numbered, strictly corresponding to each other. If a nerve is exposed, the symptoms will appear in the zone of segmental innervation corresponding to that nerve, and not just anywhere - in an arbitrary place.
Radicular symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis include:
- Decreased or lost reflexes;
- Impaired sensitivity;
- Muscle weakness;
- Radicular pain.
Innervation zones of the thoracic segments
Osteochondrosis D1–D2
- Causes pain in the shoulder, collarbone and armpit areas.
Osteochondrosis D3–D6
- causes pain of a girdling nature in the upper part of the chest. Simulates pain in the heart, an attack of angina. In women, it causes pain in the mammary glands.
Osteochondrosis D7–D8
- causes girdle pain at the level of the solar plexus. Simulates pain in the stomach, liver, gallbladder or pancreas. Reduces upper abdominal reflexes.
Osteochondrosis D9–D10
- causes pain in the hypochondrium and upper abdomen. Sometimes it imitates the so-called “acute” abdomen - sharp pain in the abdomen. Reduces mid-abdominal reflexes.
Osteochondrosis D11–D12
- causes pain in the groin area. Simulates pain in female diseases, appendicitis, and intestinal diseases. Reduces lower abdominal reflexes.
Features of pain
As a rule, the pain is constant and periodically intensifies sharply, forcing the patient to bend over and put his hand to his chest. In most cases, patients pay attention to these attacks, and not to constant unpleasant sensations. However, the true cause of the attack is compression or damage to the nerves.
And impaired blood flow due to compressed vessels leads to general weakness, dizziness and numbness of the hands.
With thoracic osteochondrosis, pain is usually:
- becomes stronger during inhalation, when lifting heavy objects or sudden movements;
- may encircle or cover the entire back;
- worsens in the evening or in a certain position.
Reflex symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis
Unlike radicular symptoms, reflex symptoms do not have clear boundaries. These may be: difficulty breathing, lack of air, pain when inhaling and exhaling, chills and “goosebumps” on the skin, intercostal neuralgia, girdling chest pain. Dyspepsia is often observed - appetite worsens, nausea, heartburn, bloating, and bowel dysfunction occur. Because of the pain, sleep is disturbed, insomnia occurs and the feeling of not getting enough sleep occurs. It is difficult to move, especially in the morning. Coordination of movements is impaired - this is reflected in the gait. General weakness, weakness. Sexual disorders. Irritability. Fast fatiguability. Various pains arise. Pressing pain in the chest area. Pain between the shoulder blades. Pain in the hypochondrium. Pain when raising arms. Pain when bending over or trying to stand up. Pain between the shoulder blades. In general, pain in osteochondrosis of the thoracic region is usually divided into two types.
Dorsalgia
- moderately severe, prolonged pain in the back and chest with periods of intensification and attenuation.
Dorsago
- acute painful “lumbago” in this area.
- Symptoms of osteochondrosis of the thoracic region depend on the stage of osteochondrosis.
- Symptoms of osteochondrosis of the thoracic region intensify when slouching or trying to straighten up.
- Symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis most often appear after 35-45 years.
- Symptoms of osteochondrosis in women appear approximately 3 times more often than in men.
You, of course, noticed that the radicular symptoms are defined quite clearly, while the reflex symptoms are very vague and non-specific. And as you know, everything that does not have clear definitions serves as a convenient cover for professional helplessness. This applies, among other things, to reflex symptoms and such a favorite concept among doctors as “age-related changes.” Surely many of you are familiar with the situation when the doctor explained the problem as “reflex” or “age-related” processes. Most people at such moments rightly believe that the doctor simply cannot figure out what is happening and is trying to veil his incompetence in the fog of these “magic words.”
At one time there was a popular phrase: “Every accident has a name, surname and position.” So every disease has its own unique symptoms. And it is the doctor’s duty to know them clearly. And then there will be no need to cast a fog and blame osteochondrosis of the thoracic region for everything. Now you understand how important it is to find an experienced and knowledgeable doctor. Both the correct diagnosis and good treatment results will depend on this.
When choosing a clinic, the main thing is to get to an experienced and knowledgeable doctor.
