The hip joint is the largest joint in the human body. This system connects the pelvic skeleton to the femur in such a way that the lower limb is mobile in different planes.
While walking, it is exposed to pressure from the entire upper body, meaning that the joint is subjected to significant stress every day. Like any systemic complex formation in the human body, the hip joint apparatus can be subject to a variety of injuries and pathologies during a person’s life: they can be associated with congenital developmental anomalies, unsuccessful mechanical action, or the presence of inflammatory processes and certain diseases.
What is the essence of the endoprosthetics procedure, why is it prescribed?
Content:
- What is the essence of the endoprosthetics procedure, why is it prescribed?
- Indications and contraindications for surgery
- Types of endoprosthetics: how a surgeon can help a patient
- How does a patient prepare for surgery?
- The day before surgery: what the patient can expect
- Carrying out endoprosthetics: intervention algorithm
- After surgery: patient's condition
- Postoperative period and return to normal life
Various degenerative-dystrophic lesions of the articular apparatus can develop in a person at any stage of his life. Their main danger is that, firstly, they only progress over time, and secondly, if medical assistance is not provided in time, a person may completely lose the ability to move independently and find himself bedridden. Diseases and pathologies of the hip joint can cause disability in the affected person.
Deforming arthrosis is especially common, in which a progressive pathological process gradually changes the shape of the articular elements, deforming them, as a result of which a person loses the mobility of the limb and constantly feels pain.
Conservative treatment in such cases is usually ineffective - it can only slow down the process, and only in the early stages. If the disease is advanced, the attending physician decides to perform endoprosthetics.
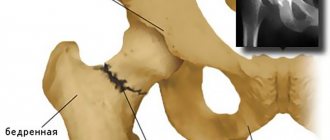
What is hip replacement? During the operation, the surgeon physically removes the affected elements of the articular apparatus and replaces them with artificial prostheses. The procedure is carried out to achieve several goals - eliminating pain in the joint, improving its mobility, returning the patient to his usual lifestyle, restoring his ability to walk and move.
Which joints most often have to be replaced with artificial prostheses?
Most often it is necessary to install artificial hip, knee, elbow, and shoulder joints. The joints of the lower extremities are especially often affected because they bear the greatest load.
Today, active developments are underway in the field of joint prosthetics in many countries around the world. There are many different types of artificial joints on the market. The multidisciplinary CELT clinic uses models of various modifications, which we consider the best choice. They fully restore the function of the limb, do not lead to the development of complications and can function successfully for a long time.
Indications and contraindications for surgery
In order to determine the need for surgery, the attending physician must first determine whether the patient has indications for it. Not every diagnosis, not every pathology and injury necessarily requires endoprosthetics. Typically, doctors are of the opinion that where the patient can be helped conservatively, it is better to start with conservative therapy. In addition, endoprosthetics surgery is complex and expensive, and not only the affected person, but also the surgeon himself needs to be specially prepared for its implementation.
Indications for endoprosthetics are:
- aseptic necrosis of the articular head;
- comminuted fractures of the femoral head;
- osteoarthritis of the joints, reaching 3-4 degrees;
- new hip fractures in patients over 65 years of age;
- false joints and non-union fractures of the femoral neck;
- joint damage caused by connective tissue diseases (ankylosing spondylitis, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus);
- tumors found in the neck and head of the femur.
What contraindications exist for the operation?
Despite its obvious value and benefits, replacing damaged joint elements is not possible in every case, and sometimes can even cause harm to the patient. Endoprosthesis replacement is not prescribed in the presence of tuberculosis, psychoneurological diseases, pathologies of the cardiovascular system, acute and chronic osteomyelitis.
Types of endoprosthetics: how a surgeon can help a patient
Depending on the extent of the planned operation, the patient may be prescribed:
- total;
- unipolar replacement of articular elements.
Total endoprosthetics means the complete replacement of all elements of the system with artificial prostheses.
Hemiarthroplasty, or unipolar replacement, is the replacement of only the head of the joint, while the original acetabulum remains in place. During this operation, only the endoprosthesis leg is implanted. Its unipolar head and acetabulum form a new joint.
