HomeClinical MedicineDiseasesDiseases of the musculoskeletal system
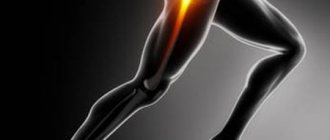
Almost every person has at least once experienced pain in the elbow joint, often accompanied by numbness in the fingers. These symptoms can occur for several reasons, including injuries and various diseases, both dangerous and not so. If you have recently suffered an injury that causes elbow pain and numbness in your fingers, then the symptoms are not particularly worrying, because the cause-and-effect relationship is obvious. The symptoms are much more disturbing when their appearance was not preceded by blows and bruises; many immediately begin to invent dangerous diseases for themselves. Let's figure out why the elbow joint sometimes hurts and the arm goes numb, and what to do about it.
Most often, pain in the elbow and numbness in the arm occurs due to various diseases. Moreover, the nature of the disease can be different: these are osteoarticular disorders, diseases of various organs, disorders of the cardiovascular system, neuralgic diseases, etc.
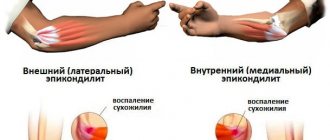
The disease epicondylitis occurs frequently in adults and is expressed in deformation of the epicondyle of the humerus. This disease is often of an occupational nature, i.e., it appears in people of certain professions who have to stand in a certain position every day.
Often, pain in the elbow and paresthesia of the fingers (numbness, tingling, goosebumps) are caused by osteochondrosis of the cervical or thoracic spine. In this case, there may be a feeling that pain is localized specifically in the elbow, although in fact there is no damage to this joint. When destroyed, the intervertebral discs become not as elastic and dense as they should be, even with small loads, for example, on the neck, the vertebrae move out of place, squeezing the nerve endings of the spinal cord, which also affect the sensitivity of the upper extremities. If there is pain in the elbow joint and numbness in the fingers, you should make an appointment with a surgeon or osteopath as soon as possible so that the disease does not lead to irreversible consequences.
If you feel that pain in the elbow and numbness in the hand are associated with a pinched nerve, this does not necessarily indicate the presence of osteochondrosis. The issue may be the so-called cubital tunnel syndrome, which also results in compression of the ulnar nerve. The syndrome can be caused by regular certain microtraumas and overexertion. The disorder often occurs in those who often like to lean on their elbows while doing their usual activities. Painful sensations arise, the fingers seem to “tingle”, this is especially typical for the little finger and ring finger. Sometimes similar symptoms are associated with another disease - neuritis. The causes of elbow pain that is not accompanied by numbness in the fingers can be completely different. This is important to consider when making a diagnosis and treatment.
What to do if pain in the elbow joint radiates to your fingers
Elbow pain and numbness in the fingers are serious symptoms that indicate many different diseases, including life-threatening ones. It is extremely important not to endure unpleasant sensations by self-medicating, but to see a specialist. The doctor may give directions for various types of examinations: ultrasound, x-rays, tomography, and prescribe treatment based on the confirmed diagnosis. There are also folk remedies to eliminate unpleasant sensations, but they all eliminate the symptoms and do not help get rid of the root cause. Even treatment with traditional recipes should be under the supervision of a doctor. Sometimes such remedies can help cope with the disorder, but they should be only part of a complete therapeutic treatment.
Tingling and pain in the hands
Tingling and pain in the arms can be caused by compressive neuropathy. When compression of the nerve is advanced, pain is tormented, and damage to the nerve can cause paralysis of the arm, loss of ability to work, and disability.
A neurosurgeon tells the story Medicīnas centrs ARS Dr. med. Janis Slesins
Why do my hands go numb and hurt?
Loss of sensation, tingling and pain in the hands can be caused by various reasons, so a thorough examination is required first. The most common cause is compressive neuropathy, or compression of a nerve. There are more than 20 types of neuropathy. The two most common diseases are carpal and cubital tunnel syndrome.
Why is it called carpal tunnel syndrome?
