Pain when climbing stairs or a strange crunch in the knees is a reason to think about it. Perhaps this is simply a consequence of overwork, or perhaps irreversible changes have already begun in the joints. How to identify the first signs of wear and tear on the knee joint and what measures to take to prevent it from getting worse?
A worn-out knee joint is an indication for endoprosthetics
What is the composition of cartilage tissue?
Cartilage is a thin, elastic tissue. There are two types of cartilage in the knee joints: fibrous (meniscus) and hyaline.
The fiber fabric is very durable and can withstand pressure. And hyaline is more elastic and covers the surface along which the joints move. Unfortunately, hyaline tissue, which is of a higher quality in composition, is poorly restored. New formations are mostly fibrous tissue of poor quality. Cartilage tissue primarily performs a connective function; the main purpose of such tissue is to reduce friction at the junctions of bones. The entire inner surface of the joint is covered with synovial fluid, which acts as a lubricant. Just as engine oil is important for a car, synovial fluid is important for human joints.
Even minimal damage to the knee sometimes contributes to the emergence and exacerbation of the disease, which can develop in women and men. However, the latter often have problems with the spine, and women are susceptible to diseases of the peripheral joints.
The cartilage surrounding the knee joint plays a significant role in human movement.
Cartilage tissue is an elastic, smooth, durable pad, its main functions are:
- load distribution while walking;
- allowing free sliding of bones rubbing against each other.
Abrasion of cartilage tissue. The joints are worn out, what should I do?
What is meant by the statement “the joints wear out”? In order for us to walk, run and jump without feeling pain, the cartilage layer in the joints must be absolutely healthy, because it is responsible for the function of mutual sliding in the joints. The cartilage layer completely covers the articular surfaces of the bones and prevents them from touching each other. For a number of reasons, cartilage can break down and wear away. This process, not accompanied by inflammation, is called arthrosis. The most common complaints are “The cartilage in the knee joint has worn away” and “The hip joint has worn away”, and now we will explain why.
Why do joints wear out?
Throughout life, the legs bear a heavy load; when running or jumping, the joints take on a weight two to three times greater than the body weight of the “owner”. Everything has a limit, so by the age of 60, the cartilage in the joints becomes thinner and wears out. For some, arthrosis begins earlier, for example, women are more susceptible to the disease due to hormonal changes, athletes - due to intense exercise, and people who lead an unhealthy lifestyle “kill” their joints with junk food, alcohol or drugs.
What symptoms indicate that the cartilage has worn away?
- Joint pain bothers me when walking and becomes more intense over time.
- If arthrosis is not treated, it progresses, and the pain sometimes bothers you even at rest.
- It feels like the bones are rubbing against each other in the joint.
- When straightening, a crunching sound is heard.
- Swelling of the tissues over the joint.
Be careful! If the skin over the joint is hot or the body temperature is elevated, the reason is not that the knee joints are worn out, this is not arthrosis. Most likely, you are dealing with gout, infectious arthritis, or rheumatoid arthritis.
What to do if the knee joint is worn out or the joint in the hip is worn out?
Unfortunately, without resorting to surgery, it will not be possible to completely restore the cartilage surface, especially if the problem is faced by an elderly person, and not a young athlete, whose body is able to fight many diseases on its own, and even more so with the help of medications. But, despite this, it is necessary to treat arthrosis at any age: the disease does not go away on its own, but only develops, and moving around will become more and more difficult every day. Conservative therapy will help relieve pain, improve quality of life and slow down the destruction of the cartilage layer. You only need to contact an experienced orthopedic traumatologist: he will prescribe treatment aimed at improving mobility in the joint and completely eliminating pain.
How to treat arthrosis conservatively?
In order to improve joint mobility, light physical activity and procedures are recommended:
- Swimming
- Massage
- Physiotherapeutic procedures
Walking on level ground
But the following are prohibited:
- Run
- Jumping
- Weight lifting
- Walking up the stairs
- Walking on uneven terrain
- Staying in a static position for a long time
Drug treatment
- Chondroprotectors. They are necessary to prevent the process of cartilage destruction, as well as for its restoration.
- In rare cases, corticosteroid injections directly into the joint cavity are prescribed. The pain disappears for several months, but then returns with renewed vigor, so the method is not used often.
- Diet for arthrosis.
- Special orthopedic shoes that reduce stress on joints.
The doctor prescribes a course of injections or tablets that have an analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect.
