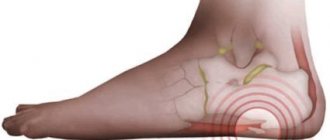
Unpleasant sensations in the hip joint can appear at a fairly young age. This may include pain, tingling, muscle tension, aches, etc. As a rule, these manifestations are caused by damage to different tissues of the bone articulation. Subchondral sclerosis of the hip joint is diagnosed in approximately 60% of cases when patients aged 30–45 years present with complaints of pain. Pathology is detected exclusively using an x-ray or MRI.
First of all, subchondral sclerosis of the acetabulum of the hip joints develops, since these surfaces bear the maximum shock-absorbing load and are less well supplied with blood than the head of the femur. To understand the pathological processes occurring in the joint and the potential causes that can provoke them, we advise you to familiarize yourself with some facts from the field of anatomy and physiology.
It is important to understand the structure of the hip joint. It is formed by the acetabulum of the pelvic ilium. The other articular surface of the ilium forms the iliosacral joint. A lot depends on the health of this joint - how well the shock-absorbing load is distributed, how protected the intervertebral cartilaginous discs are, how a person tolerates extreme physical activity, etc.
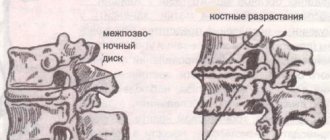
The head of the femur is located in the cavity of the acetabulum. Both articular surfaces are covered with a dense layer of cartilage tissue. Below them is the subchondral surface, which provides nutrition to the periosteum. This plate is quite thin and smooth. It is dotted with blood vessels. The cartilaginous protective layer does not have its own vascular network. It is supplied with blood through diffuse exchange with the subchondral plate. Cartilage receives most of its water and nutrients through the absorption and return of synovial fluid. It fills the joint capsule, ensures ease of gliding of bones, distribution of shock-absorbing load.
Any deterioration in the composition or viscosity of the synovial fluid begins the process of destruction in the cartilage tissue. It loses its protective ability and the load begins to be placed on the subchondral plate.
Under pressure, sclerosis of the blood vessels located in its thickness occurs. They lose the ability to provide adequate nutrition to bone and cartilage tissue. This is where degeneration and destruction of the hip joint begins.
Subchondral sclerosis of the articular surfaces of the hip joints over time leads to the fact that the cartilaginous synovial layer disintegrates. The surfaces of the bones are exposed. When making movements, they rub against each other. Cracks and chips form on their surfaces. They are filled with deposits of calcium salts. These are osteophytes, which further injure the bone tissue even more. This happens until the process of fusion of the femoral head and acetabulum begins. First, ankylosis and stiffness develop, and then contracture of the joint. The person loses the ability to walk independently and even stand on the affected side.
Unfortunately, this disease can be treated with conservative methods only at the initial stage. As osteophytes, ankylosis, contracture, and deforming osteoarthritis develop, surgery may be required. During this procedure, the doctor performs endoprosthetics (replacement) of the hip joint.
In order not to bring yourself to such a state, we strongly recommend that you consult a doctor in the early stages of this process. If you feel heaviness, stiffness, or pain in the hip joint, consult a doctor as soon as possible.
In Moscow, you can make an appointment for a free appointment with an orthopedist at our manual therapy clinic. An experienced doctor will conduct a full examination and make a preliminary diagnosis. He will then recommend the necessary examinations for you. After an accurate diagnosis has been made, an individually designed course of treatment will be recommended to you.
General information
Osteosclerosis is a pathological condition caused by an increase in bone density and thickening of bone trabeculae (beams), a decrease in the volume of bone marrow cells as a result of excessive formation of bone components, as well as compact substance.
It develops under conditions of imbalance in the functional viability of osteoclasts and osteoblasts - when synthesis processes prevail over destruction processes. Osteosclerosis can be physiological - it is noted during the development of skeletal structures in growth zones, but it is pathological osteosclerosis that is dangerous, since it leads to a decrease in the elasticity of bone formations.
