Joint arthroscopy > Knee joint > Injuries to the knee joint
Knee injuries
– rupture or sprain of tendons, bone fractures (patella, tibia, fibula, femur), damage to the meniscus. Problems like these are widespread. Injuries are often differentiated by severity - from mild tissue damage to bone fracture. Knee joint bruises usually occur due to falls. A knee injury may be indicated by pain, tissue swelling, and limited mobility. Usually the damage is accompanied by hemorrhage into the joint cavity. To make a diagnosis, the following methods are used: x-ray, ultrasound, arthroscopy, computed tomography, MRI. Treatment depends on the location and extent of the damage.
General information
Knee injuries
– occupies a leading place among other injuries. This position is associated with the features of the normal anatomy (structure) and physiology (load) of the knee joint. Most injuries occur from falls and impacts. The resulting injuries are usually minor bruises, so treatment is carried out by a traumatologist on an outpatient basis. Amateur and professional athletes also often injure the knee. Their knee joint injuries are much more serious.
Less frequently reported are cases of knee injuries in road accidents, falls from height, and at work. For patients who are involved in such an incident, damage inside the joint is typical. They are characterized by the fact that the integrity of the anatomical structure is violated. Relief of symptoms and restoration of the structure occurs in the trauma department of a medical institution. In addition to a knee joint injury, there may also be a TBI (traumatic brain injury), fractures of other bones, and organ ruptures.
A photo from the ring is the best reward for a surgeon!
Our work is done.
But now you yourself must make efforts for a speedy recovery. In our clinic, people of different professions perform operations. But I advise you to take example from athletes. When, after a while, I receive gratitude from operated patients in the form of a video report or a photograph “from the ring” - this is the best reward for us. I admit that athletes are a grateful audience. After all, their internal motivation, active life position and desire to quickly get back into shape are sometimes stronger than others. Sport for them is daily work on the body and muscles. So I would like to say one last thing to everyone who is about to undergo surgery: “If you want to recover, work!”
Knee contusion
Knee bruise
- this is damage to surrounding tissues (skin, subcutaneous fatty tissue), which is not accompanied by a violation of the anatomical structure. Against the background of this injury, inflammation of the elements that are located inside the joint occurs, as well as hemorrhages. Symptoms are often not as pronounced with other injuries. Because of this, the diagnosis is made when other injuries have been ruled out. Signs that the victim has a knee joint injury may include: pain, moderate swelling of the soft tissues, and slight bruising. At the same time, support is maintained, but the person may begin to limp and be slightly limited in some movements.
To determine pain, palpation is performed in the area of the bruise. Feeling the bones and ligaments should not cause attacks of pain, as well as pathological mobility. There may be an accumulation of fluid, at first it is blood, and after two or three weeks it is exudate. Injury to the knee structures is excluded using x-rays. Research methods such as MRI, computed tomography, ultrasound and arthroscopy are also used. Care for a knee injury is provided at the emergency room. If there is synovitis or blood inside the joint, a puncture is performed. If the patient has a slight bruise, then the main actions are aimed at maintaining peace. But for severe cases, the traumatologist applies a plaster cast for 2 - 3 weeks. For the first two days, it is recommended to apply something cold to the site of the bruise, and from the third day, UHF therapy is prescribed. The patient must visit the doctor at the appointed time and follow his instructions. If indicated, repeat arthrocentesis is performed. If the knee joint is bruised, the disability lasts 2–4 weeks.
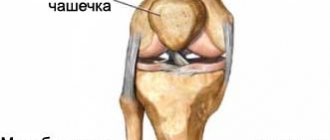
Patella dislocation.
During flexion and extension of the knee joint, the patella moves along the femoral block, like a train on rails. However, there are reasons for incorrect movement and the train derails - the patella dislocates.
Causes: improper development of the trochlea and condyles of the femur, anatomical disorders, rupture of the medial retinaculum of the patella, patella alta (high position of the patella due to an excessively long patellar ligament), weakness of the quadriceps muscle, incorrect position of the tibial tuberosity.
A large complex of conservative treatment is used to correct anatomical disorders with good treatment results. But if there is no effect or with a large number of dislocations, surgical treatment is indicated.
