Any pain is painful and requires a response. However, pain in the wrists is also unpleasant because it entails limited mobility of the hand and the inability to perform simple movements. It happens that the patient finds it difficult to fasten a button or take a mug of tea from the table.
What can cause pain in the hands when bending? How to distinguish the cause of pain from symptoms? What can help when your wrist hurts? You will learn the answers to these and other questions by reading this article.
The specialists of our clinic solve such problems. Yes , we can help you with physical therapy!
Types of pain in the hands
Types of pain in the hands
If we talk about classification, then all pain in the wrists can be divided into 2 types depending on duration:
- periodic pain in the hands,
- constant pain in the hands.
Periodic pain is more severe and occurs when trying to turn the hand, clench the fingers, or make other movements in the wrist joint. Typically, such pain indicates a recent injury, sprain or dislocation of the joint.
Constant pain , in turn, is slightly less intense, but haunts a person for a long time. Sometimes the pain is so debilitating that a patient with arthritis may get out of bed at night to take pain medication.
Causes of pain in the hands
General information about the disease
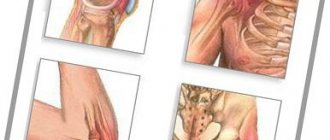
Arthritis of the hands often develops against the background of high functional load on the joints of the hand and their injury. The hand consists of many small bones connected into joints: the wrist, carpometacarpal and metacarpophalangeal. There are many blood vessels and nerves in the hand area, so all pathological processes are painful. ICD-10 disease code (other unspecified arthritis) is M13.
Arthritis of the hands often develops during adolescence as growth occurs and is accompanied by severe deformities. No less often they develop in the second half of life due to hormonal disorders, against the background of sports, domestic and professional injuries. The disease can equally develop in people of any gender.
Causes
It is not always possible to find out why the disease begins. Very often, the cause of arthritis of the hands is acute and chronic injuries to the hand. Acute injuries are often complicated by acute aseptic (without infection) arthritis, ending in complete recovery. But if an infection occurs, the inflammation can be purulent.
With constant minor trauma to the hand, most often professional, a chronic inflammatory process slowly develops with subsequent dysfunction of the joints.
In childhood and adolescence, juvenile chronic arthritis (JCA) can develop, the origin of which most often cannot be determined. After a few years, it leads to the development of serious deformities of the upper limbs. Deformation of the hands is a characteristic symptom of rheumatoid arthritis - an inflammatory process in the joints, the cause of which is an autoimmune process - an allergy to the patient’s own tissues. Genetic predisposition is of great importance in this disease.
Sometimes the disease develops against the background of reactive arthritis after infections of the upper respiratory tract, genitourinary organs, or intestinal infections. The exact causes of such lesions are not known, but they are also often associated with genetic factors. Infectious arthritis of the hands develops with gonorrhea, syphilis and some other infections.
Read more about infectious arthritis in this article.
Metabolic disorders can also cause inflammation of the hand joints. Thus, with disturbances in purine metabolism, gout develops, in which uric acid crystals are deposited in the articular and periarticular tissues, causing inflammation.
Great importance is attached to predisposing factors (triggers) that increase the risk of developing hand arthritis. These include previous infections, hypothermia, high physical activity on the hands, constant intense fine work with the hand, sports activities, stress, bad habits, poor nutrition, and hormonal changes. Arthritis of the hand often develops in tennis players, pianists, guitarists, hairdressers and people in any other professions whose work involves constant stress on the hands.
Symptoms and possible diseases
Wrist pain is the main symptom that will always be present. The person may also experience other signs of the disorder. They depend on the specific disease that caused the wrist pain.
Common symptoms include:
- Numbness in the palm and hand.
- Goosebumps.
- Burning and itching in the affected area.
- Trembling fingers, tingling in fingers.
- Increased pain at night, after intense physical activity.
- Crunching in a characteristic area.
- Weakness of the fingers when trying to grasp any object.
- Limitation of hand movements.
- Swelling in the fingers and palms. It can occur on one or both limbs.