The name of the disease, compression neuropathy, speaks about the essence of the disease – a compressed nerve. This usually occurs in the narrowest places along the nerve's path, which is why it is called canal (tunnel) disease. The nerve is compressed in the carpal tunnel - in the wrist or in the cubital tunnel - in a narrow tunnel in the middle of the elbow. Carpal tunnel syndrome is more common than cubital tunnel syndrome
What causes carpal tunnel syndrome?
The most common cause of nerve compression is heavy, monotonous manual work. This condition is more common in people who overuse their hands and fingers every day by performing the same movements, working with their arms raised, or having their arms in a tense position. In addition, this disease more often occurs in people with metabolic or hormonal disorders, in patients with diabetes, with weakened thyroid function, and with rheumatoid arthritis.
Who is more likely to have carpal tunnel syndrome?
Historically, carpal tunnel syndrome was called milkmaid's disease because it most often affected women who milked cows by hand their entire lives. Modern work has become easier, heavy manual labor has been replaced by technology, computers and modern devices, but the prevalence of this disease has not changed. Carpal tunnel syndrome in the modern world is a typical problem for computer specialists ; this disease can often be found in warehouse and office workers, as well as in those who work a lot of time at a computer or on an assembly line, as well as in teachers, hairdressers, dentists, electricians, gardeners, rural workers, and those who do a lot of handicrafts, etc. However, people who do not overload their hands with daily work are not immune from the disease. Carpal tunnel syndrome occurs 4 times more often in women than in men.
What are the first symptoms?
It all starts with tingling in the fingers, palms hurt, especially at night. The tingling and pain progresses and soon the fingers are swollen and numb in the morning. Impaired mobility in the hand gradually develops. Untreated for a long time, a nerve pinched in the wrist radically worsens the quality of life - sensory disturbances in the fingers become more pronounced, over time the wrist muscles wear out, and the hand loses strength. It becomes impossible to grasp and hold small objects, and perform even simple routine work .
Is it possible to develop a sore arm?
Working out the arm with this disease does not help, since the disease appears when there is excessive movement, from too much load. Additional movements or exercises create even more stress.
When to see a doctor?
When something tingles or hurts a little, it often goes away quickly on its own or after using painkillers. You should go to the doctor when complaints become constant and do not go away within 2-3 weeks. It is important to find out the cause of the complaints and, if necessary, perform various examinations in order to decide on the appropriate treatment strategy - wait or treat. Good information for all patients - this disease is quite treatable.
In a mild case of compression neuropathy, when symptoms have just begun to appear, it is usually recommended to take care and not put stress on the affected arm . This is not always possible, since you need to give up the usual rhythm of life and work. However, doctors have various methods to help. There are different possibilities and means to reduce painful symptoms, but one must understand that only surgery is the only way to treat this disease, since all other methods serve to reduce symptoms . Blocks, medications and orthoses alleviate the existing condition, but in the long term only surgery can help with this disease. It helps to get rid of this disease and completely forget about discomfort. Complete recovery and/or significant improvement is achieved in 90% of patients
What examinations are needed?
To determine the cause and begin appropriate treatment, you need to visit a neurosurgeon. First of all, it is necessary to clarify the location and extent of nerve damage in order to choose an appropriate treatment method that will reduce pressure on the nerve and help restore damaged fibers. Diagnosis is important, since treatment depends on it, which will be different in each case . First, the neurosurgeon visually and manually assesses the condition of the hand, then the most important examination is neurography, which helps determine the nature and level of damage to the nerve fibers. When there is something suspicious near the nerve, for example, an enlarged joint capsule or a formation of unknown nature, and additional information is required about changes in the adjacent tissues - tendons, joints and bones, then an ultrasound is performed. If there are suspicions that pain and tingling in the hand is caused by some other disease, then X-rays, electromyography, computed tomography, magnetic resonance, laboratory tests, etc. are used to clarify the diagnosis.
How to treat compressive neuropathy?
