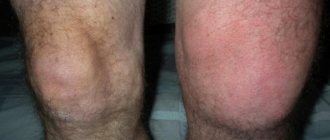
Knee pain may occur during movement (walking or bending). When the load on the knee is reduced, in many cases the pain goes away. But after some time, the pain usually occurs again. Quite often, people get used to the fact that they have painful knees, trying to limit movement and load, but this is the wrong way. Many knee conditions develop gradually over years, and if left untreated, symptoms will worsen over time, robbing a person of their quality of life and freedom of movement.
The most common causes of knee pain in women are:
- arthritis - inflammation of the joint, an independent disease or a complication of other pathologies;
- meniscopathy – damage to the meniscus, which is accompanied by acute pain during movement and, if left untreated, quickly turns into osteoarthritis;
- arthrosis – degenerative-dystrophic processes in the joints, which often result from age-related processes in the body;
- bursitis - inflammation of the joint capsule with swelling in the affected area and limited mobility;
- synovitis - inflammation of the synovial membrane, an independent disease or a complication of advanced bursitis;
- periarthritis - inflammation of the tendon, which is indicated by discomfort on the inside of the knee;
- chondromatosis - a pathology of cartilage, which is accompanied by immobilization of the joint due to severe pain;
- chondropathy of the patella - complete replacement of cartilage tissue with connective tissue due to injury;
- osteochondritis dissecans of the patella - peeling of the affected area of cartilage tissue from the bone;
- fibromyalgia – rheumatic damage to muscle tissue;
- vascular pain.
Sometimes the knee bothers you with coxarthrosis - in this case the pain is of a reflected nature. Only a specialist can determine the root cause of pain.
Periarthritis is typical for women over 40 years of age who are overweight
Surgical intervention
If pain occurs when bending the knee, you must first find out the cause of this symptom. Typically, surgery is prescribed only for serious injuries or damage, as well as if the disease is at an advanced stage of development. In this case, the pain is constant, the flexion function of the knee is impaired, and the joint is deformed. All this is an obstacle to the patient’s normal movement.
Doctors often use two surgical treatment techniques:
- The first technique is organ-preserving. Its goal is to save more of the natural tissue of the knee joint. The specialist performs the entire procedure using a device such as an arthroscope.
- The second type of surgical treatment, which is often used for complete destruction of articular and cartilage tissues, is endoprosthetics. During this procedure, the joint is replaced with an artificial implant. After complete recovery, the person regains the ability to move freely.
How to independently determine the cause of pain
Each disease has its own clinical manifestations and pain of a certain nature.
- With gonarthrosis, there is a constant dull pain during movements, the discomfort intensifies after waking up in the morning, accompanied by a crunching sound.
- With arthritis, swelling is noticeable and body temperature rises.
- With vein thrombosis, women complain of constant or periodic aching pain at night.
- Intense sharp pain will indicate damage to the meniscus.
- Rheumatism and rheumatoid arthritis cause symmetrical severe pain in both knees.
Osteoarthritis of the knee joint is well “camouflaged”: it does not cause swelling or fever
Wearing orthoses
With the help of orthopedic knee pads, you can support the muscular system and prevent the thinning of cartilaginous structures. Such products have a compression effect on the joint and soft tissues around it.
Orthoses are a good way to prevent the development of knee joint diseases; they reduce the load. There are different types of knee pads. You need to choose a product on the recommendation of a doctor. The choice is determined by the presence of a specific pathological process and the degree of its development. Orthoses differ in materials and degrees of rigidity. Such products can be elastic.
In production, a special technology of weaving compression fibers is used. With the help of a knee brace, the joint will be supported with high quality. The orthosis will protect against excessive loads. The device will help get rid of pain and stop the progression of existing pathological processes.
To prevent the occurrence of various diseases of the knee joint and unpleasant symptoms, it is necessary to adhere to a healthy lifestyle; eat right, give up bad habits and exercise.
How to get rid of knee pain
If alarming symptoms appear, go for a consultation with an orthopedist-traumatologist. You may need the help of a phlebologist or rheumatologist. It is especially important to react quickly to unexpected sharp pain, for example, after an injury.
To diagnose the cause, the doctor will order the following tests:
- laboratory blood tests - general and biochemical;
- joint puncture;
- arthroscopy;
- Ultrasound of joints and blood vessels;
- radiograph;
- MRI or CT – if necessary;
- densitometry, etc.
Use of non-traditional methods of treatment
To reduce the severity of pain when bending or straightening the knee, you can use traditional medicine. It is important to remember that such methods are used only as part of complex therapy; they are not an alternative to medications or physiotherapeutic procedures.
Traditional methods are best used if the pathological processes are chronic. It is not recommended to use them when the disease is in the acute stage. Otherwise, the inflammatory process may worsen.
