January 01, 2015
A spinal fracture is a serious injury that requires special care from others and immediate medical attention. The danger of a spinal fracture lies in the fact that the spinal cord is located in the spinal canal, and temporary pinching or complete rupture of the spinal cord or the nerve roots extending from it can lead to irreversible consequences.
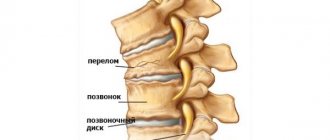
The most common causes of spinal fractures are external factors: car accidents, falls from great heights and heavy objects falling on the head or back, extreme sports, diving. However, fractures can also be a consequence of diseases associated with the destruction of bone tissue, such as osteoporosis, as well as metastasis of malignant tumors. Spinal fractures are distinguished by location and divided into two types - compression and comminuted. The most common fractures, compression fractures, occur when the spine is simultaneously bent forward and compressed, resulting in a decrease in vertebral height and a fracture in the anterior portion of the spine. Most often, such a fracture occurs in the area of transition from the thoracic to lumbar spine, that is, in the 11th and 12th thoracic vertebrae and the 1st lumbar. With a comminuted fracture, the vertebral body splits into several small fragments. The slightest displacement of the resulting fragments can lead to damage to the spinal cord, and therefore this type is considered the most dangerous. Spinal fractures can be single or multiple, complicated by damage to the spinal cord, the roots of the nerves emerging from it, intervertebral discs, or uncomplicated.
Causes of injury
The main causes of injury to the neck and other parts of the spine include:
- Catatrauma – falling from a height;
- Direct blow to the spine with a heavy object;
- Diving into bodies of water without following safety precautions;
- Road accidents, not only due to the risk of mechanical damage to the vertebrae, but also due to whiplash injury - hyperextension of the cervical spine during sudden braking;
- Gunshot wounds.
Peculiarities!
A separate group includes pathological fractures of the spine, which occur against the background of vertebral tumors or osteoporosis - decreased bone density. In this case, the vertebrae become fragile and break even with minor damage.
Diagnostics
The first thing the doctor does is an external examination.
It is carried out by palpation. The injured part is identified in the place of the ridge where the victim experiences severe pain. If vertebral fragments appear as a result of an injury, they can also be identified by palpation. To confirm the initial diagnosis, the patient is referred to a radiologist and neurologist. The first takes a picture of the ridge, where the extent of the damage is clearly visible. It is necessary to take a picture in several projections: oblique, lateral and direct. A neurologist checks the functioning of the spinal cord and nerve endings.
When the image is ready, it is necessary to interpret it. The doctor carefully examines the position of the joints, their size and shape. To diagnose as accurately as possible, you need to use special techniques. One of them is to connect the vertebrae with a contour. This technique makes it possible to clearly determine the degree of deviation and the scale of deformation of the ridge line.
In the process of treating a fracture of the thoracic vertebrae, additional X-ray examinations are carried out. This measure is very important. Additional examinations make it possible to prevent improper fusion of bone tissue, which, for example, can result in the formation of a hump. Myelography is also necessary. This procedure is a type of x-ray examination. It is performed to assess the condition of the spinal cord.
Treatment of a fracture of the thoracic spine is quite complex. Therefore, the issue of diagnosing the extent of damage to the ridge must be given maximum attention. The full list of examinations necessary for proper treatment for compression fractures of the thoracic vertebrae is quite large.
The patient needs:
- Get an electrocardiogram. It is needed to study how the injury affected the functioning of the heart muscle.
- Get tested for PSA levels.
- Get an erythrocyte sedimentation rate test.
- Take a general blood test.
- Undergo serum protein electrophoresis.
- Be examined for endocrine pathologies.
- Get bone densitometry to assess your bone density levels.
- Obtain radionuclide bone scan results.
- Undergo a regular computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging scan.
- Take an x-ray.
The most informative methods for diagnosing the extent of a fracture of the seventh thoracic vertebra are computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. They provide the most detailed information regarding the characteristics of the damage received by the ridge. Assessing bone density will help rule out osteoporosis.
Before prescribing treatment for a compression fracture of the thoracic vertebrae, the doctor must accurately identify the type of pathological changes. There are four of them.