Surgery for arthrosis
- The most popular is endoprosthetics of the affected joint. This is the replacement of damaged areas with a prosthesis that looks like a healthy joint.
- Arthroscopic joint debridement. This operation is effective only at the initial stage of arthrosis. Using an arthroscope, the doctor makes several punctures in the joint and cleans its surfaces, removing the affected areas. Walking becomes painless and smooth, but the results will last for a maximum of two years, since the disease cannot be completely cured, only stopped, and then a more complex operation has to be performed.
Periarticular osteotomy. The intervention is complex - both the operation and rehabilitation after it take a lot of time. But after periarticular osteotomy, the patient forgets about arthrosis for at least five years! The operation is performed under anesthesia. The surgeon saws the bones around the affected joint and fixes them at a different angle so that the joints do not touch the worn areas.
Patients who decide to undergo surgery and undergo treatment remain satisfied with their improved quality of life.
Causes of arthrosis in diabetics
- Frequent heavy loads on the knee joints (obesity, too long walking) create conditions for wear of the hyaline (knee) cartilage.
- Low physical activity reduces blood flow and creates complications.
- Frequent microtraumas (work in security or loading) require replenishment, healing and an increased amount of nutrients and collagen substances.
- Arthritis is inflammation of the joints, often causing their destruction - arthrosis.
- Age-related disorders of collagen synthesis. This is a protein that accounts for 25% of the total protein composition of the human body. Collagen consists of any connective tissue - cartilage, ligaments. As a person ages, collagen synthesis weakens, which provokes arthrosis, arthritis, dislocations, and fractures.
The main causes of arthrosis of the knee joint are metabolic disorders and collagen synthesis, slow blood circulation in the kneecap. It is these factors that disrupt the nutrition of cartilage tissue and do not allow hyaline cartilage to recover. All other factors only contribute to the rapid manifestation of the disease.
Articular tissues are destroyed under the influence of certain factors:
- excessive stress on the joints due to professional activities, for example, among professional athletes;
- Excess body weight is a colossal burden. As a rule, people with large body weight have impaired metabolism. These two factors provoke the destruction of the knee joint;
- hormonal imbalance and metabolic disorders in the body. In this case, biochemical changes occur in the cartilage;
- frequent bone fractures, dislocations and bruises often become a stimulus for the development of osteoarthritis even in the youngest patients;
- inflammation as a result of infection;
- pathological structure of the lower extremities or spine of a congenital nature;
- genetic predisposition. Although there is no such gene, children often inherit brittle bones and weak ligaments from their parents, as well as various disorders in the circulatory system;
- age-related changes in the body.
What to do if the joint is already worn out
Unfortunately, a knee joint that is too worn out cannot be restored and requires surgical endoprosthetics with a difficult recovery period. It lasts more than one month and does not always end as we would like - the limitation of mobility remains with the patient forever. That is why this approach is not acceptable for young and middle-aged people who want to lead an active lifestyle.
If your knee joint no longer functions as well as before, you have noticed characteristic signs of wear, but are not ready to take drastic measures, you can always find a compromise solution. The main thing is not to waste time and get diagnosed as early as possible, and then begin treatment.
In the early and moderate stages of osteoarthritis, intra-articular injections of the synovial fluid substitute Noltrex help well. The liquid endoprosthesis is evenly distributed over the surfaces of the cartilage, separates them and stops friction. It will not be possible to completely restore a worn-out joint using this method, but for some time it is quite possible to return to a normal lifestyle, without pain and with adequate physical activity.
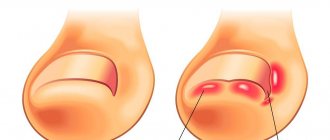
Chondromalacia patella
Chondromalacia is the process of destruction of the cartilage of the posterior surface of the patella, which is accompanied by severe pain. Chondromalacia can develop after dislocation, trauma, or instability of the patella.
Affected cartilage and patella
Symptoms
The main symptom of chondromalacia patella is a deep, dull pain that gets worse with moving your legs or sitting for a long time with your knees bent. From time to time, especially after intense exercise, effusion in the joint is possible. There are also clicks and crepitations. The pain becomes unbearable after physical activity, and after rest it subsides.
Of course, it is quite difficult to determine a disease based on symptoms; it is better to conduct a comprehensive study of the body and, based on it, the doctor will be able to select the correct treatment.
Types of Chondromalacia
There are 4 types of destructive changes in the patellas.
- Type I is characterized by changes in the central part of the patella, often due to subluxation or tilting.
