The human body has more than 300 joints: from the largest - the hip and shoulder, to the small ones - the joints of the fingers and toes. And each of them is important and necessary for health and a full life. Minor and seemingly causeless pain in the joints of the legs and arms can indicate serious disorders in the body, problems with the circulatory and metabolic systems. Therefore, contacting an osteopathic specialist at the first manifestations of joint pain will be the right and timely decision. After all, it is osteopathy, with its idea of the body as a complex interconnected system of the skeleton, joints, muscles and internal organs, that gives the most logical explanation for joint diseases and demonstrates high efficiency in their treatment.
Numbness and pain in the hand. Causes and diseases
Hand pain and numbness in the hands are usually caused by dysfunction (impaired functioning) of the cardiovascular system. Also, the causes may be neuralgic diseases of the cervical spine, pinched nerves of the hands. With heart disease, numbness of the left hand is often observed, which begins as a slight decrease in the sensitivity of the little finger and ring finger and gradually spreads along the limb to the forearm, affecting mainly the inner part.
Pain in the joints of both hands, accompanied by numbness of the thumb and index - and sometimes middle - fingers, indicates disorders in the cervical spine, possible pinched nerves, displacement of the intervertebral discs or the vertebrae themselves.
Numbness in the fingertips most likely indicates a lack of vitamins A and B in the body. This symptom is most pronounced in late winter and early spring, when the body is most depleted.
At the age of 45 years and older, numbness, reaching the complete inability to move the hand, even after slight stress on the joints (sewing, knitting, working with a keyboard), may indicate atherosclerosis of the blood vessels of the hands, as well as damage to the elbow and shoulder joints.
Many age-related diseases and previous injuries manifest themselves in the form of pain in the joints of the hands. These may be unhealed sprains, bruises and cracks of the scaphoid and lunate bones of the hand that were left untreated. The consequences of such an inattentive approach threaten partial or complete loss of mobility. Moreover, diagnosing fractures and cracks is quite simple - both with the use of x-rays and during a visit to an osteopathic doctor. The latter is also able to help with the consequences of such injuries, eliminating possible displacement of bones and damage to blood vessels, pinching of nerve endings that cause pain.
Causes and methods of treating bumps between the phalanges of the fingers
The appearance of bumps on the fingers and subsequent deformation of the terminal phalanx of the finger is a consequence of diseases of the musculoskeletal system. In each specific case, the doctor makes an accurate diagnosis, but in most cases there are two main reasons for the formation of lumps.
For what reason does the disease develop?
The first reason is arthrosis of the joint, which causes inflammation in it. It is inherited and develops due to disruption of metabolic processes in the body, decreased immunity, and hypothermia. The second reason is arthritis. It causes damage to the cartilage in the joint. Healthy cartilage is always smooth, bones slide over it easily without causing pain. If for some reason a metabolic disorder occurs in the body, a joint injury occurs and an infection occurs, autoimmune diseases arise, then this can cause wear and tear of the cartilage, in other words, the development of arthritis. It is worth understanding that a bone growth on the finger is just a side effect of the diseases mentioned. That is, with arthritis or arthrosis, the appearance of cones is possible, but not necessary. There are other reasons why formations appear on the phalanges of the fingers. These include:
- Work that places prolonged stress on the phalanges of the fingers. The range of such work is very wide - from bricklaying to professional piano playing.
- Hygroma, which is a chamber filled with a gel-like liquid. To the touch it is an elastic formation that does not cause pain. It is better to refrain from self-punctures to remove fluid. After such self-medication, the hygroma forms again.
- Fibroma. This problem occurs very rarely and is associated with pinched nerve endings.
- Skin cancer or sarcoma.
- In women, menopause.
You should not hesitate to consult a doctor if alarming symptoms begin to appear in your finger work - crunching or painful sensations when flexing/extending the phalanges.
Typical signs of disease development
The first symptoms of this disease may resemble simple irritations. These include: redness of the skin on the joint with the appearance of a tumor; the inflammatory process in the joint, like any other part of the body, causes an increase in the content of leukocytes in the blood. But the following signs give cause for concern:
- Pain caused by finger movement.