The type of pathology can be:
- Rotational. It consists of a violation of the integrity of the transverse processes of the vertebra.
- Extensional.
- Axial. The nature of the injury is associated with a decrease in the height of the posterior and anterior parts of the vertebra.
- Flexion. This indicates that only the anterior part of the vertebra was subjected to deformation and damage.
All this will allow the doctor to prescribe correct and effective treatment for fractures of the thoracic vertebrae. Despite the fact that the list of diagnostic measures is quite impressive, in most cases, an X-ray examination is sufficient to accurately identify the nature and type of damage.
Types of spinal fractures
A fracture of the spinal column can be open - with a rupture of the integumentary tissue - or closed, when the outer tissues retain their integrity.
If a patient shows signs of damage to nerve structures - the spinal cord, spinal roots, then they speak of a complicated fracture. If there are no such symptoms, then the fracture is uncomplicated.
Most often, displaced fractures are complicated when the fragments move relative to each other. Fractures without displacement are stable; as a rule, they heal without additional problems.
Based on the location of the fault line, a fracture of the body, arch or processes of the vertebra is distinguished. According to the mechanism of injury, they are divided into compression and comminuted fractures.
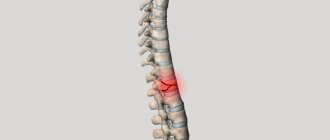
Compression
A compression fracture is a compression of the vertebral body in the vertical direction, due to which cracks form in it and its height decreases. This injury is usually caused by a sudden axial load on the vertebra, but can occur spontaneously in patients with osteoporosis, tumors or inflammatory diseases of the spine.
As a rule, a compression fracture does not require surgery and heals while wearing a brace.
Fragmentation
A comminuted fracture is more dangerous because it is associated with crushing the vertebra into small fragments. They shift, damaging neighboring structures - blood vessels, nerve fibers, ligaments, muscles. Therefore, comminuted fractures are often accompanied by heavy bleeding and pinched nerves.
In this case, surgical treatment with the installation of reinforcing metal structures is required.
Types of fractures
First aid for a spinal fracture depends on the type and severity of the injury. However, in any case, the risks of damage to the spinal substance located in the spinal canal are high.
Splinters of the vertebrae can cause injury to nerve bundles and blood vessels, of which there are many in the spinal region. The result is partial or complete immobilization of the limbs and torso as a whole. There is also a loss of sensitivity with a complete disruption of the functionality of the body.
Along with traumatic injuries of the spinal column, there are also compression injuries. The latter are more common because they are usually caused by osteoporosis, and in some cases by osteochondrosis, spondylosis and a number of other diseases. As the disease progresses, the height of the vertebrae is reduced, they are pressed, fused and overlapped. Therefore, physical and axial loads in this condition, sudden lifting of loads provoke the manifestation of a compression fracture. In this case, first aid for a spinal fracture should be provided immediately.
When one of the vertebrae is fractured, the symptoms of the damage may not appear for a long time, and in some cases, problems with adjacent vertebrae cause only aching chronic pain. They are often ignored. This is typical for young people who are keen on extreme sports, as well as for elderly patients with spinal diseases.
A comminuted fracture of the spine can result from trauma, and it can seriously harm your health. With such damage, the vertebra is crushed into fragments, often with sharp edges. Therefore, the consequence is compression of nearby muscle tissue, circulatory system, nerve endings, as well as severe injury to them. In severe cases, fragments cut tissue, blood vessels and nerve endings.
Spinal injuries can also manifest as:
- single or multiple fracture;
- injuries with and without damage to the spinal cord;
- injuries to intervertebral discs or in the absence of such injuries;
- fracture without displacement of the vertebra and with its displacement.
Fractures can cause damage not only to the vertebral bodies, they can provoke injuries to the spinous processes and arches. An open fracture poses a particular danger to humans .
Diagnosis of a fracture and its symptoms
A full diagnosis is carried out in a medical institution using radiography, magnetic resonance or computed tomography. These techniques allow us to assess not only the presence of a fracture, but also its shape and associated soft tissue damage.