- In type II, changes begin in the area of the lateral facet. The cause is also subluxation or excessive tilt of the patella.
- Type III changes are located on the medial facet of the patella. There are many reasons for the formation, including rough reduction of a strong dislocation, improper distribution of pressure due to subluxation or tilting of the patella, and reconstructive operations with moving the tibial tuberosity back.
- Type IV changes begin on the proximal part of the patella and extend to 80% of the area. Type IV most often occurs as a result of direct trauma to the anterior flexed joint.
When pathological processes occur in the knee, the cartilage tissue thins and becomes rough, and sometimes it cracks and dries out. In this case, easy sliding is impossible, but on the contrary, the bones begin to rub and cling to each other.
If treatment with medications and folk remedies was not carried out in a timely manner, then degenerative processes in the knee develop even more actively. Under conditions of reduced depreciation, the bones are flattened, as a result of which the articular area increases. Osteophytes may also appear - growths of bones that look like growths.
Due to motor deficiency, the structure of the patella joint atrophies, and the articular substance acquires a viscous and thick consistency. Thus, the cartilage stops receiving the necessary nutrients, which causes a person’s general health to deteriorate.
Due to the fact that the cartilage becomes thinner, the distance between the connecting bones is significantly reduced. While walking, strong friction occurs in the patellar joint, causing the destruction to progress, and the person is haunted by a painful syndrome and a feeling of stiffness. These symptoms appear in the morning, during rest and exercise.
But the strongest signs appear when climbing stairs, as a result of which the patient begins to limp. And in the absence of treatment with medications and folk remedies, a person loses the ability to move independently, so he uses crutches or a cane.
Diagnostics
First of all, the doctor must conduct a survey of the patient, clarifying complaints, symptoms, nature and intensity of pain. An examination of the functions of the hip joint is also required. It includes assessment of the severity of pain, the ability of the limb to serve as a support, range of motion, muscle condition, and quality of gait.
The patient is examined in both horizontal and vertical positions. In this case, when lying down, it is especially important to take into account the tilt of the pelvis, rotational deformation, and length of the legs. The Trendelenburg test is performed to evaluate the muscles of the hip joint.
The most effective way to assess joint pathologies is x-ray examination. Here you will see the presence of osteophytes, narrowing of the joint space, and deformation processes.
It is equally important to conduct a general blood test and its biochemistry, as well as a test for rheumatoid factor.
MRI will clarify all previous studies, but will also evaluate cartilage, ligaments and muscles.
Diagnostics in our clinic
X-ray data are the basis of diagnosis. They occur before the onset of pain and clinical manifestations. They reveal themselves:
- reduction of joint space;
- change in the shape of the joint surface;
- instability of the articular joint;
- bone growth at the edges and increased bone density (osteosclerosis).
As the disease progresses, the joint space takes on a wedge shape, and bumps, spines and other characteristic irregularities appear on the edges of the bones.
In addition, our clinic specialists will refer you for additional tests:
- Blood test for inflammation.
- Study of the fluid surrounding the joint.
- Arthroscopy.
Conservative treatment
Conservative treatment is based on the following procedures: rest, taking anti-inflammatory drugs, changing the training regimen for athletes. This is followed by a rehabilitation program that includes stretching the muscles and ligaments that hold the patella, and the muscles of the hamstring. It is important to do exercises to build quadriceps strength. A person also feels more comfortable with an elastic bandage on the knee joint.
Use chondroprotectors to protect your connective tissues
The most effective drugs are chondroprotectors. They contain substances such as chondroitin and glucosamine.
- Chondroitin sulfate is a polysaccharide that is also present in cartilage. This drug allows you to increase the compressive and tensile strength of cartilage tissue. After taking chondroitin, patients experience pain in the knee, the thinned tissue becomes stronger, and the person can live their normal life.
- Glucosamine restores damaged tissue and protects against mechanical damage.
These medications are recommended for use as prophylaxis. They prevent abrasion of bone tissue. It is very important to start taking this type of medication at the onset of the disease. Chondroitin and glucosamine are absolutely safe drugs that have no side effects. But if the destruction has already affected the entire tissue, chondroprotectors will not help.
For most patients in the early stages, these measures bring serious relief, but if the pain continues, this means that the abrasion has not stopped and it is necessary to proceed to surgery.
Traditional methods of treating knee joints
Many people complain of pain in the knee area. This may indicate the beginning of the development of various diseases. The most common pathology affecting the knee joints is arthrosis, which is popularly called salt deposition.
