Home|Clubfoot
Clubfoot in children is a common pathology of the development of the musculoskeletal system. It is expressed in foot deformation, incorrect physiological location of the bones of the talonavicular joint and limitation of its mobility. Externally, the defect looks like a curvature with support on the outer side, an upward turn of the plantar part and deviation of the toes inward. The disease develops on one leg or is bilateral. It is caused by abnormalities in the formation of soft tissues and bone development, due to various reasons.
Types, forms of pathology
How to treat clubfoot in a child depends on the type and degree of complexity of the disease. Pathology happens:
- congenital, noticeable already in the mother’s womb.
- acquired as a result of injuries, diseases, the course of which affects how to treat clubfoot in children, taking into account the state of health.
- typical, usually not extending beyond the feet, due only to the peculiarities of muscle development.
- atypical, arising as a result of diseases of the central nervous system, serious disorders of the musculoskeletal system of the musculoskeletal system.
When choosing a method to correct children's clubfoot, they proceed from three degrees of complexity of the disease. The first is varus contractures, which are painless and amenable to manual correction. The second degree is the soft tissue form, when the baby does not fully place his foot on the floor, and the tissues resist manual correction. The third degree is a musculoskeletal form with persistent changes, limitation of joint mobility, when treating clubfoot in children with conservative methods is impossible. In particularly difficult cases, especially over the age of 2.5 years, a tendon transplant is required for clubfoot.
Exercises to correct club feet
It's good if you have the opportunity to work out at the gym, but this is not a requirement. You can practice on the street, in the forest, in the country and, of course, at home. You must develop exercises, systematize them and gradually increase the load. You can talk to the physical education teacher at school and he will suggest some exercises for your child.
When you understand what needs to be done and explained it to your child, start doing the exercises with him. For the second lesson, take a video camera and film your child’s awkward movements.
After 5-7 lessons you will get the first results. Show your child a video of the activity. Children usually like their successes, they are proud of themselves and strive forward with great zeal. But make no mistake, you are just at the beginning of the journey. Don't forget to praise and stimulate your child.
So, you started studying. It is advisable for the child to be as focused as possible on what he is doing. First, let's run a few laps, this will warm up the muscles, and most importantly, it will help you see the problem again, especially on turns. From this day on, your child will no longer run as he pleases. Now he will learn to run and walk in a new way.
When running, you don't need speed, the main thing is to place your feet correctly. In the next lesson, you introduce a system of “additional exercises” for inattention and incorrect leg positioning (remember those same claps and push-ups). For the first few weeks, you will have to carefully observe what the child is doing, rubbing his palms together in anticipation of clapping them.
When you notice that there are fewer mistakes, offer your child the following exercise: raise your arms to your chest, clench your fists and twirl your fists in front of you while running. To begin with, you can twist your fists only in one direction, for example, towards yourself, and after several lessons the exercises become more complicated and alternate - 10 times in one direction, 10 times in the other. At the same time, you will see that all previous successes achieved in the fight against clubfoot have sunk into oblivion. It doesn’t matter, a few lessons - and your child will cope with the task assigned to him - he is reluctant to do push-ups.
You dilute running and walking around the hall with jumping on your toes. The positioning of the legs should be in the style of Chaplin. In this position, the legs should come off the floor and land in the same position. It’s good to climb stairs with this gait, preferably higher and regularly. Add to the exercises goose-stepping, jumping from a squatting position, and the like. Or ask your child to imagine that he is carrying a large, heavy watermelon. The watermelon is so heavy and big that the child is forced to walk, as they say, “half-bent,” and he needs to carry the watermelon to the end of the hall as quickly as possible, but not run.
Include exercises to externally rotate the foot in any variation. An excellent corrective pose is “sitting between the heels.” The child is on his knees, feet spread apart with toes apart. You need to slowly lower yourself and sit between your heels.