To reduce or completely eliminate nerve compression, Medicīnas Center ARS doctors have at their disposal various methods and means that will help eliminate discomfort and alleviate the painful condition for some time or completely. There are several possibilities depending on the extent of the nerve damage. In mild cases, drug therapy is used using local injections. For this purpose, both painkillers and steroid injections or blockades are used. Sometimes physical therapy helps for a while - ultrasound with medicinal ointment, magnetic therapy, electrophoresis and other procedures that relieve swelling of the hand, freeing the pinched nerve. At night, it is worth using a special orthosis that keeps the arm in the correct position and reduces pain. However, all these methods have a short-term effect. Surgery is required to completely release the compressed nerve. It gives long-term results - the ability to work normally again and sleep peacefully .
Medicīnas centrs ARS, following the latest global trends in neurosurgery, offers increasingly gentle methods of treating compressive neuropathy, replacing traditional surgical methods with modern endoscopy. This significantly speeds up recovery and restoration of quality of life.
How is the operation performed?
The endoscopic surgery is performed at the ARS Day Hospital using local anesthesia. To free the nerve, either traditional surgical methods or a newer and less traumatic endoscopic method . The patient can return home immediately after the operation on the same day. In traditional surgery, a small incision is made in the base of the palm or on the inner surface of the elbow, the canal is opened and the nerve is released from compression. After the operation, you must follow a careful regimen for a month. The endoscopic method is much more gentle for the patient - through a small incision in the skin, a miniature endoscope is inserted into the carpal (cubital) canal - a video camera and microscopic surgical instruments, with the help of which the compressed nerve is released. In this way, the surrounding tissues are preserved, a less painful postoperative period is ensured, faster recovery and restoration of ability to work, as well as minimal cosmetic defects . A significant advantage of this method is easy wound treatment, which is especially important for patients with complicated wound healing - patients with diabetes mellitus, diseases of the circulatory system, etc. The rehabilitation period after endoscopic surgery is much easier and shorter.
Medicīnas centrs ARS Riga, st. Skolas 5 Tel.7 www.arsmed.lv
Cost of operations
Video
September 27, 2019
- Pinched nerve in the elbow joint - symptoms and treatment of the disease
Ulnar nerve entrapment is a common condition and is usually not serious. However, it can cause serious complications if left untreated, such as paralysis and loss of sensation in the affected arm or hand. Timely diagnosis and treatment in most cases lead to full recovery.
The ulnar nerve is a long nerve of the brachial plexus that provides sensation to the 4th and 5th fingers and mobility of the hand and fingers. The nerve gets its name from its location near the ulna bone. The ulnar nerve begins in the neck and runs through the entire arm to the fingers, innervating the flexor muscles of the arm.
INFORMATIVE:
How can we help people in the hour of an epileptic attack?
Because the ulnar nerve runs the entire length of the arm, there are several areas along its path where it can become damaged. The pressure and irritation is called an ulnar nerve entrapment. This is the 2nd most common painful pinched nerve in the upper body, scientists say.
The ulnar nerve can become pinched anywhere along its course, but most often it occurs at or near the crease of the elbow. This disorder is known as cubital tunnel syndrome. Less commonly, the ulnar nerve becomes pinched in the wrist area.
The most common cause of a pinched ulnar nerve is compression, researchers say. It can occur when a person leans on the elbow for a long time, when the nerve slips out of place when bending the elbow, from fluid accumulation in the elbow joint, from injuries and bone spurs of the elbow, from arthrosis or swelling of the elbow or wrist, as well as from repeated prolonged flexion and extension. hands at the elbow joint.
Some symptoms of ulnar nerve entrapment may occur in the elbow joint, but most symptoms involve the palm and fingers. Many symptoms are more severe when the arm is bent at the elbow.
Symptoms of a pinched ulnar nerve include numbness and tingling in the ring and little fingers, poor hand control, difficulty controlling the fingers when performing tasks (such as typing on a keyboard or playing instruments), sensitivity to cold, pain or weakness in the elbow joint, and late stages of the disease - muscle atrophy.
