- Home /
- Blog /
- Notes of the head physician
September 29, 2018
Joint diseases can strike you at any age, completely changing your lifestyle and not for the better. The first thing that is important to remember is that joint pain is not a death sentence.
In the new article we will talk about the causes of pain, how to treat joints and what mistakes to avoid. And also how to prevent this unpleasant pain.
Features of joints and causes of their diseases
A joint is any connection between two or more bones. There are 38 pairs of joints in the human body (for a total of 76 joints). They provide mobility and flexibility to our body. Movement is a vital function, and if the disease limits it, the quality and life expectancy are reduced.
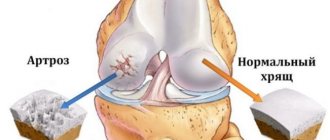
Each joint has articular surfaces - these are the surfaces of the bones that enter it, covered with a special hyaline cartilage. It is dense, elastic and is needed to protect bones from abrasion during movement. It also ensures that they match each other perfectly. It is the wear and tear of cartilage that becomes a common cause of pain, crunching, stiffness and other signs of disease in the joints.
Joints are characterized by a complex structure. Articular surfaces, capsule, cleft, synovium, periarticular muscles and ligaments - all these structures provide the motor and support functions of the joint. Damage to them can trigger the development of the disease.
Causes of diseases
Many people mistakenly believe that joint diseases only affect older people due to age-related changes and weakness of the body. But that's not true!
Joint diseases can develop as a result of:
– injuries; – excess weight; – physical activity; – incorrect posture; – flat feet; – hereditary predisposition; – nutrition with insufficient content of microelements; – diseases of internal organs; – metabolic disorders; – postponed operations; – infections.
People of absolutely any age and even those with relatively good health (for example, men and women of working age, teenagers, children, athletes, etc.) can experience the effects of these factors.
Therefore, this group of diseases is getting younger - in terms of frequency of occurrence and disability, it is second only to cardiovascular and endocrinological diseases, and their treatment is associated with large financial costs.
How to treat joints: 3 main mistakes
“Folk” methods of treatment have never brought anyone any good; they only make the situation worse. Temporary improvement masks the problem, resulting in a serious illness.
Here are the 3 main mistakes that “sick people” make:
Cleansing the body and “removing salts”
Arthritis and arthrosis are the destruction of cartilage tissue, and not the deposition of salts.
“Development” of joints through pain
This leads to the fact that the disease in its initial stage progresses to the next, more serious one. Destroying fabric cannot be restored by “development”.
It is worth noting that therapeutic exercises are extremely useful, but they have nothing to do with this Jesuit folk method.
Painkillers as the only treatment option
The most common drug in Russia is ibuprofen (a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug). Many people drink it in batches without thinking twice. This only triggers the disease and harms other organs.
Mechanism of development and types of diseases
In the pathogenesis of joint damage, doctors identify 4 possible paths:
First: the presence of inflammation in the body
This type of lesion is characterized by a sudden onset, with a rapid increase in symptoms of inflammation: swelling, pain, redness, fever. Occurs with infections, allergies, autoimmune processes in children and adults.
Juvenile arthritis It is characterized by an autoimmune process (i.e. the body destroys itself), the cause of which is unknown. Often the provocateurs are previous infections, even in a mild form (for example, vaccinations).
The disease affects large joints (knee, elbow) in children and adolescents and negatively affects their growth and development. Joint pain is accompanied by severe swelling, redness of the skin, and fever.
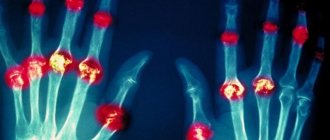
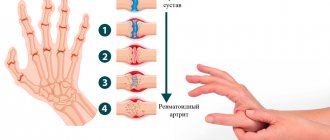
Rheumatoid arthritis Also caused by an autoimmune process of unknown cause. Women are more often affected; the average age is 45–50 years. Up to 70% of patients become disabled.
Affects a small joint (or several), for example, wrists, fingers. This affects patients' ability to work and even care for themselves. They complain of severe pain, swelling, changes in the shape of the joints and morning stiffness in them.