It is necessary to include stretching exercises, as well as static exercises, for example, such as the “rider's stance”: the legs are placed slightly more than shoulder-width apart, and with a flat, straight back, the child lowers himself into a semi-sitting position, the arms can be extended forward, and the feet should be parallel to each other. Duration of the exercise: 15 seconds - freeze in the rider's position, 5 seconds - rest. We repeat five times. Anyone you know who has done karate or other martial arts will show you this exercise and stretching exercises.
It wouldn’t hurt to include exercises to stretch the spine, thereby relieving the back. Stand with your heels together, toes apart, back straight. Place your hands down, cross your fingers and turn your hands over so that your palms are facing down. Without unclenching your fingers, raise your arms up. Now imagine that you are a plant that strives for the sun, and, swaying slightly, without lifting your heels, begin to reach up. Stretch as far as possible. Then slowly begin to lift your heels off the floor and stretch further. Having reached the limit, lower your heels one by one, while your arms continue to reach up. We do all this leisurely, slowly. Try it yourself and include this exercise in your activities with your child.
I'll tell you my proprietary secret. Tie a plastic bottle to the frame of your child's bicycle so that it is at knee level. Then, when pedaling, the bottle will prevent him from bringing his legs together. Simple and effective.
Pay attention to the shoes the child wears; often these are the ones that cause them to place their feet incorrectly.
If you have the opportunity, get your child interested in skateboarding or snowboarding. These sports will not give you a chance of clubfoot.
So you've made progress. Now take your child to a sports section or dance club. Any result needs to be consolidated.
Possible reasons
Often the disease in newborns is caused by mechanical reasons - oligohydramnios, incorrect position of the fetus during the mother's pregnancy. Due to increased pressure, the walls of the uterus press the legs closer to the fetus. Often the cause of clubfoot is neuromuscular abnormalities of fetal development:
- pathologies caused by vitamin deficiency;
- deficiency of nerve fibers;
- violations of the formation of muscles and ligaments in the first weeks of fetal life;
- toxicosis due to maternal drug use during pregnancy.
If one of the parents had a clubfoot in childhood, the child’s developmental deviations are caused by a hereditary factor. The problem of how to correct clubfoot has a genetic cause - tripling of a pair of chromosomes (Edwards syndrome), which results in clubfoot. If you do not think about the issue of correcting clubfoot, problems with the musculoskeletal system may arise in the future: due to improper support of the feet, with increasing loads, weight gain, wearing the wrong shoes, after injuries, or foot diseases. The causes of its occurrence do not have much influence on how to treat clubfoot in children; the main thing is to eliminate the pathology in time.
Signs and causes of clubfoot in newborns
Caused by anomalies in the formation of bone and soft tissues, the deformation of the child’s legs is diagnosed during an ultrasound examination by the expectant mother. Symptoms of the defect are curvature of the foot on the outer side with the sole turned upward and the toes turned inward, physiologically incorrect location of the bones of the joint.
Disorders in the formation of fetal muscles and ligaments develop in the first trimester of pregnancy (8-12 weeks). They are associated with genetic prerequisites - clubfoot of one of the parents and a number of external factors:
- a small volume of amniotic fluid in a pregnant woman, which creates mechanical pressure from the aqueous membrane, uterus and umbilical cord on the fetal legs, which is a common cause of clubfoot in newborns;
- drug use by the expectant mother;
- toxicosis during pregnancy;
- primary deficiency of nerve fibers affecting the formation of musculoskeletal tissues.
Diagnosis of the disease
An informative method of examination at the stage of intrauterine development for early detection of congenital clubfoot and treatment in the correct way is ultrasound examination of the fetus.