Early diagnosis of ulnar nerve entrapment can usually help avoid long-term loss of function and sensation in the hand and fingers, scientists say. If symptoms of the disorder persist for several weeks, you should seek medical help.
- Diseases that cause pain in human elbow joints, a list of causes and symptoms
Treatment for ulnar nerve entrapment depends on the severity of the disorder. For mild cases, treatment options include anti-inflammatory medications to reduce swelling, orthodontic braces or splints to keep the elbow in a straight position overnight, and physical therapy. In severe cases of ulnar nerve entrapment, surgery is indicated.
To prevent ulnar nerve pinching, scientists recommend avoiding any activity that involves repeated flexion and extension of the elbow, adopting a correct posture when working at the computer, keeping the elbow joint straight at night, not leaning on the elbow, and avoiding putting pressure on it. By following these rules, most people can avoid the appearance of unpleasant symptoms, experts say.
Based on materials from www.medicalnewstoday.com
At an appointment with a surgeon, you can often hear the question of why your elbow hurts and your hand goes numb. Unfortunately, there is no simple answer. Each case must be considered in the context of concomitant symptoms and the presence of chronic diseases, the musculoskeletal system, the cardiovascular system, and the endocrine system.
Causes and symptoms (cubital tunnel syndrome)
Cubital tunnel syndrome—also known as ulnar neuropathy—is caused by excess pressure on the ulnar nerve, which runs close to the surface of the skin at the elbow. You are more likely to develop cubital tunnel syndrome if you have the following factors:
- Repeated use of the elbow, especially on a hard surface.
- Keeping the elbow in a bent position for a long time, for example, while talking on a cell phone or sleeping with the arm bent at the elbow.
- Sometimes, cubital tunnel syndrome develops as a result of abnormal bone growth in the elbow or intense physical activity that increases pressure on the ulnar nerve. Baseball players, for example, have an increased risk of developing cubital tunnel syndrome because of the rotational motion required to hit the ball, which can lead to ulnar ligament damage and nerve injury.
Early symptoms of cubital tunnel syndrome include:
- Pain and numbness in the elbow.
- Tingling, especially in the ring and little fingers.
More severe symptoms of cubital tunnel syndrome include:
- Weakness in the ring and little fingers
- Decreased ability to flex fingers (thumb and little finger)
- Decreased hand strength
- Arm muscle atrophy
- Deformation of the hand
If any of these symptoms are present, your doctor may diagnose cubital tunnel syndrome based on a physical examination alone. In addition, it is possible to use special neurophysiological tests (such as EMG), which can determine the degree of conduction disturbance in a nerve fiber or muscle.
Relatively safe causes of the pathological condition
First of all, you should make sure that the pain in the elbow and numbness in the hand are not associated with a banal injury. Often, soft tissue bruises cause swelling, which puts pressure on blood vessels and veins, impairing blood circulation.
What else you need to pay attention to:
- the presence of bad habits (weakening of blood flow may be associated with alcohol abuse, smoking);
- comfort of a night's rest (uncomfortable pillow, tight sleep clothes often become a source of discomfort);
- professional duties (elbow hurts and hand goes numb with prolonged use).
The risk group usually includes professional athletes, manual workers (loaders, construction workers), and chiropractors.
When to seek help from doctors
Unfortunately, many people underestimate the danger of poor circulation. Specialists note that swelling, pain in the elbow and numbness in the hand may be the body’s first warning signs of a sharp deterioration in the condition of the heart and blood vessels, which means an increased risk of heart attack and stroke.
You should consult your doctor if:
- What to do if your elbow hurts and your hand goes numb
- unpleasant sensations occur only in the left hand;
- numbness affects other parts of the spine (neck, chest);
- discomfort does not go away for a long time.
It is very important to exclude thrombosis and other diseases characterized by blockage of blood vessels.
What diseases cause pain in the elbow and numbness in the hand?