The most effective means are:
- Pharmaceutical clay. This is an inexpensive but effective remedy with which you can improve blood microcirculation, get rid of congestion in the joint and prolong the period of remission. Pharmaceutical clay should be diluted with a small amount of water. This should result in a thick paste. It is applied to the damaged joint and covered with cling film on top. This compress is left until the morning. Duration of treatment; 10 days.
- If severe pain occurs, a small piece of salted pork lard can help. It needs to be bandaged around the knee. After a few hours, the unpleasant symptoms will decrease. This compress can be left until the morning.
- Prepare a tincture of dandelion flowers, lilac inflorescences and dry comfrey. All plants are taken in equal proportions. They need to be filled with vodka. Then you need to put the tincture in a dry, dark place, it should infuse for 2 weeks. After this, the tincture must be strained. The product should be used to rub the knee joint. Plants help restore mobility, improve microcirculation of blood and lymph, and also relieve swelling.
- Make a tincture of white acacia. You need to take a glass of dried acacia flowers, pour 100 grams of vodka or alcohol into them. The product needs to be moved to a dry, dark room, it should sit for two weeks. Next, you need to strain the tincture and use it as a rub.
- Horse chestnut tincture. You need to take half a glass of horse chestnut and pour a glass of vodka. The product should be infused for 10 days in a dark room. Next, you need to strain the tincture and use it morning and evening to rub your knee.
- To reduce the severity of pain when bending and straightening the knee, you can use ice. It must first be wrapped in a clean, dry cloth or towel to prevent cold burns. Ice should be applied to the sore joint in the morning and evening for 15 minutes. Using this procedure, you can reduce the severity of pain, get rid of swelling and prevent the development of congestion.
Treatment tactics
The earlier the disease is detected, the higher the likelihood of being cured using conservative methods. Unfortunately, this does not apply to the treatment of osteoarthritis, a disease that cannot be completely cured. However, in the early stages it is much easier to control it and stop its progression.
For other pathologies, a complex of medications, physiotherapy, exercise therapy, and massage are used. In advanced cases, surgical joint replacement with long-term rehabilitation is recommended. After such an operation it is no longer possible to fully recover; you will have to introduce a number of restrictions into your daily routine, so it is better not to bring your joints to this state.
Some experts claim that you can cure knee pain without pills or injections in just 10 minutes. Is this so and what is suggested to be used - watch this video:
Physiotherapeutic procedures
Therapy for any joint disease must be comprehensive. Physiotherapeutic procedures can reduce the need to use medications. In this case, the process of restoration of motor function is reduced.
Among the effective physiotherapeutic procedures are:
- ultrasound;
- infrared irradiation;
- magnetic therapy;
- mud therapy;
- electrophoresis;
- phonophoresis;
- laser therapy;
- paraffin therapy;
- medicinal baths;
- UHF;
- microcurrents.
Physiotherapeutic treatment is required when the exacerbation of the underlying disease subsides. Such procedures should only be prescribed by a doctor, taking into account the indications.
Complex therapy for joint diseases may include the following methods:
- taking anti-inflammatory drugs and chondroprotectors;
- injections into the joint of liquid endoprostheses - synovial fluid substitutes, for example, Fermatron, Sinokrom or Noltrex;
- physiotherapy - UHF, electrophoresis, laser, magnetic therapy (eliminate swelling, stop the inflammatory process, improve blood circulation);
- physical therapy – normalizes blood flow, strengthens the muscle corset;
- therapeutic diet - eating plant foods, fish and seafood to restore articular cartilage.
What is indicated for arthritis is prohibited for arthrosis: do not self-medicate
To keep your joints healthy, you need to take care of them from a young age. Lifestyle matters – diet, exercise. Excess weight has a detrimental effect on joint health, so this problem must be solved first. It is equally important to wear comfortable shoes and protect yourself from injury. If, despite your efforts, you notice pain in your knee, do not panic, but go for a consultation with a specialist as soon as possible.
Physiotherapy
Thanks to regular exercise therapy, good results can be achieved. Such exercises improve joint mobility and stop the development of the pathological process. Training partially helps restore the functionality of the knee joint. After training, it will be easier to bend and unbend it.
Physical therapy should only be prescribed by a doctor. Exercises can be performed when the inflammatory process has stopped and the pain has subsided. All physical therapy movements must be performed smoothly, avoiding the development of painful sensations. Main; perform the exercises systematically, daily.
Stages of inflammation of the knee joint
Any inflammatory process has 3 stages:
- alteration - actual damage;
- exudation - the formation of edema in tissues;
- proliferation - cell multiplication and restoration of affected tissues.
In the case of the knee, this process has its own peculiarity. Cartilage tissue grows very slowly, even if periarticular metabolism proceeds normally. In the case of inflammation, the destroyed area of cartilage in the knee joint may recover only partially or (in old age) not recover at all.
