Diagnosis of equinovarus foot deformity (clubfoot) in an adult and treatment of this anomaly are serious issues in orthopedics, to which many studies have been devoted. In this condition, the inner edge of the sole changes its location, turning upward and inward, and the toes are also retracted in the same direction.
Etiological factors:
- Wearing inappropriate shoes.
- Injuries.
- Diseases of the musculoskeletal system and nervous system.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Previous rickets or persistent deficiency of vitamins and minerals during the period of active growth and skeletal formation.
- Unsolved orthopedic problems at an early age.
Verification of the diagnosis and choice of management tactics are determined during consultation with a specialist individually, based on examination and radiological data.
Treating clubfoot in adults is a challenging task compared to correcting a similar problem in childhood. This is associated with the development of persistent changes in ligaments, articular surfaces, and bones, which may lead to the need for surgical assistance.
Clubfoot: Exercise therapy, conservative or surgical?
There are 4 degrees of clubfoot:
- Mild clubfoot: exercise therapy, massage, orthopedic devices are effective, since deviations are minimal.
- Medium: painful sensations occur, therapy is long and complex.
- Severe: curvature of the feet, the addition of arthritis and arthrosis requiring surgical intervention.
- Extremely severe is characterized by pronounced transformation of the affected area, involvement of the spine; manipulations in this situation are ineffective.
ORTO-N
The Ponseti method is a modern and effective method for treating clubfoot in children. Treatment using the Ponseti method allows you to quickly and in the most gentle way correct this disease. Most orthopedists around the world recognize the Ponseti method as the “gold standard” for clubfoot treatment. For the first time in the Krasnodar region, in the city of Novorossiysk, in the ORTO-N orthopedic center, the Ponseti method was introduced in the form in which it was proposed and promoted by the author and his followers.
It is advisable to begin treatment of clubfoot in children using the Ponseti method from the age of 7-14 days. The earlier treatment is started, the more malleable the foot deformation is, and the faster its complete correction will occur. Treatment consists of three main stages.
The first part of treatment is correcting the deformity with plaster casts. As a rule, for complete correction of foot deformity, regardless of severity, 6-7 changes of plaster casts are necessary with gradual correction of the deformity. Staged treatment using plaster takes from 4 to 8 weeks, depending on the severity of the clubfoot. Changing plaster casts with gradual correction of the foot occurs after 5-7 days.
Plaster casts are always applied with fixation of the knee joint to the upper third of the thigh.
- I, II, III, IV, V – staged plaster casts, with gradual correction of deformity of the middle and forefoot.
- V – the middle and forefoot are abducted 70°, subluxation in the talonavicular and subtalar joints is corrected.
- VI – the last plaster cast applied after subcutaneous achillotomy, in a position of 15° dorsiflexion.
The second important part of the treatment is closed achillotomy. The Achilles tendon in clubfoot is always shortened, which is why the vast majority of children treated for clubfoot need to have it lengthened. A gentle method of lengthening it is a closed achillotomy, proposed by Ignacio Ponseti. Achilles tendon is a complete transection of the Achilles tendon 1.5-2 cm above the point of its attachment to the heel bone. Achillesotomy, performed at the last stage of manual correction, is a low-traumatic, short-term, non-scar operation, in comparison with Z-shaped Achilles tendon plasty. Ponseti achillotomy, with timely treatment, allows one to avoid prolonged general anesthesia.
The third part of the treatment is wearing braces. After three weeks of being in a cast, you need to switch to wearing braces: special shoes attached to a bar. Only wearing braces until the age of 4-5 years allows you to avoid the return of deformity. The braces provide abduction of the foot, keep the heel bone and forefoot in abduction and prevent relapse. The foot will gradually return to the correct position (10° external rotation). The soft tissue along the medial surface will remain stretched only if the braces are used after casting. The braces consist of open-toed, high-backed boots attached to a bar. In cases where correction of one foot is required, the corrected foot in the brace is moved outward by 60-70°, and the normal foot by 30-40°. When correcting two feet, both boots are abducted 70°. The bar should be long enough so that the child's heels are shoulder-width apart.
Observation schedule for children after casting using the Ponseti method:
- After 2 weeks (to solve problems with following prescriptions).
- After 3 months (to gradually reduce the time spent in braces).
- Every 4 months until age 3 years (to monitor compliance and diagnose relapses).
- Every 6 months until age 4 years.
- Every year or every 2 years until growth ends.
Protocol for wearing braces:
- The braces are applied immediately after the last plaster cast is removed, 3 weeks after the tenotomy.
- The braces should secure the child's feet 24/7 for the first 3 months after the cast is removed.
- After this, the braces are put on the child for 12 hours at night and from 2 to 4 hours in the middle of the day, so that the total time of their use is from 14 to 16 hours during the day. This mode of being in braces is maintained until the age of 3-4 years.
At the ORTO-N orthopedic center, the treatment of clubfoot in children is carried out by a doctor of the highest category, pediatric traumatologist-orthopedist Sergey Vadimovich Kuzmichev, who is a member of the Russian Ponseti Association.
Clubfoot, psychosomatics in an adult – is there a connection?
From the point of view of this science, pathologies of the lower extremities symbolize a person’s loss of support. In children, due to their obvious dependence on their relatives, flat feet and other leg imperfections are “physiological.” In older age groups, such conditions are interpreted as a manifestation of helplessness and subordination to others. In the treatment of clubfoot in an adult patient of a psychosomatic nature, the use of massage techniques along with solving psychological problems is effective.
Prevention is quite simple:
- complete balanced nutrition;
- lack of excess body weight;
- optimally selected insoles/shoes;
- independent performance of physical therapy exercises.