Schematic representation of normal bone and osteosclerosis
Osteosclerosis may be accompanied by benign dysplasia ( melorheostosis ), inhomogeneity and spotty ossification ( osteopoikilosis ), myelofibrosis, increased fragility and failure of bone marrow tissue as in osteopetrosis . Moreover, narrowing of the bone marrow canal and its complete obliteration due to thickening of the cortical layer is possible.
Osteosclerosis occurs in the form of genetic diseases, including marble disease , which develop in childhood, as well as in the form of adult osteomyelosclerosis, which is characteristic mainly of older people.
Osteosclerosis of the shoulder joint and head of the bone
Subchondral osteosclerosis of the shoulder joint can involve both the head of the bone and the glenoid cavity of the scapula. This disease can be caused by habitual dislocation of the shoulder, destruction of the articular labrum, cervical osteochondrosis, glenohumeral periarteritis and many other pathological processes.
Progressive osteosclerosis of the humeral head is manifested by the following clinical symptoms:
- nagging or aching constant pain in the shoulder area;
- inability to freely raise the arm in front of you and when abducted to the side;
- a decrease in muscle strength and, as a consequence, a decrease in the volume of the forearm due to degenerative processes;
- increased hand fatigue when performing work that is usual in volume and length;
- pain along the brachial and radial nerves;
- destruction of joint tissue and the appearance of crunching and clicking sounds typical for this process during rotational movements in the plane of the shoulder joint.
It is possible to treat osteosclerosis of the humerus without surgery only in the initial stages. Therefore, if you experience any pain in the shoulder area, we recommend that you immediately seek medical help.
Pathogenesis
The mechanism of osteosclerosis is based on the opposite condition to osteoporosis , reflecting reparative processes in the bone - in the form of an increase in the bone-forming ability of osteoblasts. This nonspecific reaction in the form of an increase in bone mass occurs due to periosteal and endosteal ossification in response to various diseases, injuries and processes in the body. To stimulate true osteosclerosis, pathological processes are sufficient, the substrate of which is located in the spaces between the bone beams.
In addition to pathological changes in the bone—thickening of the trabeculae and compact substance—cancellous bone tissue also undergoes changes, taking on the appearance of a narrow-loop structure or a compact mass.
Traditional home remedies
Folk remedies are not effective enough, however, many patients prefer to use them.
Among the most popular are:
- cinquefoil (it is included in many ointments for joints and bones);
- propolis tincture;
- dead bees infused with alcohol;
- snake poison;
- a mixture of Vishnevsky ointment and heparin ointment.
Vishnevsky ointment
Heparin ointment
Propolis tincture
The effectiveness of such means is questionable. However, cinquefoil and snake venom are used as components of medicinal ointments.
Below are some recipes:
- Calamus roots, 250g, are infused in 3 liters of cold water and added to the bath.
- Alcohol-based honey ointment - applied under a compress for 10-15 minutes.
- A mixture of lingonberry leaves, sweet clover herb , St. John's wort and flax seeds in equal proportions is infused in water for 2 hours, and the affected areas are treated three times a day. The same mixture can be infused with alcohol and used as compresses for 10-15 minutes daily.
- An elegant solution for cat owners - the warmth of an animal sitting on a sore area is comparable to physical therapy. In addition, the purring of a cat increases the production of endorphins.
Classification
Osteosclerosis can be limited, focal, diffuse and generalized. Depending on the cause of development, it can be physiological, abnormal or idopathic, post-traumatic, inflammatory, genetic, reactive, etc.
Point transformations in bones are usually observed in fractures at the border of a healthy spine and in tissues with an inflammatory process. Generalized disorders can cover the entire skeleton, spread diffusely or focally. In addition, lesions can develop below the cartilaginous structures - subchondral, affecting the surfaces of the endplates and joints, and also develop in the vertebrae.
Osteosclerosis of the spine
Osteosclerosis of the spine is manifested by deformation of the vertebral bodies, dystrophic changes in the surrounding muscle tissue, impaired mobility of the spinal axis and a feeling of stiffness in the affected areas. Bone deformations and sclerosing processes increase the risk of compression fractures and curvatures.