Specific symptoms
Specific symptoms of wrist pain include:
- General deterioration in health.
- Hyperemia of hand tissues. Redness often appears after an injury.
- Anatomically incorrect position of the limb (after a fracture). Joint instability (after dislocation).
- Hemorrhages under the skin (after an open fracture).
- Pain when bending a limb.
- Joint deformity.
- Inability to perform any actions with the affected hand.
- Shortness of breath, pain in the chest and heart area.
- Burning, itching, tingling of the limb.
- Hyperemia of the skin, which is located above the affected area.
- Increased body temperature.
- Muscle weakness.
The listed symptoms are more common than others. They can accompany acute and chronic wrist pain. The exact clinical manifestations depend on the specific pathology that caused the pain syndrome.
Symptoms of hand arthritis
Symptoms of hand arthritis depend on the causes of the disease, its clinical form and the nature of its course. Arthritis can begin suddenly, acutely, with a disturbance in the general condition of the patient, or it can slowly and imperceptibly with gradual destruction of the joints.
First signs
Acute arthritis of the hand begins suddenly with pain, redness and swelling of the tissue. Body temperature may rise, chills, malaise, and headache may appear. This course usually forces you to immediately consult a doctor, so acute arthritis in most cases is completely cured.
The first symptoms of arthritis of the hands are pain, swelling and redness of the tissues.
In the chronic course, vague pain in the hand and wrist area first appears, then morning stiffness of the hands appears - a feeling of tight constricting gloves on the hands, which initially lasts no more than half an hour after sleep. Stiffness goes away after the start of movements. Joint pain is aching in nature; at the beginning of the disease, it appears and then disappears.
It is important to notice the first symptoms in time and immediately seek medical help!
Obvious symptoms
Gradually, the pain syndrome with arthritis of the hands increases, the aching pain becomes constant, swelling and redness appear (not always). The period of stiffness in the morning increases, the movement of the hand is impaired, first due to pain, and after a while due to dysfunction of the joint. When you squeeze the hand, a clicking sound appears, sometimes accompanied by increased pain.
Over time, the hand with arthritis of the hands becomes deformed and loses its functions. It may take on the appearance of flippers (in rheumatoid arthritis) or shorten due to the rapid ossification of growth plates in juvenile chronic arthritis. The small bones of the wrist grow together, ankylosis develops, and the hand stops bending.
Dangerous symptoms
Arthritis of the hands can become more complicated. Therefore, if the following symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor:
- acute onset of the disease with high fever lasting more than 5 days;
- a sudden rise in high temperature against the background of already existing signs of arthritis, increased swelling and redness of the hand - a sign of possible purulent inflammation;
- sharp pain, deformation of the hand and increasing swelling of the tissues are a sign of dislocation or subluxation of the hand.
The main causes of pain in the wrist
In most cases, the cause of discomfort can be a previous fracture, a dislocated wrist, or a sprained ligament.
Your wrist may hurt for the following reasons:
1. A sprain or other injury resulting from a direct blow to the wrist or a strong fall on the arm. This may cause your wrist to swell. The mobility of the arm will be limited, and the person will feel excruciating pain.
2. Frequent force loads provoke pain in the wrist. This could be a sharp grip or a strong bend of the wrist. People who engage in rowing, tennis or golf are at risk. Heavy loads provoke the occurrence of tendonitis. These are very common diseases. Tendons are contained in very narrow sheaths. Even minor tendon irritation can cause lumps.
3. Carpal tunnel syndrome. This disease most often develops in expectant mothers in the 2-3 trimester of pregnancy. The reason for the development of the syndrome is weight gain in women and swelling that appears in the second half of pregnancy.
4. Monotonous work on the computer. Frequent use of the mouse and keyboard puts a huge strain on the muscles. This kind of work keeps the brush under prolonged tension. As a result, the tendons that are located close to the nerves become swollen. In some cases, the nerve swells. A right-handed person has pain in his right wrist. The person feels regular discomfort. The ability to grasp something weakens, the palms of the hands go numb. This disease is called carpal tunnel syndrome.