Therefore, it is also worth highlighting 3 stages of the inflammatory process in the knee joint:
Stage 1
: mild pain, stiffness of movement, in the morning you need to “disperse”, patients feel that their joints are stiff from an uncomfortable sleeping position.
Stage 2
: swelling appears, pain intensifies, especially after physical exertion, the temperature of the skin over the joint rises.
Stage 3
: joint mobility is severely limited, patients suffer from pain both during movement and at rest, performing everyday tasks without taking strong painkillers is impossible.
Inflammation in the knee joint can be either acute (from 3 days to 3 weeks) or chronic (over 3 weeks). Both of these conditions require immediate treatment and elimination of the causes.
Acute inflammation in the knee makes itself felt by pain (sometimes mild - pulling or bursting, and sometimes sharp, shooting), convulsive muscle twitching, swelling, redness of the skin over the joint, and a local increase in temperature. Often the diseased joint becomes difficult to bend or straighten completely. It is difficult for patients to stand for a long time, there is a feeling of stiffness or a desire to take care of the knee.
Myth 3. Destroyed cartilage can be restored with medications.
Today, many drugs are advertised that supposedly restore cartilage. They contain cartilage components chondroitin and glucosamine. However, their action is not enough to compensate for the daily loss of cartilage cells. It turns out that for this purpose you need to take chondroprotectors for life and in huge doses. Specialists from the American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons emphasize the lack of evidence of their effectiveness. Although there may be exceptions.
The thickness of healthy cartilage is only a few millimeters
Myth 8. If there is pain under the knee, it is a Baker's cyst.
Many people make this diagnosis for themselves when they experience pain under the knee. Let's look at what happens in the case of a cyst. At the back of the knee are muscle tendons covered with a thin layer of lubricant. Tendons are located in channels in which they slide during movements. Sometimes a channel forms between the joint and the sheath, and fluid flows out and swells the sheath. A bag with a viscous fluid is formed - a cyst.
This pathology occurs in people of any age, even small children. If it is small, you can do without treatment; large cysts are removed. The formation will put pressure on the nerves and blood vessels and may burst. The cyst has nothing to do with arthrosis.
Most often, pain under the knee occurs with osteoarthritis of the knee or osteochondrosis of the spine. The cyst is not detected. The cause of pain is spasms of muscle vessels or transmission of nerve impulses from the lower back. In young people, pain is accompanied by damage to the posterior meniscus or anterior cruciate ligament. In this case, the popliteal muscles perform functions unusual for them and become overworked.
Pain under the knee often occurs with gonarthrosis
How to treat inflammation of the knee joint
Treatment of inflammation of the knee joint is aimed at relieving pain, eliminating swelling and preventing complications. It is also important to restore metabolism and microcirculation of blood in the periarticular tissues, protect cartilage tissue from destruction and stimulate its restoration.
Comprehensive treatment of inflammation of the knee joints will give the most lasting result in getting rid of pain.
In the early stages, purely conservative treatment of inflammation in the knee joint is carried out:
- pharmacotherapy;
- physiotherapy;
- diet therapy.
If there are large foci of erosion, cracks and chips in the cartilage, massive accumulations of exudate, as well as overgrowing of the joint space with osteophytes, surgical treatment of inflammation in the knee joint is carried out using:
- punctures;
- cartilage polishing;
- arthroscopy;
- periarticular osteotomy;
- partial or complete endoprosthetics.
Injecting synovial fluid into the prosthetic joint also helps relieve inflammation.
In addition to the main treatment, you need to adhere to the recommendations of doctors regarding the orthopedic regimen:
- wear comfortable low-heeled shoes;
- try not to sit for a long time in a cross-legged position;
- strengthen your muscles and relieve stress on your knees using the “bicycle” exercise as soon as possible;
- dress for the weather.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic techniques for inflammation of the knee joint are aimed at combating swelling, pain and trophic disorders, normalizing blood circulation and metabolism, strengthening muscles and ligaments, and restoring mobility to the joint. For this we use:
- low frequency pulse currents (amplipulse);
- UHF therapy (ultra-high frequency currents);
- electrophoresis (with drugs for inflammation of the knee joints);
- ultrasound therapy;
- radon, hydrogen sulfide baths and other balneological procedures;
- cryotherapy;
- paraffin therapy.
Before a course of physical therapy, you need to get a doctor's referral: some techniques can only increase inflammation.
Massage
Massage for inflammation in the knee is indicated only after the exacerbation has resolved. If the skin is sensitive and painful, there is an untreated injury, any massage effect is strictly contraindicated!
In other cases, patients are recommended to undergo therapeutic classical and lymphatic drainage massage from a rehabilitation specialist. The standard therapeutic course is 10 sessions.
