First aid courses
What is a spinal injury?
A spinal injury is a serious injury that requires emergency medical attention. Depending on the severity of the injury, this can lead to temporary paralysis or even permanent complications. Until doctors can provide emergency medical care, the victim should be given first aid for spinal injuries. Spinal injuries are often seen in athletes, the elderly, and those involved in car accidents.
What are the causes of spinal injuries?
Spinal injuries can be caused by various factors:
- Injuries during sporting events, including high-speed motorsports events
- Injuries from falls, especially from heights
- Car crashes
- Personal injury when working with mechanical equipment or tools
- Heavy objects hitting or falling on the back or body
- Any force that causes excessive twisting of the body
- Destruction of a house or building
- Street fighting, gunshot wounds, physical violence
- Electric shock
- Lightning strike
What are the signs and symptoms of a spinal injury?
Signs and symptoms of a spinal injury depend on the severity of the injury. These may vary from one person to another and may include:
- Moderate to severe pain present in the neck or back area
- Bruising or bleeding from the injury site
- The person cannot move or stand up or walk
- Bone fracture—the bone and associated ribs may be broken
- Spinal injury can lead to loss of control of arms and legs, loss of bowel/bladder control.
- Sensory disturbances (tingling and numbness)
- Visible physical deformity, unusually twisted body or head position
- Stroke and loss of consciousness
In addition, we must suspect spinal injury:
- When falling from a height higher than human height
- If dropped onto hard protruding objects
- When falling at a speed greater than a person can achieve when running
- In a car accident
- If there is a strong blow to the back, head or neck
- When you hit the bottom while diving in a pool.
In these cases, even if signs and symptoms are not observed, it is better to be on the safe side and not move the victim unless absolutely necessary.
First aid for spinal injury
- Call an ambulance (tel. 103 or 112) if there is an emergency due to an accident/injury or if serious symptoms are noted
- DO NOT move a person if you suspect a head, neck or back injury. In addition, any further movement of the head, neck or body should be avoided
- AVOID moving the person to check for other injuries or to see the location of the injury.
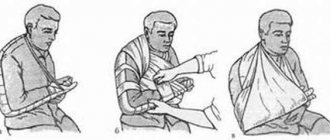
- If the person is feeling nauseous, carefully move their body to a safe side position so that the head, neck and back are in line as you move. Ask people around you for help. DO NOT roll over a person alone.
- If necessary, use towels, pillows, or hold (using your hands) the head and neck to keep it still until paramedics arrive.
- DO NOT ask the person to get up and walk around.
- DO NOT attempt to remove a helmet or other protective equipment the person is wearing.
- If there is no breathing, begin CPR (if you are trained to do so)
- If there is bleeding from other wounds, take appropriate steps (such as applying direct pressure for heavy bleeding) to stop the bleeding
Who can provide first aid for a spinal injury?
Anyone can provide first aid for a spinal injury; however, he must remember that it is imperative to seek emergency medical attention for definitive treatment of any spinal cord injury.
How can you prevent spinal injury?
Some useful tips to prevent spinal injuries:
- Use appropriate equipment to stay safe, especially when playing sports. Also learn proper sports techniques
- Fasten your seat belt while driving
- At home, remove slippery smooth surfaces that pose a risk of falling
- Supervise children during outdoor activities
- Do not attempt to drive a vehicle while under the influence of alcohol
In our first aid courses, we practice how to provide first aid in case of spinal injury.
You can ask questions about the content and organization of courses by email or by phone
First aid for spinal injury
First aid tips for suspected spinal injury:
- Call an ambulance if the above signs of spinal injury are observed or an accident occurs.
- Do NOT move the victim under any circumstances if there is a suspicion of head, neck, back or spinal cord injury. It is important to avoid any movement of the head, neck or body.
- If possible, do not move the victim, so as not to provoke painful shock and complications (displacement of the vertebrae, damage to other organs from rib fragments, damage to the spinal cord, etc.).
- If the victim is vomiting, you need to carefully move the victim onto his side, with the head, neck, back, pelvis and legs forming a straight line.
- If necessary, secure the victim's head or body with available materials: towels, pillows, sticks, boards, etc.
- It is important not to remove the victim’s helmet, clothing or other protective equipment – if any. It is necessary to immediately provide the person with access to oxygen.
- If the victim is not breathing, the patient must be given artificial respiration and chest compressions. The procedure should be repeated until the ambulance arrives.
- If there is bleeding from wounds formed after an injury, it is important to stop it. Depending on the location of the injury, apply a pressure bandage or cover the wound with a sterile cloth and press firmly with your hands.
Who should provide first aid if there is a spinal injury? Every person who is next to the victim can help him, but it is important to first call an ambulance and not try to deliver the patient to a medical facility yourself (any movement can be fatal).
Types of vertebral fractures
If first aid is required for a spinal fracture and the symptoms are identified, you need to understand what type of injury the patient has. Let's look at the two most common types of fractures - compression and comminuted.
Compression fracture
It occurs when a person’s vertebrae are severely compressed. This happens under heavy loads. In such a situation, the vertebra decreases in height. There are three degrees of such a fracture:
- the first, when the vertebral body has become less than a third lower;
- the second, when the body has decreased by less than half;
- the third, when the degree of damage led to a reduction in the size of the vertebral body by more than half.
The greater the degree, the worse the condition the victim will be. With minor injuries, the patient may not notice the injury at all. If the injury is severe, paralysis occurs.
Comminuted fracture
First aid techniques for a comminuted spinal fracture are significantly less varied. In this case, you should try to reduce the impact on the victim.
