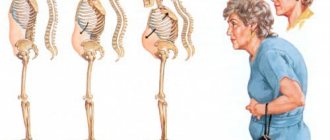
A lump on the neck in the spine area most often occurs in people over 35 years of age. The risk group includes women who spend most of the working day sitting - accountants, secretaries, managers, etc. Cervical osteochondrosis occurs as a result of muscle strain when a person spends the entire day with his head unnaturally tilted forward.
Cervical osteochondrosis is highly treatable with special gymnastics and external remedies. The main thing is not to start the problem. Otherwise, deformation of the intervertebral discs may begin, which will lead to a hernia.
Reasons for the formation of a lump
- Disease Lymphadenitis . This disease is associated with enlarged lymph nodes, in the area of the lump, the skin has a pinkish tint. This may be due to a viral or infectious disease, or inflammation of the salivary gland.
- Myogelosis . It occurs most often in women of mature age; usually a lump on the neck occurs due to physical activity. It can occur in people who often go to gyms and engage in heavy physical activity that the body cannot cope with. In this case, you need to talk to a trainer, review the exercise program and undergo a course of physiotherapeutic procedures and massage.
- Adrenal gland dysfunction . In this case, the lump in the back is very difficult to detect immediately. It is formed due to the active work of the adrenal glands. The arms and legs become thin, and the neck and face areas become covered with a layer of fat, so the lump is extremely difficult to detect.
- Osteochondrosis . The most common option. A lump on the spine can form due to spinal deformation, and is accompanied by symptoms such as fatigue, pain in the neck and back when turning the head, and dizziness. The causes of osteochondrosis are: sedentary lifestyle, sedentary lifestyle, scoliosis, poor posture. If osteochondrosis is not treated, hand motor skills and blood supply to the brain are impaired.
- Lipoma . This is a fatty tumor, a wen. The cause of this tumor is not clear, but scientists are inclined to have an abnormal metabolism. It is known that a lipoma can be of various sizes, up to 12 kg, and form a kind of hump at the back.
- Lymphogranulomatosis . This is the most dangerous type of lump on the neck. It is a large lump, without consistency. It is not accompanied by pain, so many people put off visiting a doctor because of this. There may be fatigue, fever, itchy skin. After liposuction, if the cause of the malfunction in the body is not found, the lump in the back may form again.
- Atheroma . This is a sebaceous gland cyst. It is accompanied by pain, swelling, suppuration, and high fever. Atheroma can be primary or secondary. Primary atheroma is easily treated. But the secondary one occurs against the background of skin diseases and spreads to the face and back. This is a very painful lump.
- Furuncle . Benign education. But you need to be careful with him. The boil may burst and pus may enter the bloodstream, causing blood poisoning. Is it dangerous. Consult a doctor, don't take risks. And pay attention to hygiene.
Cause 1: Osteoporosis of the bones
With age, the calcium content in bones decreases, they become more pliable and fragile. The spine loses its correct shape and bends more under the weight of the body.
Symptoms : visual defect, increasing with the onset of adulthood and old age. The risk of limb fractures increases due to minor injuries or falls. There are no independent pains. If the spinal curvature is severe, you may have difficulty breathing or swallowing food. How to confirm the diagnosis: tests, bone x-rays. What is useless: massage, poultices, gymnastics.
Treatment for a lump on the neck
Having discovered a lump on the neck, it is better not to put off the examination indefinitely in order to rule out a spinal cord tumor and get rid of it in a short time. It’s better to contact a specialist and get the necessary tests done right away, without delay.
Having found out the cause, you need to start treatment. The sooner you start treatment, the faster the results will be.
If the cause is osteochondrosis, then you need to go swimming, preferably on your back. It is also recommended to walk more and undergo a massage course twice a year. The bed must have an orthopedic mattress and an orthopedic pillow. See here how to choose a pillow for cervical osteochondrosis. Or at least the base of the bed should be hard and the pillow should be low. If you follow all these recommendations together, the lump on your neck will soon disappear. But the first step is to find out and remove the cause of osteochondrosis.
If the reason is improper functioning of the adrenal glands. Here the lump can only be removed surgically and fixed with medication.
If the lump is caused by strenuous activities in the gym, then it will be extremely difficult to get rid of it. The first step is to reduce the load on the body, because... Muscle mass is more difficult to remove than fat mass. And you need to take a massage course. Also, yoga classes give good results, but you need to practice with an experienced master.
If the reason is lipoma and atheroma, then they can only be removed with the help of a special operation. Or surgically, cutting the skin tissue, but in this case, a scar remains. Or laser, where the lump is opened and the contents are processed; this type of operation does not leave scars. Or radio wave surgery, where pus is removed using radio waves. It is painless and leaves no scars.
If the cause is an infectious disease, they undergo a special drug course of treatment. Along with this, they restore their immunity and take vitamins.
