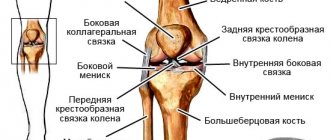
Fracture is called a violation of the integrity of the bone under the influence of an external force exceeding the strength of the bone. With an incomplete fracture, a partial violation of the integrity of the bone occurs with the formation of a fracture, crack or holey effect of the bone tissue. When treating fractures, it is important not only to restore the integrity of the bone and its anatomical shape, but also to improve the function of the damaged parts of the body.
1
Treatment of fractures
2 Treatment of fractures
3 Treatment of fractures
Bone fractures can lead to complications such as:
- disruption of vital organs (heart, lungs and brain);
- the occurrence of paralysis as a result of injury to nerve cells by bone fragments;
- infection and the appearance of purulent inflammation in the area of the open fracture.
To avoid various complications, medical care for fractures and other injuries should be provided as quickly as possible. It is very important to transport the victim to a hospital or emergency room in a timely manner!
Causes of fractures
Bone fractures are divided into traumatic and pathological .
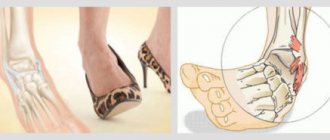
Traumatic bone fractures occur as a result of external mechanical influences. A broken leg and a broken arm most often occur when a person is hit or falls. A rib fracture, like a collarbone fracture, often occurs as a result of an unsuccessful jump and fall. A fracture of the heel bone (the so-called “skydiver’s injury”), as a rule, occurs when landing unsuccessfully on one’s feet from a height.
Others, pathological fractures , are caused by weakness and fragility of the bone itself. These include, for example, bone fractures in older women suffering from osteoporosis (a common injury in this disease is a hip fracture).
1 Treatment of fractures
2 Treatment of fractures
3 Treatment of fractures
How to diagnose?
It is usually not difficult to identify dysfunction of the hand associated with improper healing of a fracture. There are often external signs, such as pathological rotation, a hump on the back of the hand, angular deformation of the finger, and others. To clarify the nature of the bone deformation, an x-ray is usually sufficient. It is very important to photograph each finger separately in a clear frontal and lateral view.
Rotational displacement is assessed when clenching the fingers into a fist: whether there is crossing or not. And here difficulties may arise, for example, we assume that the finger is simply not yet developed and therefore does not bend, but in fact there is a slight rotational displacement, which makes it difficult to bend.
So for a complete diagnosis, both analysis of radiographs and examination by a specialist are important. After all, tendon mobility can only be assessed during examination; ultrasound or MRI are not very helpful in assessing the condition of soft tissues when it comes to fingers.
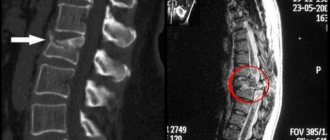
In the case of intra-articular fractures, a computed tomography scan may be ordered to assess displacement.
Types of fractures
Depending on the reasons that caused the fractures, different types of bone injuries can be distinguished.
Classification of bone fractures based on skin integrity:
Fractures can be closed (i.e., without deformation of the skin) and open (with damage to soft tissues and skin).
In addition, doctors distinguish between fractures with displacement of bone fragments and without displacement.
Classification of fractures by direction and shape:
- longitudinal fracture (fracture line parallel to the axis of the tubular bone);
- transverse (the fracture line is perpendicular to the axis of the bone);
- oblique (V-shaped), in which the fracture line is at an acute angle to the axis of the bone;
- helical fracture (rotation of bone fragments relative to their usual location);
- wedge-shaped fracture (both bones are pressed into each other, most often found with a fracture of the spine);
- comminuted (the bone is broken into several parts);
- compression fracture (all fragments are small, there is no single fracture line);
- impacted fracture (with this type of compression fracture, one of the bone fragments is firmly embedded in the other).
First aid and diagnostics
First of all, the damaged part must be immobilized, i.e. immobilize, ensuring complete rest. To do this, use medical splints and other devices, for example, improvised means (sticks, cardboard).