In general, anyone who has ever had pain and stiffness in their back can understand what osteosclerosis of the spine is. Any backache or overexertion can cause a feeling of tightness - when there is no way to bend or bend. Hardening or growths on the spine provoke the same sensations, and can also be accompanied by pain, tachycardia , difficulty breathing and even lead to kidney failure and an increased risk of femoral neck fractures . Therefore, you need to take care of the health of your spine every day, for example, do gymnastics, but if negative sensations still make themselves felt, then this is a clear sign that you need to see a specialist!
Osteosclerosis of the hip joint
The mechanism of the pathological process is based on the destruction of cartilaginous plates, thickening and enlargement of structures with bone compaction. Erosion and cracks occur in the cartilage tissue. The disease can be the result of severe injuries to the articular joint, endocrine disorders, metabolic failures, inflammatory processes, and excessive physical activity. Most often observed in obese women over 45 years of age.
Distinctive signs of osteosclerosis of the hip joint are stiffness in the lower back in the morning and at night, numbness and impaired motor functions of the lower extremities, lameness, fatigue, pain when walking, as well as disruption of the intestines and organs of the genitourinary system.
Damage to the hip joint, namely the acetabulum, can lead to aseptic necrosis of the femoral head and fractures. Treatment must begin in a timely manner, otherwise the position of the femoral head may change and excessive load will be placed on it, which will lead to serious deformations, destruction and disability.
Subchondral osteosclerosis
This is one of the manifestations of degenerative dystrophic joint disease - osteoarthritis . Increases in bone density occur due to the growth of scar connective tissue as a result of inflammation or aging. Osteophytic and bone growths with transformed neuroarticular tissue may have irregularities that increase friction and cause secondary inflammatory processes, which ultimately results in complete immobilization of the joints. In addition, osteophytes can wedge into the bone, causing chips. Subchondral changes most often occur in the shoulder, knee and hip joints, cervical and thoracic spine.
The most dangerous are considered to be osteosclerotic processes in the chest, which develop under the influence of osteochondrosis and do not cause severe stress. The pathology leads to the formation of an immovable bone tumor, which causes a lot of discomfort and various clinical manifestations.
Subchondral osteosclerosis of the endplates
The pathological process is accompanied by the replacement of the cartilage layer from below with dense bone tissue of a discharged structure, which disrupts diffuse metabolism and does not have the same protective properties of cartilage to withstand excessive loads.
When the endplates of the thoracic vertebrae are damaged, patients experience difficulty breathing, pain, and a noticeable distortion of posture occurs. The pain syndrome can completely hinder movement. The disease is considered gerontological, but sometimes occurs in younger individuals.
Subchondral osteosclerosis of articular surfaces
Pathological changes in the articular surfaces occur through the proliferation of bone tissue in the form of osteophytic growths, subsequent narrowing of the joint spaces and deformation of the joint so much that it stops bending. The lesion and deformity usually develops in the bone below the cartilaginous plate.
Pathologically changed and healthy joint
When the growths become too large, they create friction and can interfere with the movement of the joint.
Treatment
Currently, osteosclerosis of any localization is preferably treated conservatively (that is, using medications and physical therapy techniques). The use of surgical methods is required only in severe cases of the disease, when other means have proven ineffective.
It is mandatory to prescribe a treatment regimen and diet - this increases the effectiveness of procedures and drug treatment. After the operation, a fairly long recovery period is recommended. Physical activity must be strictly dosed.
Drug treatment of osteosclerosis
Drug treatment of osteosclerosis is carried out strictly as prescribed by the doctor:
- Among medications for the treatment of osteosclerosis, the most important are chondroitin and glucosamine preparations (Chondrogard and others). They allow effective restoration of bone and cartilage tissue and support the growth of normal osteons and trabeculae.
- For osteosclerosis of the knee joint, medications are prescribed in the form of tablets or intra-articular injections. The course of treatment is up to six months.
- If other joints are affected, injections are not used due to the risk of damaging the ligaments.