Psoriatic arthritis In almost half of patients diagnosed with psoriasis, the process of inflammation develops in the small joints of the hands, feet, and spine. The cause of arthritis, like the cause of the underlying disease, is unknown.
Psoriatic arthritis can affect the interdigital and large joints (elbow, knee), one or more joints, symmetrically or not.
The main manifestation is the presence of pain that spreads to the ligaments and tendons, swelling and blueness of the skin of the fingers, and limited mobility.
Gouty arthritis Develops against the background of gout, as a result of the deposition of uric acid salts in the joints. Men are affected more often than women, aged 40–50 years and over 60 years, respectively.
A characteristic feature is damage to one joint, which begins suddenly, lasts several weeks, is accompanied by severe pain and swelling, with the formation of uric acid nodules (tophi).
Spondyloarthritis in ankylosing spondylitis is a chronic lesion that affects the spine, paravertebral muscles and the sacroiliac joint of the pelvic bones.
The disease affects men more often than women, and it develops between the ages of 20 and 30. Their main complaint is pain in the lower back, sacrum, and hip joints; stiffness of movement after a period of rest (especially in the morning, after sleep).
Even with the removal of symptoms and relative well-being, without eliminating the main cause, inflammation continues to develop and will eventually cause a new exacerbation. Therefore, joint pathology often becomes chronic and leads to disability.
Second: the presence of a degenerative-dystrophic process
With this type of lesion, the joint is destroyed under the influence of physical factors. Injuries and microtraumas, constant physical activity beyond the norm, harmful effects of the environment (hypothermia, vibration) - all these pathological factors cause the destruction of cartilage and narrowing of the joint space.
Deforming osteoarthritis Develops as a result of damage and destruction of articular cartilage. Its articular surfaces become rough and sensitive to friction. Over time, the process of destruction spreads to the bones, capsule, synovial membrane, ligaments and muscles. Chronic inflammation and changes in the shape of the joint appear.
Osteoarthritis is the most common joint pathology. It reduces the quality of life of patients, causes disability and is difficult to treat. In youth, men are more likely to get sick; in old age, women are more likely to get sick.
Clinically, osteoarthritis manifests itself as severe pain and limited mobility, which worsen with physical activity. In the later stages, even rest and rest do not bring relief.
Osteochondrosis Affects the spine and is caused by degenerative processes in the intervertebral discs. Under the influence of negative factors, the nutrition of the discs is disrupted, which leads to loss of their shape (up to the formation of protrusions and hernias), aging and destruction.
As a result, the spine loses its mobility, pain, numbness, stiffness of movements, muscle weakness, difficulty urinating and bowel movements, headache, and dizziness appear. Symptoms depend on the part of the spine in which osteochondrosis has developed and can vary greatly.
Spondyloarthrosis deformans This condition is also called “facet syndrome.” In this case, the destruction process affects the structures of the intervertebral joints (capsule, ligaments, facets).
Most often it occurs in the most “overloaded” part of the spine - the lumbar. It manifests itself as pain that radiates to the leg and intensifies with prolonged walking or standing in one place.
Osteochondropathies Caused by aseptic (non-infectious) necrosis of bone tissue, for example, due to impaired blood supply. As a result, the bones in the joint are susceptible to frequent fractures. In advanced cases, patients can suffer serious injury even while sleeping.
In the early stages, the disease does not manifest itself in any way. Many sick people are athletes and people leading a “healthy” lifestyle. The former are subject to excessive stress, the latter deliberately limit their diet and deprive the body of necessary substances.
To destroy dense and elastic cartilage, the pathogenic factor must act on the joint for years, so degenerative changes are more common in old age. Or he must act with super strength, as when playing sports.
Many professional athletes become disabled in their youth. Read about what treatment methods you can use to prevent this here.
Third: congenital joint pathologies
This type of lesion is caused by abnormalities in the structure and development of joints as a result of infections and injuries to the mother, concomitant pathology, late toxicosis, and genetic diseases.