When to see a doctor
Many situations that would not normally cause people to worry are actually reasons to see a doctor. This:
- stiffness and tension in the back muscles, worsening in the evening;
- acute pain attack during sleep or in a supine position, often accompanied by suffocation;
- severe spasms when trying to “stretch” the muscles (during a spasm it can be difficult to inhale or straighten);
- frequent feeling of heaviness in the chest;
- numbness or unruliness of the hands;
- difficulty when trying to bend over, pain when raising your arms or spreading them to the sides.
Treatment of osteochondrosis of the thoracic region
As you understand, osteochondrosis is a real “tangle” of symptoms, which, by unraveling, the doctor will relieve you of pain and torment. But it is not possible to eliminate changes in the vertebrae and discs. Therefore, the words “treatment of osteochondrosis” must be understood correctly. If you are interested in eliminating pain and other suffering, then yes, it is quite possible. And if you conduct an academic discussion on the topic of returning the vertebrae and discs to their original appearance, “like a newborn child,” then no, the past cannot be returned. You need to be realistic, and then you will not fall for scammers.
Don't fall for scammers!
It is impossible to return the vertebrae and discs to their original appearance!
What method of treatment is considered the main one?
Gentle manual therapy is the main type of treatment for osteochondrosis of the thoracic region. It’s like an antibiotic for pneumonia—you can’t do without it. The remaining types - massage, medications, physiotherapy and exercise therapy - are auxiliary.
How does gentle manual therapy work?
The nutrition of the discs is directly related to the muscles surrounding the spine. In addition, the back muscles themselves are one of the constituent causes of pain in osteochondrosis of the thoracic region. Gentle manual therapy is a special method that allows you to return muscles to their natural physiology, eliminate spasms, muscle tension and improve nutrition of the discs.
Intervertebral discs are the only part of the body that does not have blood vessels and is nourished by the proper functioning of the muscles.
In addition, when performing treatment using hands, the chiropractor:
- will relieve the load from the affected vertebrae and discs and distribute it correctly;
- relaxes the muscles and helps them return to normal;
Thereby:
- relieves the patient of clamps;
- improve disk power supply;
- will restore the motor functions of the body;
- normalizes blood circulation.
Manual influence mobilizes the internal forces of the body and triggers self-healing mechanisms.
The treatment is absolutely safe.
Contraindications for mastopathy
General restrictions must be observed by patients who have been diagnosed with the disease, as well as women with a family history.
Contraindications for mastopathy are as follows:
- It is prohibited to visit the sauna, steam bath, hammam;
- It is highly undesirable to take sunbathing;
- physiotherapy should be carried out with caution;
- take hormonal medications without a doctor’s prescription;
- it is necessary to refuse massage;
- Breast surgery is contraindicated, as it can cause inflammation;
- Abortion is not recommended as it increases the risk of complications.
The menu plays an important role in the prevention of mastopathy. The nutritionist compiles a list of permitted and prohibited foods. Compliance with restrictions helps to avoid cancer and chronic inflammation in the chest.
The importance of observing contraindications
At doctor’s appointments, people are often asked about how non-compliance with contraindications affects the development of the disease. To answer this question, let’s take a closer look at each limitation:
- Bath, sauna or hammam are thermal procedures that negatively affect the condition of the mammary gland in the presence of mastopathy. As the temperature rises, the vessels dilate and blood flows to various areas of the body, thus enhancing pathological processes.
- Tanning is the body's attempt to protect itself from the sun. Prolonged exposure to the sun can cause the development of skin cancer. However, most doctors believe that sunbathing can be done in moderation.
- Physiotherapy is a procedure, the need for which depends on the type of disease. For any form of mastopathy, thermal procedures are prohibited; ultrasound treatment is carried out with caution.
- The question of using or limiting hormonal drugs is decided only by the attending physician.
- Massage is allowed only after consultation with a doctor. Any careless impact on the mammary gland can lead to injury to the nodules, tissue degeneration and their further growth. If the doctor does not prescribe such procedures, they can cause harm.
- Surgeries – surgery can accelerate the development of pathology. In the initial stages of the disease, breast correction is allowed, but after surgery it is necessary to be under strict medical supervision.
- Abortion – termination of pregnancy negatively affects hormonal levels. At the same time, carrying a baby and breastfeeding can lead to getting rid of the disease.
