Rheumatology is a field of medicine that specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the joints, spine and systemic connective tissue diseases. The discipline is considered one of the youngest in medicine - it gained independence only in the middle of the 20th century. However, connective tissue diseases have been known since time immemorial. It is noteworthy that the root “rheum” in the word rheumatology is of Greek origin (1st century BC) and is literally translated as “primary juice”. According to the ancients, rheuma formed in the brain and flowed to different parts of the body, causing systemic diseases.
There is a common belief that rheumatology is only for older people. However, this is not so: rheumatological diseases are rapidly becoming “younger”. Among the patients there are not only 40-year-olds, but also those who have not even reached adulthood.
Orthopedist or rheumatologist: what's the difference?
Rheumatologists treat a broad group of diseases involving degenerative and inflammatory diseases of connective tissue, bones and joints. There are over 200 diseases in their area of competence.
Both an orthopedist and a rheumatologist deal with diseases of the musculoskeletal system, but there are differences in the activities of specialists. The task of a rheumatologist as a specialist in the field of autoimmulology is the treatment of chronic joint diseases, that is, not caused by a sudden injury.
The main task of an orthopedist is the diagnosis and treatment of disorders in the musculoskeletal system. This applies to both congenital and acquired pathologies. While a rheumatologist focuses on connective tissues and joints, an orthopedist studies all the structures that allow a person to move.
The rheumatologist and orthopedist may work closely together. The coordinated actions of two specialists at once help patients quickly regain good shape. Treatment is prescribed individually - it all depends on the type of disease, medical history, age, and condition of the patient. Most often, pharmacological therapy in combination with physiotherapeutic procedures is prescribed for the treatment of rheumatic diseases.
In what cases should you contact a rheumatologist?
There are signs that indicate that you cannot postpone a visit to the doctor. These symptoms include:
- pain in muscles, joints and bones;
- the pain is periodic and intense, often occurring not only in one, but also in several joints (over time, the disease takes on a symmetrical form - symptoms appear in the joints on both sides of the body);
- pain is accompanied by low-grade fever and/or swelling, and/or rash, redness of the skin;
- ailments in the abdominal cavity, and they are not caused by problems with the stomach or intestines;
- redness of the skin in the joint area;
- a feeling of stiffness in movements (problems with holding objects in the fingers, difficulty bending over, moving);
- joint deformation, swelling;
- weather sensitivity;
- morning stiffness of joints;
- increased sweating;
- pale skin;
- chronic state of drowsiness, fatigue, general weakness
The sooner you see a doctor, the better the prognosis for recovery will be. Remember that relieving pain and refusing to see a specialist can ultimately lead to disability. Timely diagnosis and treatment is the best investment in health and a guarantee of maintaining an active, full life.
What is arthritis?
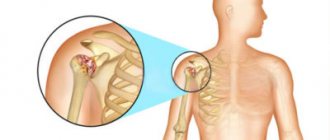
Arthritis is inflammation of one or more joints.
An orthopedic surgeon treats arthritis.
In acute arthritis, as a rule, there is pain and a feeling of stiffness during movement. In addition, pain may occur at certain intervals (for example, in the evenings, during sleep at night, or upon awakening).
With chronic arthritis, pain can become constant.
In the absence of adequate treatment for a long time, the following occur:
- joint redness,
- swelling and/or deformation of the joint,
- impaired mobility (up to complete immobilization of the joint).
Which doctor should I see for arthritis?
If you have been diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis, you need to see a rheumatologist. With a rheumatological profile, in addition to the joints, internal organs (heart, kidneys, etc.) may also suffer, so rheumatoid arthritis should be treated by a rheumatologist.
The treatment of allergic, gouty and infectious arthritis is carried out by specialists of the relevant profile (allergists, rheumatologists and cardio-rheumatologists).
Orthopedic doctors successfully treat all other types of arthritis in children and adults (caused by sports and household injuries, excess body weight, age-related changes in joints).
What to look for when choosing a rheumatologist
Rheumatic diseases affect the functioning of vital organs and systems. That is why, when choosing a doctor, you should pay attention to the capabilities of the clinic.
Find out:
- Are consultations with related specialists provided?
- Does the medical institution have a modern diagnostic facility?
- If a rheumatic disease is diagnosed, are there opportunities for physiotherapeutic procedures?
Our Clinic fully meets all requirements and standards in the field of diagnosis and treatment of rheumatic diseases. The team consists of experienced doctors with extensive experience. There is all the necessary diagnostic equipment and facilities for laboratory tests and physiotherapy.
How is the first appointment and diagnosis carried out?
