Author
: Grachev Ilya Illarionovich
Editor
: Efremov Mikhail Mikhailovich
Date of publication: 05/13/2014 Date of update: 05/24/2021 All doctors of the clinic
- Elbow pain during/after coronavirus and ARVI
- Diagnostics
Pain in the elbow joint is not uncommon. It can be a consequence of injury, inflammation, tumor and a host of other diseases. Sometimes painful sensations occur against the background of various intoxications, previous infections and diseases of the internal organs. To figure out why elbow pain appears, you need to see a doctor. You can learn everything about the causes, symptoms and treatment of such conditions from this article.
Injuries
If the elbow joint hurts when pressed, you need to check for bruises, dislocations and sprains. Acute sensations may not appear immediately after the injury, but after 1-3 days. You can injure your hand at home, during training, or through excessive physical activity. Often, such a symptom is accompanied by swelling, a feeling of heat at the site of injury, difficulty in flexion and extension, and discomfort in the entire arm. Elbow pain that persists for more than 2 days, or even worsens, is a reason to immediately consult a doctor.
Preventive measures
In order for the compression of the fingers to occur normally, the training to not cause discomfort, and for the elbow to not go numb when bending, it is necessary to promptly eliminate all those factors that can provoke the pathological condition. Prevention plays a huge role here. It provides for the implementation of the following rules:
- Athletes or people performing complex work are required to perform daily therapeutic exercises to flex and extend the joint.
- You should not lean on your elbow for a long time while working at the computer or reading books. This provokes cubital tunnel syndrome.
- It's important to eat right.
- It is advisable to prevent any injury to the elbow joint.
- You should avoid hypothermia and visit saunas or steam baths.
- Provide quick and effective treatment of all inflammatory and infectious processes in the body.
- If you feel numbness in your hand, you should urgently consult a neurologist.
Be that as it may, if an elbow hurts, a person cannot fully work or rest. It is advisable to avoid all those factors that can provoke such a pathological condition. An active and healthy lifestyle is the main method of preventing the disease.
Pavel Valerievich Evdokimenko, a rheumatologist and psychophysiologist, academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, provides useful information about performing gymnastics:
Osteoarthritis and osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a disease of the joint with the destruction of cartilage and its other structures, as a result of which a person’s arms hurt in the elbow joints, inflammation appears and functions are impaired. A characteristic sign of osteoarthritis is marginal bone growths - osteophytes. Osteoarthritis is a disease without a pronounced inflammatory nature, caused primarily by wear and tear of the joint due to age-related changes, injuries or stress. In modern medicine, they have come to the conclusion that any process of destruction of joint tissue causes inflammation, so today these concepts, osteoarthritis and osteoarthritis, have become synonymous. With osteoarthritis, the elbow hurts with exertion. The destruction processes in this case develop due to the thinning of the cartilage inside the joint, which leads to a change in the structure of the ligaments and bones. In a relaxed state, the hand does not cause discomfort, but with strong pressure or other loads, for example, lifting a heavy bag, pain and burning appear. Without treatment, the disease can spread to other joints, worsening a person's overall well-being and quality of life. Unlike osteoarthritis (or osteoarthritis), arthritis of the elbow joint is a disease accompanied by a pronounced inflammatory process. Arthritis is manifested by severe swelling and local fever. Progressive arthritis of the elbow joint reduces the mobility of the limb and significantly reduces the amplitude of possible movements. Without proper treatment, the risk of joint contracture increases, a complication in which the arm is forced to be fixed in one position.
Methods of pain relief
First aid can be provided to yourself immediately, especially if acute pain occurs:
- eliminating any physical activity;
- fixing the injured elbow in one, half-bent position (a scarf will help);
- ensuring rest of the injured limb;
- for swelling, a cold compress will help (put ice in a bag, wet a towel or take a bottle of chilled liquid), apply periodically for 10-15 minutes, then wait half an hour;
- Painkillers will help eliminate pain: ointments (Traumel S, heparin ointment or Lyoton-gel);
- if the pain is unbearable, then painkillers Ibuprofen, Analgin or Nise will help.