However, already at the stage of providing emergency care, one can suspect a spinal fracture in the victim. The following signs indicate this:
- Acute pain in the back or cervical region, when a nerve is pinched, the pain radiates to the arms, legs, chest;
- Visual deformation of the neck or other parts of the spinal column;
- Unnatural head position;
- Smoothing of the curves and grooves of the spine;
- Hematomas in the area of injury;
- Weakness or complete immobility in the limbs - in the lower ones with a fracture of the thoracic or lumbar regions, in the upper and lower ones with a neck injury;
- Loss of sensation in the torso, arms, legs;
- Breathing disorders – frequent ineffective breaths or slowing them down;
- Improper functioning of the heart up to its complete stop;
- Disorders of urination and defecation.
With an open fracture in the wound, bone fragments can be seen with the naked eye.
The most dangerous injury is a fracture of the cervical spine. If the spinal cord is damaged at this level, paralysis of the entire body occurs, including the respiratory muscles, which leads to asphyxia. In addition, neck injury is often accompanied by damage to the arteries supplying blood to the brain, which leads to death or disability.
Showing signs of spinal damage
Let's look at the symptoms of a spinal column fracture:
- At the site of injury, the victim feels intense pain in an acute form. Loss of consciousness often occurs or a drop in blood pressure is observed. If a person suffers from osteoporosis, cancer problems and other chronic spinal diseases, and has already encountered pain, then the pain will be less pronounced.
- If the nerve endings are damaged or compressed by swollen tissues, and injury to the spinal cord is observed, then paralysis of the limbs is likely to develop. There are risks of partial or complete loss of sensitivity.
- A fracture of the cervical segment of the spinal column leads to an unnatural position of the head. In this case, the muscle tissue is in a contracted state, and breathing is impaired. The result is death. First aid for a spinal fracture with such symptoms should be performed as quickly and accurately as possible.
- Damage in the cervicothoracic area provokes difficulty breathing, and sometimes a complete cessation of respiratory activity.
- When the lumbar segment is damaged, pain appears in the abdominal area. In this case, the victim may complain of problems with urination or incontinence.
- Damage to the sacrum and coccyx occurs as a result of falls on the buttocks or a blow to this area. Hematoma and swelling appear in the damaged area. A person is unable to move or simply stand on his feet.
Thanks to timely and correct diagnosis of injuries, first aid for a spinal fracture can alleviate the condition of the victim and reduce the risks of complications.
First aid
If you suspect that the victim has a spinal column injury, you should in any case seek medical help, even if the diagnosis is ultimately not confirmed. It is best to call an ambulance and assist the patient yourself until it arrives.
What needs to be done first
- Assess the patient's condition and signs of life. If breathing and heartbeat are absent, begin cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
- If there is no immediate threat to life, the victim is placed on a hard, flat surface in a supine position. It must be moved as carefully as possible with the help of 3-5 people, so as not to cause displacement of fragments. In some cases, it is generally better to leave the victim in place until doctors arrive, if this does not pose a danger to him.
- If the patient is unconscious, has motor restlessness, or requires independent transportation to a medical facility, then it is permissible to build a rigid stretcher, for example, from boards, sticks, doors, and secure the victim on them using belts or wide ties.
- In case of a neck injury, you should place a low bolster under the back of your head, and use two more bolsters to secure your head from the sides.
- If vomiting begins, the victim's head should be carefully turned to the side to avoid aspiration.
- A hypothermic pack can be applied to the injured area.
- The open wound is treated with an antiseptic solution - chlorhexidine or hydrogen peroxide, and then a loose cotton-gauze bandage is applied.
Note!
If the patient is bothered by intense pain, then it is permissible to use analgesics (analgin, dexalgin), preferably in the form of intramuscular injections. However, if the pain is tolerable, then it is better not to give him unnecessary drugs.
What absolutely should not be done
If a spinal fracture is suspected, some manipulations are strictly prohibited:
- Attempts to sit or put the victim on his feet;
- Self-reduction of displaced vertebrae;
- Transporting the patient in a sitting position;
- Do not pull or pull the patient by the arms or legs;
- Water and food should not be given to a person who is unconscious or has difficulty swallowing.
Features of first aid for children with a spinal fracture
In children, spinal fractures are quite common due to increased mobility and incomplete formation of bone tissue. Moreover, such injuries heal relatively quickly and rarely cause complications.