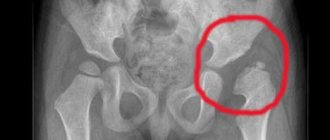
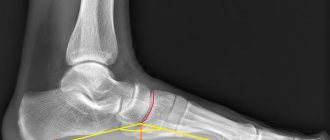
It is necessary to visit an orthopedic doctor after the birth of the child, and, if necessary, take an x-ray of the baby’s feet in functional positions. The information value of X-ray diagnostics increases with the possibility of considering its results over time. Depending on the mechanism and causes of the development of the defect, the forms of this disease are distinguished:
- typical , which develops at the stage of formation of organs and systems of the fetus, is characterized by a delay and disruption of the formation of all structures of the foot;
- secondary , developing as a result of pathological processes in the neuromuscular system;
- caused by arthrogryposis (severe damage to the joints and spinal cord);
- positional , considered as a malformation of muscle-ligamentous structures, without damage to bones and joints.
Diagnosis of the disease
How clubfoot in a child can be cured and how quickly is determined by timely diagnosis. Congenital pathology is detected:
- in the womb by ultrasound examination of the fetus;
- at the first medical examinations of the baby;
- when the baby is not yet walking, attentive parents themselves notice the abnormal development of the legs, turn to the doctor with the question of whether clubfoot can be corrected for a child under 2 months old;
- Acquired pathology in children over 1 year of age is diagnosed by observing the position of the legs when walking.
An effective method for diagnosing abnormalities in the development of the legs is palpation during an in-person medical examination. If a specialist has questions about the deformation of children’s feet, a referral for an x-ray is issued to confirm the diagnosis. It is important to immediately decide how to treat clubfoot in a child without triggering the course of the disease.
An effective method for diagnosing clubfoot in children occurs during an in-person examination during palpation. If a specialist has questions about foot deformities in a child and to confirm the diagnosis, the doctor will order an X-ray of the feet.
You can make an appointment with a specialist by phone: 8 (800) 555-84-21 on weekdays from 9.00 to 19.00 Moscow time Or through the form on the website Sign up for a free consultation
Signs of congenital and acquired forms of the disease
Making a preliminary diagnosis and starting to correct congenital clubfoot allows the presence of four symptoms that are noticeable during an ultrasound of the expectant mother already at the 16th week of fetal development:
- Dropping of the outer edge of the foot while raising the inner edge.
- The backs of the clubfooted feet “look” at each other.
- Bending the plantar part of the leg with raising the heel.
- Deviation of fingers inward.
A number of additional signs allow you to diagnose the defect after birth and decide how to begin treating clubfoot in a child. This is a smaller size of the foot relative to a healthy leg with unilateral pathology, displacement of the heel along the axis of the leg, limited mobility of the ankle joint. Serious concern about how to cure clubfoot in a two-year-old child or older is necessary if he walks, “raking” his legs like a bear, puts them not completely (on tiptoes), with his toes inward, leaving characteristic marks in the sand.
If you make a mistake, please do some push-ups!
You explain to your child that you will help him ensure that the exercises are performed correctly. As soon as the child makes a mistake, you clap your hands and he must, for example, do five push-ups. But, if he himself noticed the mistake and slammed, the push-ups are cancelled. In this simple way you can wean your child from slurping, squelching, saying the word “damn”...
The technique is very effective, just don’t give up. A bargain is a bargain. Explain to your child that push-ups are not a punishment, but additional exercises that will help him become stronger, but the child does them only for inattention.
How to effectively treat clubfoot in children?
At an early stage of the disease, doctors answer in the affirmative the question of whether it is possible to permanently correct clubfoot in a 2-month-old child.
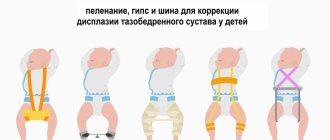
Even conservative therapy with fixation of the baby’s feet, massage, and physical therapy, starting from the first week of birth, will help. For a baby under one year old, this option is best suited. For children under 2 years of age, it is also effective when using orthopedic shoes and splints worn at night. The results of clubfoot treatment in older children from the age of 8 will be strengthened by sports activities, swimming and dancing. If conservative methods do not help, surgery is needed. When advising on how to cure clubfoot in a child, eliminating consequences and relapses, most orthopedists recommend the Ponseti method. Consisting of staged plaster casting from the toes to the upper third of the thigh, it helps correct the position of the foot in several planes. 6-7 changes of plaster casts will be required depending on the complexity of the case. To completely correct the defect, children under 1 year of age undergo a minor outpatient operation under local anesthesia. The doctor cuts the Achilles tendon to allow more dorsiflexion and free movement of the foot.