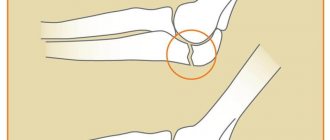
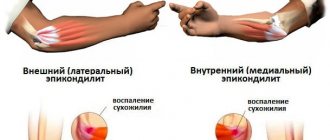
Epicondylitis
If your arm hurts on the inside or outside of the elbows, epicondylitis can be suspected. It is also called the disease of tennis players and golfers: the destruction process affects the elbow joint, the surrounding tissues and muscles of the forearm - right or left, and extremely rarely - both. Ordinary movements are easy, but with monotonous exercises or increased loads, or performing rotational movements, a nagging pain in the elbow joint appears. Patients with epicondylitis react acutely to flexion and extension of the elbow, wrist and clenching of the hand into a fist. Permanent microdamage to the elbow joint leads to inflammation, impaired blood flow, scarring and muscle spasms. The disease especially often worries people over 40 years of age, whose profession involves constant “work with their hands” - athletes, machinists, drivers and even office workers.
Treatment
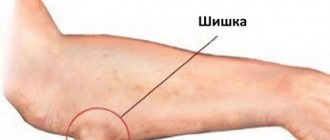
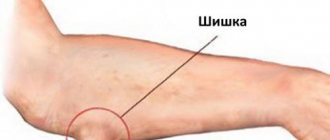
If the patient cannot clench his hand into a fist, his elbow begins to crack when moving, and a lump has appeared on the side (left or right) that hurts greatly, then he should not delay treatment.
Drug treatment
Depending on what pathology provoked the pathological condition, the person is prescribed the following medications:
- NSAIDs in tablet form or steroid injections: Colchicine. They can eliminate pain and reduce the intensity of the inflammatory process. If a patient’s elbow is very painful due to gout, then he is additionally prescribed the diuretic Allopurinol.
- Chondroprotectors: “Arthra”, “Chondroitin”. They are used to treat damage to the cartilage tissue of joints.
The drug "Chondroitin" can be bought in pharmacies from 480 rubles, and treatment with "Arthra" tablets will cost about 2000 rubles
- B vitamins: Milgamma. They help fight neurological causes of pain.
- Local warming and pain-relieving ointments: Voltaren, Fastum-gel.
- Antibacterial drugs to eliminate signs of purulent arthritis and bursitis. They are prescribed to the patient in the form of injections.
- Vasodilator medications that help restore blood circulation in the joint.
- Muscle relaxants to eliminate muscle spasms.
Drug therapy is only part of a comprehensive treatment. It is complemented by other ways and methods of combating pathology.
Non-drug treatment of pain syndrome
If bending the arm and clenching a fist is difficult for the patient, the elbow begins to crunch, hurts a lot and even goes numb, the following methods can be used to restore the functionality of the joint:
- Reducing the load on the left or right elbow joint using orthopedic devices: orthoses, bandages.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures: UHF, electrophoresis with dimexide, laser and magnetic therapy, mud or paraffin applications, ozokerite.
- Aspiration of joint fluid, as well as drainage of the synovial bursa (if fluid accumulates inside it).
You can clearly see how the drainage procedure works in this video:
- Shock wave therapy.
- Professional massage using medicinal ointment.
- Physical therapy, manual therapy, and x-ray treatment.
- Simple therapeutic exercises.
In the most extreme cases, elbow pain can be treated with surgery. It involves replacing bone damaged by injury and eliminating its fragments. If the elbow hurts severely, the patient will be advised to go to bed. The joint may be encased in plaster at that time. Despite the fact that some dystrophic diseases cannot be completely cured, the fight against them must be continued.
Elbow pain: treatment with folk remedies
Despite the fact that the pain is localized in the inner part of the joint, on the side or on top, it must be treated in any case. To do this, in combination with other methods of therapy, you can use folk remedies. If clenching a fist or bending your arm is difficult, the following recipes will be useful:
- Fresh cabbage or burdock leaves will help eliminate swelling. They need to be beaten a little with a hammer and tied to the affected elbow overnight. The sore elbow should be treated in this way until the discomfort subsides.