The main difficulty in providing pre-medical care to children is that they are more mobile than adults, so it is more difficult to achieve complete immobilization. If it is difficult to explain to a child that it is important to lie still, then it is advisable to secure him with bands on an improvised stretcher, and also firmly hold his head and limbs. Sometimes the child can be distracted with an interesting story until the ambulance arrives.
Emergency assistance for the elderly
In older people, vertebral fractures often develop against the background of osteoporosis and falls associated with age-related coordination problems. Such damage is poorly restored, since regeneration proceeds more slowly than at a young age.
The general rules of first aid for the elderly remain unchanged. However, the main danger is that the fractures may be hidden. Against the background of a minor injury and constant back pain, which often affects older people, even serious damage can go unnoticed for some time. Therefore, it is important, even in the case of a normal fall, to take the patient to a medical facility to exclude a fracture.
How to avoid mistakes
First aid for a spinal fracture requires clear and strict adherence to the procedure and coordinated manipulations. The more accurately all procedures are performed, the higher the likelihood of the victim avoiding serious complications, although the type of injury itself is extremely dangerous and causes serious impairment of functionality. It is expressly prohibited:
- seat the victim or transport him to a medical facility in a sitting position;
- lift the victim to a vertical position, put him on his feet, even if you provide him with support;
- stretch or jerk the upper or lower limbs, trying to get rid of their unnatural position. Here it is important to remember how first aid is provided for broken limbs;
- on your own, without waiting for qualified help, to realign the affected areas of the spinal column;
- try to give the victim medicines or water if he is unconscious or there are disturbances in respiratory and swallowing functions.
A spinal fracture can have serious consequences. Complications may be associated with instability of the spinal column, when neurological disorders and kyphotic deformity in the form of curvature begin to progress. In severe cases, the victim will experience complete or partial loss of mobility and sensitivity. Death is also possible.
In any case, a person who has suffered a spinal fracture needs to receive pre-medical first aid. An ambulance must be called and transported to a medical facility. Accurate diagnosis of injuries and their treatment conservatively or surgically is carried out only in a hospital setting.
Features of resuscitation for a fracture
Resuscitation measures for spinal injuries are carried out according to general rules: the airways are cleared of foreign bodies, vomit and blood, and then mouth-to-mouth artificial respiration and chest compressions are performed. For 2 passive breaths, make 30 presses on the base of the sternum.
However, there are several nuances:
- Before carrying out resuscitation measures, the patient must be moved to a hard horizontal surface.
- Turning the victim's head to clear the airway should be done with extreme caution if a neck fracture is suspected.
- When pressing on the chest, it is important not to displace the patient; for this, the force application vector must be directed strictly perpendicularly.
- During mouth-to-mouth artificial respiration, the victim’s head should not be thrown back too far. This will not only make the manipulation ineffective, but will also increase damage to the neck.
First aid
It is very difficult for a person who understands little about medicine to determine whether a blow to the spine led to a fracture or a severe bruise. It is necessary to immediately bring the victim to his senses, preventing him from making sudden movements that could aggravate the condition. Also, those helping should not panic; their movements should be coordinated and firm.
As soon as the patient has returned to a normal psychological state, even the slightest movements of the body should not be allowed. It is necessary to explain to the patient that he should not stand up, sit down, or change his body position to one that is comfortable for him. You should immediately call for medical help, leaving the patient in the same position.
If it is impossible to call a doctor, you should try to assess the severity of the patient:
- the patient must be conscious;
- he should have a clear pulse;
- presence of breathing is required;
- The patient must have pain and tenderness in the extremities.
If a patient is diagnosed with all four factors, there is a high probability of a favorable outcome and a fairly rapid recovery. The patient can begin to be transported according to the rules.
If the slightest movement leads the victim to a state close to painful shock or gives rise to severe pain, there is swelling at the site of the injury, most likely a fracture has definitely occurred. Therefore, if medications are available, you can try to stabilize the patient’s condition.
To do this, the wounded person is given analgesics, for example, novocaine. If the swallowing reflex is normal, the patient can take the tablets orally. If even the slightest problems with breathing and swallowing are observed, taking tablet medications is prohibited. This can lead to dysphagia (abnormal constriction of the larynx), which can cause the patient to choke and die.
You can give and administer medications only if you know their dosages and contraindications.