Wrist injury
Injury can be caused by a fall or a strong blow. The injury can result in a fracture of the smallest bones of the wrist. Sometimes it is quite difficult to recognize an injury due to unclear symptoms. The main symptoms of injury are pain, swelling, and wrist deformity. Untimely treatment can negatively affect the motor abilities of the hand.
A sprain occurs from sharp bending of the arm. The ligamentous apparatus consists of the radius, ulna and wrist. This damage causes terrible pain. The hand loses its mobility.
Inflammation of tendons and ligaments
Inflammation occurs in the tendon walls. They are responsible for the mobility of the muscles of the entire arm. The disease is called tenosynovitis. Regular, monotonous hand movements cause pain in the wrist. People of certain professions are at risk. Tendons are located in narrow sheaths. Regular movement of the hand causes irritation and inflammation. Lumps may form. The main symptoms of tendovaginitis are aching pain, crunching and crackling. The process of developing the disease is quite long. The wrist hurts a lot when bending, it is difficult to grasp an object with the hand.
Carpal tunnel syndrome
This disease is accompanied by pain in the wrist of the right hand. The main reason for the occurrence of tunnel syndrome is monotonous, monotonous, long-term work. This pathology is typical for people of certain professions. For example: surgeons, musicians, tailors. This disease also affects people who work on computers. Such activity provokes pinching of the nerve, which is located in the narrow canal of the wrist. Symptoms of the disease: pain from wrist to elbow, burning, weak fingers, tingling. It is difficult for a person to carry out daily work.
Rheumatoid diseases
The most common disease is rheumatoid arthritis. This is a systemic disease in which the immune system is weakened. It can affect not only the wrist, but also other joints.
The body begins to produce antibodies that attack its own tissues. This causes inflammation and damage to the joint. The pathology is chronic and protracted. Women aged 30 to 50 years are at risk.
Dystrophic changes in the joint
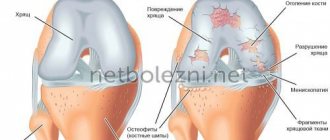
With arthrosis, the cartilage that covers the surface of the joint becomes damaged and wears out. The wrist becomes deformed and pain occurs. Joint dystrophy is diagnosed much more often than arthrosis of the wrist joint. Elderly people are at risk. In exceptional cases, the disease occurs in adolescents and even children.
How dangerous is the disease?
The hand is the most active working organ of a person, therefore the main danger of arthritis of the hand is dysfunction, the formation of ankylosis (immobility) of the joints of the hand. Dysfunction develops gradually as the disease moves from one stage to another.
Stages
There are 4 stages of the disease, during which functional failure develops:
- Initial.
The stage of inflammation, which cannot always be seen during instrumental examination. This is the beginning of inflammation of the synovial membrane. It thickens and begins to secrete an increased volume of inflammatory exudate. Externally, this is manifested by the appearance of transient pain and slight swelling. - Explicit.
Inflammatory phenomena intensify, the amount of exudate increases, the synovial membrane grows in the form of soft granulations - pannus, occupying a significant part of the joint cavity. Pain and swelling of the tissues increase and become constant. - Formation of soft ankylosis.
The loose tissue of the pannus becomes dense and connects the surfaces of the bone joints, forming their immobility. The flexion of the hand is impaired, and the pain continues to bother me. - Formation of bone ankylosis.
Instead of connective tissue, bone tissue grows and complete immobility of the joint develops with loss of function and disability. The inflammatory process in the joints continues, so pain and swelling remain.
Any form of arthritis has serious complications, so you should not delay treatment.
See how easily the disease can be cured in 10-12 sessions.
Possible complications
At different stages, the disease can cause different complications:
- purulent inflammation involving periarticular tissues in the process; in the absence of adequate treatment, it can develop into sepsis;
- subluxations and dislocations of the affected joints – are accompanied by pain and require emergency assistance;
- shortening of the upper limb in juvenile chronic arthritis;
- complete loss of limb function, disability.
