- Why does pain occur?
- Types of pain
- Possible diseases
- Diagnostics
- Treatment tactics
- Our doctors
Pain in the knee joint not only causes discomfort, but can also cause decreased mobility. Sometimes it occurs as a consequence of a dangerous systemic disease. If severe pain in the knee appears after an injury, you need to contact a trauma surgeon. In all other cases, it is worth visiting a therapist to prescribe an examination, and based on its results, treatment.
Causes of knee pain
Unpleasant sensations in the knee joint can be caused by various conditions. Causes of pain:
- inflammation;
- injury;
- degenerative changes in the joint;
- accumulation of fluid or blood in the joint capsule;
- damage to nervous tissue.
In the latter case, the pain does not arise in the knee itself, but only radiates (“gives”) into it. In this situation, treatment will not specifically target that area.
Choosing who to contact
Which doctor you need to see if your knee is swollen depends on the circumstances under which the problem arose and how it manifests itself.
Knee joints can also hurt because a nerve is pinched somewhere. Such cases are treated by a neurologist, but for neurological reasons the joint does not swell.
Pain that occurs gradually over several weeks and then manifests as swelling usually indicates chronic illness. This may be arthritis (inflammation of the joint) or arthrosis (non-inflammatory deformity), inflammation of the ligaments, tendons, joint capsule and other components of the knee joint. These diseases are dealt with by a doctor whose specialty is the treatment of the spine and joints. He is called an "orthopedist". Regardless of why the knee hurts and is swollen, this is the doctor who will definitely be recommended to contact, if not to treat the disease, then to eliminate its consequences.
Types of pain
Depending on the cause of the occurrence, patients report different types of unpleasant sensations. Types of knee pain:
- acute, strong - occurs during injuries and acute inflammatory diseases;
- drilling - when bone tissue melts;
- pulsating - characteristic of chronic joint damage;
- dull - occurs in chronic degenerative diseases;
- shooting - characteristic of damage to nervous tissue;
- burning - when nerve endings are compressed.
The conditions under which pain occurs are also important. If it appears at rest, they speak of systemic diseases. Pain when walking is more common with inflammatory pathologies.
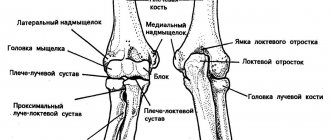
Which doctor treats hand joints?
If you have problems with the joints of your hands, then your disease is most likely associated with damage to the cervical spine, nerve impulse pathways, or cartilage tissue.
Contact your healthcare provider if you experience any of the following symptoms:
- Neurologist. Painful sensations in the wrist joint and fingers at the end of the working day
- Osteopath or orthopedist. When you move your hands, crunching and clicking sounds appear. Feels limited mobility, stiffness in the morning
- Chiropractor or osteopath. Sharp pain with any movement, trying to raise your arms or bend them at the elbows
- Orthopedist, osteopath or chiropractor. Pain in one or more joints of the arm, decreased muscle strength, difficulty performing normal movements
Diseases that cause knee pain
Unpleasant sensations in the musculoskeletal system are not always associated with damage to the musculoskeletal system. Pathologies that cause knee pain:
- arthrosis is the most common cause;
- bursitis, osteochondritis, arthritis and other inflammatory diseases;
- tuberculosis is a form of infection that affects bone tissue;
- osteomyelitis is a dangerous complication of injuries and some diseases;
- neuritis - most often localized in another area, but radiating to the knee;
- gout - the deposition of uric acid salts limits joint mobility and causes discomfort.
Treatment is directly related to the reason why knees hurt. Therefore, it is important to correctly establish the etiology of the pathological process, which only a doctor can do after examination.
Read also: Leg pain: causes and treatment
Prevention
The key to healthy knees is reducing the load on them. To do this, you need to avoid gaining weight, and use protective knee pads when doing physical exercise. When running, it is advisable to choose springy surfaces - soil, special treadmills, and not asphalt. If you receive even minor injuries, you should definitely consult a doctor, without hoping that the pain will go away on its own.
And most importantly. If your knee is swollen, you need to quickly decide which doctor to go to. The longer the inflammatory process in a joint lasts, the less chance there is of completely restoring it. If not cured in time, the process will become chronic, and it will be much more difficult to get rid of its consequences, sometimes even serious ones that require constant treatment of diseases.