No special preparation is required to visit a doctor. It is enough to take with you a medical card and the results of the latest studies, if available (urinalysis, blood tests, ultrasound, etc.).
A visit to a rheumatologist consists of several stages. The first of them is a detailed interview, that is, obtaining information about the declared ailments.
The rheumatologist may ask:
- Where exactly is the pain concentrated (for example, which joints hurt, maybe the pain affects the entire limb or several fingers)?
- Is the pain worst at night or during the day?
- Is morning stiffness accompanied by morning stiffness and how long does it last?
- Was there swelling of the joints or redness?
- Are the symptoms episodic or chronic?
- Does the pain get worse when you are immobile?
- How intense is the pain?
- Was the symptoms preceded by an infection (eg, urinary tract infection, pharyngitis)?
The survey may focus on other symptoms, comorbidities, or even illnesses that run in family members. Questions that seem to be unrelated to the problem that is the reason for consultation (for example, bad habits or intestinal diseases in parents) should not come as a surprise.
The next step is an examination, and the doctor evaluates not only the condition of the joints. Depending on your symptoms, your rheumatologist may also examine your skin, nails, lymph nodes, or abdomen.
Unfortunately, it happens that the first visit does not provide grounds for making a final diagnosis and drawing up a treatment plan. Sometimes, even with the efforts of the doctor and painstaking preparation on the part of the patient, there is not enough information to make decisions. This is due to the fact that some rheumatic diseases take years to develop, and the full picture appears only with time. In any case, you cannot do without additional examinations.
Frequently asked questions about the disease
Arthritis and arthrosis, what is the difference?
Arthritis is inflammation of the joint, and arthrosis is the result of metabolic disorders.
Is it possible to do massage with arthritis?
As prescribed by a doctor and only at the rehabilitation stage or during remission.
Do they take into the army with arthritis?
It all depends on the condition of the joint. People with bone deformities, as well as in the presence of an acute inflammatory process, are not accepted into the army.
Is it possible to heat joints if you have arthritis?
This can only be decided by the attending physician, since it all depends on the form and type of arthritis. You definitely shouldn’t use heat during a purulent process or after an injury.
Joint inflammation is a serious disease. Without timely medical care, it can lead to disability. Therefore, at the first signs of arthritis, you should consult a doctor. The specialists of the Paramita clinic in Moscow will help you in any case, even if you have suffered from joint pain for years. Come and see for yourself!
Literature:
- Nasonov E.L. Pharmacotherapy of rheumatoid arthritis from the perspective of evidence-based medicine: new recommendations // RMJ. 2002. T. 10. No. 6. pp. 294–302.
- Korpela M., Laasonen L., Hannonen P. et al. Retardation of joint damage in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis by initial aggressive treatment with disease–modifying antirheumatic drugs: five–year experience from the FIN–RACo study // Arthritis Rheum. Vol. 50. R. 2072–2081.
- Smolen JS, Aletaha D., Machold KP Therapeutic strategies in early rheumatoid arthritis. Best Pract. Res//Clin. Rheumatol. 2005. Vol. 19. R. 163–177.
Themes
Arthritis, Joints, Pain, Treatment without surgery Date of publication: 09/30/2020 Date of update: 04/03/2021
Reader rating
Rating: 5 / 5 (1)
Treatment methods and follow-up features
The course of treatment by a rheumatologist depends on the specific disease and its severity. Unfortunately, in the case of degenerative and inflammatory diseases of bones, joints and connective tissue, treatment is usually long-term.
In most cases, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used to relieve rheumatic pain. Sometimes antibiotics and stronger analgesics may be prescribed. In severe cases, glucocorticosteroids are used, which suppress the immune system and have a powerful anti-inflammatory effect.
These and other drugs, which in addition to alleviating the symptoms of the disease, also inhibit the destruction of joints. Reception should be started as early as possible to avoid unpleasant complications and degenerative changes. It should be remembered that the nature of most rheumatic diseases is such that the pills must be taken constantly; withdrawal may cause a relapse.
Physiotherapy is also very important, thanks to which you can stop the progression of the disease, and sometimes even restore some motor functions of damaged joints. The doctor may prescribe procedures such as:
- Kinesitherapy . The technique is based on performing active and passive exercises that are designed to improve the functioning of diseased joints.
- Medical massage . Reduces muscle tension and stiffness, improves local blood circulation and blood supply to tissues.
- Electrophoresis . The procedure is a method of delivering drugs directly to the affected organ. The technology is based on the use of weak electric current discharges and injections. Electrophoresis helps reduce swelling, reduce pain, and speed up cellular metabolism.