If the patient is unconscious, he most likely suffered from painful shock and spinal cord injury. Sometimes this occurs due to severe pinching of the nerve root.
If the patient is not breathing and a pulse cannot be felt, it is necessary to immediately resuscitate the victim. Before starting, you should clear your mouth of vomit, if any. After this, artificial respiration must be performed.
- The patient needs to pinch his nose and cover his mouth with a thin cloth, the oral cavity remains unclenched.
- After this, a deep breath of air is taken and the patient exhales sharply into the oral cavity, the nose is immediately released after exhalation. In this position, the patient will exhale passively.
- If the wounded person does not breathe, the action must be repeated.
- It is also recommended to perform indirect cardiac massage. It is done in between artificial respiration. To do this, it is better to involve a second assistant.
- He should stand at his side, placing his hands side by side on the patient's heart. For a better effect, they can be clasped in your fingers.
- The arms are extended at the elbows and straightened to their full length. After this, strong pressure is applied to the chest.
- The chest is pressed 3-5 cm, the pressure is intense, usually 1 click per second.
- After every 30 presses, artificial inspiration is performed twice.
Attention! If the patient shows no signs of life, the heart should be started in this way before the ambulance arrives. If transportation is carried out independently, this must be done all the way until the wounded person is in the hands of doctors.
Transportation of the victim
It is better not to move a patient with a vertebral fracture on his own, but to wait for rescuers and paramedics. However, in some cases this is not possible. For example, if there is no mobile communication in a remote area or there are no necessary institutions to provide medical care in nearby areas.
In such a situation, the patient is transported on a rigid stretcher (boards, door panels). It must be securely secured with belts or ties, and when moving, act harmoniously to avoid shaking and tilting. Therefore, it is more convenient to carry out transportation with three or five people.
Important!
If only a standard soft stretcher is at hand, then it is permissible to carry the patient in a prone position.
If the neck is broken, a cushion is placed under it or an improvised Shants collar is made from bandages, cardboard, or fabric, which limits the mobility of the cervical spine.
Treatment
Therapy includes 2 directions: surgical intervention and conservative techniques. Less commonly used is traction and bone realignment.
Conservative technique
Non-surgical therapy is used for non-displaced injuries and if the spinal cord is not damaged. The patient requires bed rest for 1 to 3 months. If there is a neck injury, the patient is put on a Shants collar. After removing the collar, the patient should wear a corset that fixes the bones for another 6 months. During this period, you cannot play sports.
The patient is recommended a complex of exercise therapy, which strengthens the muscle corset and protects the vertebrae from displacement and excess load. The load on the muscles gradually increases: at first the patient does only breathing exercises, over time he begins to do arm exercises, etc. All loads on the body and the exercise therapy complex are agreed upon with the attending physician.
Basic medications for conservative treatment:
- Medicines with calcium. They are designed to speed up bone healing. These are Calcemin and other vitamins enriched with calcium.
- Drugs that prevent the destruction of cartilage tissue - Dona, Alflutop.
- Drugs that prevent inflammation, relieve pain (Ketorolac, Diclofenac, Nimesulide).
- Ointments and creams for topical use (Voltaren, Fastum gel).
Operation
Injuries with damage to the spinal cord, subluxations, fragments of the spinal process and other complications are recommended to be treated surgically. Indications for surgical intervention are prescribed by doctors individually.
The main function of the operations is to protect the spinal cord, stabilize and strengthen the affected spinal segment. After surgery, treatment is similar to conservative treatment (bed rest, medication, etc.).
Dangerous consequences of wrong actions
If key rules are violated during first aid or transportation of a patient, this can lead to serious consequences:
- Improper fusion of bone fragments;
- Visual deformation of the spinal column;
- Development of massive bleeding from a damaged vessel;
- Spinal cord injury with subsequent paralysis or cessation of breathing and cardiac activity;
- Rupture of the spinal root and disruption of the arm or leg;
- Damage to the brain due to a decrease in its blood supply due to a neck injury.
Many of these complications can lead to death or disability. Therefore, when providing pre-medical care to a patient with a broken spine, it is important to be careful and not overdo it. If the life of the victim is not directly in danger, then sometimes it is better to refuse to move him and wait for rescuers and doctors.
