At least 50% of all women in the postpartum period face the problem of discomfort and pain in the joints. This is especially true for young mothers who practice natural breastfeeding. This condition not only has a negative impact on the quality of life, but also interferes with the normal care of the newborn baby.
Not every nursing woman can afford to regularly visit the hospital for a comprehensive examination of the body, but joint pain in the postpartum period requires timely diagnosis and comprehensive treatment. In addition, when breastfeeding, there are a number of restrictions on taking medications, so the use of certain medications should be agreed with a medical specialist.
The influence of pregnancy and lactation on the condition of the musculoskeletal system
The process of bearing a child is accompanied by a number of changes in a woman’s body. Global hormonal changes affect the metabolism of calcium, phosphorus and vitamin D3, as a result of which young mothers and pregnant women very often develop osteoporosis. During the period of breastfeeding, the female body uses its own reserves to saturate milk with vitamins and minerals, so lactation very often leads to an aggravation of the deficiency of certain biologically active elements.
In addition, in the process of bearing a child, a woman’s load on the osteoarticular system increases, which is fraught with the appearance of joint pain in the postpartum period. Breastfeeding women often complain of pain in the lower back, knee and elbow joints, as well as in the pelvic area.
The specifics of caring for a newborn baby play an important role in the formation of joint pain. Another common cause of joint pain during breastfeeding is excess weight that a young mother gains from bearing a child. But, despite this, there are methods that help a nursing mother lose weight without harm to the baby. We talk about them in the article at the link https://vskormi.ru/mama/kak-pohudet-kormyashhej-mame/.
Pathological causes of joint pain
Before the onset of pregnancy or during the process of bearing a child, one or another pathology of the musculoskeletal system could have formed in the female body, which made itself felt during lactation. There are such pathological conditions that can cause joint pain in nursing women:
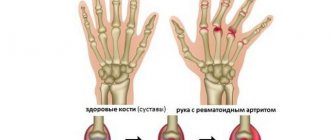
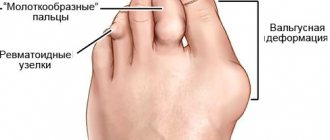
- Rheumatoid arthritis. During pregnancy, the clinical symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis remain invisible, but during breastfeeding they become fully apparent;
- Ankylosing spondylitis. This disease often develops in women during pregnancy. Clinical symptoms of ankylosing spondylitis are usually regarded as a manifestation of general fatigue of the body. With this disease, pain disturbs the woman in the lumbar region, in the joints of the hands, hip joints and in the lower jaw;
- Reactive arthritis. This disease is a consequence of previously suffered infectious pathologies. If during pregnancy a woman suffered from an infectious-inflammatory disease, then during lactation she may experience symptoms of reactive arthritis.
If joint pain occurs, a nursing mother should pay attention to the following signs:
- Increased body temperature and signs of general intoxication of the body (including chills);
- Deforming changes in the joint area, local redness of the skin and the presence of swelling;
- Headache, dizziness, increased fatigue and general weakness.
The listed symptoms indicate the development of a generalized inflammatory process of an infectious or autoimmune nature. These clinical manifestations are a reason to immediately contact a medical specialist.
- Instructions for use of the drug Stop Arthritis (Super, Forte, Normal) for arthritis and arthrosis
Causes
The development of the disease is due to a number of reasons. Moreover, many experts argue that all the causes of the disease have not been fully identified. However, several factors can be identified:
- Genetic predisposition of the patient. It often happens that before pregnancy the patient suffered from various types of arthritis, including rheumatoid arthritis. The disease has developed into a chronic form. It quieted down for a while. And during lactation a relapse occurred. At this time, the health of the nursing mother is unstable and shaky, and any risk of pathology is quite high.
- Bruises and other types of injury can also cause the development of the disease.
- Excessive physical activity and unbearable stress on the joints. If a nursing mother is engaged in backbreaking labor associated with excessive work of the joints, the disease may begin to develop as a result of a negative effect on the connective tissue.
- Various viral infections can contribute to the development of arthritis as a consequence of the disease.