- Ultrasound therapy . The method promotes the resorption of swelling and helps in the restoration of damaged tissue.
- Acupuncture . The technique helps to get rid of pain and accelerates regeneration processes.
Along with therapy, the doctor will give recommendations regarding lifestyle. The topic of proper nutrition with limited salt and maintaining a healthy body weight, as well as other preventive measures will be discussed: quitting smoking, maintaining a drinking regime, minimizing stress, etc.
Approach to treating the disease in our clinic
The Paramita clinic (Moscow) has developed its own approach to the treatment of arthritis. First of all, a thorough diagnosis of arthritis is carried out (examination by a doctor, laboratory and instrumental diagnostics, including MRI) and only then comprehensive treatment is prescribed. It includes the most modern European methods of treatment and the latest medications, as well as time-tested traditional oriental methods that came to us from China and Tibet.
The doctors at our clinic have successful experience in treating arthritis of various origins. The pain that has bothered our patients for years can be eliminated already in the early stages of treatment. Even with advanced diseases, several courses of treatment allow you to return to normal life, prevent relapses and forget about pain.
We combine proven techniques of the East and innovative methods of Western medicine.
Read more about our unique method of treating arthritis
Additional diagnostic methods
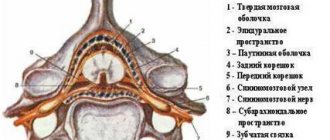
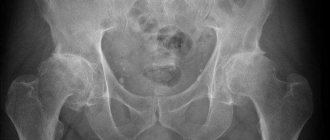
Despite the enormous progress in medicine, the importance of traditional X-ray examinations of bones and joints cannot be overestimated. If in doubt, more extensive imaging, such as a CT scan or magnetic resonance imaging, may be needed. Ultrasound examination is becoming increasingly important. The study allows us to evaluate early inflammatory changes in joints, periarticular tissues and peripheral nerves.
In some cases, histopathological examination of biopsied tissue may be required to make a diagnosis. In this case, hospitalization may be required because some procedures involving tissue collection can only be performed in a hospital setting.
The doctor will also order laboratory tests. Along with a traditional general blood test, a proteinogram (analysis of the protein composition of the blood) and rheumatic tests may be required. In some cases, consultations with specialists in other fields of medicine may be required: pulmonologist, endocrinologist, cardiologist, hepatologist and others.
What diseases does a rheumatologist treat?
A specialist in rheumatology treats many diseases. Among them:
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- psoriatic arthritis;
- rheumatic fever;
- vasculitis;
- gout;
- ankylosing spondylitis;
- osteoarthritis;
- chronic inflammation of connective tissue: systemic lupus erythematosus, systemic sclerosis, dermatomyositis, polymyositis, Sjogren's syndrome;
- osteoporosis;
- sarcoidosis;
- fibromyalgia, etc.
Many joint problems are temporary, but when rheumatic disease sets in, it makes sense to act early before permanent changes occur. Modern rheumatology is moving in such a direction that images of joints deformed by the inflammatory process can only be found in archival photographs in textbooks.
Etiology and pathogenesis - why and how the disease develops
The causes of arthritis are not always identified. Sometimes there is not one reason, but several, this is:
- Local infection.
Pathogens can enter the joint through small blood and lymphatic vessels from nearby tissues when they are inflamed - boil, abscess, phlegmon. Acute arthritis develops. If it is not treated, it will either go away on its own or become chronic, which is always problematic to treat. - General infection.
For example, with tuberculosis or gonorrhea, bacteria enter the joint through the circulatory or lymphatic system. Tuberculous or gonorrheal arthritis develops. - Toxic-allergic effects in any infectious diseases.
It is not the infectious agents that enter the joint, but their waste products. They have a toxic effect on joint tissue and cause allergic inflammatory reactions of varying strength. - Autoallergy
is an allergy to the body's own tissues. Under the influence of various mechanisms (most often after an infection or in the presence of a permanent focus of infection, for example, chronic tonsillitis), malfunctions of the immune system occur. Immune cells and antibodies begin to perceive joint tissue as foreign and attack them, causing a long-term, difficult-to-treat inflammatory process. Such diseases include rheumatoid arthritis. - Injuries.
Through open injuries, infection can enter the joint, causing inflammation. Closed injuries lead to the development of aseptic (without infection) inflammation, which is then sometimes accompanied by an infection that penetrates through the blood from distant foci.
Predisposing factors that increase the risk of developing the disease are hypothermia, excess weight (high load on the joints), a sedentary lifestyle, hormonal disorders, heavy physical activity and frequent injuries.
Read about post-traumatic arthritis in this article.