- Additionally, general strengthening treatment, phosphorus and calcium preparations, and vitamin D may be prescribed, which improve the metabolism of minerals in the bones. It is possible to prescribe hormones that regulate bone mineralization.
Physical therapy and exercise
Physical activity is extremely important for the normal formation of trabeculae. A set of exercises is selected taking into account the localization of pathological changes and the nature of bone lesions.
For osteosclerosis of the lower extremities, the most effective exercise is considered to be an exercise bike, walking, running and squats. If the shoulder joints are affected - rotation, raising and lowering the arms.
Pull-ups and push-ups are not recommended. Affected elbows and hand joints require flexion, extension and rotation. A special restraint (knee pad, elbow pad) must be worn on the affected joint to limit mobility.
An approximate set of exercises for patients with osteosclerosis of the knee joint:
- Warm-up – raising on toes – 20 times, rotating the knee joint – 10 times in each direction.
- Squats – 20-30 times, more is possible if you are in good physical shape.
- Exercise bike - 30 minutes, or run 30 minutes.
- Stretching – bending over with straight knees.
- Completion – slow walking for 2-3 minutes.
You should check the set of exercises with your doctor - the same techniques are not suitable for all patients. If the spine is affected, you can perform some of the exercises while sitting or lying down.
Physiotherapy
Among the physical treatments for osteosclerosis, preference should be given to massage with warming oils and ointments. You can also use anti-inflammatory ointments and gels. This procedure should be carried out by a professional massage therapist to avoid the risk of accidental injury.
This is especially important when it comes to osteosclerosis of the spine - an insufficiently qualified massage therapist can cause pinched nerves or the appearance of a hernia.
In addition to massage, other types of physiotherapy are indicated:
- Warming procedures are also necessary that increase blood circulation and improve tissue nutrition - infrared irradiation, magnetic therapy.
- Electrophoresis is prescribed with chondroprotectors and painkillers , and less often with anti-inflammatory drugs.
- It is possible to use UHF and ultraviolet irradiation to increase blood circulation in diseased bones.
Physiotherapy methods are used as additional to the main treatment regimen.
Surgical intervention
Considered a last resort. It is prescribed in cases where other methods have proven ineffective, as well as for deformations and bone fractures. Operations for osteosclerosis can be divided into two types – therapeutic and restorative.
X-ray after surgery
Restorative traumatological operations are prescribed for severe spinal deformities and vertebral osteosclerosis, which cannot be restored in other ways, as well as for fractures and dislocations of bones and joints. This involves repositioning the fragments, restoring the normal structure and fixing it with the help of traumatological structures.
Therapeutic operations for osteosclerosis - transplantation of healthy bone tissue into the affected area. The method is effective, but is associated with risks for the patient, like any operation.
Causes
- physiological (functional) - occurring in areas of bone tissue growth;
- genetic predisposition or hereditary marbled disease with a defect in the gene encoding carbonic anhydrase II , which leads to a deficiency of this enzyme;
- various myeloproliferative diseases and melorheostosis - benign congenital dysplasia that causes bone hardening;
- osteopoikilia - congenital multiple sclerosing osteopathy;
- excess body weight;
- endocrine disorders, including diabetes mellitus ;
- inflammatory and reactive processes, including lupus erythematosus ;
- cancer formation;
- intoxication;
- injuries and fractures;
- passive lifestyle;
- wear and tear of cartilage due to age, prolonged stay in certain positions;
- heavy physical activity, sports and types of work.
Symptoms
The clinical picture is usually long-lasting and asymptomatic. Changes in the musculoskeletal system can cause the following symptoms:
- numbness of the limbs;
- sensation of a foreign body in the joint;
- a feeling of stiffness and a decrease in the range of motion of joints - flexion, extension, rotation, bending, etc.;
- discomfort and pain in the joints, especially during physical activity;
- neurological manifestations caused by pinched nerve endings: ringing in the ears, dizziness, headache, auditory and visual disturbances;
- it is difficult to inhale and exhale;
- with lesions of the hip joint, disorders affecting internal organs, for example, the genitourinary system, are possible.