Exacerbation of the disease - what to do?
In some clinical forms, the disease occurs in waves, with exacerbations and remissions. In case of severe exacerbation with severe pain, redness and swelling of tissues, you should:
- take any pill from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) - Diclofenac, Meloxicam, Nise, etc.; apply an external agent (gel, ointment) with the same agents to the skin, for example, Diclofenac ointment; Menovazin, an anesthetic solution for external use, is also suitable;
- lie down in bed, give the hand an elevated position, placing a pillow under it;
- call a doctor at home.
There is no stumbling block for diagnosis
Only a specialist can correctly determine the cause of pain and give a diagnosis. First of all, a therapeutic examination is carried out. The doctor makes a preliminary diagnosis and writes a referral for a subsequent examination by a specialized specialist, who establishes an accurate conclusion based on the results of medical studies:
- clinical symptoms and anamnesis;
- examination and assessment of joint functionality;
- general clinical tests;
- MRI, ultrasound, CT.
Features of the course of arthritis of the hands in different types of disease
Arthritis of the hand can be a manifestation of various diseases, so its symptoms, course and consequences will also be different.
Post-traumatic and purulent arthritis
The addition of a purulent infection can occur with any type of disease. Most often this happens after open injuries, but sometimes the infection enters the joints through the bloodstream from distant foci of infection. If the infection does not occur, the disease is acute and ends with complete recovery.
The onset of the purulent process is acute, with fever, headache, and malaise. The hand is very painful, it swells sharply, and the skin turns red. Movements are severely limited due to pain. When such symptoms appear, the patient requires surgical assistance.
Chronic post-traumatic arthritis of the hands develops with frequent minor injuries to the hand in people involved in certain sports (tennis players), musicians (pianists), hairdressers, etc. In the absence of help and continued injury, a permanent dysfunction of the joint occurs.
Rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis
Damage to the small joints of the hands develops frequently. Characterized by symmetrical joint damage and a slowly progressive course. Initially, moderate transient pain and stiffness of movement appear in the morning, lasting no more than half an hour and passing through physical activity. Arthritis of the fingers also develops.
After some time, some swelling appears over the affected area, the pain becomes constant, night pain and severe morning stiffness bother you. The swelling may increase or decrease, but the pain does not go away. Redness of the hand is rare.
If you do not consult a doctor in a timely manner, then deformation of the hands gradually appears - they take on the shape of flippers and completely or partially lose their function.
Reactive arthritis
Develops two weeks after a genitourinary or intestinal infection, sometimes after sinusitis, otitis media or tonsillitis. More often, the pathological process involves the joints of the lower extremities, but sometimes also the upper ones, for example, the wrist joint.
The disease most often occurs acutely, with pain, redness and swelling of the tissue. The prognosis is favorable: with adequate treatment, complete recovery occurs. But sometimes the course is initially chronic, in which case, with a long course, the function of the joint may be impaired.
Chondroprotectors: what are they, how to choose, how effective are they?
Joint pain at rest
Infectious arthritis
Hand damage most often occurs with gonorrheal arthritis. The inflammatory process is acute, with pain, swelling and redness of tissues, an increase in general body temperature, and malaise. Goes away after treatment for gonorrheal infection. Chronic course is rare.
Juvenile chronic arthritis (JCA)
It occurs in childhood and adolescence and can be of multifactorial origin. It often occurs chronically, but there is also a subacute course. A feature of this type of hand arthritis is frequent damage to the joints of the hand and fingers, a long course and the formation of disability over the next seven years.
Deformation of the limbs (shortening) occurs due to the premature closure of bone growth zones.
Gouty arthritis
Metabolic disease - deposition of uric acid salts in articular and periarticular tissues. Inflammation of the small joints of the hands is rarely the only symptom of the disease; usually its appearance is combined with the development of arthritis of other joints, the thumb is especially often affected. During an attack of gout, the area over the affected joint swells, turns red, and the pain is very severe. With frequent repetition of inflammation in the same joint, joint function may be impaired: the hand stops bending.