Frequent manifestations of congenital pathologies are birth injuries, for example, hip dislocation or clavicle fracture (more information about the types, diagnosis and treatment of birth injuries can be found here).
Congenital dysplasia of the hip joints Develops as a result of a violation of the formation of all articular structures in the prenatal and postpartum period. Predisposing factors are heredity and tight swaddling. Girls are more susceptible to this pathology than boys - the incidence rate is 80% and 20%, respectively.
With dysplasia, the shape of the joint is changed, and its ligaments are too elastic. This causes displacement of the femur and impairs the mobility of the hip joint, which can lead to disability.
Congenital clubfoot A deformity in which, due to damage to the ankle joint, the foot deviates inward relative to the lower leg.
Clubfoot most often affects boys and in half of the cases it is bilateral. If the defect is not corrected in time, the child will not be able to walk normally and will remain disabled.
Marfan syndrome A genetic pathology in which the patient has elongated bones in the arms and legs, as well as hypermobility (excessive mobility) of the joints.
In the early stages, many congenital joint pathologies can be eliminated completely or development can be slowed down using conservative methods. Late diagnosis and treatment can lead to dysfunction of support and movement, even disability.
You can learn about how a woman can prepare for pregnancy and childbirth in order to avoid congenital pathologies in her child here and here.
Fourth: diseases of the muscles and ligaments of the joint
Pathologies of this group often develop as a result of increased physical exertion and hypothermia.
Tendonitis Inflammation and destruction of a tendon. It is accompanied by tension and painful sensations, especially in the weather.
Myositis Development of inflammation in the periarticular muscles. It is accompanied by pain when palpating the affected area, which intensifies with movement.
Bursitis The inflammatory process is localized in the joint capsule. Often professional athletes (wrestlers, runners, weightlifters) suffer from it.
Synovitis Damage to the synovial membrane with accumulation of fluid in the joint cavity. Accompanied by pain, swelling, and stiffness of movement.
Relationship between disease and type of joint
There is a certain pattern in which joint is affected by which pathology. Some of them even have their own specific names.
For example, the knee joint can be affected at any age, regardless of the gender and type of activity of the patient. But damage to the meniscus and cruciate ligaments is more common in athletes. Gonarthrosis - in older people. Arthritis of infectious origin - in children.
Pain in the shoulder joint can be caused by glenohumeral periarthritis, cervical osteochondrosis, osteoarthritis.
The elbow joint is characterized by damage to the periarticular tissues - epicondylitis or “tennis elbow”, “golfer’s elbow”.
The hip joint is more likely to suffer in older people. As a result of osteoporosis and coxarthrosis, they are at risk of femoral neck fracture.
Pain in the small joints of the hands and feet is observed with rheumatoid, psoriatic, and gouty arthritis.
But despite the specific manifestations, diagnosing articular pathology often causes difficulties, which is fraught with late initiation of treatment and the risk of complications.
Risk factors
Risk factors for the disease include:
- hereditary predisposition;
- heavy physical labor, heavy load on the finger joints;
- overweight, excessive alcohol consumption;
- long-term wearing of uncomfortable tight high-heeled shoes;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- hypothermia of the feet.
If your work often puts stress on the joints of your fingers and toes, or you have relatives who suffer from arthrosis of small joints, you should think about prevention. We will talk about it at the end of the article.
Symptoms and diagnosis
Among the complaints that concern patients with articular pathology are:
– Soreness; – Swelling and puffiness; – Change of shape; – Stiffness of movements; – Inability to perform normal range of motion.
Doctors call them joint syndrome. Doctors call them joint syndrome. Redness of the skin, rashes and dense nodules are also possible. Among the general symptoms, patients often complain of increased temperature in the affected area or the whole body, and increased fatigue.
Reading the previous section, you may have noticed that all these symptoms occur in almost any joint pathology. Therefore, it is impossible to make a clear diagnosis based only on your complaints - you need an examination and consultation with a doctor.
During the examination of the patient, the doctor not only pays attention to his complaints. To make an accurate diagnosis, it is important to know the time of their occurrence, which joint is affected, whether it is one or several, whether the lesion is symmetrical and other factors.
