- August 1, 2018
- Workouts in the gym
- Valieva Olga
Osteochondrosis of any part of the spine (cervical, thoracic or lumbar) can become a source of pain and discomfort. Once the disease has been diagnosed, it will remain with the patient forever. Over time, osteochondrosis can lead to the development of scoliosis, lordosis or hernia. These illnesses are not mutually exclusive. At the same time, these diseases can provoke the development of osteochondrosis. The patient has only one thing left to do - adjust his lifestyle so that it does not cause complications with the spine. Exercises in the gym for osteochondrosis can both aggravate the course of the disease and alleviate it.
Symptoms of spinal diseases
Before you go to the gym to build a beautiful body, you should be examined by a doctor. One of the first questions he will ask will be about whether you have back pain. Every second person over 15 years of age has some kind of spinal pathology. Moreover, this does not depend on gender or lifestyle. Most often, spinal diseases occur during the primary school years.
Constantly sitting at a desk, head tilted down - this position is unnatural for the human body, hence numerous pathologies of the spinal column.
You should think about choosing special exercises in the gym for osteochondrosis of the cervical and thoracic regions if the following symptoms bother you from time to time:
- darkening of the eyes;
- dizziness;
- loss of consciousness and fainting;
- shooting pains from the spine to the internal organs;
- problems with vision and hearing;
- inability to take a deep breath;
- frequent breathing problems;
- crunching in the bones when trying to turn your head or tilt your body to the sides;
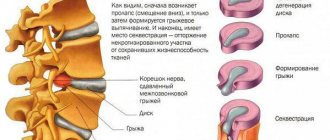
- herniated intervertebral discs.
ComprehensiveGuaranteed Security
Over the last century, the life of mankind has changed a lot. The percentage of people engaged in heavy physical work has decreased significantly. A significant part of the population suffers from physical inactivity. The result of this was an increase in the number of many diseases, including hypertension, coronary heart disease, obesity, diabetes and osteochondrosis. The occurrence of the latter can be due to various reasons, but among them the opposite is often the case - increased physical stress on the spinal column.
Many categories of people are susceptible to it, especially those who, due to their occupation, are forced to lift heavy weights, or who maintain a static body position for a long time. Professional athletes also fall into this category. Over the years, approaches to sports have changed, and the bar that athletes must achieve is increasingly raised. Therefore, the load on this category of people gradually increases and becomes truly extreme. Moreover, one should not think that this applies only to representatives of strength sports - weightlifting, bodybuilding, powerlifting. Professionals from various martial arts (boxing, karate, etc.) also have to lift significant weights. This is especially true for those who work more in throwing techniques - after all, you need to lift a very heavy opponent.
Such loads lead to regular compression of the intervertebral discs and, as a consequence, to osteochondrosis and disc herniation. The lumbar vertebrae are most susceptible to this disease, although the cervical spine is often affected (especially in wrestlers).
Participants in sports where the load is asymmetrical are also at risk of developing a hernia. Moreover, it can appear absolutely anywhere. The reason for this is the appearance of an imbalance in the back and abdominal muscles - one half is more developed than the other, which entails lateral compression of the discs.
However, any professional athlete has a training regimen that exhausts any body, even the most naturally strong and resilient. Added to this are the injuries that occur regularly. Therefore, gymnasts, figure skaters, football players and others sooner or later develop spinal osteochondrosis for one reason or another. It is known that Andrei Arshavin, and Evgeni Plushenko, and many other athletes at one time underwent treatment to restore their backs. It has already been proven that the best means of preventing and treating spinal diseases, and especially osteochondrosis, is traction. Kinetrak medical equipment allows you to perform traction on the neck, chest and lower back, relieving muscle spasms and eliminating pain.
This device makes it possible to act specifically on the affected (based on MRI) department due to the installation of sensors in the right place. This is done using a roller, which allows you to concentrate efforts on the problem area. They also perform vertebral massage. The procedure is carried out strictly in doses, taking into account the characteristics of the person and the response to treatment.
Diagnosis of osteochondrosis
Depending on the location of the disease, orthopedics distinguishes the following types of osteochondrosis:
- cervical spine;
- thoracic region;
- lumbar region;
- common osteochondrosis is one that is located in several areas at once.
