Arthritis of the knee joint or feet occurs due to injury or as a complication of certain diseases.
At first, patients note the appearance of pain when moving, and redness of the skin in the affected area may form.
As the disease progresses, the synoval membranes become inflamed, bone growths form, and the cartilage begins to gradually harden.
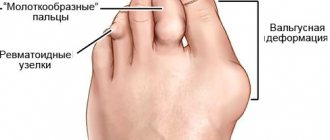
In some cases, abscess formation occurs, as well as joint deformation.
Over time, the muscles of the joint atrophy, which affects a person's gait.
If arthritis of the legs is left untreated and the joint is seriously damaged, the patient may become disabled, and at a late stage of the disease only endoprosthetics can help.
What is arthritis?
Arthritis is a collective name for various diseases of the joints, which are united by one common property - inflammation.
It affects both the joint itself and adjacent tendons, ligaments and bones, often leading to their destruction. Arthritis typically manifests as pain, swelling, redness of the skin over the affected joint, and limited mobility. The most common types of pathology are: rheumatoid, gouty, septic, reactive and idiopathic. Arthritis and arthrosis are interrelated phenomena, but not the same thing. Arthritis is inflammation of the joint, arthrosis is destruction, wear and tear of the joint. These phenomena almost always accompany each other, but they cannot be equated.
Reactive arthritis in facts and figures:
- Most often, inflammation develops in the knee, ankle and foot joints
- Symptoms of reactive arthritis often do not last long and may go away on their own without treatment. But sometimes the disease is serious and can become chronic.
- In most patients, symptoms last no more than 12 months
- Men aged 20–50 years are most often affected
- Reactive arthritis is often called Reiter's syndrome, but in fact it is just one of its varieties.
- The disease is also often confused with infectious arthritis. Infectious arthritis differs from reactive arthritis in that there is an infection in the joint.
Causes
Like any other inflammatory disease, arthritis has its own causes. Joints may be affected:
- for various infections (tuberculosis, brucellosis, borreliosis (developing after a tick bite), chlamydia and other diseases);
- with metabolic disorders (gout, hemochromatosis);
- with increased bleeding due to hemorrhages in the joint (hemophilia, thrombocytopenic purpura).
Important! In general, the arthritis listed above can usually be treated well if the underlying condition can be controlled.
Another thing is joint damage as a result of autoimmune inflammation (when the body’s immune system, instead of eliminating foreign cells, attacks its own). The most common arthritis in this category are rheumatoid or lupus arthritis, as well as ankylosing spondylitis (ankylosing spondylitis). They cannot be completely cured, but stable remission can be achieved.
Why does reactive arthritis occur?
Most often, the culprits are bacteria that cause an infection of the intestines and genitourinary system. The infectious process provokes an inflammatory reaction in the joint, although the microorganisms themselves do not penetrate into it. Moreover, the symptoms of the underlying disease can be so weak that the sick person does not even notice them - joint disorders come to the fore.
Why does inflammation occur in the joint? The main reason is the distortion, perversion of the body’s defense mechanisms. The most common pathogens: chlamydia, salmonella, shigella, yersinia, campylobacter. In relation to the joint itself, reactive arthritis is not an infectious disease. They cannot become infected. But you can get an underlying infection.
Symptoms
Arthritis can occur acutely with severe symptoms or as a sluggish chronic process without pronounced symptoms in the initial stages of the disease. In this case, a person may not pay attention to the symptoms for a long time and consult a doctor late, when the process is already difficult to stop. Main signs of arthritis:
- pain (at rest and with exercise);
- stiffness or limited mobility;
- swelling (local tissue swelling);
- redness of the skin in the joint area, with active inflammation it becomes hot;
- deformation (violation of shape) of the joint and limbs (in later stages);
- increased body temperature, fatigue and/or weakness, loss of appetite.
How to treat arthritis of the legs and feet?
When carrying out medical procedures, methods of etiopathogenetic and symptomatic drug therapy are used, as well as a complex of restorative and rehabilitation measures.