Gouty arthritis
Which doctors should you consult if your wrist hurts?
To find out the cause of wrist pain, you need to contact such specialists as:
- Therapist
- Traumatologist.
You should visit a doctor after an injury, regardless of its origin. If it is not possible to get to a traumatologist, then you need to go to see a surgeon.
- Orthopedist.
A doctor is consulted when, in addition to pain in the wrist, a person notices swelling in a characteristic area, and when moving, a creaking and crunching sound is heard. Pain may also occur when moving the thumb and index finger. These symptoms indicate peritendinitis.
- Rheumatologist.
Symptoms that should force a person to contact this specialist: paroxysmal pain (they can last from several hours to several days), redness in the joint area, local increase in body temperature. When a joint becomes deformed after the end of an attack of pain, gout or pseudogout can be suspected. Other signs may indicate a systemic disease: rashes on the skin and mucous membranes, a burning sensation when emptying the bladder, an increase in body temperature up to 37.5 °C, chills, headaches, weakness, sweating during sleep. These symptoms are also characteristic of infectious arthritis. It can be caused by gonorrhea, tuberculosis, brucellosis.
- Neuropathologist.
This doctor will provide care to a patient with carpal tunnel syndrome. It often develops in pregnant women and in people who work at a computer. The development of this pathology is indicated by symptoms such as: pain, burning and itching in the wrist, trembling in the fingers (all fingers suffer except the little finger). It is difficult for a person to hold an object in the palm of his hand. The hand may swell, and numbness often occurs in the forearm area. The hand becomes cold and skin sensitivity worsens.
If it is difficult for a person to understand which doctor he needs to see, then first he should visit a therapist.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of arthritis of small joints of the hands is established on the basis of examination and questioning of the patient and is confirmed by laboratory and instrumental studies:
- Laboratory tests
- reveal the content of components confirming the inflammatory process, the presence of infectious pathogens and antibodies to them, as well as rheumatoid factor. - Instrumental
:- Ultrasound
– reveals the presence of excess fluid in the joint; - radiography
- the presence of bone changes (narrowing of the joint space, bone ankylosis); - MRI
– presence of changes in soft articular and periarticular tissues; - arthroscopy
- endoscopic examination, allows you to see the inner lining of the joint and all changes in it; During diagnostic arthroscopy, you can take fluid or a piece of tissue for examination.
Diagnosis of finger joint pain
To identify the causes of the disease, the following types of research are used:
- Magnetic resonance imaging. MRI of the hand joint is the most effective and accurate way to identify the location of an inflammatory or post-traumatic process;
- X-ray;
- CT scan;
- Ultrasound;
- electrospondylography;
- puncture (extraction of liquid contents of the joint capsule).
Important!
Only a doctor can prescribe a specific test, having previously studied the characteristics of the symptoms.
Treatment of hand arthritis
How and with what to treat arthritis of the hands, the doctor decides after examination and establishing a final diagnosis. Any treatment carried out without examination will not be effective, since different types of arthritis are treated differently. In any case, the patient is prescribed an individually selected comprehensive treatment. It includes:
- drug therapy;
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- Exercise therapy, massage;
- reflexology (RT);
- traditional methods of treatment.
If conservative therapy is ineffective, surgical treatment methods are prescribed.
Read our article “Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in women.”
Drug therapy
For hand arthritis, the following medications are prescribed:
- NSAID groups – relieve pain, inflammation and fever. The most effective NSAID drug is Diclofenac, but it causes irritation of the gastric mucosa, so today more modern drugs of this group are prescribed - Meloxicam, Celebrex, Nimesulide in the form of injections (injections), tablets or capsules for oral administration and external agents (ointments, creams, gels). ).
- For severe swelling and pain that cannot be relieved with NSAIDs, glucocorticoid hormones are prescribed in the form of short courses of oral tablets, intravenous infusions or intra-articular injections. They perfectly eliminate all unpleasant symptoms.