With the doctor's permission, light self-massage with external medications for inflammation in the knee joints can be done at home to improve tissue trophism. You need to massage not the sore knee itself, but the entire leg from the hip to the ankle joint, performing rotational movements without strong pressure for 10-15 minutes. Even if inflammation was diagnosed in only one knee, both need to be massaged. The massage should be performed once a day and stopped at the first discomfort.
Exercise therapy
Therapeutic exercises after inflammation of the knee joint are performed with the greatest care and under the supervision of an instructor. You can start exercises in the complete absence of pain (including when bending) and muscle atony, as well as effusion in the joint. The loads are constantly increasing, and rehabilitation involves 3 stages.
- Passive strengthening (up to 1.5 months).
- The patient sits on the floor with a straight back, legs straight. The kneecap slowly rises up by the tension of the femoral muscles, and is fixed at the top point for several seconds.
Starting position: lying on your back, arms at your sides, weights on your legs. We bend the healthy leg (the foot is on the floor), slowly raise the sick one up (we pull the toe towards us) to 45 degrees to the floor. We fix the position for 3-5 seconds.
- I.p. - lying on your stomach, legs straight, arms along the body. Bend the leg at the knee joint 45-90 degrees and hold for 5 seconds.
- Active rehabilitation (1.5-2 months).
- We perform shallow squats as far as the condition of the joint allows.
I.p. - standing, hands on your belt. We make soft, smooth lunges forward and backward alternately with both legs.
- Preferably: swings with an expander (we fasten the loop on the foot, and fasten the expander at a level of approximately 20 cm from the floor). I.p. - standing, hands on your belt, back straight. When performing, we try to pull the toe towards ourselves.
- Final rehabilitation (up to 4 months).
At this stage, training on a simulator is recommended. If this is not possible, do the following exercises:
- I.p. - sitting on a chair, back straight. Bend and straighten your legs until a burning sensation or pulsation appears.
I.p. - with your back to the wall. We “slide” down, bending our legs approximately 60 degrees and fixing ourselves in this position for 30 seconds.
- I.p. - standing in front of a chair, hands on the back. Holding your back, gradually squat so that your thigh is perpendicular to the floor.
Diagnostics
Based on the nature of the pain and the appearance of the affected joint, even a non-specialist can make a preliminary diagnosis (arthritis or arthrosis). But hurry to your local clinic to confirm your assumptions!
A doctor examines a patient's sore knee. Photo: chayanuphol/freepik.com
Which doctor should I contact?
If you have joint pain, you should make an appointment with your local physician. He performs the functions of a medical dispatcher: he records complaints and clinical symptoms, refers the patient for examination and, based on its results, decides which doctor should be consulted for each specific patient. A variety of specialists are involved in maintaining joint health:
- arthrologist,
- traumatologist-orthopedist,
- rheumatologist,
- vertebrologist (if the spinal joints are affected),
- podiatrist (if we are talking about foot joints),
- surgeon,
- oncologist,
- neurologist (if the joint has already been treated, but the pain remains),
- nutritionist (if your joints hurt due to metabolic disorders, such as gout, or if you are overweight).
What tests and research should I do?
The examination begins with the simplest - a clinical (finger) and biochemical (from a vein) blood test for signs of inflammation, as well as a general urine test. In some joint diseases, the kidneys are involved in the pathological process. Excess uric acid salts in the urine may indicate gout as a cause of joint disease.
Laboratory examination of the synovial fluid located inside the joint helps to detect the inflammatory process and clarify its nature. It is obtained by puncturing the joint capsule - puncture. If necessary, a histological examination of a fragment of the synovial membrane lining the joint cavity from the inside is performed.
A proven diagnostic method is radiography of the joint in two standard projections. It will help visualize narrowing of the joint space, bone spurs, osteoporosis and osteosclerosis (areas of low and high bone density, Fig. 3).
Figure 3. X-ray of the right wrist. Development of osteoporosis (b, c) during treatment with human monoclonal antibodies. Arrows indicate two-layer sclerotic stripes after two courses of the drug. Source: Elsevier Ltd/The Lancet
Currently, magnetic resonance imaging provides comprehensive information about the condition of the joint.
Myth 2: If your knee hurts, it needs rest.
Of course, you cannot engage in active sports if you have acute pain. With arthrosis, there is usually a slight inflammation in the knee, so the pain makes itself felt when walking, going down, or going up stairs. Painkillers and intra-articular injections of the Noltrex synovial fluid prosthesis can be dealt with, but not immobilization.
During movements, blood circulation is activated - the joint receives the necessary nutrition and oxygen. If this does not happen, it will wear out even faster. For arthrosis, you should select special exercises with minimal load on the damaged joint, relieve pain, but under no circumstances go to “bed rest”.
Exercise therapy for arthrosis is designed with minimal load on the damaged joint