Treatment
Not all medications can be used for therapeutic purposes in women during breastfeeding. If, in the opinion of the doctor, the risk to the mother's health is a priority, then the nursing woman is advised to interrupt natural feeding for the entire period of therapy. Depending on the cause that provoked joint pain in a nursing woman, a medical specialist prescribes the following treatment options:
- Lotions and compresses from medicinal preparations;
- Drug therapy, which includes non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, glucocorticosteroids, chondroprotectors, muscle relaxants and multivitamin complexes;
- Techniques of hardware physiotherapy (UHF, electrophoresis, magnetic therapy, paraffin baths);
- A set of therapeutic gymnastic exercises;
- Herbal teas that do not affect the lactation process;
- Therapeutic massage sessions.
In addition, it is important for nursing women who suffer from joint pain to review their diet. It is necessary to discuss the composition of the diet with your doctor, since dietary restrictions should not affect the qualitative and quantitative composition of breast milk. During lactation, you should not practice self-medication, since the use of certain pharmaceutical and folk remedies can lead to a deterioration in the general condition and negatively affect the body of the newborn baby.
Subscribe to our VKontakte group
← Previous articleNext article →
Which ointment to choose for joints during breastfeeding (BF) is of interest to many nursing mothers who have had to deal with joint pain. It’s not even worth talking about the benefits of naturally feeding a baby, however, this period does not always have a positive effect on a woman’s body. During breastfeeding, various undesirable phenomena may occur in the form of deterioration of tooth enamel, hair loss and pain in the joints of the legs and arms.
What is the treatment?
The doctor may prescribe the following comprehensive measures:
- physiotherapy;
- gymnastics;
- taking various medications;
- diet;
- use of folk remedies;
- wearing a bandage and using an orthopedic mattress for sleeping.
Breastfeeding is a period when it is advisable to avoid drug treatment. You also need to monitor your posture, do not lift heavy things, and strengthen and stretch your muscles. Therapeutic exercise depends on which joint and how severely inflamed it is. It is possible to use folk remedies: decoctions, infusions and compresses. Anti-inflammatory herbs, vitamin complexes, ointments and gels are common to relieve painful symptoms and are safe during breastfeeding.
What do women face during breastfeeding?
Such a pleasant time for a mother and her newborn baby, like the period of breastfeeding, can cause women significant discomfort and often this is pain in the nipples caused by cracks. Destruction of tooth enamel is a common problem in breastfeeding women, so during this period it is especially important to monitor your diet and take calcium-containing medications prescribed by your doctor. Some women during lactation complain of headaches, which are caused by tension in the nervous system and changes in the spine caused by pregnancy and constantly carrying the baby in their arms. But most often, when a child is breastfeeding, nursing mothers are bothered by joint pain.
Return to contents
Causes of joint pain
During pregnancy, the hormone relaxin is produced.
At first glance, there is no relationship between painful discomfort in the osteoarticular system and breastfeeding, but specialized doctors say the opposite and explain it as follows. Usually, joints hurt when feeding due to a lack of calcium in a woman’s body and an excess of the hormone relaxin, the active production of which occurs during pregnancy. Produced by the ovaries and placenta, relaxin is necessary to facilitate labor. And remaining in the woman’s blood for some time after childbirth, the hormone provokes joint pain. But this is not always the cause of joint pain; quite often breastfeeding women have knee pain due to the development of arthrosis or arthritis.
The cause of joint pain may be another. After childbirth, a woman’s body undergoes serious changes, one of which is poor posture, as a result of which the load on the spine and knees increases significantly. The condition is often worsened by carrying the baby in one arm or feeding in an awkward position. As a result, muscles are overloaded, spasms appear and joints become inflamed. Many mothers use a sling, but not all wear it correctly. This has a negative impact on the spinal column and puts stress on the knee joints.
If you experience severe pain in the knee joints, you should not self-medicate and delay going to the doctor; it is better to take therapeutic measures recommended by a specialized specialist as soon as possible.
Return to contents
Causes of joint pain in a nursing mother
After childbirth, a woman’s immunity is reduced, she is in a stressful state, and certain factors of a physiological or non-physiological nature contribute to the development of diseases.