In this case, the leg of the prosthesis is fixed in the bone with special bone cement or using a dense attachment. If a patient has weakened bones due to osteoprorosis, a more appropriate method is to strengthen the head of the prosthesis with cement.
Another differentiation involves dividing endoprosthetics operations into the following types:
- primary;
- revision.
The first type means that the joint is being replaced for the first time. In the second case, there is a need to eliminate problems associated with the operation of a previously installed artificial joint or its parts.
Implants for primary and revision surgery differ somewhat in design and functionality.
Another, separate type of endoprosthetics is the replacement of articular surfaces. This type of operation is increasingly used in relation to young patients. Superficial endoprosthetics makes it possible to preserve the native bone structure as much as possible, especially in the proximal femur.
Features of surgical interventions at the CELT clinic
Replacement of destroyed joints with endoprostheses in the multidisciplinary CELT clinic has some features.
Our surgeons practice minimally invasive interventions. All operations are performed through small incisions, with minimal tissue trauma and blood loss. A small, neat scar remains at the intervention site. The rehabilitation period takes a minimum of time, the patient can quickly return to their normal lifestyle. Restoration of performance also occurs in the shortest possible time.
How does a patient prepare for surgery?
Preparations for this complex operation begin several weeks before the scheduled date. Before hospitalization in a hospital, the patient must undergo a thorough examination, namely:
- visit a therapist;
- take x-rays and MRIs of the joint;
- pass a series of tests (blood, urine and others).
The results obtained are relevant not only for the surgeon, but also for the anesthesiologist, who, based on them, will select the appropriate drug to put the patient into a state of medicated sleep.
The patient must obtain permission for surgery from a physician - for this it is necessary to assess the condition and stages of all concomitant diseases in acute and chronic forms.
For example, the presence of hypertension in the affected person can become a serious obstacle to endoprosthetics. In this case, before a planned operation, the affected person must adjust the course of treatment in such a way as to stabilize blood pressure within normal limits as much as possible.
Under the supervision of a doctor, the patient begins to do a set of exercises for the muscles of the whole body in advance - this is necessary to achieve normal muscle shape during the operation. In addition, after the operation, the patient will need to get used to using crutches, walkers, and canes, which will require certain physical effort and level of training from his arms and torso.
It is advisable to choose crutches and walkers for yourself in advance so that during the recovery period you will be able to move more or less independently. You can even practice walking on crutches in advance.
Excess weight in a patient creates additional stress on the endoprosthesis - this must be taken into account when prescribing endoprosthesis. If the operation is planned for a distant date, an overweight patient should, if possible, take up the issue of losing weight, at least putting his diet plan in order.
2-3 weeks before surgery it is necessary to stop taking certain medications - this issue must be agreed with the attending physician, anesthesiologist and surgeon. All medications, including over-the-counter ones, that the affected person takes must be reported to the doctor in advance.
Preparation also includes a moral aspect, because during the period after the operation at home the patient will most likely need the help and care of another person, he may feel pain and inconvenience due to the need for significant restrictions during rehabilitation.
The home environment will also need to be prepared for the patient’s discharge after prosthetics:
- all frequently used items should be placed at hand level;
- if you don’t have a radiotelephone at home, it’s better to buy one;
- patients living in private houses with several floors should minimize the need to move across floors, for example, by moving their own bedroom to the ground floor;
- furniture should be rearranged so that it leaves enough space for walking with walkers and crutches;
- all rugs should be removed, and electrical wires, if they pass through walking areas, should be hidden;
- for small necessary items it is better to buy a small soft bag;
- If there are animals at home that can get underfoot, it is better to hand them over to relatives or friends for the first few weeks after surgery.
Rehabilitation after endoprosthetics
At the first stage, mainly basic rehabilitation models of simulators are used. The exercises are simple, without rotation in the hip joint. This activates the muscles and increases the range of motion of the leg. When the patient achieves the desired results, the next stage begins.
