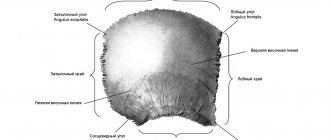
The sacrum is a large, wedge-shaped bone. It is located between the pelvic bones, at the base of the spinal column, and is responsible for one of the main functions of the lumbopelvic region. A cruciate fracture is much less common than a simple injury.
The cause of injury can be the location of the bone, because under heavy loads the sacroiliac part is subject to the greatest pressure.
Anyone who has encountered a similar problem is interested in how long it takes for a sacral fracture to heal, how serious it is and what the consequences are. In this article we will try to give detailed answers to these questions.
general information
The sacrum is part of the lumbopelvic region of the human skeleton. This area is subject to heavy loads, which can cause damage. The main lobes of the sacrum include:
- Base;
- Channel;
- Top;
- Lateral, anterior and posterior planes.
The bone connects to the coccyx, pelvic bones and lumbovertebral region. Its parameters may differ for people of different genders. In men, the sacrum is curved, wide and elongated.
Fractures of this bone account for 1/3 of all cases of its injuries, and only 20% of them are injuries to only one sacrum. The remaining percentage is due to damage in combination with the pelvic bones.
Division into types
A sacral fracture is divided into several types, differing from each other in their severity:
- Uncomplicated (also known as stable) – breaking of a bone without displacement of its pieces and without rupture of the bone ring of the pelvis, which does not bring any particular danger. It also does not injure blood vessels and nerves.
- Complicated fracture (or unstable), requiring special treatment. Almost always it is accompanied by injury to nerves and blood vessels. In addition, there is usually a shift of bone fragments, which causes damage to the integrity of the pelvic ring and muscle tissue.
Systematization of a sacral bone fracture is also carried out taking into account the location of the injury:
- Vertical view - passes through the pelvic bones, left and right sacral joints;
- Horizontal fracture - breaking of the lower section of the sacral joint, without compromising the integrity of the bones of the pelvic region;
- Oblique type - diagonal damage to the sacral joint, which usually affects the pelvic bones;
- Comminuted form is an injury in which a fragment of bone is formed, and the edges of the fracture are torn.
Possible problems
A fracture of the sacrum can be accompanied by serious consequences, since this area is connected to the spinal column. The situation is especially complicated when there is a shift.
With this pathology, the following may appear:
- Violation of the integrity of the venous plexus in the lumbosacral area;
- Trauma to the artery in the hypogastric region;
- Trauma to the artery in the middle part of the sacrum;
- Rupture of the abdominal bursa and rectum;
- Pathological changes in the spinal cord.
Possible complications
The consequences of a sacral fracture appear if a person is careless about the requirements to limit motor activity and loads on the spinal column. Often this is exactly what happens - the patient is discharged from the hospital and thinks that he is healthy, starts playing sports or lifting heavy bags, and here lies his main mistake.
The list of common consequences:
- improper fusion of bones;
- acquisition of chronic pain syndrome;
- the appearance of problems with the pelvic organs, including sexual dysfunction;
- disruption of excretory processes in the body;
- change in posture;
- difficulty walking;
- loss of sensation in tissues and limbs.
Treatment and consequences of a sacral fracture are always a controversial point; success largely depends on the doctor and his attentiveness. However, you yourself influence whether the listed complications will occur to you. Take the requirements for the rehabilitation period seriously - this is important so that in the future you do not suffer an even more dangerous injury and remain disabled.
Origin of injuries
There are several causes of a sacral spine fracture:
- Road accident. In car accidents, the risk of injury to the sacrum is high. Sometimes they are complicated by shear.
- Osteoporosis is a deterioration in the density of bone tissue, as a result of which it is easily injured. With this disease there is a high probability of sacral fractures. The disease is dangerous because its manifestations become noticeable already in the last phase of its development. Elderly people are most susceptible to it. This can cause disability and even death. Signs of osteoporosis include pain in the spine and chest, fatigue and curvature of the spinal column.
- Mechanical damage usually occurs due to a fall. This type of fracture accounts for about 20% of all injuries in this area.
- Compression of the pelvic bones in the anteroposterior direction.
How to treat a sacral fracture
Treatment of a sacral fracture is a rather lengthy process. Its success depends on whether the person is ready to comply with the regimen and other requirements of the attending physician. There are several main methods: from conservative treatment and exercise therapy to surgical intervention. Let's take a closer look at them.
Conservative treatment
The first obvious option in the treatment of a sacral fracture is to immobilize the patient and reduce the load on the sacral region. Bed rest is indicated for several days. Point anesthesia is used with control of the patient's position.
Depending on the degree of damage to the fibers and ligaments, therapeutic exercises gradually begin - it is necessary to restore normal motor ability. In addition, ointments are prescribed to reduce swelling and relieve bruising at the site of injury. You will also need to take care of a balanced diet rich in foods with calcium.
Physiotherapy
Physical therapy is aimed at gradually returning mobility. At the initial stages, it is performed in a lying position, gradually adding small loads and stretching work.
Operation
Surgery is necessary if an accident leads to the separation of pieces of bone. In this case, the surgeon will need to remove the debris and restore the integrity of the tissues and muscles in the injured area.
Symptoms
For the most part, a sacral fracture has subtle symptoms, which is why it is difficult to immediately identify. The patient may not experience any discomfort, and the only visible signs are slight swelling. Sometimes its clinical manifestations are similar to injuries to other parts of the spine or pelvic bones, which makes diagnosis very difficult.
But still, the main sign of a fracture is pain in the pelvis and lower spinal region. Pressing on the swollen tubercle causes painful suffering. With serious fractures, pain may be felt in the groin or lower back. These phenomena can be combined with bleeding, which is sometimes profuse.