The most commonly affected joints and body parts are:
- Legs. During the period of bearing a child, a large load falls on the lower limbs. After giving birth, a woman spends all her days on her feet taking care of the baby; it is for these reasons that her knees hurt in the first few weeks after childbirth.
- Hand joints. When carrying a child, feeding, or doing household chores, there is a huge load on the joints of the fingers and hands.
- Neck. The causes of pain are: incorrect wearing of the sling, incorrect tilt during breastfeeding, uncomfortable sleeping position.
- Back. The back muscles are very weakened after childbirth and take on the entire load until the pelvic bones and abs are restored.
Return to contents
Physiology
Pregnancy is the happiest moment in a woman’s life, but it is overshadowed by a significant load on the internal organs, which has a negative impact on the mother’s health. During pregnancy and childbirth, the center of gravity shifts and joint pain occurs. During the first 2 months after the birth of the baby, the mother’s body is restored, until the movable joints return to their previous state. And also in the postpartum period, the gait changes, stretched abdominal muscles and weak articular ligaments return to their original state. As a result, the knees and hip joints are subject to excessive stress.
Hormones in a nursing mother
Restoring hormonal levels is a long process that is influenced by a large number of factors:
- schedule;
- daily diet;
- psycho-emotional state;
- ecological situation;
- past viral infections.
The fragility of joint joints is caused by an excessive level of relaxin.
After childbirth, hormonal changes occur in the body. Under the influence of increased levels of the hormone relaxin, which increased tenfold by the time of birth, the ligaments become soft, elastic, allowing the pelvic bones to be mobile and move apart. But since the effect of the hormone does not apply only to the pelvic ligaments, the rest also weaken. A woman during lactation is at risk of getting a sprain or injury, because relaxin decreases for a long time after the birth of a child.
Joint inflammation
This is a reaction of the body that occurs most often under the influence of bacteria. The inflammatory process mainly affects the ankles, wrists, hips and finger joints. Diseases develop in which the joint space decreases, and the joints of the arms, hands and other joints hurt. Pathologies include: bursitis, synovitis, periarthritis, osteoarthritis, gout, rheumatism. General symptoms:
- acute pain;
- skin redness, swelling.
- crunch;
- joint deformity;
- local temperature increase.
Return to contents
Lack of calcium
The baby receives from the mother all the vitamins it needs through breast milk. To avoid exhaustion of the mother’s body, it is necessary to ensure sufficient consumption of important microelements, including calcium. You need to get at least 1.5 g of Ca from foods per day. The lack of a microelement in the body can be compensated for by a balanced and nutritious diet. A nursing mother's diet should include: cottage cheese, yogurt, peas, beans, sesame seeds, apples, bananas and pumpkin. The following symptoms indicate calcium deficiency:
- pain in the muscles of the limbs;
- cramps in the calf muscles;
- spasm of the limbs;
- brittle nails and hair;
- crumbling of teeth.
Return to contents
Autoimmune diseases in nursing mothers
These are pathologies in which leukocytes destroy the body’s own cells, mistaking them for foreign ones. Rheumatoid arthritis is a disease characterized by joint destruction. This leads to debilitating pain, deformity and loss of mobility. If an autoimmune disease is detected, a woman should remain calm, since during lactation her general condition and mood can aggravate the disease. The following reasons for the development of diseases are identified:
- genetic predisposition;
- hormonal imbalance;
- excessive physical stress on the joints;
- viral infections.
Return to contents
What to do?
It is necessary to take medications only after examination by a doctor.
Nursing mothers should begin joint treatment only after a doctor’s examination and a diagnostic examination, which will help determine the true cause of pain in the joints. If diseases of the musculoskeletal system have not been identified and the doctor has confirmed the relationship between breastfeeding and joint pain, then to normalize the condition the woman will need to follow the following recommendations:
- Maintain correct posture. The back should be straight, the shoulders should be pulled back, and the chin should be parallel to the floor or other surface.