- The need to make extra effort to bend or straighten the finger.
- Beginning of lump formation.
In addition, a decrease in the number of lymphocytes in the patient’s blood can be a warning signal about the development of the disease. These are cells that support the immune system. If there are fewer of them, the likelihood of infections entering the body increases, which can cause arthritis. It has already been mentioned that this is one of the possible reasons for the appearance of bumps. If a patient exhibits at least some of these symptoms, it would be wise to undergo testing.
Diagnosis of finger joint seals
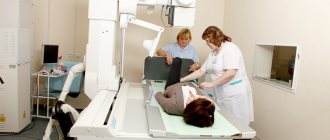
During the first visit with a complaint about such symptoms, a rheumatologist will examine the affected area and take an anamnesis. Sometimes this is enough to accurately determine the cause of pain in the phalanges of the fingers. In other cases, it may be necessary to take a puncture, do an x-ray or magnetic resonance imaging. To verify the presence or absence of a malignant tumor, histology of the lump tissue is prescribed. For this, a biopsy is used.
Treatment of bone formations
Each patient is prescribed his own therapy. But it is still possible to define general methods. In turn, they are distributed for treatment with drugs, traditional medicine, and prevention. The group of drugs includes the following drugs:
- Painkillers.
- Anti-inflammatory action.
- Hormonal.
- Chondroprotectors.
- Vitamins.
Despite the abundance of treatment methods in traditional medicine, you need to exercise caution and consult your doctor before using them. You need to understand that traditional medicine does not replace scientific medicine, but only complements it. Among these additions are the following:
- Mustard powder is mixed with camphor oil. Take 50 grams of both ingredients. Whites from two chicken eggs are added to them, and this entire mixture is diluted with 70% alcohol until a homogeneous mass is formed. The finished medicine is applied in a thin layer to the sore spot and wrapped in a clean piece of natural material. The bandage is not removed for two hours, and the interval between procedures should not exceed four days.
- Squeeze out as much juice as possible from pre-chopped garlic, moisten a clean piece of natural cloth with it and wrap it around the bone growth. Repeat the procedure for a week.
- Dip a fresh cabbage leaf into boiling water, then pull it out and spread it with liquid honey. Coat the bones on your fingers and wrap with cling film. Continue treatment for two weeks and apply the bandage at night.
- Celandine oil can save you from severe pain. This drug is purchased at a pharmacy or obtained by manual processing of the plant. To do this, pass celandine through a meat grinder and infuse the pulp in vegetable oil. This method is not applicable for patients suffering from allergies.
In case of hygroma formation, similar treatment methods are taken.
Apply cabbage leaves or make lotions from celandine juice. The sore spot is steamed in salt water, smeared with honey, and wrapped in woolen cloth. Honey and peeled aloe are added to rye flour. This paste is applied to the sore spot overnight. Before using any type of traditional medicine treatment, you must agree with your doctor. Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr
Occupational diseases of the hand joints
Pain in the joints of the hands can be caused by regular overexertion, performing monotonous physical exercises, or adverse external influences on the joints. Most injuries and illnesses resulting from such exposures can be classified as occupational.
Thus, the joints of the hands often suffer in the following categories:
- People who spend a long time at the computer. In right-handed people, the right hand is more likely to suffer, while in left-handed people, the left hand is more likely to suffer. Due to the constant presence of the hand in the same position - on the computer mouse - swelling of the ligaments (tendons) and the nearby nerve occurs. Over time, increasing pain in the wrist can lead to numbness and even complete inability to move the hand. The disease is called “Tunnel syndrome”;
- Pregnant women. “Tunnel syndrome” also manifests itself in them, becoming most obvious after 3-4 months of pregnancy. Typically, pain in the joints of the hands is preceded by swelling, characteristic of late pregnancy. They, combined with growing body weight, lead to pinching of the carpal nerve. Pain sensations can be expressed in varying degrees from minor discomfort in the joint to complete numbness of the hands. Usually, after the birth of a child, the functionality of the joints is restored;
- Pianists, tailors, laundresses, cleaners. As a result of constant loads falling mainly on the tendon muscles responsible for the work of the thumb, pain in the hand is localized precisely in this area. Diagnosing the disease at an early stage makes it relatively easy to cope with. The main thing is to contact an osteopath before changes and the formation of scar tissue growths begin. This is usually preceded by severe pain, inflammation and swelling in the joints;
- Crane operators, carpenters, builders working with breaker tools. The so-called Kienbeck disease (avascular necrosis of the wrist bones) develops as a result of severe trauma or regular microtrauma of the hand joint. The disease is caused by poor circulation in the wrist area, which causes severe pain in the hand joint, and later changes and destruction of bone tissue begins. Usually the joints of the hand that is a person’s working one suffer.