The patient is not able to lie in a supine position, because he cannot tolerate discomfort only on his side and stomach.
The following symptoms may also occur:
- Hematoma;
- Detachment of skin in the damaged area;
- Lightheadedness and vomiting;
- Headache;
- Increased pain when sitting;
- Pain radiating to the legs;
- Painful bowel movements;
- Frequent urination;
- Failure of the female menstrual cycle.
A displaced sacral fracture can cause injury to the rectum or even the walls of the abdominal pouch. During palpation, the doctor may feel peculiar steps at the fracture site. In addition, a neurological disorder may be provoked due to the fact that the nerve endings of the cauda equina of the spinal cord and the superior gluteal nerve are injured.
If the 1st and 2nd roots of the sacrum are damaged, the motor function of the body becomes difficult.
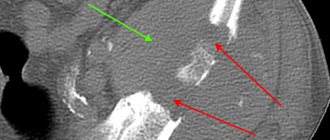
Diagnostic methods
A detailed medical examination is required to diagnose a sacral fracture. This disorder can be most accurately identified using x-rays in direct and anterior projection. As additional measures, sagittal and oblique X-ray projections are performed.
To establish an accurate medical conclusion, the following research methods are also used:
- CT;
- MRI.
MRI gives the most informational and accurate results. In addition, this procedure is painless and harmless.
Diagnosis if there is concern for a sacral fracture should be comprehensive to exclude the development of other pathologies: neoplasm, thrombophlebitis of the iliac and pelvic veins, gynecological malaise, inflammation in the pelvic area.
Treatment
First aid for breaking the sacral bone is to eliminate the pain, which can be extremely severe. Upon admission to the hospital, the doctor should place the patient on the couch, placing a pillow or cushion under the sacral area, and apply a novocaine blockade.
There is no special treatment for sacral fractures. Conservative methods are usually prescribed to eliminate the problem. Strict bed rest must be observed for 2-4 weeks. The surface of the lying area on which the patient will remain all this time must be hard.
It is recommended to use a wide cushion placed under the lumbar spine. This will minimize the load on the damaged area and ensure reposition (comparison of fragments) of displaced fragments.
Sometimes the patient can roll over onto his side for a short time, but only if the pain does not increase with these actions. It is allowed to sit down only after 1-1.5 months. It will take 2-2.5 months for the body to fully recover.
Drug therapy
The treatment complex for a lumbosacral fracture also includes taking painkillers - intravenous and intramuscular injections. In most cases, pain is relieved thanks to novocaine presacral blockade. Injections are given in the area of the sacroiliac or spinal canal.
Rehabilitation and recovery
How long does it take for a fracture to heal? On average, rehabilitation after a sacral fracture lasts from 1.5 to 2.5 months. During this time, the victim regains full mobility and the muscle mass lost during treatment is restored.
Throughout this time, the patient is prescribed mandatory physiotherapy procedures, a course of physical therapy and massage sessions. In combination, each of the methods significantly helps to reduce the intensity of pain and restore the previous full functionality of those affected by damage to bones, blood vessels and internal organs. For a faster recovery, the patient is often recommended to purchase a special corset.
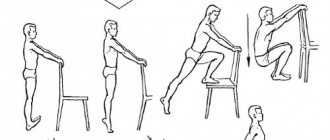
Exercise therapy
All exercises are selected by a specialist strictly taking into account the nature of the fracture and the age of the patient. Exercises are included in the complex in stages. Physical activity should increase gradually in order to eliminate complications that arise due to the unacceptable intensity of therapeutic exercises.
The entire gymnastics course is divided into 4 stages, and each of these stages must be carried out under the supervision of a professional rehabilitation specialist.
The first stage begins with the simplest exercises. Lying in bed, the patient raises his legs at right angles and develops the respiratory muscles, makes circular rotations with his feet, squeezes and unclenches the fingers of the upper and lower extremities.
At the same stage a little later:
- raises and lowers the pelvis, resting on the palms and feet;
- bends and straightens legs at the knees;
- feet slide along the bed.
It is important to repeat each exercise up to 6 times during the day.
Old injury
Some people do not take any action when they receive a sacral fracture, mistaking it for a minor bruise. The consequence of this attitude is the transition of trauma into an old form. This only takes 5 days.
The human body is capable of healing itself, but sometimes this leads to complications. A callus may form at the fracture site, since the damaged area needs to be filled with something and connect the broken bone.
Bone fusion without medical supervision most often occurs incorrectly and with deformation. The curvature can be noticeable even externally. And in the future, there is a high risk of developing coccygeal neuritis, which will be constantly accompanied by pain, regardless of body position.
Moreover, the pain syndrome will increase when sitting on a chair. Such phenomena cannot be cured, since they are already chronic. An old sacral fracture can only be repaired through surgery.
First aid
For a victim with signs of a fracture, it is first of all important to provide emergency medical care. But before the team of specialists arrives, in order to avoid irreversible consequences, all actions should be kept to a minimum and the victim should be treated with extreme caution and care.
To avoid displacement of bone fragments, it is better not to touch the victim. But you still have to perform some necessary actions.
- Lay the victim on his stomach on any flat, hard surface.
- To relieve tension in the pelvic muscles, carefully spread the victim’s legs and leave them in a semi-bent position.
- To hold the limbs in this position, place a cushion of clothing or a rolled blanket under the victim’s feet.
- If a person experiences severe unbearable pain, give him any analgesic (Baralgin, Pentalgin, Analgin, etc.).
It is important to transfer onto a stretcher as synchronously and carefully as possible. This requires the participation of at least two people.
Any available cold applied to the injured area will help prevent the development of edema. Right down to frozen foods from the refrigerator. But such a compress should be kept at intervals of 10–15 minutes to prevent excessive hypothermia of the tissues.