“Widow’s hump” - what can be done
In the initial stage of the fight against the “withers” or “widow’s hump”, homemade manual massages and simple gymnastics , designed to enhance local metabolism and strengthen muscle tissue that forms correct posture . Massages should be light and gentle (see examples in the video below), in this case regularity is much more important than attacking the problem “at once” with diligence worthy of better use. No rolling pins or other devices!
But if the “withers” have existed for quite a long time, are hard to the touch, and in general on the body in the “fat trap zone” the subcutaneous fatty tissue is dense fibrous tissue, then you will not achieve anything with self-massage. In some cases, patients cannot even fully reach the back of their neck with their hands (reduced mobility of the shoulder area), much less stretch this area on their own.
Hardware procedures will come to the rescue : vacuum roller massage and cavitation (ultrasonic lipolysis). In some cases, lipolytic injections are additionally prescribed - but they are an additional technique and only work well in combination.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies should not be excluded from the course of treatment. White cabbage is the best remedy for resolving bumps on the neck. Compresses are made from it, after beating it, releasing the cabbage juice, the leaf is placed on the cone, then cellophane is placed, and a diaper, scarf or handkerchief is placed on top, and left overnight. You can also coat the leaf with honey to enhance the effect. But if suppuration is detected, then the cabbage lotion cannot be used. In this case, you can apply an aloe leaf. There are also absorbable ointments on sale, but they can be used if the lump was formed as a result of accidents or injuries.
You can regularly apply herbal compresses (chamomile, sage) to the problem area of the neck.
Keep your body in great shape, lead an active lifestyle, walk more, smile, be positive, eat more vitamins and minerals, and do physical therapy.
Furuncle
This is a neoplasm that forms at the site of damage to the skin and infection with Staphylococcus aureus. It is purulent-necrotic in nature. It is characterized by a small bump that rises above the skin. When it matures, the capsule bursts and its contents (pus) erupt out. When this does not happen, the inflammatory process increases, causing a lot of inconvenience. The danger of a boil is that if it is removed and treated incorrectly, there is a high probability of relapse.
The following categories of people are at risk:
- obese;
- not observing the rules of personal hygiene;
- those who like to squeeze out pimples and blackheads.
Type of pain
Aching pain, which is accompanied by the formation of a tubercle filled with purulent contents.
Localization
The pain is concentrated directly in the area of the boil, but can spread to the entire area of the neck.
Diagnostics
The furuncle is visualized during a contact examination, but for a more accurate diagnosis the following studies will be required:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- blood for sterility;
- scraping from the surface of the boil, which makes it possible to identify the causative agent of the inflammatory process;
- consultation with an immunologist to determine the level of immunity and resistance to pathogenic microflora.
Treatment
In the case where the boil has clear boundaries and ripens on its own, this process must be accelerated. Ointments and creams are used that help draw out the abscess from the skin. Dressings are done frequently - 3-4 times a day, each time wiping the fistula with an alcohol solution, disinfecting the surface.
Onions have proven themselves well. A cut of the onion is fried in a dry frying pan for 2-3 minutes until softened, after which it is applied to the cone, wrapped tightly with a sterile bandage.
At an advanced stage of the boil, its artificial excision is required. To do this, a small incision is made with a scalpel, after which the boil cavity is cleaned using special surgical instruments.
Lump on a child's neck
A child may develop a lump on the spine as a result of some kind of injury. It may be accompanied by vomiting, dizziness, and nausea. The child must be urgently taken to the hospital, where he will receive emergency care. Don't try to get rid of it yourself.
Children need to strengthen their immune system, drink a complex of vitamins in the cold season, and take sunbathing in the warm season.
Any lump on your neck should be taken seriously. From benign neoplasms, without treatment, they can easily turn into malignant ones.
Squeezing out the bump is strictly prohibited! Do not heat, do not cool! All treatment should be carried out only after examination. Most often, the lump is removed with a laser; this leaves no scars and the rehabilitation period is very short. Take care of yourself!
Diagnostics
First of all, ultrasound is used to look for fatty deposits. An X-ray examination is carried out if osteochondrosis of the cervical spine or curvature is suspected. Magnetic resonance imaging is universal and is most likely to immediately determine the source of the development of pathology and growth of the hump. Blood and urine tests will not give any results.
The truth about treatment: analysis of the effectiveness of all tactics
Do medications help?
In the acute period, doctors prescribe medications for pain, inflammation and swelling for local and internal use to relieve painful manifestations of the disease. The basis of such drug therapy is NSAIDs:
- Indomethacin;
- Ibuprofen;
- Meloxicam;
- Diclofenac.
In addition to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for pain, specialists prescribe medications from a series of analgesics:
- Analgin;
- Spasmalgon;
- Ketorol.
If the clinical picture is aggravated by muscle hypertonicity, muscle relaxants are recommended to relax the spasmodic muscle structures. Among the most used muscle relaxants are Mydocalm and Siralud.
With constant debilitating pain, which NSAIDs and analgesics cannot cope with, a transition to treatment with strong hormonal or anesthetic drugs is carried out. These include glucocorticosteroids, lidocaine and novocaine. Using powerful hormone-containing and anesthetic agents, only as prescribed by a doctor in specialized conditions, the patient is given a course of spinal blockades. In the very near future, a person with such a critically unsafe diagnosis needs to undergo surgery.