Diagnostics
A comprehensive examination for knee pain includes physical, laboratory and instrumental methods. Diagnostic measures:
- examination - swelling and redness in the joint area;
- palpation - salt deposition, limited mobility;
- radiography - degenerative changes in bone and cartilage tissue;
- MRI - the exact location of the pathology and its nature;
- general blood test - detection of an infectious process;
- biochemical blood test (rheumatoid factor, C-reactive protein, urea) - detection of signs of rheumatic diseases.
All data obtained should be analyzed by a competent surgeon or orthopedist. Based on the results, treatment is selected taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient: gender, age, weight, concomitant diseases.
What is needed for diagnosis
An examination in a situation where the knee is swollen will help clarify which doctor to contact. Mandatory stages of diagnosis:
- determining the circumstances under which pain and swelling occurred;
- examination: the doctor must feel the knees, compare one with the other, evaluate their mobility;
- X-ray examination: traumatologists usually take an image of only the diseased joint, orthopedists and other specialists - of both.
If X-ray findings are insufficient to assess the condition of the joint, doctors may recommend an ultrasound (US), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or computed tomography (CT) scan.
Treatment
The treatment regimen depends on the diagnosis. For short-term pain relief, ointments based on non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Diclofenac, Finalgon) are used. If the pathology is widespread, it is advisable to prescribe NSAIDs systemically in the form of tablets. In case of chronic lesions, the drug is administered directly into the joint capsule.
In cases where pain is caused by damage to the nervous system or an infectious process, treatment is carried out by a specialist - a neurologist or an infectious disease specialist.
When your knees hurt, you don’t need to think about what to do or how to treat it. It is better to immediately consult a doctor for a full examination. This will help to stop the development of the disease in a timely manner and avoid complications.
Dear patients! Remember that only a qualified doctor can make an accurate diagnosis, determine the causes and nature of the disease, and prescribe effective treatment. You can make an appointment with our specialists or call a doctor at home by calling 8-(4822)-33-00-33
Be healthy and happy!
How to treat sore knees
There are two main directions of treatment - surgical and therapeutic. They usually start with therapy. The exception is complex fractures, when the joint needs to be actually reassembled, or bone fragments need to be fixed so that they do not damage the soft tissue. In other cases, surgical intervention is resorted to only if it was not possible to help the patient through therapeutic means. Nowadays, a gentle technique for restoring the condition of the joint cavity is actively used - arthroscopy.
Therapeutic treatments include medications, physical therapy, limited mobility, orthoses—joint-relieving devices—and exercise therapy. At the same time, it must be remembered that all these methods, which work well in specific phases of the disease, can seriously harm if they are applied at the wrong time.
Arthrosis of the knee joints (gonarthrosis) - symptoms and treatment
Conservative - anti-inflammatory drugs, painkillers, muscle relaxants, vascular, chondroprotectors, compresses, kinesiotaping, physical therapy, physiotherapy, orthoses.
Minimally invasive - paraarticular blockades (Novocaine + medication relieves pain and inflammation), injection of artificial lubricant into the joint itself, plasma lifting.
Surgical - arthroscopy (a low-traumatic method of treating intra-articular pathologies and removing damaged structures), endoprosthetics.
Drug treatment (drugs for the treatment of arthrosis of the knee joint)
Conservative methods are most effective at the initial stage of the disease.[9][16] They help reduce pain and temporarily slow down the destruction of cartilage. In stage II, more effective methods are needed.[8][23] The introduction of hyaluronic acid preparations into the joint cavity is used to reduce friction and trauma to the cartilage. There is no clear evidence for the restoration of cartilage, but it is good for lubricating surfaces. “PRP therapy” (plasmolifting) is the injection of platelet-rich plasma into the knee joint, which is obtained from the patient’s own blood by centrifugation.[4][13][18] It nourishes cartilage and promotes its restoration, since autoplasma platelets contain numerous growth factors and cytokines that promote the regeneration of damaged tissue.
Surgical treatment and endoprosthetics
Endoprosthesis replacement is a common and effective surgical method for treating severe gonarthrosis,[16][24][25] which allows you to maintain limb mobility and the ability to lead a full life subsequently. This is a high-tech operation lasting approximately one and a half hours. In the postoperative period, long-term rehabilitation and development of the joint are necessary.[16][18] After 25-30 years, when the artificial joint wears out, it needs to be replaced again.