At the second stage of rehabilitation, an expanded range of new exercises is used for a deeper impact on the muscles that control joint movement. This allows you to make a block multifunctional Bubnovsky simulator (MTB).
The simulator eliminates dangerous axial loads, exercises are performed easily and comfortably. During training, special cuffs are used, and exercises are performed in a physiological mode.
At this stage, the main function of the joint is restored - rotation, that is, rotation. All classes are conducted under the supervision of an instructor and the supervision of the attending kinesiotherapist.
At the third stage of rehabilitation, the main task is to relieve the patient of additional support: crutches or a cane. Restore posture, return to the usual walking pattern, get rid of lameness.
The patient continues the course of training on simulators, but is supplemented by walking training in front of a mirror and, possibly, if indicated, articular ground gymnastics, sauna therapy, and cold douses.
In three rehabilitation courses, specialists at Dr. Bubnovsky's center completely return a person to a normal lifestyle and work. The sooner you start rehabilitation after hip replacement and take a preliminary course of preparation for surgery, the faster the recovery process will go.
After rehabilitation, the kinesiotherapist draws up a plan for individual physical activity for the patient, indicating the amount and type of everyday stress, restrictions and recommended exercises, and also draws up a plan for taking preventive classes at Dr. Bubnovsky’s center in the future.
Sign up for a consultation
Prices in your city
Russia
- Russia
- Kazakhstan
- Azerbaijan
- Belarus
- Kyrgyzstan
- Latvia
- Uzbekistan
- Ukraine
Moscow
- Adler
- Almetyevsk
- Anapa
- Angarsk
- Arkhangelsk
- Astrakhan
- Balashikha
- Barnaul
- Belgorod
- Biysk
- Blagoveshchensk
- Bratsk
- Bryansk
- Vladivostok
- Vladimir
- Vologda
- Voronezh
- Grozny
- Ivanovo
- Irkutsk
- Yoshkar-Ola
- Kazan
- Kaliningrad
- Kaluga
- Kemerovo
- Korolev
- Kostroma
- Kotlas
- Krasnodar
- Kyzyl
- Leninogorsk
- Magnitogorsk
- Makhachkala
- Moscow
- Naberezhnye Chelny
- Nazran
- Nalchik
- Nizhnekamsk
- Nizhny Novgorod
- Novodvinsk
- Novokuznetsk
- Novosibirsk
- October
- Omsk
- Pavlovo
- Penza
- Permian
- Petrozavodsk
- Pskov
- Pushkino
- Rostov-on-Don
- Ryazan
- Samara
- Saint Petersburg
- Saransk
- Saratov
- Sarov
- Sevastopol
- Sergiev Posad
- Smolensk
- Sochi
- Stary Oskol
- Sterlitamak
- Tambov
- Tomsk
- Tula
- Tyumen
- Ulan-Ude
- Ulyanovsk
- Ufa
- Khabarovsk
- Khimki
- Chelyabinsk
- Yaroslavl
Select a branch
- m. Aviamotornaya - Moscow, st. Aviamotornaya, 10, building 2
- m. Academicheskaya - Moscow, st. Dm. Ulyanova, 31
- metro station Altufyevo - Moscow, Altufevskoe highway, 70, building 2
- m. Bagrationovskaya - Moscow, st. Novozavodskaya, 27A
- m. Belorusskaya - Moscow, 1st st. Yamskogo Polya, 24
- m. Boulevard Dm. Donskoy - Moscow, st. Feodosiyskaya, 2
- metro station Butyrskaya - Moscow, 17th proezd Maryina Roshchi, 4, building 1
- m. Kashirskaya - Moscow, Kashirskoe highway, 43, building 4
- Khodynka metro station, CSKA metro station, Polezhaevskaya metro station - Moscow, Berezovaya Roshchi passage, 12
The day before surgery: what the patient can expect
To undergo endoprosthetics, the patient must be admitted to an inpatient clinic or hospital. After hospitalization, he is examined again by a therapist, a surgeon, and an anesthesiologist talks with him.