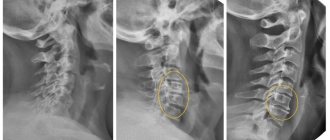
Usually, a visual examination and palpation is enough for an experienced orthopedist to determine what exactly was the cause of the patient’s pain and discomfort. He can also give precise recommendations regarding the choice of exercises in the gym for osteochondrosis. In some cases, MRI, radiography or computed tomography may be required to clarify the clinical picture. Sometimes you need to make sure that there is no herniation of intervertebral tissue and evaluate the condition of the muscle corset.
If the condition seems satisfactory to the orthopedist, he will allow you to choose gentle exercises in the gym for osteochondrosis and scoliosis. Recommendations regarding intensity and duration, as well as working weight, are given to each patient separately based on the individual clinical picture.
Stages of development of osteochondrosis
Depending on the stage of the disease, you should choose exercises in the gym for spinal osteochondrosis:
- stage one, which is characterized by destruction of the fibrous ring - the patient does not yet feel significant pain and discomfort, the appearance of cracks in the discs is just beginning;
- stage two is characterized by the appearance of protrusion (protrusion of the disc into the spinal canal);
- stage three may be accompanied by rupture of the fibrous ring and leakage of the nucleus - in this regard, it is very dangerous to put a serious axial load on the spine;
- stage four is characterized by the appearance of ossified growths on the vertebral bodies, or, as they are called in medical language, osteophytes.
At each of these stages, pinching of nerves and endings by the vertebrae may occur, as a result of which vision and hearing may begin to deteriorate, the functioning of the vestibular apparatus may deteriorate, symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia may develop, cerebral circulation may be impaired, and problems with the cardiovascular system may arise.
What are the benefits of jumping rope for a healthy body?
Jumping rope exercises are of great value for maintaining health and physical activity. Regular exercise helps replace a lot of other sports equipment. Thanks to jumping, you can maintain the muscles of the whole body in working condition and normalize the functioning of internal organs.
It has been proven that training with a jump rope works effectively in different directions:
- Together with proper nutrition, they help reduce excess weight.
- Help strengthen the muscles of the upper and lower extremities, neck, back and abs.
- They train the cardiovascular system, increase its resistance to physical activity, and improve blood circulation.
- Helps improve gas exchange and increase lung capacity.
- Normalize metabolism and hormonal levels.
- Strengthen the immune system.
- They improve your mood.
Features of training for osteochondrosis
In no case should you ignore the disease and exercise in the same way as a completely healthy person. Exercises in the gym for osteochondrosis should be agreed upon with an orthopedist or at least a sports doctor. The following points are strictly prohibited:
- working with extremely high working weights;
- work in the cardio zone with a heart rate above 140 beats per minute;
- acrobatic and plyometric exercises in which injuries are possible;
- static exercises in which the patient is forced to be upside down and other non-physiological positions;
- incorrect execution of basic exercises;
- depending on the stage of the disease, any types of squats and deadlifts may be prohibited;
- Before each workout in the gym, if you have lumbar osteochondrosis, you should perform a joint warm-up;
- Stretching at the end of each session should be done carefully and smoothly - no sudden jerks.
Exercises with a barbell for osteochondrosis
Squats with a barbell on the shoulders, beloved by all athletes, are an extremely difficult and traumatic exercise. Even experienced bodybuilders often perform it incorrectly, let alone beginners in strength sports. This is one of the most dangerous exercises in the gym for osteochondrosis.
To pump up your leg muscles, you can replace squats with a barbell on your shoulders with a bench press. Deadlifts with a barbell for the back muscles can be replaced with exercises with dumbbells or working on a rowing machine. You can do the bench press with a barbell, but in no case with extreme weights. You need to carefully monitor the technique and at the slightest deterioration in your health, refuse to perform the exercise. The bench press with a barbell can be replaced by flattening dumbbells or classic push-ups.
