Meniscal injuries are one of the most common knee injuries. Most often it occurs in athletes and able-bodied people aged 18-40 years. The optimal treatment method for knee injuries is arthroscopy. This is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that is less traumatic. The surgeon performs all manipulations through small incisions, under visual control (for this, an arthroscope with a camera is inserted into the joint cavity).
During the operation.
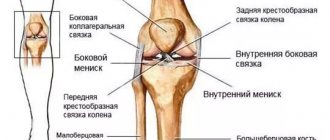
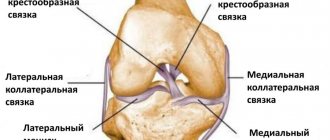
Indications for meniscus arthroscopy
Arthroscopic intervention is indicated for serious injuries of the knee joint, when doctors suspect or have already discovered damage to intra-articular structures. Arthroscopy can be performed for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. In the first case, it allows you to identify ruptures and tears of the menisci, damage to the cruciate ligaments, synovial membrane, articular cartilage, etc. In the second, it makes it possible to restore the integrity of the structures of the knee joint without opening the joint cavity and minimally injuring the soft tissues.
Arthroscopy is used for significant damage to the meniscus when conservative treatment is ineffective. If possible, doctors try to perform partial resection of the meniscus, plastic surgery, or suture. Total meniscectomy (complete removal) is used only in extreme cases. After all, complete removal of the meniscus leads to an increase in the load on the articular cartilage and further development of arthrosis. At the same time, plastic surgery and resection make it possible to preserve the functions of the knee and avoid degeneration of cartilage tissue after surgery.
Types of meniscus damage
Preparation and anesthesia
Even at the planning stage of surgical intervention, the patient undergoes a series of tests and undergoes a full examination. If there are no contraindications, the doctor sets a date for the operation and tells you how to properly prepare for it. During preparation, the patient should carefully follow all the specialist’s recommendations. At least 12 hours before arthroscopy, the patient should stop eating, drinking and smoking (as anesthetic drugs must be administered on an empty stomach). 30-40 minutes before the administration of painkillers, the patient is given premedication. Its essence lies in the administration of tranquilizers and hyposensitizing drugs. Premedication reduces the patient's anxiety and enhances the effect of anesthetics.
Arthroscopic meniscus procedures are usually performed under spinal or regional anesthesia. In the first case, painkillers are injected into the spine and thereby block the nerve roots that are responsible for the innervation of the lower limb. In the second case, the femoral and sciatic nerves are blocked, infiltrating nearby soft tissues with anesthetics.
In rare cases, for special indications, the operation is performed under general anesthesia. In this case, anesthetics are administered intravenously, and the patient is breathing independently or breathing through a laryngeal mask. Local anesthesia for arthroscopy is used extremely rarely due to its weak analgesic effect and short duration of action.
Make an appointment
NEARMEDIC is a network of clinics throughout Moscow, equipped with operating rooms and hospitals, and provided with highly qualified specialists. Find the clinic that is most convenient for you on the map in the “Contacts” section and make an appointment with a surgeon. Below on the page you will find cards of surgeons and anesthesiologists with appointment addresses, photographs, short biographies, and reviews. Here you can make an appointment with your chosen doctor.
You can also make an appointment with a doctor through the appointment form on the website, by calling the general telephone number of the control room or by calling the clinic that you have chosen. Need some advice? Call us and we will be happy to answer your questions.
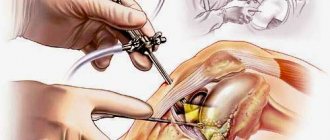
Description of operation
The operation begins with anesthesia and treatment of the surgical field. The skin in the area of the knee joint is carefully shaved, after which it is treated several times with antiseptics. This is necessary in order to prevent infection from entering the synovial cavity where manipulations are performed.
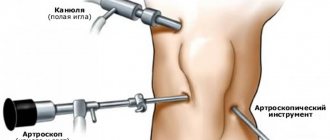
All arthroscopic interventions are performed under visual control. To visualize intra-articular structures, an arthroscope is inserted into the joint cavity, which is a tube and an ocular head rigidly connected to each other. The image from the arthroscope is displayed on a screen in the operating room, allowing the surgeon to control his actions and the patient to monitor the progress of the surgical procedure.
First, the patient's leg is bent and a cannula is inserted through a small incision. Then it is unbent and the arthroscope is inserted through the cannula. Instruments for arthroscopic manipulation are inserted through small incisions 4-5 mm long. After the operation, the arthroscope and all instruments are removed, and the postoperative wounds are sutured and sealed with adhesive tape.
Arthroscope.
Types of meniscus repair
For meniscus injuries, several types of arthroscopic techniques are used:
- suturing;
- meniscus repair;
- partial resection of unstable meniscal fragments;
- total meniscectomy (complete removal).
Meniscus seam
Today, physicians prefer arthroscopic meniscal repair because it produces better clinical and radiographic results than partial and total meniscectomy. The integrity of the meniscus is restored by suturing or using plastic surgery. This operation allows you to stabilize movements in the joint and achieve uniform distribution of axial load on the articular surfaces of the thigh and lower leg. And this, in turn, reduces the risk of subsequent development of osteoarthritis.
On the other hand, with severe injuries it is not always possible to restore the integrity of the meniscus. Therefore, doctors often have to perform a partial resection or remove it completely. This produces less favorable results.
Benefits of arthroscopic meniscectomy
The meniscus is subjected to the necessary manipulations without making complex incisions on the outside. Thus, it is recommended to remove the meniscus or its fragments using the cavity method only if there are concomitant pathological changes in the knee joint that do not allow endoscopic surgery. The meniscus is sutured using general anesthesia or epidural anesthesia, so the patient does not experience pain.