- The skin around the affected joint can be smeared and rubbed with alcoholic tinctures of mustard, honey or turpentine. In some cases, the patient may have a burning sensation. If it is strongly expressed, then it is better to refuse to use such means.
- Application with clay will help eliminate pain and numbness in the elbow. The raw material must be heated to 45 degrees, treat the joint with vodka, and then apply gauze and a layer of clay (1 cm) on it. To improve the effect, the compress should be wrapped in a woolen cloth. It lasts only an hour, however, several such procedures will help improve fist clenching and get rid of pain. Perhaps your hand will stop going numb.
- Compress with warm sea salt. Its temperature should be 65 degrees.
- Laurel oil has a warming effect. You need to smear it on the skin directly above the affected joint.
- If your elbow hurts, a folk remedy such as fresh celery juice, which can be rubbed into the joint or taken orally, will help overcome the discomfort. Treatment is carried out over 14 days.
Folk remedies, as well as drugs, cannot completely cure systemic or degenerative diseases of the musculoskeletal system. However, they help to significantly improve the patient’s life.
Elena Malysheva gives excellent advice on what to do for bruises in the area of interest to us:
Bursitis
Pain when bending and straightening the arm can also signal bursitis. When a joint is damaged, the cells of the synovial membrane actively produce fluid that accumulates inside the joint capsule. As a result, a characteristic lump or swelling usually forms on the outer side of the elbow, and the process of its enlargement is accompanied by pain, a local increase in temperature and redness of the skin. Acute bursitis is characterized by severe pain and limited range of motion. In the chronic form, a moderate burning sensation is felt, the elbow seems thickened. In some cases, bursitis leads to complications - a purulent process. To determine the specific type of disease, a puncture may be prescribed.
Objectives of massage for arthrosis
For arthrosis, massage performs several functions:
- relieves pain, allows a person to reduce the amount of drugs taken orally;
- has an anti-inflammatory and absorbable effect, which is important if arthrosis is accompanied by accumulation of fluid in the joint cavity;
- improves metabolism in periarticular tissues, accelerates recovery processes in damaged cartilage;
- strengthens the periarticular muscles, prevents further damage to cartilage.
Osteochondritis dissecans
Osteochondritis dissecans is the death of a part of the bone, in this case in the elbow joint, in the area of the articular cartilage. With this pathology, cartilage tissue and a fragment of adjacent bone are separated and displaced into the joint cavity, causing pain - moderate and intensifying with movement. In later stages, symptoms such as “jamming” of the joint, a reduction in the range of motion, and chronic synovitis—inflammation of the joint membrane—are observed. The disease develops due to a local disturbance of blood flow in the elbow joint, most often occurring in men under the age of 30. Separately, it is worth noting such a dangerous symptom as a burning sensation in the shoulder or elbow of the left arm, associated with chest pain, decreased blood pressure and rapid pulse. Such signs may indicate the onset of a myocardial infarction, so if they are detected, you must urgently call an ambulance.
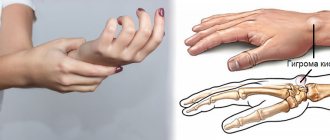
Elbow structure
When most people hear the word “elbow,” they think of the bend of the joint (hitting with the elbow). In the old days, this was the name for the place from the wrist to the bend of the elbow; there was even such a measure of length: elbow - 35.6 cm. It is anatomically correct to distinguish:
- Shoulder - from the shoulder to the elbow joint.
- The joint itself.
- Forearm - from elbow to hand.
The elbow joint is a trochlear-shaped complex joint of three simple joints united into a common ligament. The three bones of the human body (radius, ulna and humerus) together with the corresponding muscles (biceps, triceps and brachialis) make it possible to bend and straighten the arm, raise and lower it, and also perform other actions.
Joint structure diagram
Diagnosis of pain
For elbow pain, diagnosis begins with a consultation. The doctor conducts a survey to find out whether the patient has had any past or recent injuries, surgeries or treatments, and whether there are any hereditary factors that may affect the current condition of the joints. Next, the joint site is examined and felt (palpation), joint mobility and reaction to various positions of the limb are assessed. Most likely, to make a diagnosis you will have to visit several doctors - a surgeon, osteopath, neurologist, as well as a rheumatologist if you suspect rheumatoid arthritis - an autoimmune disease of the joints. A visit to a traumatologist may be required if there are injuries, dislocations, or sprains.