Regardless of the chosen treatment method, the load on the foot is limited, which eliminates its trauma - if necessary, the joint can be immobilized using plaster tape, and the patient can move around using crutches for these purposes.
Depending on the type of arthritis, oral, parental and local forms of NSAIDs, which have anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties, may be prescribed. If arthritis is infectious in nature, then antibiotics are prescribed if necessary.
Stages of the disease
In chronic arthritis, exacerbation phases are usually followed by remissions. The onset of the disease is called debut and is characterized by the formation of pain and the appearance of stiffness in the affected joint.
There are 4 stages of arthritis:
- Stage 1. At this stage, the body becomes infected and there are no symptoms. There may be stiffness of movement and pain with intense stress on the joint.
- Stage 2. Pathological processes begin, joint tissues become thinner, which provokes inflammation. At this stage, erosive formations appear on the bones, swelling develops and the temperature rises, the skin turns red, and the movement of the joints is accompanied by a crunching sound.
- Stage 3. Mobility is limited, and there is constant tension in muscle tissue. Deformation of the joint tissue develops. People with stage 3 arthritis are often assigned a disability.
- Stage 4. The changes become irreversible, the joint cannot move. The bone heads of the joints are fused together.
Without treatment, arthritis can be aggressive and lead to joint destruction. Timely treatment helps keep the disease in remission, during which it does not manifest itself.
Types of the disease depending on the course
Slowly progressive rheumatoid arthritis means that the disease develops over many years, gradually affecting the joints. The joints themselves do not suffer very much. This is where treatment helps and you can maintain a fairly comfortable standard of living.
The rapidly progressing type is characterized by frequent and severe exacerbations, joint damage is severe, treatment helps little. A person's quality of life deteriorates noticeably.
The simplest and easiest type for the patient is a disease without noticeable progression. You can live with it until you are very old without particularly suffering from symptoms.
Diagnostics
To diagnose arthritis, instrumental and laboratory research methods are used. But in order to quickly and accurately make a diagnosis, it is necessary first of all to conduct a detailed collection of complaints, clarify the anamnesis and examine not only the affected joints, but also other organs. In particular, conduct auscultation (listening) to heart sounds and lungs.
Which doctor should I contact?
To begin with, go to a therapist (or a pediatrician if the child needs help). The doctor will examine problematic and healthy joints, determine the degree of limitation of their mobility and prescribe the necessary examination. Based on the results of the examination, the patient will be referred for a consultation with a rheumatologist to clarify the cause and type of arthritis and prescribe specific treatment.
Diagnostic methods
Additional research methods are needed to confirm the diagnosis. Necessities include:
- C-reactive protein and ESR (indicate the presence of a systemic inflammatory process and the degree of its activity);
- Rheumatoid factor (confirms rheumatoid arthritis);
- Antibodies (ANA, ACCP);
- Antigen HLA-B27 (identified in ankylosing spondylitis);
- General blood analysis;
- Joint puncture for analysis of synovial fluid (for septic arthritis, hemophilia, gout).
Instrumental research methods usually use radiography of joints or computed tomography. With their help, you can assess the degree of narrowing of the joint space and the condition of the articular surfaces (ulcerations, bone growths - osteophytes). Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is used to assess the condition of ligaments and cartilage.
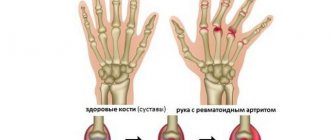
Figure 1. X-ray of hands with arthritis. Source: Frank Gaillard
Treatment
The approach to treating arthritis must be comprehensive. Its main tasks are to alleviate the patient’s condition and prevent further destruction of the joints.
Drug treatment
Among the drugs that are used to treat arthritis, three main groups can be distinguished:
- Analgesics - reduce pain and sometimes inflammation in the joint. Among them: non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (ibuprofen, nimesulide), acetaminophen (paracetamol). For severe pain, opioid analgesics (tramal) are sometimes prescribed.
- Drugs that influence the course of the disease: immunosuppressants (methotrexate, hydroxychloroquine, leflunomide) and targeted immune drugs - necrosis factor alpha inhibitors (infliximab, adalimumab, etc.). These medications aim to suppress inflammation and achieve remission.