Untreated arthrosis leads to complete destruction of cartilage and exposure of bone, as well as the formation of osteophytes and complete deformation of the joint. This disease can turn a person into a disabled person. Let's try to figure out what kind of disease this is, its symptoms and methods of treatment.
- What is arthrosis of the knee joint
- Causes of the disease
- Symptoms of the disease
- Principles of treatment Use of non-steroidal drugs
- Drugs for cartilage restoration
- Use of creams, ointments and compresses
- Application of injections
The tibia and femur in the human knee joint are covered with articular cartilage. There is also a second type of cartilage tissue, which forms menisci that act as shock absorbers or layers.
Types of Chondromalacia
The destroyed tissue of the knee joint brings quite big problems into a person’s life: constant pain and decreased motor activity. Nowadays, modern methods of surgical restoration of cartilage tissue are used in medicine:
- tunneling method;
- arthroplasty method;
- microfracture method;
- replacement of defects with chondrocytes.
Tunneling
Tunnelization is a mild surgical intervention during which channels are formed in the bone tissue adjacent to the cartilage. These actions make it possible to mechanically remove increased intraosseous pressure and normalize microcirculation, which provides tissues with the necessary amount of oxygen.
After the procedure, discomfort and pain disappear. The leg functions almost normally and within a day after the operation you can move around calmly.
A contraindication for this procedure is an inflammatory infectious process in the joint itself or its structures.
Arthroplasty
Arthroplasty is endoprosthetics. This is a fairly effective and efficient method of restoring cartilage tissue, which is in quite high demand. During the procedure, all affected areas are removed and replaced with artificial prostheses.
Artificial cartilage works no worse than natural cartilage
After the surgical procedure, the patient has complete pain relief and an improved quality of life for many years.
Contraindications include active and systemic infection, neurological pathologies affecting the legs and impaired peripheral circulation.
The goal of this method is to stimulate the formation of cartilage tissue in a natural way. Microfracture is used when large-scale destruction of structures occurs, that is, the destruction reaches the bones. In the damaged area, the surgeon uses special instruments to make small holes so that multifunctional cells can escape and become the basis for replacement cartilage.
This operation is prescribed for very large tissue lesions. This technique was invented not so long ago, but it has proven to be quite effective and efficient. The essence of the method is this: samples of healthy cartilage tissue are taken from the joint using a special arthroscopy method. Next, healthy cells are grown in a special laboratory, which are placed on the damaged areas using repeated arthroscopy and the leg is restored to normal.
This operation cannot be performed on people over 50 years of age and children under 16 years of age. There are also contraindications for chronic, destructive changes in the structures of the knee joint.
Only a doctor can choose a technique after a comprehensive diagnosis of the body and determination of the degree and cause of cartilage destruction.
The cartilage tissue surrounding the knee joint is designed in such a way that damage can occur even with minimal stress if it is not applied correctly. However, patellar injury will not occur if the knee joint is enclosed in a reliable corset of ligaments that fix the bone in the correct position.
Regeneration of cartilage tissue located next to the knee joint can only occur if the required amount of necessary substances enters the cartilage. If there is a deficiency of synovial fluid, which acts as a lubricant, the nearby knee joints will be destroyed.
Almost no blood flows into the patella area, because articular cartilage does not have capillaries. Therefore, if the patient’s diet is not balanced, then his recovery is impossible. If medical recommendations are not followed, the cartilage takes the vitamins and microelements it needs from the synovial substance.
In order for the soft tissues of the knee joint to recover as quickly as possible, it is necessary to maintain a high level of the main constituent elements of cartilage tissue - chondrocytes. This is only possible if the nutrition of the synovial fluid is complete.
But, if the knee is constantly motionless, then the nutritional components will not get into the soft tissues.
The right diet
In order for the cartilage in the knee to recover, the patient needs proper nutrition. It is advisable to consume only fresh products of natural origin. But this does not mean that only plant products should be present in the diet.
The first thing to exclude is:
- fast food products;
- fatty and fried foods;
- carbonated drinks.
Poor nutrition helps reduce acidity and stops the production of growth hormones. All healthy foods should be consumed in small portions and often (about six times a day).
Sports activities
The content of growth hormones in the bloodstream is related to the intensity of physical activity. Consequently, intense exercise restores cartilage tissue in the knee joint.