With such a fracture, the vertebra is crushed and two or more fragments appear. The fracture can be open or closed. In the first case, the fragment breaks through the tissue on the back.
This type of injury is especially dangerous because sharp bone fragments can damage surrounding tissue, cause bleeding, and affect nerves.
Symptoms
The main symptoms of spinal injury are:
- pain in the area of injury;
- restriction of movements;
- Bruising, bruising, and swelling of the skin may occur.
With moderate damage to the nerve fibers, numbness and tingling of the extremities may occur.
Symptoms of spinal injury aggravated by spinal cord damage can vary from minor motor impairments to complete paralysis, gastrointestinal disturbances, etc.
Main Causes of Injuries
By knowing the mechanism of injury, more appropriate care can be provided. Most often, spinal injuries occur as a result of:
- road accident;
- falling from a height;
- childbirth;
- incorrectly dosed physical activity;
- blows on the back;
- domestic and industrial incidents;
- unsuccessful jump into the water;
- knife and gunshot wounds;
- a number of chronic diseases.
If you want to find out in more detail what first aid is needed for a spinal fracture, and also to understand whether a person’s spine is damaged, you can read an article about this on our portal.
Road accidents are one of the most common causes
On a note! In road accidents, the cervical part of the spinal column is most often damaged; in the workplace, the lower back or sacrum is damaged.
Common Causes of Spinal Fracture
First aid for a spinal fracture begins with determining the cause. Trauma occurs for several reasons:
- compression under heavy load;
- strong stretching;
- side twist;
- multidirectional load acting on the spinal column.
Fractures happen to all kinds of people. The cause may be an awkward fall or a jump from a height and landing on straight legs. Children and people whose diseases lead to a decrease in bone thickness are also at risk. You should beware of situations in which you may fall or receive a vertical blow to the head.
How can you tell if a victim's spine is broken?
First of all, let us recall the signs of a spinal fracture:
- the back muscles are tense;
- a person complains of pain in the back, lower back, neck; painful sensations intensify when pressing or trying to make a movement;
- he experiences paralysis of his arms or legs;
- the neck bends unnaturally (in some cases the cervical region swells, breathing becomes difficult);
- numbness occurs in the injured area - control over the damaged part of the body is lost.
Types of injuries
When providing first aid, it is important to first understand, if possible, what is damaged in a person. Injuries are classified according to a variety of characteristics. And with each of them there will be some help.
There are different types of spinal injuries
Table. Types of injuries depending on the nature of the lesion.
| View | Characteristic |
| Fractures | This is one of the most serious injuries. When fractures occur, the entire structure of the spinal segments, elements of the blood flow, and soft tissues surrounding them are disrupted. In most cases, a spinal fracture is life-threatening. The most common fracture occurs in the cervical region. |
| Dislocations | In this case, the vertebrae are displaced relative to each other and the joints between them are damaged. It is also most common in the cervical region, less often in the lumbar region. |
| Intervertebral disc ruptures | With such an injury, the outer part of the intervertebral disc is ruptured or the inner part is displaced, usually accompanied by damage to the nerve endings. |
| Paraplegia | Damage to the spinal cord, resulting in paralysis of the limbs. |
| Long-term pressure syndrome | Occurs due to prolonged compression of soft tissues and blood vessels. The main signs are dysfunction of most other organs. |
| Bruises | With such an injury, the structure of the spine is preserved. But as a result of bruises, bruises may appear, tissue necrosis begins, there is damage to nerve endings, and the quality of the movement of cerebrospinal fluid deteriorates. Most often, the injury is observed at the junction of the thoracic and lumbar parts, less often in the cervical region. |
Regarding the location of the injury, they are classified by the name of the parts of the spine; there are also those that affect several parts of the spine at once.
On a note! The most common injuries are to the lumbar and sacral regions, and in about ¼ of all cases - to the thoracic and cervical regions.
Consequences of spinal injuries
What should you not do if you suspect a spinal injury?
Providing first aid for spinal injuries is very different from first aid techniques for injuries to other parts of the musculoskeletal system. The main task of the people providing assistance is, if possible, to keep the victim’s body motionless until the doctors arrive. This will prevent the situation from getting worse. Thus, the victim should not be allowed to stand up or walk - damaged vertebrae can move and pinch the spinal cord.
Providing care for spinal injuries
It is strictly forbidden to sit a person down, stand him up, or pull his limbs. You cannot try to straighten dislocations on your own. It is prohibited to give medications to a person who is unconscious or has impaired swallowing and breathing functions.
Diagnosis and treatment
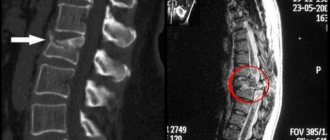
If you suspect a spinal injury, you should consult a doctor immediately. The diagnosis is made based on examination of the patient, medical history, complaints and results of instrumental studies. If you suspect a spinal injury, your doctor will give you a referral for the following tests:
- X-ray;
- Magnetic resonance imaging;
- CT scan;
- angiography (examination of blood vessels with a contrast agent).
Treatment tactics depend on the nature, location and severity of the injury. Conservative techniques are used for minor injuries, as well as as maintenance therapy. It is also often prescribed to wear special corrective devices (collars, corsets).
Surgical operations are aimed at decompressing the spinal cord and restoring normal blood supply. Reconstructive interventions are also performed on damaged areas of the spine.
Patients with suspected spinal injury are advised to undergo immediate hospitalization. Timely and correct medical care can reduce the negative effects of injury and speed up recovery. Trust the professionals - contact SM-Clinic.