How to replace jumping rope with osteochondrosis
The choice of exercises should be done under the supervision of a specialist. You can start classes only after his approval. Most often, doctors recommend swimming and water aerobics. Training can take place individually or as part of a group, under the guidance of an experienced trainer. These sports have a gentle effect on the condition of the muscles of the whole body. Thanks to the even distribution of the load, the risk of injury is minimized.
In the initial stages of osteochondrosis, light jogging is allowed. During classes, you need to carefully monitor your condition. If discomfort occurs in the area of localization of the pathological focus, it is necessary to stop training.
The pain syndrome, exhausting the patient, depletes his nervous system. The patient becomes irritable and tearful. You can reduce stress and improve your mood by doing yoga or Pilates. These sports help to gently influence muscle stretching and help improve microcirculation in the affected area.
Exercises with dumbbells for osteochondrosis
Exercising in the gym with osteochondrosis is much less dangerous than with a barbell or barbell. However, if performed incorrectly, they can also cause harm.
Using dumbbells requires the athlete to have a much greater sense of balance. When working with a rod, axial load does not cause such difficulties. But when doing exercises in the gym with dumbbells for osteochondrosis of the lumbar region, problems with the functioning of the vestibular apparatus may develop.
If after training the patient feels tingling or pain in the lower back, the gait becomes awkward and unsteady, the legs give way, the training should be stopped. If a nerve is pinched in the lumbar spine, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract may develop, but more often the patient simply begins to be haunted by pain of unknown origin. Therefore, it is better not to take risks - at any stage of osteochondrosis, it is better to engage only in physical therapy. Taking risks and doing strength training is sometimes an unnecessary luxury. Sacrificing your health for the sake of muscle relief is a dubious pleasure.
Cardio training for spinal diseases
Jumping, running, plyometric and acrobatic exercises in the gym with osteochondrosis of the cervical spine are prohibited. If a patient with such a diagnosis tries to subject himself to such a load for at least ten minutes, he is almost guaranteed to feel dizzy and his vision will go dark. This is a natural reaction to a shaking of the spine in a sick person. There is only one way to avoid it - to refuse such physical activity.
Cardio training for chondrosis of the lumbar and thoracic region occurs mostly without problems. In some cases, depending on the clinical picture of the disease, the treating orthopedist may even allow the patient to exercise on an ellipsoid and treadmill.
Stretching for diseases of the spine
Stretching exercises in the gym for osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is one of the few loads that is not only not prohibited, but is encouraged in every possible way. Proper stretching improves blood circulation, does not shake the vertebrae and does not provoke the appearance of an axial load on the spine. To avoid causing dizziness and loss of consciousness, stretching should be done as slowly as possible, with smooth movements. Usually in gyms, trainers organize stretching hours - during this period, everyone is given an educational program on how to stretch for each muscle group. If you do these exercises regularly, your body becomes flexible and beautiful.
Pilates and callanetics classes are also good - these two types of exercise do not involve sudden movements and the use of power sports equipment. Thanks to this, you can pump up all the muscles and not create a risk of injury to the spine.
Why you shouldn’t jump rope if you have osteochondrosis
Loads on the spine that occur during jumping are contraindicated in case of illness. They contribute to sharp fluctuations in pressure inside the intervertebral discs, which causes compression.
Patients who neglect the advice of doctors risk aggravating the course of the disease and causing the development of complications.
Possible consequences of jumping when sick
Exercising with a skipping rope can provoke an exacerbation of osteochondrosis and make the pain more intense. In the long-term prognosis, in patients who love to jump rope, the disease progresses faster and its course is more severe than in patients who follow medical recommendations.
Jumping can lead to the formation of disc protrusion, and subsequently to the formation of a hernial protrusion.
There is a high chance of developing undesirable effects that require immediate medical attention - pinched intervertebral nerve or an existing hernia.
Swimming and exercise in water
This is exactly the type of exercise that orthopedists recommend that people with spinal diseases perform regularly. In water it is impossible to make such a sudden movement that would lead to injury. Swimmers have athletic bodies with well-developed muscles. So it is too early for orthopedic patients to be upset that they will not be able to build a muscle corset. Regular swimming will help build muscle mass in your arms, back and stomach.