Physiotherapy and kinesitherapy
Methods of physiotherapy and kinesitherapy for the treatment of arthrosis of the knee joint are ineffective.
Diet therapy
A diet is only needed to maintain a normal weight; there are no restrictions on the consumption of certain foods for gonarthrosis.
Does blockade help with gonarthrosis?
For arthrosis of the knee joint, a para-articular block is used - an injection of the drug into the soft tissues around the joint. During the procedure, the area of inflammation and pain points near the joint are determined, the skin is treated with alcohol, and hydrocortisone with an anesthetic is injected into this area.
Therapeutic exercises for arthrosis
Therapeutic exercises are useful both for patients suffering from gonarthrosis and for the prevention of this disease. Effective exercises:
- full flexion and extension of the leg, lying on your back;
- Raising a straight leg up while lying on your back.
When do you need a rheumatologist?
Contact your rheumatologist if you experience the following symptoms for 1-2 weeks:
- joints hurt;
- stiffness persists in the morning, it takes at least half an hour to massage it and bring it back to normal;
- elevated body temperature persists;
- joints are swollen or deformed, there is swelling;
- the skin around the joint feels hotter to the touch than the surrounding tissue;
- experience weakness in the limbs or muscle pain;
- noticed bluish-pink nodules on the skin;
- Do you have cases of rheumatism among your relatives?
In the video, an experienced rheumatologist will talk about new approaches to the treatment of osteoarthritis:
In what cases are they referred to an arthrologist?
An arthrologist treats pathologies affecting joints and periarticular tissues. His competence covers diseases such as:
- osteoarthritis;
- osteoarthritis;
- bursitis;
- periarthritis;
- tendinitis;
- osteoporosis;
- Bekhterev's disease.
It is the arthrologist who accurately establishes the diagnosis and treatment regimen. It is to him that a patient with symptoms characteristic of damage to the joints and adjacent tissues should be referred first. If the joints hurt, the doctor will prescribe painkillers and directly treat their causes.
To make an accurate diagnosis, the patient will have to undergo a series of general and special blood tests, take a picture of the joint, undergo an ultrasound examination and clearly describe to the doctor the provoking factors and the nature of the pain.
Who is a rheumatologist
Rheumatology is a science that studies disorders of connective tissue and joints. The most common pathology in this category is rheumatism. The disease occurs as a result of streptococcus infection, for example after a sore throat, scarlet fever or other illness. Sometimes its cause is immune damage or genetics. Rheumatic diseases are chronic and require close medical supervision.
Despite the fact that rheumatologists are considered narrow specialists, in fact they deal with a large number of diseases - more than two hundred. Among them:
- connective tissue diseases (rheumatism);
- joint diseases (arthritis, gout, osteoarthritis, infectious arthritis);
- systemic pathologies of internal organs.
Most often, rheumatologists treat rheumatic and rheumatoid arthritis, juvenile arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, gouty arthritis, osteoporosis, bursitis, rheumatism, systemic scleroderma, Raynaud's phenomenon, systemic lupus erythematosus and vasculitis, acquired rheumatic heart defects.
A rheumatologist also treats joints, but specializes in inflammatory processes
Side knee pain
Lateral knee pain is one of the most common pain complaints after injury. It may happen suddenly or develop gradually. These types of symptoms are quite common in runners and people who participate in sports that require activity, such as twisting or sharply turning a limb. Pain on the side of the knee can cause limited mobility and other symptoms such as swelling or jerking in the joints (knee twitching, popping).
The most common symptoms reported by patients are tingling on the side of the knee, a burning sensation, knee pain after running, walking or at rest. As a rule, imaging allows you to very accurately determine the extent of damage to the structures of this joint. They use X-rays, ultrasound of the knee joint and the most accurate magnetic resonance imaging. Sometimes a diagnostic procedure called exploratory arthroscopy is necessary. This is the case when the clinical picture is unclear and there is insufficient information from studies conducted to date.
External knee pain
There is no single cause of pain, but there are several reasons why you may have knee pain. More common:
- Athletes: runners, cyclists, martial artists, gymnasts.
- After an injury that pushes the knee outward (away from the other leg).
- In those who do exercises that involve twisting or rotating the knees
- In people who tend to be bent at the knees or bow-legged, putting stress on the outer knee
Also, pain in the knee on the outside can be caused by injury. Only a professional doctor can make a diagnosis.