The most dangerous condition is considered to be one in which discomfort most often occurs on the left side of the chest. In this case, you must immediately call an ambulance. Doctors must rule out a pre-infarction condition.
In addition to the cardiovascular system, other parts may also be affected. Most often, the described symptoms affect the spine and nerve endings.
- Rheumatoid arthritis provokes an inflammatory process that can manifest itself as pain in the elbow and numbness in the hands.
- Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine causes disturbances in the functioning of the circulatory system. Intervertebral discs do not receive enough nutrients and oxygen and are gradually destroyed.
- Atherosclerosis is characterized by the accelerated formation of cholesterol plaques on the walls of blood vessels. The lumen decreases, and interruptions in blood flow begin.
- Neoplasms in the brain or spinal cord. Fortunately, such diseases are diagnosed quite rarely. The tumor compresses the nerve endings, causing discomfort.
- Raynaud's disease can be determined after a hardware examination. The elbow hurts and the hand goes numb due to pathological damage to small vessels.
Separately, it is necessary to highlight tunnel syndrome. This disease develops during prolonged work at the computer. Symptoms of the pathological condition occur when the nerve responsible for wrist movements is compressed.
Pinched ulnar nerve: why the little and ring fingers go numb
Ulnar nerve entrapment is a common condition and is usually not serious. However, it can cause serious complications if left untreated, such as paralysis and loss of sensation in the affected arm or hand. Timely diagnosis and treatment in most cases lead to full recovery.
The ulnar nerve is a long nerve of the brachial plexus that provides sensation to the 4th and 5th fingers and mobility of the hand and fingers. The nerve gets its name from its location near the ulna bone. The ulnar nerve begins in the neck and runs through the entire arm to the fingers, innervating the flexor muscles of the arm.
INFORMATIVE:
Not stupid and not lazy: perhaps on the right in dyslexia?
Because the ulnar nerve runs the entire length of the arm, there are several areas along its path where it can become damaged. The pressure and irritation is called an ulnar nerve entrapment. This is the 2nd most common painful pinched nerve in the upper body, scientists say.
The ulnar nerve can become pinched anywhere along its course, but most often it occurs at or near the crease of the elbow. This disorder is known as cubital tunnel syndrome. Less commonly, the ulnar nerve becomes pinched in the wrist area.
The most common cause of a pinched ulnar nerve is compression, researchers say. It can occur when a person leans on the elbow for a long time, when the nerve slips out of place when bending the elbow, from fluid accumulation in the elbow joint, from injuries and bone spurs of the elbow, from arthrosis or swelling of the elbow or wrist, as well as from repeated prolonged flexion and extension. hands at the elbow joint.
Some symptoms of ulnar nerve entrapment may occur in the elbow joint, but most symptoms involve the palm and fingers. Many symptoms are more severe when the arm is bent at the elbow.
Symptoms of a pinched ulnar nerve include numbness and tingling in the ring and little fingers, poor hand control, difficulty controlling the fingers when performing tasks (such as typing on a keyboard or playing instruments), sensitivity to cold, pain or weakness in the elbow joint, and late stages of the disease - muscle atrophy.
Early diagnosis of ulnar nerve entrapment can usually help avoid long-term loss of function and sensation in the hand and fingers, scientists say. If symptoms of the disorder persist for several weeks, you should seek medical help.
Treatment for ulnar nerve entrapment depends on the severity of the disorder. For mild cases, treatment options include anti-inflammatory medications to reduce swelling, orthodontic braces or splints to keep the elbow in a straight position overnight, and physical therapy. In severe cases of ulnar nerve entrapment, surgery is indicated.
To prevent ulnar nerve pinching, scientists recommend avoiding any activity that involves repeated flexion and extension of the elbow, adopting a correct posture when working at the computer, keeping the elbow joint straight at night, not leaning on the elbow, and avoiding putting pressure on it. By following these rules, most people can avoid the appearance of unpleasant symptoms, experts say.
Based on materials from www.medicalnewstoday.com