In order to swim in the pool, you will need to get a certificate from a dermatologist confirming the absence of skin diseases. To avoid any difficulties with your first training sessions, you can use the services of a trainer. There are also people in the pool, as well as in the gym, who will help you establish the correct technique for various swimming styles.
Sports that are recommended for people with osteochondrosis
Exercises in the gym for osteochondrosis of the thoracic and lumbar spine can be performed with dumbbells and a barbell. If cervical chondrosis is diagnosed, you should avoid performing any weight-bearing exercises. As a last resort, you can use light dumbbells.
Orthopedic patients are very upset by the fact that strength training is prohibited. Don’t be upset, because you can find a relatively safe alternative to traumatic exercises. You can still effectively load your back using:
- pull-ups on the bar (various types of grip);
- pull of the upper block to the chest/behind the head;
- traction of the lower block to the belt;
- one-arm dumbbell row;
- back pull-down at the lower block with a one-handed handle;
- hyperextension;
- reverse hyperextension.
The legs and gluteal muscles can be exercised with exercises in a hack machine, as well as performing leg presses while lying on your back. Working on an ellipsoid is also almost always safe. The exception is the late stages of osteochondrosis, when any movement provokes pain.
What not to do
With regard to bodybuilding, the worst limitation of all that osteochondrosis imposes is the inability to perform half of the exercises with free weights, especially a barbell. In particular, both cervical and lumbar (the most common) types of osteochondrosis exclude:
- squat and half squat with a barbell on the shoulders from behind;
- squat with a barbell on the shoulders in front (that is, when the bar rests on the collarbones);
- deadlift of a barbell or dumbbells;
- bending over with a barbell on your shoulders;
- pulling dumbbells or barbells to the chest or stomach;
- classic deadlift.
And the good news is that almost all of these exercises can be replaced by working in a simulator. In this case, the rate of mass gain will, of course, decrease, but the detailing will go “like clockwork,” and we will maintain the overall good shape. You can strengthen your back and buttocks without a barbell using:
- pull-ups on the horizontal bar;
- traction of the upper block (both behind the head and to the collarbones);
- traction of the lower block to the stomach;
- active work with a Roman chair - performing direct and reverse hyperextension, but without weights on the shoulders and with the hands not behind the head, but crosswise on the chest.
As we will see for ourselves soon after starting training, they quickly relieve the initial symptoms of osteochondrosis in any department due to their ability to accelerate the regeneration of bones and cartilage. This is the natural result of the body's attempt to provide stressed muscles with everything they need to repair and grow.
However, it is precisely at this moment that it is important for us not to overstrain ourselves - in the sense that the rate of tissue regeneration cannot be infinitely high, and it always increases gradually.
Therefore, for the next six months, or even more, we need to forget about performing the approach to failure or use the 1-2 repetition technique (work with maximum weight).
“Warming up” before training also needs to be done with caution. Jogging and jumping rope, which are classic in all respects (most often used before training the lower leg muscles) are no longer suitable for us. Therefore, it is better to use a bicycle or skis, setting the route to difficulty 2 or higher.
It is better to complete each approach not by simply stretching the muscles being loaded this time, but by hanging on the horizontal bar - of course, without weights, swinging and other “acrobatics”. You should visit the pool 2-3 times a week.
It is advisable to do this after training, but only if there is such an opportunity. And it is doubly advisable to attend regular (not sports/therapeutic/exotic) relaxing massage sessions twice a week.
If you want to get more information like this from Alexandra Bonina, check out the materials on the links below.
Additional useful information:
- My free books, videos and master classes
- My exercise programs and video courses
- My printed books (available in major online stores)
- Free online marathon “How to save your face from old age”
See more useful materials on my social networks:
YouTube | VKontakte | Yandex.Zen | Instagram | Telegram | Facebook
Denial of responsibility
The information in the articles is for general information purposes only and should not be used for self-diagnosis of health problems or for therapeutic purposes. This article is not a substitute for medical advice from a doctor (neurologist, therapist). Please consult your doctor first to know the exact cause of your health problem.
I will be very grateful if you click on one of the buttons and share this material with your friends