- Lift carefully. It is worth understanding that the child, despite his small size and lightness, has weight, which increases with age and it becomes increasingly difficult for the mother to hold him in her arms and take him from the crib. You should not make sudden movements and, when lifting your baby, it is important to keep your back straight, slightly bending your knees and hip joints. It is necessary to use the strength of the lower extremities as much as possible, strain the abs and muscle tissue of the buttocks.
- Stretch marks. It is recommended to do exercises to prevent muscle spasms and prevent joints from becoming stagnant. Physical education should be moderate, especially in the first time after childbirth, so it is recommended to consult your gynecologist first.
Return to contents
Pain therapy
For joint pain, it is recommended to take painkillers approved by your doctor.
If joint pain is severe and significantly worsens the quality of life of a nursing mother, doctors prescribe painkillers. It is extremely undesirable to independently treat joint pain, since only a doctor knows what medications are allowed for breastfeeding. Typically, during the lactation period, women are prescribed traditional medicine and vitamin complexes to relieve joint pain.
Ibuprofen is allowed during breastfeeding, the dosage of which is 0.2-0.4 g twice a day. To relieve pain localized in the joints of nursing mothers, Diclofenac-Acri ointment is used. It has an exclusively local effect and practically does not enter the bloodstream. The popular "Paracetamol" is used with caution. The drug can eliminate joint pain in women during breastfeeding. It is safe for the feeding period, since only about 1% of the composition passes into breast milk.
Entry published by ilake · January 2, 2014
2
Girls!! Looking for support!!! Who had to take long breaks from breastfeeding and get sick during breastfeeding, please share what you did? Did you feed and endure it, or did you take a break and for how long? Were you able to return to GW???
I won’t describe my path to my second child, but everything happened!!! We were all just happy!!! I was flying like I had wings!!!! I dragged a stroller to the 5th floor; massage, exercises for my daughter, walking, feeding, intensive cleaning, etc. There were problems during pregnancy and the first 3 months, but we resolved everything...
BUT a month ago my joints began to hurt sharply. My daughter is now 4 months old. I went to doctors - the diagnosis is not clear, blood tests are generally normal, x-rays - it looks like arthrosis, but there are some doubtful points. The rheumatologist doesn’t say anything intelligible, either arthritis or arthrosis. He says: I don’t see an acute process, decide to feed or stop breastfeeding. BUT I’m only getting worse, more and more pain is appearing, in new joints - my hands, wrists, ankles, knees hurt (despite local treatment with ibuprofen and demixide compresses)
All this treatment is undesirable and even as they say in the instructions, it is impossible, but after consultation with a gynecologist and pediatrician, it was decided to carry out a course of treatment without stopping breastfeeding), the course has not yet been completed. The gynecologist says to be patient for another month, otherwise after the break the child will not latch onto the breast. It’s very scary that I don’t know what it is, how to treat it and when it will go away, whether there is any point in taking a break from breastfeeding. My daughter doesn't eat from a bottle. And I really want to breastfeed her... well, at least until 6 months... I don’t know if I can stand it.
Maybe someone had something similar. share what you did?
Consultation with a rheumatologist / Albina, St. Petersburg December 1007, 2018
During pregnancy, my finger joints began to hurt. The middle one is especially strong on the left hand. It really hurts all the time. When I warm up for a long time it goes away. The child is large and grows quickly and takes up a lot of calcium. Although I constantly drink various calcium and vitamins, now I am on ferlatum ful, the pain continues and the joint is already deformed. Very sad. My fingers are very beautiful, long, graceful. How to stop the deformation? I am breastfeeding - many pills are not allowed. My mother’s fingers are also deformed, but this happened after the age of 60. What should I do? Should I register with a rheumatologist?
The Ask a Doctor service offers an online consultation with a rheumatologist on any problem that concerns you. Expert doctors provide consultations around the clock and free of charge. Ask your question and get an answer immediately!