However, after training, a person should not feel very tired, his condition should be cheerful. And if the knee joint is damaged, then the intensity of physical activity should be discussed with a trainer and doctor, who will tell you how and what exercises can and should be done. But it should be remembered that training always begins with stretching and warming up the whole body.
There are many diseases that affect the knee joints. Anyone who faces this problem knows that in most cases long-term treatment is required. The use of folk remedies in addition to the main therapy helps to avoid taking a large number of medications that cause side effects. In mild cases, such methods can provide relief without traditional drug intervention.
At an appointment with a rheumatologist
The rheumatologist at our clinic determines the method and course of treatment taking into account the following indicators:
- the degree of development of the disease and involvement of joints in the process;
- how long the disease has been progressing;
- is there any pain syndrome?
Basic treatment requires the following measures:
- Decreased activity in the joint area.
- Weight loss in the presence of obesity.
- Administration of metabolites in courses intramuscularly.
- Cartilage restoration therapy (intramuscular injections of stimulants in courses).
- As an additional treatment, anti-inflammatory therapy is used and quinol drugs are prescribed.
- If inflammation is present, a course of hormonal therapy is sometimes prescribed.
- It is necessary to undergo a course of massages, a set of physiotherapeutic measures, and sanatorium-resort treatment.
Treatment of advanced cases is carried out through a surgical operation such as joint replacement.
For the treatment of polyarthritis of the joints, arthritis, arthrosis, you can contact our clinic.
What causes wear and tear on the knee joint?
Wear and tear of the knee joint develops due to arthrosis. What factors provoke this disease? In many cases, heredity and genetic predisposition play a decisive role.
Obesity and excess weight can also lead to arthrosis, because extra pounds create an unbearable load on our knee joint. But it also happens that the causes of arthrosis remain unclear.
It is likely that the disease can be triggered by changes occurring in chondrocytes - the cells of the cartilage tissue of the knee joint. Changes in the subchondral bone also cause the cartilage to lose elasticity and thin, making the joint more vulnerable to stress.
Another reason for the development of arthrosis is the natural aging of the human body, during which degenerative changes occur in cartilage tissue. We should not forget about such important factors as a history of injuries to the knee joint and congenital pathologies of its development.
In these cases, the disease is known under the name secondary arthrosis of the knee joint. It develops as a result of injuries and damage to the meniscus, fractures, and joint damage caused by excessive stress.
The latter problem is often faced by athletes, and also, as we said earlier, by people who are overweight. What signs indicate wear and tear on the knee joint?
- Pain and lumbago that occurs after standing for a long time.
- Pain that occurs when walking on an uneven surface, on stones or a field.
- Shooting when climbing stairs. They can be so strong that they can even cause a person to fall.
- Pain that occurs when standing up after prolonged sitting.
- Crunching in the knees.
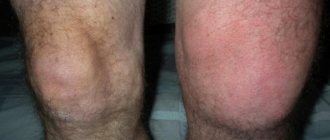
- In some cases, you may be worried about inflammation of the knee joint. The main thing is to be able to distinguish such inflammation from ordinary fluid retention. When inflamed, the knee area becomes swollen and red. The inflammation may affect one or both knees, but the legs and feet do not become swollen.
- As the disease progresses, there may even be a slight deformation of the knee joint, a change in the silhouette of the knee as the joint is pulled inward. Why is this happening? This knee deformity is a consequence of deformation of the knee joint itself.
- As a result of changes caused by arthrosis, one can observe the appearance of osteophytes - pathological growths on the surface of bone tissue.
Secrets to maintaining knee health
If you suspect wear and tear on your knee joint, consider making lifestyle changes to avoid serious and long-term treatment for osteoarthritis.
- Avoid heavy mechanical stress on the knee joint, such as long walks. If you have to travel a long distance, take rest breaks.
- Maintain an optimal weight. It is no coincidence that people with arthrosis are recommended to lose weight, since this puts extra stress on the joints.
- The key to healthy joints is a strong immune system, and you can support it with calcium, phosphorus and magnesium. Most of them are found in fresh fruits and vegetables, as well as nuts.
- Add legumes, cod, gelatin, eggs and brewer's yeast to your diet. They promote the restoration of cartilage tissue.
- Products containing vitamin C are very beneficial for joint health - rosehip infusion, lemon, orange, kiwi.
- Swimming is a safe and beneficial sport for the musculoskeletal system.
Sometimes orthopedists recommend additional magnesium tablets.
Vitamin C provides invaluable health benefits when taken in the correct dosage: