It turns out that people suffered from such a disease as ankylosing ( ankylosing spondylitis ) back in ancient times. Archaeological scientists came to these conclusions when studying Egyptian mummies. They discovered a human skeleton where the sacrum, pelvic bones, lumbar vertebrae and 10 thoracic vertebrae were fused into a single bone, which is extremely typical for ankylosing spondylitis.
In the mid-16th century, an attempt to describe the skeleton of a person with the same disease was made by the Italian Renaissance surgeon Realdo Colomno. But only the outstanding Russian doctor and scientist Vladimir Bekhterev at the end of the 19th century was the first to systematize the signs of spondyloarthritis. In honor of this scientist, this disease in Russia is often called ankylosing spondylitis.
Ankylosing spondylitis is a relatively rare rheumatological disease that affects about 2% of the world's population. This disease is predominantly “male”, and it is typical for young men (from 15 to 40 years). Ankylosing spondylitis is 5 times less common in women.
1
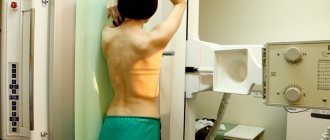
X-ray of the pelvis
2 Diagnosis of ankylosing spondylitis
3 Fluorography
What is spondyloartitis
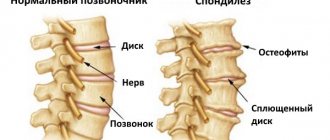
Ankylosing spondylitis is a chronic inflammation of the axial skeleton - the spine and iliosacral joints, leading to gradual ossification of the joints and limitation of their mobility (ankylosis - stiffness of the joint due to fusion of bones with each other). The term “ seronegative spondyloarthritis ” refers to a whole group of diseases, the common clinical manifestation of which is inflammatory damage to the spine, and the laboratory manifestation is a negative rheumatoid factor (i.e., seronegativity for this factor).
The following diseases are types of seronegative spondyloarthritis:
- Ankylosing spondylitis (ankylosing spondylitis);
- reactive arthritis;
- psoriatic spondylitis;
- spondyloarthritis in Crohn's disease;
- undifferentiated spondyloarthritis.
Common manifestations of this group of diseases include:
- pain and stiffness in the lumbar spine and buttocks (projections of the sacroiliac joints), increasing at rest and decreasing with movement;
- presence of the HLA-B27 gene;
- pain and swelling in the joints of the lower extremities, often asymmetrical;
- frequent damage to ligaments and tendons (discomfort in the heels, Achilles tendon).
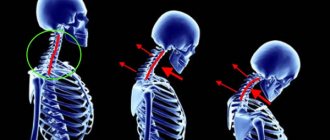
A distinctive feature of ankylosing spondylitis is changes in the ligaments of the spine, their compaction and gradual ossification. This leads to the fact that the human spine loses its flexibility and becomes as rigid as bamboo.
Unfortunately, at the initial stage of the disease, spinal spondyloarthritis is confused with osteochondrosis and incorrect treatment is prescribed. It can often take several years for a correct diagnosis to be made. If treatment for ankylosing spondylitis is not started on time, it can lead to immobilization of the spine and joints, complications such as interruptions in the functioning of the heart, damage to the lungs and kidneys. Disability due to spondyloarthritis is by no means uncommon in the case of improper or delayed treatment.
Reiter's disease - symptoms and treatment
When an infectious agent enters the body, a lesion first appears in the genitourinary organs. In men, inflammation of the urethra and prostate develops (urethroprostatitis); in women, the cervix of the uterus (cervicitis) and the uterine appendages (adnexitis) become inflamed.
Sometimes the process is acute, but more often it has an erased form. Chlamydial infections usually have a chronic, relapsing course.
Symptoms of nongonococcal urethritis can be noticed 7–28 days after unprotected sex. Scanty mucopurulent discharge from the urethra or only unpleasant sensations in it when urinating appear.
The first symptoms of Reiter's disease appear 2–4 weeks after the infection. Body temperature often increases: in acute forms it can rise to 39 ˚C and above, in subacute and chronic forms - up to 37.1–38.0 °C [3][8].
The patient develops eye symptoms : conjunctivitis, uveitis and episcleritis develop with photophobia, lacrimation, eye pain, redness, mucous or purulent discharge from the eyes. Conjunctivitis occurs in 53% of patients with urethral chlamydia [10]. It can be explained both by damage to the conjunctiva by chlamydia and by an immune reaction. It is usually bilateral and mild. It occurs with redness of the eyes and lasts 1–2 days.
In 20% of patients, eye damage develops in the form of acute or chronic anterior uveitis. If the process affects the optic nerves, then vision decreases [4][6][8][10].
1–1.5 months after an acute genitourinary infection or exacerbation of a chronic lesion, asymmetric arthritis of the legs like a “staircase” from bottom to top (for example, right ankle - left ankle - right knee - left knee, etc.). Usually 1–3 joints are inflamed, but sometimes the process affects more than four joints (polyarthritis).
Arthritis is accompanied by pain that worsens at night and in the morning. The patient is also concerned about morning stiffness, swelling and redness of the joint area. Heel pain is typical due to inflammation of the heel tendon (tendinitis) and periarticular bursae (bursitis) in the heel area. Heel spurs can form quite quickly. It is with urogenital arthritis that a sausage-shaped deformation of the toes is observed.