You should not drink alcohol the day before surgery. Meals during the day should be light, excluding foods that contribute to gas formation in the intestines.
10-12 hours before the start, it is forbidden to consume food and liquid. In the evening, you can do a cleansing enema and take a laxative.
The surgeon may require removal of hair from the surgical site, as well as removal of polish or gel coating from the nail plates.
Carrying out endoprosthetics: intervention algorithm
Before sending the patient on a gurney to the surgical ward, he will be asked to put on a compression stocking on the opposite leg, or bandage it up to the knee with an elastic bandage - this will prevent the formation of blood clots.
Next, the patient is given anesthesia - general or regional. Both types imply that the patient is in a state of medicated sleep, however, patient reviews of regional anesthesia are more optimistic - it is easier to wake up after it, and, in addition, even after waking up, pain relief continues for some time.
When the patient falls asleep, a catheter is inserted into his bladder.
The entire duration of the operation is usually 1-2 hours. In the process, the surgeon separates the damaged elements of the joint and installs artificial parts of the prosthesis in their place. To remove accumulated blood, a silicone drainage tube and a special “accordion” are installed in the wound to collect fluid from the postoperative wound.
After completing all the manipulations, the surgeon sutures the incisions, treats the wound and applies a certain type of bandage.
Complications
If the operation is performed incorrectly or if the specialist’s recommendations are not followed, the following complications are possible:
- Decreased joint mobility.
- Infection and accumulation of pus.
- Pain syndrome at rest and during movement.
- Implant dislocation (extremely rare).
- Formation of blood clots and varicose veins.
- Allergic reaction to the implant.
- Loosening of the apparatus.
To avoid serious consequences, follow all instructions from a specialist during rehabilitation. Find out all the contraindications in advance and undergo a comprehensive diagnosis. If, after surgery, acute pain in the joint appears and the body temperature rises, contact your doctor immediately.
After surgery: patient's condition
When the surgical procedures are completed, the patient is transferred to a ward under the supervision of a doctor. At first, he is prescribed antibacterial therapy with antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs. On the first day after surgery, the patient can already move in bed, but not too actively.
On the second day, you are allowed to sit up in bed, do breathing exercises and a certain type of exercise therapy - a therapeutic physical training complex.
Dosed exercise in the form of walking with support (crutches, walkers or playpen) begins on the third day.
Within a few days after prosthetics, the catheter is removed from the bladder. The normal condition after the intervention will be swelling of the leg, pain in the groin and in the joint itself, radiating to the limb. The patient may be prescribed pain medication.
Treatment of a postoperative wound consists of daily replacement of a sterile dressing, as well as cleaning its surface with aseptic solutions. Sutures can be removed 10-14 days after surgery. Then the patient is discharged from the hospital home. The rehabilitation process lies ahead of him.
Rehabilitation program at the Federal Scientific and Clinical Center FMBA
The Federal Scientific and Clinical Center of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency has developed a special rehabilitation program after endoprosthetics of large joints.
The early postoperative rehabilitation program lasts at least 3 days and includes the following components:
- Drawing up an individual program: a plan according to which your recovery will take place.
- Physical rehabilitation with an instructor: physical therapy with special exercises selected for you individually, taking into account the preoperative status and characteristics of the operation. An experienced and qualified instructor supervises the implementation and progress throughout the classes.
- Activation. An important component of rehabilitation. After surgery, the patient has a new, expanded range of motion and must learn to function within the new capabilities. For the first time after surgery, walking will be carried out with the help of additional devices, so the rehabilitation course includes learning to walk with crutches.
- Hardware physiotherapy (Electromyostimulation to prevent the development of muscle wasting, cryotherapy is an effective method of physiotherapy that accelerates the recovery process and other methods).
- Mobilization of the joints of the limbs - passive movement in the joints of the limbs to restore range of motion using the hands of a rehabilitation therapist or devices for passive movement development.
If pain occurs during rehabilitation, pain-relieving manipulations are performed (nerve blocks, installation of an epidural pump, etc.), which will help avoid discomfort and make rehabilitation comfortable and effective.