- In subacute and chronic cases, drugs that suppress immune processes (basic therapy) are prescribed: Methotrexate, Sulfasalazine, Azathioprine, etc.
- Medicines from the group of biological agents that include antibodies and cytokines (MabThera) also suppress immune reactions.
- If the cause of the disease is an infection, drugs are prescribed that suppress it.
- Antihistamines to reduce allergies - Claritin, Erius, Cetrin, etc.
- Chondroprotectors - agents that restore cartilage tissue of joints - Teraflex, Dona, etc.
- Vitamins and minerals that restore metabolism.
Drug treatment for arthritis of the hands is carried out using drugs from the NSAID group, drugs that suppress immune processes, and other drugs.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
Depending on the stage of the disease, physiotherapeutic procedures are added to the drug treatment of arthritis of the hands, which significantly enhance the therapeutic effect and accelerate the process of tissue restoration:
- at the stage of inflammation
- electrophoresis and phonophoresis with painkillers, anti-inflammatory drugs; - at the recovery stage
- magnetic therapy, laser therapy, thermal procedures (paraffin, ozokerite).
In a state of stable remission of arthritis of the hands, sanatorium-resort treatment is recommended - mud, baths in combination with hardware physiotherapeutic techniques. Kavminvod sanatoriums are perfect.
Crunching in joints - when to worry
Intra-articular injections of hyaluronic acid
Massage
These procedures are done in a state of remission. Both therapeutic massage performed by a massage therapist and self-massage are very effective. You can independently perform the following most effective, but at the same time gentle massage movements every day after applying massage oil to your hands:
- rubbing the back surface: with sliding movements of one hand, rub the back surface of the other in the direction from the wrist to the fingertips; then change hands;
- rubbing the side surfaces of the fingers: interlock your fingers and move your hands so that the side surfaces of the fingers are rubbed;
- rubbing the palms: with the fingers of one hand, forcefully rub the palms of the other in the direction from the wrist to the fingers;
- soft massage movement “hand washes hand”;
- stroking hands with light sliding movements.
Daily massage improves blood circulation, helps revitalize metabolic processes and restore tissue.
Physiotherapy
Physical therapy (physical therapy) complexes are prescribed by a doctor. It is better to undergo the first training sessions under the supervision of a physical therapy instructor, and then continue at home. The following exercises will help improve your well-being:
- rolling an apple or a tennis ball
- roll a medium-sized apple (to fit in the palm) or a tennis ball between the palms, actively pressing on the soft tissues; also actively roll the apple on the table; - rolling chestnuts between palms and fingers
- take 2-3 chestnuts at once and roll between palms and fingers, as well as on a smooth table surface; - clenching and unclenching a fist
- clench your palms into a fist and hold it tense, then sharply unclench it with all fingers straightened like a fan; repeat 10 times; - beating out the rhythm with your palm
- with open palms, beat out any clear rhythm on the table (march, rap, whatever you like); - flexion-extension
- place your elbows on the table, raise your forearms parallel to each other; make a simultaneous tilt of the hands forward, then back, right and left; repeat everything 5 times.
Therapeutic gymnastics helps improve blood circulation, restores the strength of muscles and ligaments, improves joint mobility, and prevents the destruction of cartilage. It is carried out in a state of remission.
Reflexology
Therapeutic exercises with a ball and reflexology will help cure arthritis of the hands
An ancient Chinese method, successfully integrated into modern medicine. It is based on a reflex effect on the entire body, as well as on individual organs and tissues through certain points on the human body. Most often, the effect is carried out using acupuncture (acupuncture), but you can also cauterize (warm up) the points with wormwood cigarettes, do acupressure and use other techniques. This method has proven itself in the treatment of hand arthritis.
Traditional methods
Folk remedies (herbal decoctions and tinctures) are also actively included in complex treatment as additional methods. But the doctor prescribes them ,
self-medication should be excluded. Traditional recipes:
- compresses from dry elm bark; grind the raw materials, grind them into powder, dilute with water to a pasty state, transfer to a napkin and apply to the affected joints; Apply polyethylene and insulation on top and leave overnight; perfectly relieves pain and swelling;
- ointment from dried poplar buds; crush the raw materials in a mortar, add the same amount of melted butter and rub into your hands several times a day; analgesic effect.