Disease of the Joints of the Fingers: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment
The article talks about inflammatory damage to the joints of the hands - rheumatoid arthritis. The symptoms of the disease, causes and treatment methods are described.
The most common disease of the finger joints is rheumatoid arthritis. It appears more often in middle-aged and elderly people, less often in children. The disease is inflammatory in nature and has a chronic course. The outcome of arthritis is severe deformation of the joints.
The causes of the disease have not yet been fully established
The essence of pathology
Rheumatoid disease of the hand joints is a chronic systemic disease that causes erosive and destructive damage to the synovial membranes of small joints, such as the fingers.
Causes
The causes of the development of pathology have not yet been reliably established. It is known that the disease is of an autoimmune nature, that is, lymphocytes perceive joint cells as foreign. Research has shown that hereditary predisposition plays a significant role in the occurrence of the disease.
Provocateurs for the development of arthritis can be:
- infectious diseases - influenza, sore throat, ARVI, rubella, herpes;
- hypothermia;
- age;
- mechanical damage;
- hard physical labor;
- stress;
- pregnancy, breastfeeding, menopause.
It has been noted that women are more prone to the disease than men, and pathology occurs more often in them.
Clinical picture
In rheumatoid disease of the hand joints, symptoms are caused by inflammation and deformation of the fingers. The disease may hardly manifest itself for a long time.
The first symptoms for a long time may be:
- chronic fatigue;
- causeless weight loss;
- jumps in body temperature from 37* to 38*;
- increased sweating;
- feeling of stiffness in the hands (tight glove syndrome).
The onset of rheumatoid arthritis can be acute or subacute.
As the disease progresses, characteristic manifestations appear:
- swelling of the joints of the fingers of both hands;
- joint pain that occurs in the middle of the night and decreases during the day;
- decreased sensitivity and mobility of the middle, index and thumb fingers;
- dry skin;
- necrosis of the subungual area;
- the appearance of rheumatoid nodules;
- the occurrence of dislocations and subluxations.
Depending on the symptoms, there are 4 degrees of development of pathology:
- First stage . Onset of the disease. There is mild pain in the joints, morning stiffness, lasting no more than half an hour. At this time, some ordinary actions (turning the key in the door, opening the water tap) cause slight difficulties.
- Second stage. There is swelling of the joints, crepitus when flexing and extending the fingers. The pain intensifies, stiffness continues for half a day.
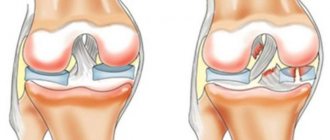
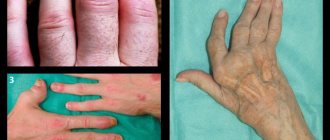
- Third degree . The patient experiences severe pain, the joints of the hands are deformed (pictured). Due to difficulty in movement, a person cannot care for himself. The skin over the joints becomes red and swollen.
- Fourth stage . Irreversible changes occur in the joint tissues. The articular cartilages fuse together. Finger mobility and self-care skills are completely lost.
Arthritis of 3 and 4 degrees is an indication for disability.
Deformed finger joints
Diagnostics
Diagnostics and treatment are carried out by a rheumatologist. To establish a diagnosis, it is necessary to conduct clinical, laboratory and instrumental examinations.
- Clinical examination. Swelling and hyperemia of soft tissues over the area of the affected joints of the hands, subcutaneous nodules and erosions can be detected.