Answers from doctors + 1Complain Elena Furmanova, December 26, 2018 Pediatrician Hello, have you taken rheumatic tests? Did you do an X-ray of your hands? ComplainAlbina, December 26, 2018Client Elena, no, they didn’t do anything. All rheumatologists have appointments a month in advance. And it’s so difficult for me and my child to manage my time Complain Viktoria Druzhikina, December 26, 2021 Neurologist, Therapist Hello. First you need to get examined. X-ray of the hands, rheumatic tests, general blood test. + 1ComplainAida Karabekyan, December 26, 2021 Pediatrician Hello Albina. Perhaps the cause is not hypocalcemia. What examinations were taken? Of course, it is advisable to see a doctor in person, you can start with a therapist, get tested (CBC, biochemical blood test, rheumatic tests, do an ultrasound and/or x-ray of the joints, etc.). And don't wait until the breastfeeding period is over. + 1ComplainElena Furmanova, December 26, 2018 PediatricianComplainYana Dudkina, December 26, 2021 Therapist, Gastroenterologist Good afternoon. Do an ultrasound of the joints that are more of a concern. X-ray will be less informative. Rheumatic panel, b/c and general blood test. Without tests it is difficult to guess Complain Ekaterina Danilenko, 26 December 2021 Rheumatologist Show a photo of the joint. What tests have been done? ComplainNina Izvozchikova, December 26, 2018 Infectious disease specialist Hello! Contact a rheumatologist. You will be prescribed an examination and treatment. Make warm hand baths and lubricate with anti-inflammatory ointments. Complain Marguba Azmetdinovna, December 26, 2021 Pediatrician Hello! Calcium without Vit D is not absorbed, and Vit D is fat-soluble.. If there are problems with the gastrointestinal tract (cholecystitis, for example, a flexed cervix, then calcium also will not be absorbed sufficiently). Normalize the diet, check the ultrasound OBP ALT AST ALP . ur calcium, phosphorus and vit D blood, blood rheumatic tests. Do an x-ray or ultrasound, densitometry ComplainAnastasia Stepashkina, December 26, 2021 Hematologist, Therapist Hello, now take Vitrum for nursing and take rheumatic tests, x-rays of the hands ComplainKonstantin Tishchenko, December 26, 2021 Orthopedist, TraumatologistComplainVictoria Petrova, December 27, 2021 Rev matologist, therapist Similar questions on the topic: Taking Methotrexate for GV1 answer November 23, 2018 Maria, St. Petersburg Question closed All joints bake, RA and A-CCP are negative 15 answers June 11, 2019 Question closed Systemic scleroderma 6 answers August 9, 2020 Yulia Question closed Decoding of biopsy results 21 answers October 9, 2020 Ivan Question closed Is it possible to do anything to help with arthritis of the foot joint? 1 answer January 25, Anna The question is closed. What should I do? what if I haven't found the answer to my question?
If you have a similar or similar question, but you have not found the answer to it, get your 03 online consultation from an expert doctor.
If you want to get a more detailed consultation with a doctor and solve the problem quickly and individually, ask a paid question in a private personal message. Be healthy!
During pregnancy, a woman's body undergoes significant changes and also experiences extreme stress, especially during childbirth. After the baby is born, such stress can lead to complications, such as pain in the joints of the hands, fingers and feet.
Half of women who have given birth complain that their knees hurt after childbirth, their arms hurt, and it hurts to stand up or squat. Usually the discomfort goes away over time when the body is fully restored, but sometimes it needs help. Why do my knees hurt and how to deal with it?
- How to treat arthritis in dogs
What to do to identify the disease?
In the process of determining a possible disease and making a diagnosis, the doctor studies information about the medical history, determines whether there is swelling of the joint through palpation, and determines the degree of pain and limited movement of the joint. He also prescribes a number of laboratory tests, such as:
- blood and urine collection for analysis;
- X-ray of the joint;
- MRI and CT scan of the diseased joint;
- densitometry;
- Ultrasound;
- arthroscopy;
- puncture.
Return to contents
How does childbirth affect joints?
The nature of pain is not difficult to understand if you understand the impact on the body of the process of bearing a baby and the birth itself. In most cases, unpleasant sensations are of a physiological nature and disappear within 1–2 months.
While in the womb, the fetus is completely dependent on it. He receives all the necessary nutrients, vitamins and microelements from his mother. If a pregnant woman’s diet does not have enough calcium, magnesium or potassium, the baby will not have enough nutrients.