Let's look at each symptom in more detail:
Soreness: Occurs in almost every pathology. Doctors distinguish several types of it:
– Inflammatory – intensifies closer to the morning, after a period of rest. Characteristic for rheumatoid, juvenile, gouty arthritis, spondyloarthritis.
– Mechanical – appears during physical activity or a change in body position, often in the late afternoon, goes away after rest. Characteristic of osteoarthritis, osteoarthritis, osteochondrosis, pathology of periarticular tissues.
– “Starting” - occurs in the first 15–20 minutes of physical activity after a period of rest. Characteristic of osteoarthritis.
– “Blocked” - caused by pinching of a cartilage fragment in the joint space, as a result of which the joint “jams”. May be accompanied by a crunching sound. Occurs in osteoarthritis.
– Constant – persists, regardless of load and time of day, may intensify at night. Characteristic of osteochondropathy, osteomyelitis, tumors and bone tuberculosis.
Number of affected joints:
– One (monoarthritis): for juvenile, gouty, psoriatic arthritis. – Two to four (oligoarthritis): for rheumatoid arthritis, spondyloarthritis. – More than four (polyarthritis): for rheumatoid, gouty arthritis.
Symmetry of the lesion:
– Symmetrical: for rheumatoid arthritis. – Asymmetrical: for spondyloarthritis, gout, osteoarthritis. – “Migratory”: for gout.
Morning stiffness in the joints: The patient feels it as the impossibility and tension of movement. It happens in the morning and is associated with the accumulation of fluid in the joint cavity overnight. Characteristic of rheumatoid arthritis, spondyloarthritis.
The doctor also pays attention to general complaints: - Increased body temperature; — Redness of the skin, the presence of a rash on it; — Damage to internal organs.
To make an accurate diagnosis, laboratory (blood and joint fluid tests) and instrumental studies (radiography, CT, MRI, ultrasound) are required.
Platelet Rich Plasma
It is known that platelets contain growth factors and substances that are potential chondroprotective agents. Therefore, PRP can be successfully used to stimulate regenerative processes in articular cartilage. Note that a good effect of treatment can only be achieved with plasma containing at least 1,000,000 platelets per 1 μl.
PRP is obtained by two-stage centrifugation of venous blood. The resulting material is administered in an amount of 5 ml three times with an interval of 2-3 days. Being absolutely safe, this technique allows you to improve the functional state of the joint and improve the patient’s quality of life. Note that the use of platelet-rich plasma is more effective in young patients with minor degenerative changes in the joints.
Which doctor should I contact?
Joint pain signals the development of the disease, so you should immediately go to the doctor. Timely medical care will help you avoid complications and make a successful recovery. Diseases of the musculoskeletal system can be treated by doctors of several specialties.
First of all, you need to visit a therapist. He will take a medical history and conduct a full examination. After this, he will refer you to a highly specialized specialist: rheumatologist, infectious disease specialist, neurologist, traumatologist, rheumatologist, chiropractor.
Highly specialized specialists will either confirm or refute the diagnosis made by the therapist. After this, the doctor selects individual treatment taking into account the patient’s age, the complexity of the disease and the individual characteristics of the patient.
Tell everyone:
Stromal-vascular fraction of adipose tissue
Nowadays, MMSCs obtained from bone marrow and adipose tissue are used in regenerative medicine. Moreover, the use of the latter is more justified due to their easy production, high proliferative potential and low aging coefficient. Note that from an equivalent amount of adipose tissue, 1000 times more multipotent mesenchymal stem cells can be obtained.
The stromal vascular fraction (SVF) is the totality of all nuclear-containing cells (including MMSCs) that can be obtained from subcutaneous fat by enzymatic digestion. This substance has a pronounced regenerating, anti-inflammatory, antiseptic and immunomodulatory effect. According to many scientists, SVF of adipose tissue has many advantages compared to cell engineering methods and MMSC cultivation.
Fact! The preparation of SVF does not require cultivation, which can be complicated by microbial contamination, genetic transformation or spontaneous differentiation. This makes the stromal vascular fraction a more attractive product for use in clinical practice.