- Compliance with a diet is a necessary condition for detecting mastopathy. Coffee, alcohol, spicy, fatty and fried foods can negatively affect the course of the disease. Vegetables and fruits containing vitamins and antioxidants will bring benefits.
One of the factors that provokes the appearance of cancer is smoking. Physical overload can also cause harm. Sports activities when sick should be moderate.
Restrictions depending on the type of disease
The list of contraindications is determined by the type of disease. Let's pay attention to the most important points:
- Fibrous mastopathy is a disease that often affects young women and goes away on its own after childbirth. It is important to exclude any thermal procedures and tanning, which contribute to the degeneration of nodules into oncology. Sports activities are permissible, but only with a professional trainer. Physiotherapeutic treatment and contraceptives are used with caution, under the strict supervision of the attending physician.
- Cystic mastopathy is a disease with an impressive list of contraindications, since the risk of complications is high. Heat and sun baths, massage, physiotherapy and increased physical activity can cause harm.
- Fibrocystic mastopathy is a mixed form of the disease, which requires strict adherence to the doctor’s recommendations. This form of mastopathy often affects women over 40 years of age. When identifying it, it is necessary to pay attention to the psychological status and observe the work and rest regime.
When diagnosing a specific type of disease, you should consult your doctor. He will give recommendations that will help avoid complications.
Prevention of osteochondrosis of the thoracic region
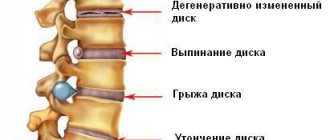
To avoid relapses, create comfortable conditions for sleeping and working. Watch your weight and eat right. Keep up your physical activity. But the main thing is not to neglect your health and not to skimp on it. Don't let things take their course. After recovery, try to do at least one maintenance session of gentle manual therapy once every three to six months - this will reduce risk factors. Don’t forget, advanced osteochondrosis leads to complications - protrusion and disc herniation. Remember: your health comes first!
Advanced osteochondrosis leads to complications - protrusion and disc herniation.
Lifestyle recommendations for mastopathy
The development of the disease is influenced by the patient’s lifestyle. In order to avoid complications, it is necessary:
- Sleep for at least eight hours - this amount of time is necessary for proper rest.
- Playing sports - moderate physical activity will help avoid hormonal changes.
- Avoid stress - the absence of factors that negatively affect the psycho-emotional state supports the body's defenses.
- Spending time outdoors – daily walks help strengthen the immune system.
- Choosing the right bra - seamless underwear of the appropriate size, made from natural fabrics, prevents the development of mastopathy.
- Taking vitamins and microelements helps strengthen the body's defenses.
These recommendations are included in the mastopathy prevention program. By following them, you can eliminate the progression of the disease and achieve positive dynamics in the early stages.
What forms can fibrocystic disease have?
Most often, mastopathy is diffuse in nature and manifests itself:
- predominance of the glandular component (edema, proliferation of glandular tissue) - the most favorable form;
- the predominance of the fibrous component (swelling, enlargement of interlobular connective tissue septa, their pressure on the surrounding tissue, narrowing of the lumen of the ducts, up to their complete fusion;
- the predominance of the cystic component (the presence of one or more elastic cavities filled with liquid contents, clearly demarcated from the surrounding tissues of the gland);
- mixed form (increased number of glandular lobules, proliferation of connective tissue interlobar septa).
A less favorable form of mastopathy is nodular. In this form, as a rule, against the background of the changes described above, there is the presence of one or more nodes, most often representing an adenoma or fibroadenoma.
Fibroadenoma is a fairly common benign tumor of the mammary glands. Occurs at any age, but more often in 20-40 years. In some cases, especially in adolescents, fibroadenomas can grow quickly and reach significant sizes (up to 10-15 cm). According to various authors, the degeneration of benign fibroadenoma into a malignant breast tumor occurs in 1.5-2%.
Also, the nodular form can be represented by atypical hyperplasia (proliferation of glandular tissue). The percentage of degeneration of this nodular formation increases to 20%.
It is also worth recalling a very special manifestation of mastopathy - bloody discharge from the nipple of the mammary gland. As a rule, the cause of such discharge is an intraductal formation (papilloma), which can ulcerate and bleed. Such symptoms should be a serious cause for concern for a woman and promptly seek medical help.