Surgery
In the acute period, surgical treatment is carried out for a purulent inflammatory process: the pus is removed, the joint cavity is washed with an antiseptic solution.
Surgery is sometimes required for long-term, wave-like arthritis with severe pain and swelling: part of the synovial membrane is removed (synovectomy). This gives a positive result and brings relief to the patient.
When a complete loss of joint function occurs, endoprosthetics is performed - replacing the destroyed joint with an artificial one.
Read about new treatments for rheumatoid arthritis in this article.
How to treat hand joints?
All existing treatment methods, both ultra-new and traditional, which the Alan Clinic Center for Neurology and Orthopedics uses in its work, are the safest and exclude surgical intervention.
The treatment process is always a comprehensive program with an individual approach to each of our patients. These treatment methods, consisting mainly of non-drug methods, are available not only to ordinary patients, but are acceptable for the treatment of infants, pregnant and lactating mothers.
We have at our disposal the following methods:
- Manual therapy
- Osteopathy is treatment done by a doctor, with a gentle effect on the musculoskeletal system, nervous and vascular systems, and internal organs.
- Medical massage
- Acupuncture - exposure to biologically active points with microneedles.
- Laser reflexology is a painless effect on reflexogenic zones and points.
- Tsubotherapy is a gentle effect on the reflex points of the body.
- Pharmacopuncture is the introduction of medicinal drugs of natural origin to the source of the problem.
- Plasma therapy is the introduction of the patient’s own purified blood into the site of the disease.
- Isometric kinesiotherapy - individual gymnastic techniques/exercises, according to indications, with elements of joint massage.
- Kinesiotherapy using the Exart installation
- Kinesio taping
- Ozone therapy is treatment with active oxygen.
- Physiotherapy
- Physiotherapy with enzyme preparations
- Medical droppers
- Hirudotherapy - treatment with leeches.
- Botulinum therapy is treatment with botulinum toxin.
- Intra-articular injection of synovial fluid endoprostheses
- Intra-articular blockades
All methods are recognized by official medicine, and doctors using them have appropriate certificates. The decision on the need to use certain medications during the course of treatment is made by the doctor, based on the complexity and severity of the disease, concomitant diseases, as well as the diagnosis.
Treatment approach in our clinic
At our clinic, specialists have developed a special approach to treating this disease. After a thorough examination of the patient (including an MRI), a comprehensive treatment is prescribed, which includes:
- modern developments in medical science: the latest medications and regimens for their use, physiotherapeutic and other non-drug methods that eliminate the main manifestations of the disease and suppress its progression;
- Traditional oriental methods influence the body as a whole, restoring the functioning of all its organs and systems, which leads to the suppression of the pathological process in the joints.
This combination allows you to quickly and painlessly relieve the patient of all unpleasant symptoms, and then suppress the progression of the disease and restore joint function. Details about the treatment methods used can be found on our website.
We combine proven techniques of the East and innovative methods of Western medicine.
Read more about our unique method of treating arthritis
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
In case of injury, immobilization is carried out with a splint or the arm is suspended in a scarf. Cold is applied. In case of intense pain, a painkiller is given. For pain of non-traumatic origin, the hand is provided with rest; in the absence of signs of inflammation, local anesthetics and warming agents are used. Severe pain, significant swelling, hyperemia of the wrist, general hyperthermia, weakness, weakness indicate the presence of an inflammatory process that requires immediate specialized treatment.
Conservative therapy
The basic treatment for wrist pain is a special regimen that reduces the load on the hand. The patient is given a plaster splint, the use of orthoses is recommended, and the exclusion of certain types of physical activity is recommended. In case of traumatic injuries, reposition or reduction is performed. Patients are prescribed:
- Drug therapy.
Healing gels and ointments are applied to the affected area. For some diseases, NSAIDs and chondroprotectors are prescribed orally or by injection. - Intra-articular injections.