If a hip or shoulder bone is broken, a splint is applied, covering 3 joints at once. In other cases, it is enough to cover 2 adjacent joints - before and after the fracture site and bandage it securely. If there are bone fragments, under no circumstances should you pull them out yourself. It is also necessary to disinfect the wound to prevent infection of the skin and blood.
To diagnose, you need to seek emergency help as quickly as possible or visit a doctor - therapist, surgeon, or orthopedist. The specialist conducts an external examination and identifies complaints. The patient also undergoes an x-ray to confirm the diagnosis. The picture can be taken in 1 or 2 projections.
Fracture treatment
In a hospital or other medical institution, an x-ray is taken, with the help of which the diagnosis, location, nature of the damage and the direction of displacement of bone fragments are clarified.
Then the doctor sets the bone fragments (repositions them). This is done only after pain relief. If the fracture is not clearly visible, an incision may be made in the patient's skin. The injury site is secured with plaster or other medical device.
In case of severe injuries, surgical treatment of the fracture is performed; bone fragments are secured using plates, nails and screws. The fracture site is then fixed (immobilized) to ensure proper fusion of the bones.
In some cases, bone traction is required. In this case, a steel pin is attached to the bone below the site of injury, and a weight is attached to the two ends of the pin.
It should be noted that the rate of bone healing depends on the patient’s age, type of fracture, degree of bone mineralization and the presence of concomitant diseases.
Currently, modern devices such as the Ilizarov apparatus and orthosis .
1 Treatment of fractures
2 Treatment of fractures
3 Treatment of fractures
Treatment of fractures using the Ilizarov apparatus
The Ilizarov apparatus is used to reliably connect bone fragments in open and comminuted complex fractures. The spokes passing through the bones of the damaged limbs are attached to rings, which are secured with special transition elements. If necessary, this allows you to compress or stretch certain areas of the bone.
Using this design, you can not only fix a fracture, but also influence the rate of bone fusion. In addition, the Ilizarov apparatus allows you to move with a broken leg.
The process of installing and removing the Ilizarov apparatus
Installation of the device is carried out under local or general anesthesia. Two wires are passed over the fracture through parts of the bones perpendicular to each other. And the ends of the spokes are secured to the bone using clamps. The entire time the design is worn, it is necessary to properly care for it and wipe the knitting needles with a disinfectant solution.
Removal of the Ilizarov apparatus, as a rule, is carried out in the same clinic where the installation took place, or any other medical institution in which the corresponding traumatologist works. Removal of the Ilizarov apparatus is carried out using anesthesia.
Treatment of joint and bone diseases using an orthosis
An orthosis includes several types of orthopedic devices that are used to treat joints. These can be corsets, bandages, orthopedic shoes, as well as orthopedic insoles.
Orthoses can be used in the following cases:
- fixation and unloading of the spine and joints;
- restoration of musculoskeletal function after various injuries (used to treat fractures, dislocations, sprains and bruises);
- correction of deformities of the musculoskeletal system (kyphosis, scoliosis);
- pain relief from arthritis, arthrosis, osteochondrosis, etc.;
- protection of the spine and joints during increased physical activity.
But most often, an orthosis comes to the rescue in cases where it is necessary to fix a damaged joint.
Types of orthoses
According to their purpose, orthoses can be divided into 3 large groups:
- orthoses for the joints of the lower extremities (ankle orthosis, knee orthosis, hip joint device, orthopedic shoes and insoles);
- orthoses for the joints of the upper extremities (shoulder brace (scarf or orthosis), wrist orthosis, finger braces and elbow pads);
- orthosis for the spine (postpartum and prenatal bandages, collar splints, corsets).
Orthoses come in soft , rigid , semi-rigid and splint types . Most often, the degree of rigidity determines its purpose. For example, a soft ankle orthosis (or knee orthosis) resembles a bandage that is used to prevent joint diseases.
The rigid device is somewhat similar to plaster; it is a rather complex structure made of plastic and metal inserts. Prescribed for injuries, fractures, after surgery, for dislocations, when it is necessary to immobilize the joint.
The splint is used to restore an arm or leg after surgery or injury. The splint differs from an orthosis in that it has a different design, in which there are no hinges.