Marble disease is manifested by anemia due to the excessive development of the number of bone osteophytes against the background of a sharply reduced volume of red bone marrow.
Osteoarthritis can lead to complete immobility, difficulty breathing and disability of the patient.
Subchondral osteosclerosis of articular surfaces
Bone osteosclerosis is a degenerative process associated with rarefaction of the tissue structure and filling of the resulting gaps with foreign inclusions. Due to this, scarring and thickening of the bone head occurs in the projection of the articular surface. Unfortunately, subchondral osteosclerosis of the articular surfaces can often be diagnosed at a late stage. This is the reason that most patients are treated exclusively with surgical methods.
But it is worth knowing that osteosclerosis of the articular surfaces can be recognized at an early stage, when restoration of the structure is possible using manual therapy methods. To do this, you need to know only the most basic primary signs of trouble.
In this material, we invite you to learn about what osteosclerosis of the joints is and how it is formed. The article provides information about the potential causes of this pathology and current methods of treatment without surgery.
A visit to an experienced doctor will help dispel all doubts. You can make an absolutely free appointment with a podiatrist at our manual therapy clinic. If you are concerned about pain and discomfort in the large joints of the upper or lower extremities, call and make an appointment with a doctor. During the examination, he will be able to make an accurate diagnosis and tell you how you can restore the health of your musculoskeletal system.
Tests and diagnostics
Densified bone tissue becomes less transparent to the action of x-rays, that is, the intensity of the bone shadow increases and therefore osteosclerosis can be detected through x-ray examinations. The main radiological symptoms are:
- an increase in the number of bone beams in relation to the area of the bone itself;
- the presence of osteophytic neoplasms;
- narrowing of the medullary canal;
- thickening of individual beams in the bone;
- alternation of foci of osteosclerosis and areas of osteoporosis ;
- finely looped trabecular pattern.
To obtain a clearer picture and understand the nature of the changes, CT and MRI can be performed. To determine the degree of bone compaction, densitometry is performed, and to identify disturbances in the conduction of nerve impulses, electroneuromyography is performed.
Sanatorium treatment
Sanatorium treatment of osteosclerosis involves walking and exercise in the fresh air, proper nutrition, and a therapeutic regimen. It is advisable to go to sea and mud sanatoriums, where there are unique natural factors that improve the condition of bones and joints.
Sanatorium treatment of osteosclerosis
Patients with chronic bone damage are recommended to go to sanatoriums 2 times a year, preferably in spring and autumn. If the patient does not have such an opportunity, it is necessary to find it at least once a year.
A ticket to a sanatorium is prescribed by the attending physician; if necessary, a certificate of incapacity for work can be issued for this time.
Diet for osteosclerosis
Diet for osteoarthritis of the knee joint
- Efficacy: no data
- Timing: constantly
- Cost of products: 1700-1800 rubles. in Week
The best diet for osteosclerosis is a diet that enhances metabolism, strengthens and makes the body strong, so the menu should include:
- proteins - optimal sources are dietary poultry, eggs, seafood, fish and vegetable protein from legumes and other vegetables;
- complex carbohydrates - cereals, crispbread, whole grain bread, vegetables, dried fruits, fruits and berries, which additionally contain many vitamins immune- boosting substances ;
- calcium – you need to consume dairy and fermented milk products every day;
- healthy fats – various unrefined vegetable oils, seeds and nuts.
Nutrition and diet
Diet is not the main treatment. However, some dietary adjustments are required. First of all, you should think about the amount of food - you should not overeat, food should completely cover a person’s energy needs, but not exceed them.
When the bones of the lower extremities and spine are affected, it is very important to normalize weight if there is excess weight.
Required and permitted products:
- milk and dairy products, preferably low-fat;
- dietary meat and offal – liver, heart;
- fresh fruits - apples, grapes, pears, bananas;
- cereals, primarily buckwheat and pearl barley.
These products contain calcium, which is necessary for the construction of normal bone tissue, supporting healthy regeneration processes and trabecular formation. Foods that should be limited are bread and pastries, especially white ones, sweets, alcohol and fatty foods.