There are open and arthroscopic techniques for stabilizing the patella, which are determined based on examination and the causes of instability. For diagnosis, radiographs of the knee joints in 2 standard projections and axial (skyline view), MRI are important, and computed tomography (CT) may also be needed.
After the operation, you are prescribed to wear a special orthosis that limits movement in the knee joint, walking with crutches, classes with a rehabilitation therapist, exercise therapy and ERT.
Restoration of joint function can be expected within 2 months from the date of surgery, return to sports is closer to 4 months.
Make an appointment
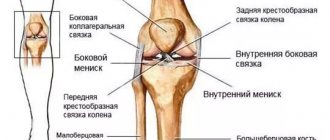
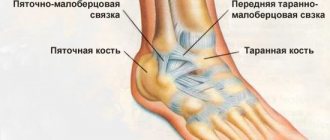
Ligament damage
The medial and lateral collateral ligaments, the anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments (ACL, PCL) take part in the formation of the knee joint. All injuries to these structures can be divided into partial and complete. A preliminary diagnosis can be made by studying biomechanical processes. Pain during supination (turning the leg outward) indicates damage to the medial collateral ligament. If the patient has problems with pronation (turning in on the inside), then the lateral collateral ligament may be injured.
Injuries to the ACL and PCL usually occur after direct impacts, hyperextension (overextension), and rotation of the hip with a fixed shin. Such injuries are typical for athletes (basketball players, wrestlers, track and field athletes). Other reasons that may cause a sprain or rupture of ligaments include carelessness in everyday life, road accidents, falls from a height. When an injury occurs, severe pain occurs.
A rupture of the ACL is accompanied by a click, which is not the case with the PVD. With such injuries, instability of the knee joint and a feeling of displacement when walking are observed. When visually assessing the patient's condition, swelling of the soft tissues in the knee area and hemorrhage inside the joint are observed. The last symptom may be absent if the posterior cruciate ligament is torn. The reason is that damage to adjacent structures - the posterior part of the knee joint capsule - is possible. Because of this, blood enters first into the popliteal fossa, and then into the space between the fascia. On palpation, the patient has a pronounced pain syndrome.
Injury to the medial and lateral collateral ligaments is accompanied by abnormal lateral mobility of the tibia, and the ACL and PCL are characterized by “drawer” displacement. During the acute phase, the patient is prescribed local anesthesia. When the sensation of pronounced pain disappears, instability of the knee joint remains. In order to avoid pathological displacements while walking, the leg should be wrapped with an elastic bandage. Over time, there is a gradual decrease in muscle mass due to atrophy, as well as symptoms of post-traumatic arthrosis.
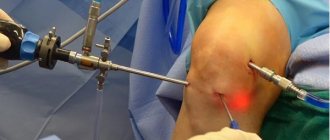
When performing an X-ray of the knee, a narrowing of the joint space is observed. Using MRI, you can find out about the condition of the ligaments. Diagnosis is best done through a procedure such as arthroscopy. This is a minimally invasive diagnostic method for visualizing structures on a monitor screen. In addition to diagnostics, arthroscopy is also used to restore the integrity of ligaments. Tears are eliminated through conservative treatment. Arthrocentesis is also performed and a cast is applied for four weeks. Afterwards, the doctor may prescribe physical therapy and massage. If a ligament rupture occurs, it is repaired through surgery (stitching, plastic surgery). During the rehabilitation period, a number of physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed for a speedy recovery.
Rupture of the connective tissue of the quadripses and part of the patella (the ligament itself) can occur with a strong blow, as well as with simultaneous overstrain of the thigh muscles and sharp flexion of the lower leg. When injured, sharp and intense pain manifests itself, and gait is disturbed (the leg bends reflexively). Blood does not enter the joint cavity. Palpation of the damaged area is accompanied by increased pain, there is no displacement and pain in the bones.
Conservative treatment
For minor injuries or incomplete rupture of the internal meniscus, treatment can be carried out non-surgically. But even in such cases it is always complex and consists of:
- Providing rest for the injured limb, which is achieved by applying tight bandages made of an elastic bandage or a plaster splint.
- Carrying out complex drug therapy aimed at improving the patient’s well-being, preventing further destruction of the internal meniscus and improving the course of metabolic processes, which helps speed up recovery.