Reception of specialists and provision of medical services at the Doctor Pozvonkov Center for Progressive Medicine is carried out by appointment.
Causes and consequences of clubfoot in adults
True clubfoot in an adult is a consequence of lack of attention from parents and orthopedists during the growth and development of the child. The deformation of the foot bones in this case is permanent. You can correct it with long-term special physical exercises. The main reason is intrauterine developmental disorders of the bone and ligamentous apparatus. This happens against the background of intoxication in the body of a pregnant woman (smoking, drinking alcoholic beverages and certain medications can play a negative role).
Acquired clubfoot in adults most often develops against the background of excess body weight gain. These cases account for more than 80% of all diagnosed diagnoses. With the development of obesity, a slight shift in the center of gravity occurs, as a result of which the physiological position of the pelvic bones changes. An incorrect angle of fixation of the femur in the hip joint begins to form. In this case, increased physical stress begins to be placed on the knees, which is compensatoryly redistributed to the ankle joints. Their deviation to the lateral sides gradually develops. When such a person walks, the main load falls on the outer edge of the foot.
This negatively affects shock absorption properties. A reverse pathological process begins, in which secondary deformation of the knee and hip joints begins. Incorrect posture develops with displacement of the lumbar vertebrae. A patient who has been suffering from clubfoot for a long time develops a characteristic “Winnie the Pooh figure”: the lumbar curve is smoothed, the buttocks are pulled inward, the thoracic spine is curved, the back becomes round and massive, since it bears the main load during any movements. When walking, you can see the body swaying with weight shifting from one foot to the other.
All this is fraught with negative consequences:
- venous blood flow in the pelvic cavity and lower extremities is disrupted;
- numerous prolapses of internal organs are observed (dislocation of the liver, stomach, gallbladder, poppies, rectum, kidneys);
- the vital capacity of the lungs decreases;
- signs of arthrosis of large joints (hip, knee, ankle) appear;
- thrombophlebitis, deep vein thrombosis, and trophic ulcers of the lower leg occur.
Therefore, when this pathology is detected in an adult, it is necessary to correct the situation as early as possible. Moreover, for diagnosis it is enough to look inside the shoes that you have been wearing for at least 2 months. You will notice that there are no significant abrasions in the area where the base of the thumb rests. But in this case, the deepest notches will be present along the outer edge of the insole. Even the minimal degree of clubfoot with this “test” will reveal itself at the first examination.
If you still have doubts, contact an orthopedist who, in addition to a visual examination, will conduct a number of diagnostic measures. The most important are x-rays, which will show the degree of deformation of the bone cartilage tissue.
Prevention of congenital clubfoot
There is no specific prevention. It is important for a pregnant woman to avoid exposure to adverse factors, lead a healthy lifestyle, and follow the gynecologist’s prescriptions. After the birth of the baby, you must strictly follow the recommendations of the orthopedist. The team of experienced specialists at the SM-Doctor clinic will help your child get rid of clubfoot. Our orthopedic traumatologists will conduct a comprehensive examination and draw up a program for improving the health of the musculoskeletal system. Sign up for a consultation at convenient office hours!
Treatment of congenital clubfoot
The treatment method is chosen by a pediatric orthopedic traumatologist, focusing on the severity of the disease and the general clinical situation.
In the vast majority of cases, persistent conservative treatment is sufficient to correct the situation. The most active treatment is carried out from the first days of life, while ossification is incomplete and it is possible to bring the foot to the physiologically correct position without much difficulty. A combination consisting of the following methods is prescribed:
- therapeutic exercises to maximize ankle mobility and prevent muscle atrophy;
- foot massage;
- soft fixation in physiological position with flannel bandages;
- after being brought into the correct position - splint, cut or stage-by-stage plaster immobilization;
- after plastering - wearing special anti-varus high orthopedic shoes (braces);
- physiotherapy – pine baths, paraffin.
Correctly selected conservative treatment allows you to cope with the disease in the first year of life.
If conservative methods fail to get rid of clubfoot, surgery is performed, but not earlier than 1 year. The surgical plan is developed individually, the position of the bones and joints is changed, and the ligamentous apparatus is adjusted. The scope of intervention is determined by individual data. After surgery, plaster immobilization is required for up to 6 months.
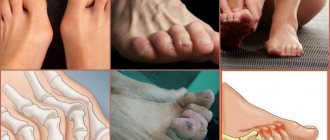
How to determine clubfoot in a child by external signs
- The fingers are curved inward, deviated from their normal position.
- The arch is high, the heel and toe are at different levels.
- The arch of the foot is raised upward along the inner edge.
- Waddle gait, “raking” with legs.
- Calluses on the outside of the big toe.
- The sole of a shoe wears out unevenly, with the heel wearing out the most.
- Footprints in sand or other irregularly shaped surfaces.
- The baby gets tired quickly when walking.
- With moderate damage, the shin and knees may not be directed straight, but towards each other.
- Movement in the ankle is limited.
How the system helps identify clubfoot in a child
Medical supervision of children is organized in a systematic manner.
- Modern Doppler ultrasound systems make it possible to diagnose bone deformations at the prenatal stage of development. If abnormalities are detected in this way, the baby, upon birth, will be specifically examined by neonatologists and orthopedists.
- If the baby is born healthy, he undergoes a routine orthopedic examination at established intervals. Pathological signs may be detected on it. In the early stages. A pediatrician who sees the baby much more often can also refer you to a specialist unscheduled.
This organization of medical care reduces the number of undetected cases of the disease. Another factor that allows you to notice and treat clubfoot in a child in a timely manner is the attentiveness of the parents. It is necessary to clearly know which symptoms are alarming, and if they are detected, seek medical advice in a timely manner.