However, the baby will still get what it needs - from the mother’s bones and joints. As a result, the bones will become more fragile. This is why it is so important to eat well and take the vitamins prescribed by the gynecologist. Otherwise, the woman will feel that her hip joint hurts, her knees hurt when bending, and so on.
The second factor is excess weight. In 9 months, a woman gains at least 9–12 kg, or even 20–30 kg. Bones and joints experience additional stress, which results in pain after delivery.
Pain in the legs and back can be explained by a shift in the center of gravity, which occurs in all pregnant women. Sometimes such sensations are associated with injuries to the musculoskeletal system during childbirth.
Why does it hurt to bend your arms and legs, why is it difficult to squat and stand up?
Often after childbirth, women experience hip pain. Discomfort may appear earlier - in the third trimester. In later stages, the body produces the hormone relaxin, which relaxes the hip joint. This prepares the body for upcoming childbearing by making it easier for the baby to pass through the hip bones.
After giving birth, my mother sometimes has pain in her arm joints. During contractions and pushing, women grab the bed, handrails, and strain their muscles, which creates significant stress on the joints. After this it hurts even to straighten your fingers.
The second reason for heaviness and pain in the hands is everyday chores. The mother of a newborn often has to carry the baby in her arms, which causes fatigue and pain when bending her fingers.
- Arthritis in a dog:((
The consequences of epidural anesthesia can affect a woman’s musculoskeletal system. In some cases, after such anesthesia, pain in the knees and other joints may appear.
During difficult births, sometimes the pelvic bones spread too far apart and the tailbone deviates. In this case, you should contact a traumatologist as soon as possible.
Symptoms
- The inflammatory process affects several joints at once. The joints of the feet and hands, knee joints and joints in the neck area are usually affected.
- Painful sensations during physical activity. Swelling and stiffness.
- Stiffness when trying to move, especially in the morning after sleep.
- The disease can occur in wave-like periods. Remission gives way to relapse.
- Deformation and damage to the joint, problem with the structure of the tendon.
- Fatigue and general lethargy. Apathy gives way to irritation. A stressful state is observed throughout the entire disease. As the quality of life deteriorates, the patient feels unhappy. Due to painful sensations, a nursing mother cannot fully provide care and concern for the child.
- Lack of appetite.
- Loss of body weight. The patient may suddenly lose weight for no apparent reason.
Diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis in a nursing mother
If the development of an illness is suspected, the specialist examines the patient, clarifies her medical history and listens to all the patient’s complaints. In order for the diagnosis to be accurate, the specialist prescribes a series of examinations, the results of which will give an accurate picture of the course of all the processes of interest in the body.
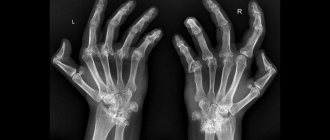
- X-ray examination of the limbs. In the image as a result of the examination, the specialist clearly sees clear signs of the disease. In the wrist joints, the disappearance of joint gaps is observed, that is, the space between the bones decreases and the boundary between the small adjacent bones of the wrist is erased. And in the fingers and toes, “usures” are noticeable - this is the formation of erosion of the bones in the area of the metacarpophalangeal and metatarsophalangeal joints. The listed anomalies allow the expert to draw a conclusion about the development of pathology. In a serious stage of the disease, the picture shows the fusion of the ends of the joint of the adjacent bones. This anomaly indicates complete immobility of the joint.
- It is necessary to take a general blood test. As the disease develops, the ESR level in the blood will increase. Thus, the presence of an inflammatory process is revealed.
- Blood is also taken from a vein. This study was carried out due to the need to identify markers of the inflammation process.
Solution
After the birth of a child, most women establish breastfeeding, during which a limited number of medications are allowed. Buying and taking medications on your own is strictly prohibited. The most natural and seemingly safe drugs can negatively affect the health of a newborn. Active and auxiliary components pass into breast milk and may harm the baby.
