Description of the disease
It is not at all necessary to engage in extreme sports in order to break an arm or leg: car accidents, slippery winter sidewalks, wobbly stools and stairs with chipped steps regularly deliver patients to trauma departments of hospitals in Kyiv and the region.
Treatment of fractures and the long recovery period that follows are not always painless. To ensure that the limbs regain mobility and full functionality, the help of a highly qualified orthopedic traumatologist is necessary. Our clinic has specialists of this level, and we are ready to provide and monitor the entire treatment process.
Treatment of fractures: what fractures are treated at the Ladisten Clinic
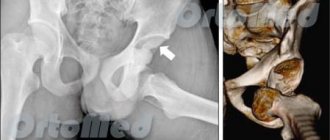
Treatment of fractures is a long, complex and labor-intensive process. Breaking is not building. Getting injured is easy, everyone is at risk. Going to the gym, rollerblading and cycling, slippery floors in restaurants, winter ice, osteoporosis[1] - the dangerous factors can be listed endlessly. Repairing a broken bone is difficult, but possible. The Ladisten Clinic treats open and closed fractures of varying complexity and location. A unique technique allows you to speed up the fusion process and quickly return a person to normal life.
Application therapy Lyapko
Lyapko applicators in various modifications (plates, rollers, application belts, application tapes) are an original, powerful device with many health-improving therapeutic capabilities. Their action is based on the principles of traditional Chinese medicine - superficial multi-needle acupuncture, as well as on the general physiological mechanisms of life.
Mechanisms of action of the applicator
The high healing effect of Lyapko applicators is due to a combination of intense reactions:
- reflex-mechanical;
- galvano-electric;
- immunological.
The clinical effects of the multi-needle therapy method are manifested in analgesic, antispasmodic, anti-inflammatory, anti-edematous, neurotrophic and immunomodulatory effects. Also in the regulation of the functions of the autonomic nervous system, normalization of the processes of excitation and inhibition in the central nervous system.
How are fractures treated?
A fracture is a violation of the integrity of a bone. There are two ways to restore it:
- Conservative _ Fractures of the arm, leg, finger and other organs are treated with a cast. The bone tissue grows together well. This mainly applies to closed injuries when the skin is not damaged. But the treatment of injuries and open fractures of the limbs is much more difficult.
- Operational . With an open fracture, the skin is damaged. The risk of infection increases, and the bone itself is difficult to return to its place and fix in the desired position. Polytrauma and multiple fractures after an accident often require surgery. The limb is returned to its place, bone fragments are collected, if possible. If fusion is not performed correctly, complications or disorders of the musculoskeletal system may occur. Then correction of limb disproportion is required.
Prevention and first aid for fractures
The term “fracture” usually refers to a bone injury in which its integrity is partially or completely disrupted. The fracture can be complete or partial, open or closed.
This serious injury requires mandatory and urgent medical attention.
Why do bones break?
Fractures most often occur due to a fall or blow, but some diseases can weaken the bones and cause them to break.
In addition, small cracks in the bone, called stress fractures, can occur from overuse.
The most common causes of fractures:
- blows; - unnatural body movements; - excessive physical activity; - falls; — accidents; — osteoporosis; - tumors of the bone and adjacent tissues.
Symptoms of a fracture:
- unnatural, deformed appearance of the limb; - swelling, large hematoma or bleeding; - severe pain in the injured limb; - numbness or tingling in the tissues of the injured limb; - limited mobility or complete loss of mobility.
First aid for fractures:
1. Stay calm. A broken bone requires urgent medical attention, so immediately take the victim to a medical facility or call an ambulance.
2. Do not move the victim, do not bend the injured limb or pull on it! Do not attempt to straighten a broken limb if the fracture is open.
3. Try to immobilize the injured limb. If the fracture is closed and you know how to apply a splint, do it. If you do not have knowledge of first aid, do not take any action with a broken limb.
4. If the fracture has caused an open wound, cover it with a clean bandage to stop the bleeding, but do not attempt to clean it or treat it with anything.
How are fractures treated?
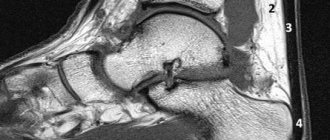
Attention! A fracture cannot be cured at home: it can lead to serious complications, including death. An X-ray examination is required to assess the severity of the fracture and order the examination.
Depending on the complexity of the fracture, surgical treatment or fixation of the broken limb with a splint or plaster may be prescribed. The victim may also need to be hospitalized.
How long does the treatment last?
Simple, uncomplicated fractures usually heal within four to six weeks. Some require treatment for several months, depending on the complexity of the injury and the presence of complications.
The pain usually goes away before the bones heal. However, while the bone is being restored, the muscles can seriously atrophy, and the tendons and ligaments can lose their elasticity.
Rehabilitation after fractures takes some time and includes exercises to develop flexibility, balance, and strengthen muscles and increase their mass.
To avoid repeated injuries, serious physical activity is possible only after complete restoration of the function of the injured limb.
The most important
A fracture occurs due to injury or disease that breaks the bone. The first signs of a fracture are pain and deformation of the limb.
Remember that fractures cannot be treated at home. Be sure to call an ambulance and, until it arrives, provide rest to the injured area of the body.
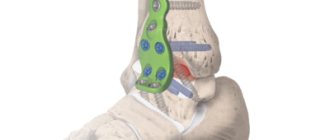
External fixation device in the treatment of fractures
Modern traumatology widely uses external fixation devices (EFDs) to restore damaged bones. The origins of their use were laid by Fabricius Hildanus back in 1614. A prototype of the first AVF, similar to a huge frame with screws. he created in 1629. Since then, attempts have been made to perfect the design. The peak of development occurred in the 50s of the Soviet era, when Ilizarov created his apparatus with spokes and rods. It is still studied and used all over the world.