Attention! The “Towards Life” project provides the opportunity for free treatment!
The importance of treatment, negative consequences of advanced disease
Timely treatment of clubfoot in children will correct the situation. Knowing how to effectively treat clubfoot in children, experienced orthopedists will return the child to a full life. You will have to walk around for a short time in orthopedic shoes - braces, gradually reducing the duration of wearing. After the main part of the treatment, from the first months from birth to the age of two, the baby is put on them only at night. The Ponseti method almost does not cause relapses, the muscles retain flexibility and strength, and the operation is low-traumatic. The wound from it heals quickly without scars, skin tightening, or discomfort when wearing shoes, which cannot be said about surgical treatment of advanced pathology.
It is advisable to correct congenital clubfoot in infants in the first months after birth, while the tendons and muscles are most extensible. When the child begins to walk, the pathology becomes more complicated, the standard regulations of the Ponseti method may not be enough, and additional surgical intervention for clubfoot with tendon transplantation will be required. An advanced disease threatens:
- muscle atrophy;
- dysfunction of the joints;
- subluxation of bones;
- scoliosis;
- loss of the ability to walk normally;
- disability.
Clubfoot: Exercise therapy, conservative or surgical?
There are 4 degrees of clubfoot:
- Mild clubfoot: exercise therapy, massage, orthopedic devices are effective, since deviations are minimal.
- Medium: painful sensations occur, therapy is long and complex.
- Severe: curvature of the feet, the addition of arthritis and arthrosis requiring surgical intervention.
- Extremely severe is characterized by pronounced transformation of the affected area, involvement of the spine; manipulations in this situation are ineffective.
Project “Towards Life” for children's health
Having discovered abnormal development of the baby’s feet, parents are wondering how to treat clubfoot in a growing child to quickly correct the defect without recurrence of the disease. The answer is provided by the unique project “Towards Life”, specially created to help children in need. The qualifications, experience of the doctors involved, and treatment with progressive methods guarantee the success of the therapy. The children we helped grow up healthy, not inferior in development to their peers.
Treatment for clubfoot in all children within the project is free. Thanks to the financial support of the Rusfond charitable foundation, children receive highly qualified medical care without paying the cost of plastering, surgery, or materials. Nonresident patients arriving in Yaroslavl for long-term treatment are provided with housing for the period of their stay. You can find out how to cure clubfoot in a child for free under the Towards Life project by email or phone. Calls from Russia are free.
For all questions, you can consult by phone: 8 (800) 555-84-21 on weekdays from 9.00 to 19.00 Moscow time
Shoes for club feet. Braces from
Requirements for photographs provided for online consultation on clubfoot
Our patients
Anastasia
| BEFORE AFTER | Age: 8 months Diagnosis: congenital bilateral severe atypical clubfoot Attending doctor: Vavilov Maxim Alexandrovich |
Miroslav
| BEFORE AFTER | Age: 5 weeks Diagnosis: congenital bilateral severe clubfoot Attending doctor: Vavilov Maxim Alexandrovich |
Alexander
| BEFORE AFTER | Age: 1 year 4 months Diagnosis: congenital right-sided severe clubfoot Attending doctor: Vavilov Maxim Alexandrovich |
Sofia
| BEFORE AFTER | Age: 3 months Diagnosis: bilateral clubfoot Attending doctor: Vavilov Maxim Alexandrovich |
| BEFORE AFTER | Age: 3 months Diagnosis: bilateral clubfoot Attending doctor: Vavilov Maxim Alexandrovich |
Maria
| BEFORE AFTER | Age: 3.5 years Diagnosis: congenital bilateral clubfoot Attending doctor: Vavilov Maxim Alexandrovich |