- Hormonal drugs: glucocorticosteroids (prednisolone, dexamethasone) are used as anti-inflammatory drugs. To achieve the desired effect, they are administered in a special “pulse therapy” mode, in which large doses of drugs are administered in a short period of time.
Local
As local therapy, drugs with an anti-inflammatory component (Voltaren, diclofenac) are used.
Physiotherapy, massage, gymnastics
In addition to drug treatment, physiotherapy is used in daily practice: medicinal electrophoresis, magnetic and electrotherapy, the use of cold/heat (compresses, paraffin, etc.) and balneotherapy (medicinal mineral waters).
To restore range of motion in the affected joint and overcome stiffness, special exercises and a regimen of therapeutic and preventive training are needed. The most effective exercises for stretching the affected joint are stretching.
In turn, therapeutic massage helps to increase joint mobility and relieve pain; it is prescribed by a rehabilitation doctor.
Diet
Regardless of whether you have an illness or not, you should eat a balanced diet, remember to eat five vegetables and fruits a day, and limit your intake of salt and sugar. It is worth eating less processed meat products - sausages, bacon, sausages, as they contain a lot of salt and saturated fat. If the joints of the legs or spine are affected, then in this case the doctor may recommend reducing body weight (especially if the person is obese). This helps to redistribute and reduce the load on the joints.
Diet plays a special role in the prevention and treatment of gouty arthritis, the purpose of which is to reduce the concentration of salts and uric acid in the body. Alcohol, beef, and meat by-products are prohibited; it is recommended to eat lean fish, poultry, vegetarian soups, and drink more water.
Surgery
If conservative methods do not bring the desired result and the disease continues to progress, then in this case they resort to surgical treatment methods. The most common of them is joint replacement or fixation in a stationary state - arthrodesis.
In the first case, when it is impossible to restore mobility to the affected joint and the patient is bothered by chronic pain, the joint is replaced with an artificial one by endoprosthetics. It is possible to replace not all joints, but only large ones - knees, hips, ankles, shoulders, elbows and wrists.
Figure 2. Knee joint endoprosthesis. Source: Lee Health/Vimeo
But what to do with smaller joints? If the joints of the hand or spine are affected, they are closed, connecting each other into one fixed structure. This procedure is called arthrodesis: it is used to relieve pain.
Folk remedies
It is better not to resort to any methods of self-medication. If a person develops symptoms of arthritis, they should consult a doctor; this is the only way to prevent further development of the pathology in a timely manner.
Possible complications
Among the most dangerous and threatening complications of arthritis are:
- joint deformation (it occurs in every fifth patient) with limited range of active movements, the ability to walk and live a full life;
- systemic inflammation (with rheumatoid arthritis or lupus erythematosus), when the pathological process spreads to other organs and systems;
- damage to the joint and surrounding ligaments, which leads to limited mobility;
- tunnel syndrome - occurs when the median nerve is compressed in a narrow space of the hand due to inflammatory tissue swelling in rheumatoid arthritis. This leads to wrist pain, numbness of the thumb, index, middle and half of the ring finger and impaired motor function;
- spinal cord injury - when the process is localized in the joints of the spine.
Rheumatoid arthritis - indications for hospitalization
Treatment for joint diseases is long-term, the pathological process is prone to progression, so the patient must be under the supervision of specialists. Indications for hospitalization for arthritis are: moderate and high degree of activity of the process, continuously relapsing course, development of complications. In addition, the patient is recommended to stay in hospital if it is necessary to adjust the treatment regimen.
Prevention
Speaking about the prevention of arthritis, it is worth mentioning that there are factors that cannot be changed. This is due to the natural aging process, family history, and gender (some types of arthritis occur more often in women)
Losing weight and exercising can help - remember that WHO recommends at least 150 minutes of physical activity per week.
And do not forget to use protective devices for your elbows and knees during training and cycling rides, and follow the correct exercise technique. This will help protect your joints from additional damage.