When installing the device on a broken limb, the bones are pierced with special knitting needles, tightened and fixed with screws from the outside. This is done to join the fragments and stabilize the position of the bone. A person can safely move with the structure, restoring blood circulation and tissue exchange. This way the rehabilitation goes faster. With the help of the Ilizarov apparatus, even complex injuries can be treated, for example, fractures of the femoral neck, pelvis and others.
Unfortunately, world experience has shown that the device has a number of disadvantages. Those same needles pass close to nerves and arteries and can touch them. The bones are at risk of infection. Osteomyelitis is deadly and difficult to treat. Even a treated bone infection can leave a number of unpleasant consequences.
General recommendations
In the old days, healers, when treating fractures, practiced this method: they used a small file to cut copper powder from an old copper coin. A little of this powder (1/10 gram) was stirred in milk or sour cream, or rubbed with egg yolk and given to the patient orally, 2 times a week. This accelerated the healing of fractures.
You need to eat food rich in vitamins and microelements such as: manganese, copper, zinc, phosphorus, calcium, magnesium, vitamins B6, B9, B12, C, D, K. All these elements help absorb calcium and protein - from which the body and will build bone tissue.
It is advisable to use mumiyo internally and externally (in solution) on the fracture area.
In the first days, with pathology of muscles, bones and joints, you need to remain calm, but in the future you need to gradually increase physical activity. If muscles do not work, they quickly weaken and atrophy. Without load, the functioning of the ligamentous-articular apparatus is disrupted, which prolongs the process of recovery and recovery from injury, and increases the likelihood of injuries in the future.
After removing the cast, the muscles are always painfully tense, require gradual stretching, and the joints need to be “developed.” After removing the plaster, pain can appear in almost all parts of the back, since immobilization of both the upper and lower extremities after fractures leads to a gross violation of the stereotype of movements of the whole body and the appearance of pronounced asymmetries of the body.
Therefore, to prevent the appearance of muscle pain in the back, from the first days of the fracture, you should use flat applicators on your back for 20-30 minutes in the evening, roll your back with the “Large Roller M”, “Universal Roller M” in the morning and afternoon for 3-5 minutes (until a uniform pink color appears). Do a back massage using the Pharaoh massager.
When applying a plaster in the first days, severe swelling and increased pain at the fracture site often appear, leading to the need to cut into the plaster.
First of all, you need to use any flat applicators: “Romashka M”, “Insoles Plus”, “Quadro”, “Chance” on the lumbosacral zone of the spine, where the innervation to the limb comes from - the main zone, if there is access there.
Then it is recommended to act on all free surfaces of the legs above and below the fracture site (plaster cast), as well as on the healthy leg, focusing on the symmetrical site of the fracture, this reflexively reduces swelling and pain on the damaged limb. The impact can be carried out either with a flat applicator or with a roller. You can also use static-dynamic applicators: “Magic tape “Health”, belt “Universal M”, belt “Baby”. They need to be fixed on the limb for a longer time from 30 to 60 minutes 2-3 times a day.
For injuries, use the same technique. If the skin over the injured area of the limb is not damaged, then you can act on the site of injury. In case of bruises, to avoid the occurrence of swelling, hematomas, you can fix any flat applicator, application tape or roll it with a roller to this place.
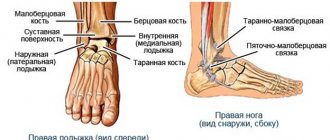
Application zones (Fig. 2): main 7.8; additional 18; auxiliary 26, 28, 30, (22, 27, 29).
Fig.2
Apply appliqué insoles to the feet or roll them with the “Large Roller M” or “Universal Roller M”.
The duration of exposure on the fractured side is 2 times longer than on the healthy leg. For example, we apply static applicators to the lumbosacral area and the sore leg for 15–20 minutes, and symmetrically to the healthy leg for 5–7 minutes. The same technique for injuries.
Additional recommendations. Good results are achieved by short-term effects on symmetrical zones of a healthy limb, correspondence zones on the hands and feet, used in Su Jok therapy (Fig. 3)
You can roll with a “Needle Ball”, “Large Roller M”, “Universal Roller M”, “Face Roller M”, and also press with the “Speck” applicator.
Fig.3
Improved technique
The Ladisten Orthopedics and Traumatology Clinic offers an alternative solution. Its founder, Dr. Veklich, improved the Ilizarov apparatus. The Veklich apparatus is installed in a minimally invasive way. It can be used to increase height or correct disproportion of limbs.
In case of bone injuries, surgical intervention to install the device cannot be avoided. Its design is almost identical to the Ilizarov apparatus, but instead of spokes, titanium rods with a diameter of 6 mm are used. The rod can be applied only on one side, reducing the risk of osteomyelitis significantly. It also does not come into contact with nerves and blood vessels. The entire structure is not too bulky and reliably holds damaged bone fragments.
Complications during the rehabilitation stage
During the rehabilitation stage after a limb fracture, a person may encounter a large number of complications. These complications do not happen to everyone, and they depend on the type of fracture, as well as the patient's level of care and self-care.
Many complications during the rehabilitation stage are associated with fractures that required surgical intervention. For example, during a surgical procedure, blood vessels or soft tissues may be injured, and after the operation, bleeding or suppuration of the wound may occur.
Complications such as improper healing of the fracture or the formation of a false joint, as well as skin necrosis, embolism, thromboembolism, etc. are possible.
Complications during the rehabilitation process are rare if treatment is carried out competently and the patient is well monitored. But the occurrence of complications also greatly depends on the person himself, so he must strictly follow the instructions of his doctors and observe the motor regimen prescribed to him.