Usually the problem is solved comprehensively. First you need to undergo an examination to understand the exact cause of the pathology. If there is an urgent need, the doctor will prescribe medications approved during lactation. Therapy is supplemented with diet, therapeutic exercises or massage. A comprehensive approach gives a positive result and a long-lasting therapeutic effect.
Medications
Depending on the nature of the pain, several groups of drugs are prescribed:
- NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs);
- corticosteroids;
- chondroprotectors;
- vitamins, mineral complexes, biological additives;
- products for external use (gels, ointments, creams).
When the problem is caused by a lack of calcium, magnesium or potassium, the woman is advised to take vitamin complexes (Calcium D3 nikomed, Pantovegir, etc.). The diagnosis must be made after laboratory tests.
Discomfort and pain are effectively eliminated by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. However, in this case, the therapy will be incompatible with breastfeeding.
Ointments for external use are relatively safe and are not absorbed into the general bloodstream. It should be understood that these remedies alone will not give a noticeable effect.
Diet and drinking regime
A proper diet can pursue 2 goals - reducing excess weight and replenishing missing vitamins and microelements. When losing weight, your diet should be balanced. Mom should not lose nutrients, especially when breastfeeding (the baby should receive all vitamins, proteins, fats and carbohydrates).
Prohibited products:
- baked goods, sweets;
- canned or pickled foods, semi-finished products;
- sausages, sausages;
- carbonated drinks;
- too salty or spicy food;
- fried foods (foods need to be cooked by boiling, stewing or baking).
Allowed (useful) products:
- dairy and fermented milk products (natural, without preservatives, flavors, stabilizers, with a short shelf life);
- vegetables, fruits, berries;
- lean meat and fish;
- fatty fish rich in omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids;
- porridge;
- nuts and dried fruits;
- vegetable oils.
It is necessary to drink clean water (tea, coffee or compotes do not count) in sufficient quantities. Water is essential for the normal functioning of the body and helps you lose weight. Proper drinking regimen will relieve swelling, which can also cause pain in the knees or arms.
Joint exercises and massage
Physical therapy exercises are selected depending on the location of pain. When a woman has severe knee pain after childbirth, she needs to alternately raise her legs bent at the knee joint and stay in this position. Over time, increase the number of repetitions.
For pain in the pelvic bones, you need to work out the hip joints. Gradually, squatting and standing up will not cause discomfort. It is useful to do health-improving exercises for all muscle groups. This will strengthen the body and improve your figure.
Therapeutic massage must be prescribed by a doctor and performed by a specialist. Otherwise, there is a risk of getting the opposite effect.
ethnoscience
Joint problems worry many, and traditional medicine has in its arsenal many means of combating them. Among them there are those that are suitable for nursing mothers. You can use the following recipes:
- Infusion of bay leaf. It removes excess salts. Pour 500 ml of boiling water over 25–30 leaves and keep on low heat for 15–20 minutes. Leave for a couple of hours and then drink several times throughout the day.
- Jellied meat and chicken cartilage. They contain a lot of collagen, which is necessary for joints.
- Warm baths for feet and knees. A decoction of chamomile, lemon balm, and lavender is suitable.
- Alcohol tinctures for compresses from propolis or horseradish. Soak gauze in the tincture, apply to the sore spot and wrap with cling film.
Prevention of joint diseases
Preventive measures to help avoid discomfort:
- proper and balanced nutrition;
- active lifestyle, regular walking;
- swimming or a set of exercises for pregnant women;
- wearing low-heeled shoes;
- straight posture;
- avoiding heavy loads and sudden movements.
Share with friends! References:
- https://vskormi.ru/mama/bolyat-sustavy-pri-grudnom-vskarmlivanii/
- https://etosustav.ru/diskomfort/vazhno/bolyat-sustavy-pri-grudnom-vskarmlivanii.html
- https://www.babyplan.ru/blogs/entry/195892-grudnoe-vskarmlivanie-i-bolezn-mamy-sustavy/page/2/
- https://sprosivracha.com/questions/104119-bolyat-sustavy-palcev-kormlyu-grudyu
- https://vseprorebenka.ru/rody/posle-rodov/bolyat-koleni-posle.html