1 Treatment of fractures
2 Treatment of fractures
3 Treatment of fractures
Signs
Symptoms of a fracture do not always make it possible to accurately establish a diagnosis. In some cases, additional diagnostics are necessary to help identify it. The vague nature of the signs sometimes leads to an erroneous diagnosis and, in this regard, a distinction is made between absolute signs of a fracture (reliable), which raise no doubt about the deformation of the integrity of the bone from pressure, and relative (indirect) - those that are subsequently diagnosed as a bruise.
The absolute sign of a bone fracture is characterized by:
- pronounced unnatural position of the limbs;
- mobility of the bone in an uncharacteristic place, on the line of injury;
- a peculiar crunching sound (crepitus) when moving;
- the presence of an open wound with a noticeably prominent bone fragment;
- change in limb length;
- loss of sensitivity in the skin caused by rupture of nerve trunks.
If all reliable signs of a fracture or one of them are detected, then the patient can be confidently diagnosed with a fracture.
Relative symptoms of fractures:
- pain at the site of impact, especially when moving the injured bone, as well as during axial load (if a tibia fracture, apply pressure to the heel area);
- swelling of the fracture site that occurs within a short time (from 15 minutes to 2 hours). This symptom is not accurate, since a bruise may be accompanied by swelling of the soft tissues;
- the appearance of hematomas. Does not immediately appear at the site of injury; when the site pulsates, it is a sign of ongoing subcutaneous bleeding;
- absence or decrease in mobility of the injured limb, complete or partial limitation of the functioning of the injured or nearby bone.
When diagnosing one of the above symptoms, one cannot speak of the presence of a fracture, because they are also a sign of a bruise.
Classification into absolute and relative signs of a fracture helps, using knowledge of symptoms, to determine with complete accuracy what kind of damage the patient is susceptible to and to establish the severity of the injury. If there are indirect signs of fractures, additional x-ray examination is necessary to establish an accurate diagnosis.
Treatment of fractures at the MedikCity clinic
If you need emergency and professional help, then contact the paid emergency room of the MedicCity clinic!
We work every day from 9.00 to 21.00. X-rays work for you in the same mode, and we perform MRIs around the clock!
Experienced traumatologists use in their work all the advanced methods of treating fractures, as well as modern, high-quality materials, in particular plastic plaster, which is lightweight, does not deform from water and is comfortable to wear.
Types of modern plastic plaster
One of the easiest is Scotchcast . The patient practically does not feel its weight, and the body breathes in it. Scotch tapes are available in various colors, which slightly “brightens up” not the easiest period in a person’s life. Among the disadvantages, it can be noted that the plaster cannot be exposed to water (it is put on with a special cotton-rag stocking, which serves as a layer between the rough material and the skin), and it can only be removed with the help of a specialist.
Softcast is a bandage made of a very flexible, elastic material, which allows it to be used for sprains and sprains. In cases of fractures, the bandage is worn together with adhesive tape. This plaster is made from fiberglass fabric impregnated with polyurethane resin and is therefore water resistant. In this case, the cast ensures the flow of air to the injured limb.
HM-cast is a synthetic mesh with large cells, made in the shape of a sleeve. It is very light, but you only need to wear it with a special synthetic stocking. This product can be used for water procedures; it is very light in weight and is available in various sizes, which makes it convenient for treating limb fractures of different locations. This cast allows X-ray penetration, allowing specialists to monitor bone healing without removing the cast.
Turbocast is the most common plastic gypsum with high strength. A cotton stocking is not worn under this cast, so you can take water procedures in the turbocast. Another plus is that this material has a working memory, so it can be heated and used repeatedly. A turbocast plaster cast looks aesthetically pleasing and is easy to use (it can be hygienically treated with a soap solution).
In our clinic you can replace the uncomfortable old plaster cast with a modern lightweight turbocast bandage. Follow our promotions! Very often there is a discount on the plaster replacement procedure.
If necessary, the doctor will quickly and professionally install an orthosis for you and remove the Ilizarov apparatus. If you need to remove an Ilizarov apparatus, you can find out the cost of the service by phone.