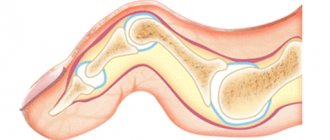
- Radiography. You can see changes characteristic of this disease depending on the stage of development - thinning of bone tissue, periarticular osteoporosis, reduction in the clearance of joint spaces, deformation, dislocations and subluxations of joints.
- Blood analysis. Detects a positive rheumatoid factor in the blood serum, an increase in ESR.
Diagnosis of the disease at the beginning of its development is difficult, since the symptoms of early arthritis can be nonspecific and observed in other diseases. Late diagnosis leads to rapid progression of the disease and the development of irreversible changes in the joints of the hands.
Changes in finger joints on x-ray
Treatment
Treatment of finger joint disease is carried out comprehensively. In the early stages, the disease responds well to conservative treatment.
Therapy is aimed at:
- reducing the aggression of the body’s immune system against joint tissue cells;
- elimination of the inflammatory process;
- compensation for damages.
Drug therapy remains the most effective way to treat this disease. But no less important methods during the rehabilitation period are various physical procedures, massage and specially designed exercises.
If conservative therapy is ineffective, surgical intervention is performed. This may be arthrodesis - fixing the joint in the desired position, or replacement of the joint if it is completely damaged. A specialist will tell you more about the operations in the video in this article.
Other causes of pain in the joints of the hands
Pain in the joints of the hands can be localized not only in the area of the hands. The shoulder and elbow joints are no less often affected. Typically, their lesions are caused by injuries to the arms, spine, as well as diseases and age-related changes that lead to thinning of the cartilage tissue in the joints. In each specific case, treatment may be different, depending on the complexity and severity of the disease. Only an experienced osteopathic specialist can diagnose why there is pain in the hand, crunching in the joint and other hand mobility disorders.
Osteopathic treatment of pain in the joints of the hands
Pain in the joints of the hands is not always caused directly by damage to these joints themselves. On the contrary, the root causes of the disease are often quite distant from the hands. That is why treatment can only be effective if it is aimed at eliminating the root causes. This is exactly the approach practiced by osteopaths. At the same time, complex methods are demonstrated to be highly effective for pain in the hands, when manual techniques are combined with moderate physical activity, and at the same time, the patient’s diet is corrected and the original source of the disease is affected.
At the first stage of treatment, pain in the arm joint is always relieved. This makes the patient's body more responsive to osteopathic influences and allows him to completely relax during the session. Since the sessions themselves are carried out with fairly long breaks (1-2 weeks), which are necessary for the body to recover and adapt to the changes made to its functioning by the osteopath, it is recommended to fix the joint in a stationary position for this period. For this, splints, corsets, various support bandages, etc. can be used.
After the pain in the hand joint is eliminated, the osteopath begins to relieve muscle spasms and eliminate blocks that interfere with normal blood circulation in the areas near the joints and throughout the body as a whole. Restoring blood supply to the affected area helps to improve tissue nutrition, as a result of which the pain no longer returns, and the joints themselves begin to gradually recover.
During the recovery stage, proper nutrition is very important, which will allow the body and damaged areas to receive the entire necessary set of microelements, vitamins and nutrients. Thanks to the gradual renewal and restoration of tissue, the joints of the hands acquire lost mobility, not only the pain goes away, but also the sensations of numbness and discomfort.
To maintain the improving condition of the hands, the joint must be gradually loaded to consolidate positive trends and strengthen the muscles of the hand. Physiotherapeutic procedures and physical therapy exercises must be carried out under the strict supervision of a specialist and be standardized. If the pain returns to the joints of the hands, it is necessary to reduce the load.
In parallel with the treatment of the hands, the root causes of the disease are affected - the spine, cervical spine, internal organs. Osteopathic techniques are aimed at improving blood supply and metabolism in the body as a whole, which, of course, has a positive effect on the functioning of all its systems. The advantage of turning to an osteopath in this case is that by treating pain in the hand, he simultaneously gets rid of other deeper disorders that became the root cause of this pain.
Pain in the hand joint is not always a disorder specifically in the wrist area, so traditional treatment using symptomatic methods may not be effective. While an osteopath, who perceives the problem more broadly, can help in just a few sessions.