The joints of the hands are rarely affected and mainly during a very acute onset of reactive arthritis, mainly after an intestinal infection.
Reiter's disease is classified as a group of seronegative spondyloarthritis. This is a group of diseases that are distinguished by a common laboratory sign (lack of rheumatoid factor in the blood) and similar clinical manifestations: damage to the sacroiliac joints and overlying parts of the spine. This explains another typical symptom of urogenic reactive arthritis - back pain . Most often the lumbar and lumbosacral spine hurts, but sometimes the disease affects the thoracic and cervical spine. The pain occurs at night and intensifies in the morning. The mobility of the spine is not significantly affected.
skin manifestations may appear in the form of psoriasis-like rashes, painless, self-healing ulcers in the oral cavity, ulcer-like changes on the head of the penis around the urethra (circinar balanitis), etc. According to various authors, such symptoms appear in 20–70% of cases [8] .
Causes of spondyloarthritis
Until now, scientists cannot name the exact causes of ankylosing spondylitis.
One possible reason is hereditary predisposition. The majority of patients (about 96%) with ankylosing spondylitis are carriers of the HLA-B27 gene, which is believed to have structural similarities to certain infectious agents. As a result of the formation of cross-reacting antibodies, the body’s immune system ceases to distinguish “self” from “foreign” cells and begins to destroy the cells of its own body. This is how the autoimmune inflammatory process in the joints begins.
It has been suggested that Bechterew's disease is a psychosomatic disease, which can be triggered by the patient's mental characteristics or severe prolonged stress. Studies have shown that many patients lack psychological flexibility in solving problems, but are dissatisfied with themselves, their lives, work, family, etc.
1 Preventative massage
2 Preventive massage
3 Diagnosis of ankylosing spondylitis
Factors that provoke secondary spondyloarthritis are:
- inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system;
- intestinal infection (dysentery, salmonellosis, yersiniosis, etc.);
- disruption of the endocrine system;
- hypothermia of the body, etc.
Symptoms of spondyloarthritis
The symptoms of spondyloarthritis are quite varied. According to various estimates, the onset of the disease in 75% of cases is accompanied by lower back pain, in 20% by joint pain, in 5% by eye damage and other symptoms.
The picture is complicated by the fact that the time from the onset of the disease to the manifestation of typical symptoms of ankylosing spondylitis in men is 4-5 years, in women - 10-20 years. And the interval between relapses can range from several months to several years.
Symptoms of ankylosing spondylitis often resemble manifestations of osteochondrosis. The patient feels a sharp pain in the lower back, radiating to the leg, or pain in the neck, radiating to the arm. At the initial stage of spondyloatritis, pain may disappear for a while after massage or taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. However, unlike osteochondrosis, with ankylosing spondylitis, after some time, previously effective drugs are powerless, and the person begins to think about treatment.
Over time, the mobility of the spine decreases and a hump appears. This is what leads to the formation of the “petitioner pose” characteristic of this disease.
In the future, damage to the eyes and kidneys may develop.
The disease has a chronic course. A few years after the onset of the disease, in half of the patients the cervical spine is involved in the process.
Complete ossification and immobility of the spine can occur within 14-20 years.
1 EchoCG
2 ECG
3 MRI joints
Symptoms
- a constant feeling of stiffness and pain in the sacroiliac region. This pain may also radiate to the gluteal area and legs. Pain becomes stronger at night;
- pain in the heel bones, which is typical for young people;
- stiffness and constant pain in the thoracic spine;
- increased ESR in a blood test.
If these main symptoms persist (for 3 months or more), an urgent consultation with a rheumatologist is necessary!
Diagnosis of ankylosing spondylitis
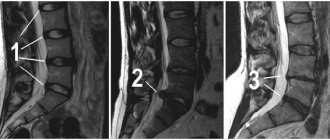
If spondyloarthritis is suspected, the rheumatologist will refer the patient for an X-ray examination of the pelvic bones, which allows visualizing the condition of the sacroiliac joints. At the onset of the disease, changes may be insignificant, but a repeat image after 1-2 years makes it possible to conduct a comparative analysis of the changes that occur as the disease progresses. A more informative method for diagnosing ankylosing spondylitis is MRI, which allows you to see changes in the joints even earlier and better.
Detection of the histocompatibility antigen HLAB27 is an important argument in favor of the diagnosis of spondyloarthritis.
Among laboratory tests, the determination of ESR and C-reactive protein (CRP) is considered mandatory (see rheumatological examination). These indicators allow you to assess the intensity of the inflammatory process.
To identify extra-articular manifestations of the disease, a biochemical blood test, ECG, echocardiography and fluorography are prescribed.
The greatest difficulty is identifying ankylosing spondylitis in the early stages. For this, it is important not only to assess the structural changes of the skeleton and laboratory test data, but also to study the family history, as well as the clinical features of the course of the articular syndrome, which requires a certain professionalism on the part of the doctor.
1 Fluorography
2 General blood test
3 Immunological blood test