The list of advantages of endoscopic resection of the medial meniscus with an arthroscope includes the following:
- Maximum accuracy in diagnosing damage and destruction of the meniscus.
- Almost complete absence of external damage to the skin and soft tissues.
- Low level of blood loss during removal of the meniscus and its fragments.
If you are concerned about the meniscus in your knee, then the doctors at Vash Doctor Group will take care of solving the problem with the least risk and discomfort, returning your usual quality of life.
How does meniscus repair work?
Arthroscopic interventions are performed without opening the joint cavity, which significantly reduces postoperative rehabilitation. With arthroscopy, tissue is damaged much less than with other operations. And the scars remain almost invisible due to the small size of the incisions.
The first few days after the operation, the person is in the hospital, and the attending physician carefully monitors his condition. At this time, the patient takes prescribed medications and performs special exercises under the supervision of medical staff. His post-operative wound is carefully cared for. After discharge from the hospital, the patient continues to exercise and care for the wound, but on his own. At the same time, he follows all the recommendations given by the doctor.
The duration of rehabilitation is usually 8-12 weeks. After this period, the patient is allowed to return to their usual lifestyle and even play sports. He can return to office work even earlier - in 2-3 weeks. And to physical labor - after 4-6 weeks.
Early healing stage (first 7-10 days)
After arthroscopy, the patient is allowed to stand up immediately after the anesthesia wears off. At first, doctors recommend using crutches or a cane. At the early healing stage, the person is allowed to walk carefully within the apartment, avoiding the appearance of pain in the knee.
During this period it is also recommended:
- Apply an ice pack wrapped in a towel to your knee 4-5 times a day. It should be kept for at least 15-20 minutes. This will help relieve knee pain and speed up recovery.
- Wear compression garments or bandage the limb with an elastic bandage from the foot to the middle third of the thigh. This precaution is necessary to prevent thromboembolic complications in the postoperative period.
- Give an elevated position to the shin and knee joint. In bed, the operated limb should lie on a pillow, above the level of the heart.
- Perform special exercises at least 2-3 times a day. Each workout should last 20-30 minutes. Daily exercises are needed to train muscles and normal restoration of limb function.
If swelling and redness of the skin appears in the area of the knee joint, it is necessary to reduce the load on the limb or temporarily stop performing exercises. And if swelling persists for more than two or three days, you should see your doctor.
Late healing stage (days 10-14)
At this stage of rehabilitation, weight-bearing exercise on a stationary bike, cycling and resistance exercises are added to physical therapy. In this case, the patient still has to use crutches when walking.
Third stage (starting from the third week)
During this time, a person can perform various exercises, but sports are still prohibited. If there are no contraindications, one month after surgery the patient is allowed to walk in an orthosis with full weight bearing on the operated leg. During the second month, a person performs functional exercises that help restore muscle strength, train endurance and completely restore the range of motion of the limb.
Knee brace.
At the end of the second month, the patient can return to a free motor mode, including sports.
Possible complications after surgery
Arthroscopy is one of the safest knee surgeries. However, even after it, complications, both early and delayed, can occur.
These include:
- Complications caused by anesthesia. They may occur as a result of individual intolerance to drugs, the patient’s serious condition, or errors by the anesthesiologist.
- Hemarthrosis is a massive hemorrhage into the joint cavity. It occurs extremely rarely and practically never occurs after arthroscopy.
- Thromboembolic complications. With adequate prevention and wearing compression garments, they are rare. In exceptional cases, patients experience thrombosis of the veins of the lower extremity or pulmonary embolism (TEPA).
- Joint fluid leakage. With excessively rapid resumption of physical activity, synovial fluid can leak from the joint cavity and enter the periarticular tissue. To avoid this, early loading of the limb should be avoided.
- Nerve damage. Damage to nerve branches during surgery can cause paresthesia in the knee joint. In this case, the patient may feel a “crawling sensation” after arthroscopy.
- Sprained medial collateral ligament. Occurs rarely if the surgeon performs enhanced manipulations, increasing the distance between the femur and tibia for better access to the meniscus.
- Deforming osteoarthritis. Develops late after arthroscopy, as a result of progressive damage to articular cartilage. It is difficult to treat and over time can lead to impaired function and mobility of the knee.
Infectious complication.
The risk of complications largely depends on the experience and skill of the operating surgeon, as well as the level of the institution where the operation takes place. If you want to protect yourself, try to be treated in the best clinics, and choose the best specialist as your attending physician.
Infection
Infectious complications are rare, occurring in only 0.1-0.42% of patients. The causative agent of septic arthritis is most often Staphylococcus aureus. The disease is acute and usually does not cause difficulties in diagnosis. In rare cases, it may have a subacute, more “insidious” course.
Classic signs of septic arthritis:
- acute pain;
- severe swelling;
- skin redness;
- fever;
- increased ESR and neutrophilic leukocytosis in the blood.
Infectious inflammation.
Note that the absence of typical symptoms of arthritis does not mean the patient is completely healthy. Infection can be excluded only through bacteriological examination of the synovial fluid. The analysis should be done at the slightest suspicion of septic arthritis.
During arthroscopic procedures, doctors may not prescribe prophylactic antibiotics to patients. This, like intra-articular corticosteroids during arthroscopy, increases the risk of infectious complications.
Treatment for septic arthritis can take anywhere from a few days to 6 weeks. In some cases, parenteral administration of antibiotics is sufficient for patients. Sometimes patients require lavage and drainage of the joint cavity. The choice of treatment usually depends on the severity of the arthritis.