Causes of the disease
The list of reasons that can cause a compression fracture of the thoracic spinal column may include:
- Fall from a great height;
- A strong blow that fell on the area of the thoracic vertebrae;
- Osteoporosis and associated fragility of bone structures;
- The presence of malignant tumors;
- Metastases;
- Tuberculosis;
- Excessive physical activity;
- Injuries at work;
- Accidents;
- Sports injuries.
This is not a complete list of all possible factors that can lead to a compression fracture. The age of the patient is also an important factor. The risk of getting a fracture even with the slightest blow is much higher in older people, due to age-related changes occurring in the body.
Consequences of the disease
If the patient managed to notice the symptoms of a compression fracture and consult a doctor, then the most favorable situation awaits him. The specialist will select the right treatment that will help get rid of pain and restore the spine.
However, if seeking help was delayed, treatment was not carried out or was carried out in bad faith, complications will arise that can lead to adverse consequences, including the appearance of a hump and disruption of the functioning of internal organs.
Video: “Compression fracture of the spine”
Treatment and prognosis
Treatment with conservative methods is possible only in case of uncomplicated fractures. But even with this course, X-ray monitoring is carried out every 5-7 days. It is carried out to identify the degree of regeneration and reposition (comparison, fusion) of damaged tissues. Surgical treatment is required in case of splintered and explosive bone injuries. When correct retention and reposition of bone fragments is possible only in an operating room.
Medication methods
The use of medications is necessary to relieve pain and traumatic shock. As well as restoration of lost functions of the spinal cord (can be achieved only in 30-40% of cases). Depending on the general clinical picture, location and type of fracture, the following groups of drugs can be used as part of a comprehensive treatment and rehabilitation program:
- drugs for anesthesia and pain relief (including narcotic opioid analgesics);
- nootropics (“Piracetam”, “Biotropil”, “Phenibut”);
- cholinomimetics (“Diazepam”);
- corticosteroid hormones (hydrocortisone, prednisolone);
- vasodilators (alpha blockers, beta2 antagonists);
- regulatory peptides (peptide bioregulators);
- oxygen carriers, etc.
The drug Phenibut
Drug correction is always used simultaneously with methods of stimulating muscle functions and the functioning of the pelvic organs (for example, electrical stimulation).
Spinal immobilization
Immobilization (fixation, immobilization) of the spine during fractures is necessary to prevent displacement of bone fragments. This method is used for stable fractures, that is, without displacement.
As immobilization methods, a plaster splint (Lorenz bed), bandages soaked in a solution of polymeric materials and various immobilizing dressings, which are applied after treatment with antiseptics, can be used.
Spinal traction
Spinal traction using various devices using weights is called traction therapy. The most effective and frequently used method is skeletal traction. With it, bone fragments are retained due to stimulation with weights. Their weight depends on the location of the damage and can be more than 5 kg. The weight is attached to a pin that passes through the bone. Therefore, the procedure in most cases requires additional anesthesia.
Spinal traction process
Note! The skeletal traction method allows achieving high results in the treatment of patients with various spinal fractures. But at the same time it has significant disadvantages. The main one is forced long-term immobilization of the patient. Therefore, such patients need additional preventive measures, especially the prevention of bedsores.
Rehabilitation after treatment
The rehabilitation course for such patients is selected individually and may include:
- therapeutic and health-improving physical education;
- massage;
- physiotherapy (magnetic therapy, acupuncture, electrophoresis, UHF);
- long-term passive development of joints (CPM therapy).
Complete restoration of the damaged segment occurs within several years. Therefore, a rehabilitation program is usually drawn up for a minimum of 6-12 months.
Video - Transporting a patient with spinal fractures
A spinal fracture is one of the most dangerous types of injuries to the musculoskeletal system. It can lead to instant death of the patient from massive blood loss or crushing of the spinal cord. Of great importance in forming a favorable prognosis and further recovery of the patient is the timely provision of first aid and proper transportation of the victim. In order for a person to competently carry out emergency measures, he must know the basics of providing such assistance. And also be able to control your emotional state. If it is not possible to cope with severe fear, the use of mild sedative medications is allowed. Under no circumstances should you exceed the recommended dosage. This may have a negative impact on concentration while moving the victim.