Since pain accompanies many diseases, the examination must exclude tumors and infections. Standard laboratory tests include blood and urine tests, as well as blood biochemistry. This list can be supplemented by tests prescribed by specialists: taking a sample of synovial fluid, tests for rheumatoid factor, C-reactive protein, etc. A comprehensive examination is necessary to timely and accurately determine the cause of the elbow joint disease.
In addition to examination, consultations and tests, diagnostics include:
- ultrasound examination - allows you to see damage to the structure of the joint, signs of inflammation, fluid accumulation, pathological changes in cartilage;
- radiography - shows the condition of the bones that form the joint, reveals bone growths, calcium deposits, deviations in the size of the joint space;
- computed tomography - helps to see all pathological, inflammatory and destructive changes in bone tissue;
- magnetic resonance imaging - reveals degenerative processes, tumors, injuries, foci of infections and inflammations.
Based on the diagnostic results, treatment is prescribed that eliminates the cause of elbow pain and alleviates the patient’s condition.
Diagnostic measures
Some pathologies of the forearm and elbow joint do not require additional examination. For example, the diagnosis of epicondylitis is often made only on the basis of anamnesis, external examination, and palpation of the damaged area.
Other pathologies need to be confirmed through further examination:
- X-rays;
- MSCT, MRI;
- Ultrasound;
- ECG;
- Electroneuromyography (ENMG);
- General and biochemical blood tests.
Changes in bone structures are clearly visible on MSCT and x-ray. In case of soft tissue disease, it is advisable to do ultrasound, MRI, and ENMG.
No. 6. Do children receive therapeutic massage?
In childhood, massage, as a rule, has different goals than in adults diagnosed with arthrosis. This pathology is rare in children. Therefore, they are prescribed massage courses to strengthen the musculoskeletal system, increase muscle tone and improve blood circulation. In the case of children, only delicate practices are used - stroking, rubbing, kneading, etc.
If there are pathologies, the doctor prescribes a special children's massage, including in the treatment of arthrosis in a child. Much more often, massage is practiced in children in infancy, with umbilical hernia, colic, muscle wasting and other pathologies. To prevent recurrent diseases, corrective massage is prescribed. And in order to strengthen the child’s health and increase immunity, it is preventive.
In children, massage has more preventive rather than therapeutic purposes.
No. 1. For arthrosis, do they massage the damaged joint directly?
First of all, the affected areas are kneaded, but local exposure is not enough to treat arthrosis of the shoulder, elbow, knee or other joint. With this disease, it is important to comprehensively work out all the muscles in the following sequence: vertebrae from upper to lower, femoral area, knees, legs, feet. Of course, this is the task of a specialist, so you need to go to such sessions on the recommendation of a doctor, and not very often. At home, it is enough to massage the damaged joint using a certain technology.
General massage sessions are useful for arthrosis of any joints
No. 5. How long should a massage session last for arthrosis?
It depends on the affected area and technique. The duration of the session can range from several minutes to two hours. At this time, the massage therapist uses methods such as rubbing, kneading, stroking, vibration, etc. If there is no pain or discomfort, the effect can be very long. The main thing is to achieve a relaxing effect, because the main purpose of massage is to relieve pain.
With the help of massage you can temporarily get rid of pain in the knee joint. A specialist tells and shows how to do this:
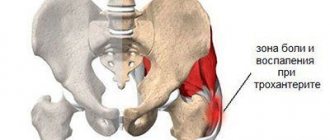
No. 9. How is massage performed for coxarthrosis?
Massage for arthrosis of the hip joint is performed in a lying position on the stomach, side or back. The muscles should be as relaxed as possible. They start with light, shallow techniques - stroking the upper part of the buttocks and lumbar region, then squeezing with the edge of the palm and kneading around the hip joint. The force of pressure in the massaged area increases gradually. If the pain is not severe, rub around the joint, dotted and circular. The complex is repeated 2-3 times and ends with shaking and stroking.
The duration of a massage session for coxarthrosis is 8-10 minutes