During degenerative processes, chondroprotectors, analogues of synovial fluid, are injected into the joint. For persistent pain syndrome, blockades with hormonal agents are performed. - Physiotherapeutic activities
. In the treatment of diseases and injuries of the wrist, UHF, ultrasound, electrophoresis, magnetic therapy, laser therapy, and other techniques are used. - Other non-drug methods
. Patients are taught complexes of therapeutic exercises, massage, manual therapy, and kinesiotherapy.
General clinical recommendations
To prevent exacerbation of the pathological process and its progression, the following recommendations must be followed:
- follow all doctor's orders;
- conduct courses of anti-relapse treatment;
- promptly treat all acute and chronic diseases;
- avoid colds and hypothermia, especially of the hands;
- do not lift heavy objects, do not engage in long-term painstaking activities involving the hands;
- avoid prolonged stress;
- get rid of bad habits.
Prevention
Prevention of arthritis of the hand is especially important for people with a family history (close relatives suffering from this pathology). To prevent the development of the disease, you need:
- lead a healthy active lifestyle, eat right;
- do not overload your hands with heavy physical work and long, tedious painstaking work;
- do not smoke, do not abuse alcohol;
- avoid hypothermia of hands;
- promptly treat all diseases and hormonal disorders.
How to eat healthy
Only gout requires a special diet; it is imperative to adhere to its requirements. For other types of arthritis, a healthy diet is sufficient. Fatty meat and dairy products, fried, spicy, smoked, and canned foods should be excluded from the diet. It is necessary to limit sweets, baked goods, and sweet carbonated drinks. The diet should contain a lot of fresh vegetables, fruits, cereals, and low-fat animal products.
Nutrition for finger arthritis
Proper nutrition for arthritis of the fingers has several goals:
- strengthening joints and saturating them with nutrients;
- improvement of metabolic processes in cartilage tissue;
- reduction of inflammation;
- improvement of collagen production with normal fiber structure;
- strengthening the immune system;
- prevention of allergic reactions;
- recovery for the primary disease, if arthritis is caused by gout, psoriasis, diabetes or another disease;
- achieving optimal body weight.
For example, zinc and selenium, which are essential in the diet of patients with arthritis, are involved in the production of enzymes in the synovium of the joint. Enzymes, in turn, remove decay and oxidation products from the joint. If they are not removed, they settle on the surface of the cartilage, making it uneven, less slippery, and are also absorbed by collagen fibers and disrupt their structure.
Although even a complete and balanced diet for arthritis of the fingers cannot stop the process of destruction of the joint without additional treatment, it should not be underestimated.
Frequently asked questions about the disease
I have arthritis in my hand since childhood. Will they take me into the army?
If the function of the joint is impaired, then no.
I had arthritis in my wrist after gonorrhea. Can it be completely cured?
Infectious arthritis can be completely cured if the correct treatment is prescribed in time.
What is the best way to smear your brushes so that they don’t hurt?
You need to consult your doctor. The best painkillers are Voltaren emulgel and Menovazin rubbing solution.
Arthritis of the hand joints is best treated in the early stages. But if you were unable to seek medical help in time, then do not be discouraged: everything can be treated.
At the Moscow Paramita clinic, arthritis of the hands is treated at any stage. Our patients forget about pain after the first acupuncture sessions. Further rehabilitation therapy takes place in comfortable conditions and is completely painless. We will restore your health!
Literature:
- Shelepina T.A. Rehabilitation therapy in the complex treatment of JRA. Pediatric rheumatology. !995, 13 – 16.
- Blokhin V.N. Trauma and reconstructive surgery of the hand. Orthopedist, traumatologist and Prosthetics, 1973, 6, 63-38.
- Woog PHNFular Publishers, Basle, 1978.
Themes
Arthritis, Joints, Pain, Treatment without surgery Date of publication: 11/17/2020 Date of update: 04/03/2021
Reader rating
Rating: 4.67 / 5 (3)