Curled fingers
Why does he curl his fingers? | What to do? | How to treat?
Curled fingers are one of the characteristic features of old people from fairy tales. We imagine Baba Yaga or the Sorcerer exactly like this: wrinkled, bent and with curled fingers. But the disease that leads to this appearance of the hands really exists and does not affect only old people. What is the name of the disease that causes crooked fingers? Most likely, the heroes of fairy tales suffer from the late stages of Dupuytren's contracture. And the disease usually begins at about 45 years old - now no one considers this age to be elderly.
WHY DOES THE FINGERS CURL?
The disease was first described in the 17th century, but then doctors could not figure out the reasons and tell what to do if the fingers curled. For a long time, Dupuytren's contracture, also known as palmar fibromatosis or French disease, was considered incurable.
Today, too, there is no consensus on the reasons for curling fingers. But there are basic hypotheses about the origin of the disease:
- Heredity.
Often patients with Dupuytren's contracture have or have had relatives with a similar condition. Since the disease is more common in men, it is transmitted, as a rule, through the male line: for example, crooked fingers on the left hand of a grandfather, uncle, father, and the patient himself. It has been proven that Dupuytren's contracture is transmitted according to an autosomal dominant trait: that is, it will definitely manifest itself if there is a breakdown in the genome. The degree of manifestation may vary, as can the age of onset and the speed of development. - Labor activity.
Many patients with Dupuytren's contracture have worked all their lives in a harmful environment: they were exposed to radiation, worked on vibrating machines, and regularly received microtrauma to the joints and tendons of the hands. Some sports are also recognized as a risk factor. - Metabolic diseases.
According to statistics, patients with diabetes often notice in old age that their fingers curl. What does this mean: most likely, metabolic disorders also affected the connective tissue, affecting the most vulnerable tendons - the palmar tendons.
Bad habits and unfavorable ecology become additional reasons. Curls the fingers in those patients who do not see a doctor for a long time, even after noticing the unnatural position of the little or ring finger.
CURLING FINGERS: WHAT TO DO
The insidiousness of palmar fibromatosis is that it practically does not manifest itself in the first stages, and certainly does not interfere with life. The patient may not realize that oblong lumps on the palms are the first stage of Dupuytren's contracture. Pain in the joints of the hand when moving occurs when the fingers have already partially lost mobility. These are the second and third stages of the disease. If the patient does not ask why there are crooked fingers on the hands, what this condition is called and how to treat it, he risks getting an extreme degree of Dupuytren's disease. Irreversible changes in the joints, constant pain, inability to use fingers and ultimately disability.
CROOKED FINGERS: HOW TO TREAT
With this diagnosis, surgery may be prescribed. However, dealing with the French disease of crooked fingers can be much easier, more effective and faster. In this case, you can do without surgery. Needle aponeurotomy helps patients with contractures forget about the disease for a long time, regardless of the reason for curling their fingers.
Advantages of the method:
- There is no need to cut the skin, which means there are no long-healing wounds or stitches.
- The procedure is quick, orthopedists at Doctor Ost MC perform it within a few minutes. The very next day after aponeurotomy, the patient can return to normal activities. Complicated rehabilitation is not required.
- The effect is noticeable almost immediately; within a month, finger mobility returns. For comparison, after a conventional operation, it takes the patient about a year to restore the injured tissue. In this case, the result of surgical intervention may be inferior to needle aponeurotomy.
The success of needle aponeurotomy depends on the experience of the doctor and the neglect of the case. The degree of restoration of finger mobility varies from person to person. Highly qualified orthopedic doctors work at Doctor Ost MC. They will be able to correctly diagnose, distinguish arthritis from Dupuytren's contracture and help the patient regain the mobility of his hands. The main thing is to see a specialist as early as possible.
Perhaps fairy tale characters with crooked fingers really can't be helped. But attentive patients who care about their health have every chance of a full recovery!
Question and answer
“My mother’s fingers are curled up on her hand, she can hardly move them, can this be cured at your Doctor Ost without surgery?”
Read a specialist's opinion >> or
Ask a question