- Performing physiotherapeutic procedures, the importance of which increases when signs of chronicity of the process are detected.
- Regular exercise therapy (PT) to prevent the development of complications and loss of muscle tone.
- Carrying out a course of therapeutic massage after removing the plaster cast, which helps to activate blood circulation, eliminate swelling and preserve muscle mass.
Recovery after removal of the cast, with proper conservative treatment and the absence of complications, lasts 1.5-2 months.
Drug therapy
All patients with injuries of the internal meniscus are prescribed a complex of medications:
- Painkillers from the NSAID group, which also have anti-inflammatory properties. They help reduce pain and inflammation in the joint.
- Corticosteroids. Used for severe inflammation in the joint resulting from injury.
- Chondroprotectors. Prescribed to increase the rate of regeneration of damaged cartilage and reduce the risk of its destruction.
- Vitamin complexes. Indicated to improve metabolic processes and provide cartilage tissue with the substances it needs.
Exercise therapy
From the first days of conservative treatment, patients are required to engage in exercise therapy daily. For each patient, a set of exercises is selected individually.
During the period of immobilization of the affected limb, it is necessary to perform general developmental exercises for all muscle groups using the healthy leg. As for the injured limb, at first you need to perform special exercises that will use its thigh muscles.
Also, before removing the cast, it is necessary to lower the affected leg down for a short time, and then return it to a higher ground. This will reduce the risk of obstruction of blood flow from the leg.
After removing the plaster cast, patients are prescribed exercises to restore the functions of the lower limb. They consist of performing rotational movements with the foot, engaging large joints, and tensing all the muscles of the affected leg. But the load, as well as the nature of the exercises, is selected separately for each patient in accordance with the characteristics of his recovery.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic methods are usually used after the end of the acute period. Most often, patients are advised to take the following courses:
- UHF;
- magnetic therapy;
- electrophoresis with corticosteroids or anesthetics;
- ozokerite.
These types of effects ensure increased blood circulation in the affected area, which helps eliminate inflammation, accelerate regeneration processes and reduce swelling.
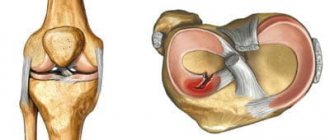
Meniscal injuries
Meniscus injury
– one of the popular problems with the knee joint, which occurs with greater frequency in athletes (football players, basketball players, track and field athletes, skiers). This injury is no less common in people who dance, do heavy work, and are artists. Without preliminary mechanical action, damage to the menisci can also occur with arthrosis of the knee joint. The nature of the injuries ranges from small tears to complete ruptures. Often, damage to the meniscus is combined with injury to other structures of the knee.
The acute period is characterized by the following symptoms: pain, swelling, swelling, stiffness of movement. There may be exudate inside the joint. Within three weeks, the symptoms of the inflammatory process disappear, and the signs of meniscus injury become more pronounced. This is expressed in the appearance of a painful cushion at the level of the joint space. The following clinical picture is also recorded: pain when going down the stairs, making circular movements with a bent shin, or the “Turkish” position.
X-rays are not used for diagnosis (only to exclude other damage). Arthroscopy or MRI is usually prescribed. Ultrasound diagnostics of the knee joint is rarely performed. Treatment is prescribed based on the examination results. Small tears can be repaired with therapy. More serious damage can only be eliminated through surgery. Possible operations may include suturing, resection, or complete removal of the menisci. The latter is rarely performed due to the increased risk of arthrosis.
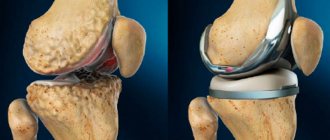
Fractures in the knee joint
Violation of the integrity of the patella is possible if the anterior part of the knee is damaged. In this case, acute pain syndrome occurs, problems with bending the leg, swelling of the soft tissues, and hemorrhage in the middle of the joint. Diagnosis is made using an X-ray of the knee. If the patella fracture is not displaced, then treatment is conservative. The leg is immobilized for 6 to 8 weeks. If there is displacement, surgical intervention is performed. During the rehabilitation period, physical therapy, physiotherapeutic procedures, massages, and pain relief are prescribed. Full recovery is observed within 2 - 3 months.
list