All of the listed drugs act purely symptomatically: there will be no effect in terms of reducing the hernia component. In fact, they only temporarily relieve pain by blocking the transmission of nerve-pain impulses in the problem area. They also have a moderate anti-inflammatory effect. All intervertebral deformations and degenerations still do not disappear.
Note that limiting yourself only to drug therapy, even if it helps to get rid of pain, is the height of recklessness. With this approach, a hernia of the cervical spine will soon remind itself, and next time in a more vivid manifestation. But the worst thing is that, living only on painkillers, intervertebral pathogenesis will actively progress, increasing the risk of disability more and more every day.
Achieving stable remission through a drug regimen in complex combination with other conservative methods, as observations show, is not always achievable. If the initially prescribed complex treatment for 3 months, maximum 6 months, does not lead to tangible and lasting improvements, the patient is recommended to undergo surgery.
Long-term internal use of pain medications or their injection method is fraught with the development of side effects - stomach ulcers, liver and kidney diseases, hematopoietic and immune systems. External agents - gels, creams, ointments - have less negative reactions. But in terms of the strength of the analgesic effect they provide, they are significantly inferior to oral medications and injections.
It is impossible not to say a few words about popular chondroprotectors, the action of which is aimed at improving metabolism and activating nutrition in osteochondral structures. Remember, their benefits have been clinically confirmed exclusively for osteochondrosis that has not developed into a cervical hernia. It is acceptable to use such drugs for small protusions as a preventive measure for further degeneration of the cervical intervertebral disc. But! When hernia has already occurred, chondroprotectors are ineffective or “don’t work” at all. When a global restructuring of the disk contents into an irreversible (!) non-viable state has already occurred, they do not provide any therapeutic or prophylactic benefit.
Kinds
Thus, it is already clear that all neoplasms are divided into malignant and benign. Benign tumors often do not pose a serious threat to human life and health, only sometimes they can cause radicular syndrome, vertebral compression fractures and other complications. They are most common in young people, while the risk of developing cancer progressively increases with age.
A compression fracture is a destruction of the vertebral body with a decrease in its height along the entire perimeter, and more often in the posterior part with the formation of a defect that looks like a wedge.
It is malignant tumors that pose a particular danger, but they are formed in the spine initially, that is, they are primary, in less than 4% of cases. Almost always they are metastases, i.e. secondary tumors formed as a result of malignant cells entering the spine and surrounding tissues through the blood or lymph flow from tumors of other organs, usually the prostate gland, mammary glands, kidneys, thyroid gland , lungs, bladder.
Most often, metastases affect the lower thoracic and upper lumbar spine. Malignant cells that enter them and begin to multiply put pressure on nerve fibers, intervertebral discs, and the spinal cord; they can provoke a decrease in the density of the bone structures of the spine and cause instability of the vertebrae. This leads to the fact that patients may not only suffer from manifestations of radicular syndrome, but may also encounter signs of spinal cord damage, death of nervous tissue, vertebral compression fractures, and spondylolisthesis.
On the other hand, primary tumors of the spine, although rare, can also metastasize to other organs, including bones, liver, lungs, lymph nodes, brain, etc. Most often, the spine is affected by the following types of malignant tumors:
- Chondrosarcoma - forms from cartilage tissue on the vertebral arches, but quickly spreads to adjacent structures of the spine and ribs. Most often, chondrosarcomas are diagnosed in the lumbosacral region.
- Ewing's sarcoma is an oncological disease characteristic primarily of children, in which a malignant tumor forms in the vertebrae and surrounding soft tissues. This is a highly aggressive neoplasm, prone to metastasize in the shortest possible time to other parts of the skeleton, lymph nodes and lungs. Often its development and growth leads to the formation of a hematoma in the spine, which significantly worsens the patient’s condition and increases the risk of complications.
- Chondroma - is formed from the remnants of the notochord, i.e. embryonic cells from which the spine was formed during fetal development. Most often, chondroma affects the sacrococcygeal spine.
- Osteosarcoma is the most common malignant tumor of the spine. It is found in 50% of cases of confirmed spinal cancer. Osteosarcoma is formed from bone tissue and is prone to active metastasis.
- Reticulosarcoma is formed from lymphocytes and tends to cause acute neurological disorders, severe pain and provoke fractures of the affected vertebrae.
Malignant tumors extremely rarely form intramedullary, i.e., they affect the substance of the spinal cord. This could be, for example, a neuroectodermal tumor arising from neutral precursor cells. But due to the peculiarities of their location, such tumors are inoperable, i.e. they cannot be subjected to radical treatment. Their growth is suppressed by conservative means, so such neoplasms have an unfavorable prognosis.
The best prospects open up for extradural, i.e., those formed in the bone, and extramedullary intradural tumors, i.e., located within the spinal membranes. They can be removed surgically, which significantly increases the chances of a full recovery.
Benign tumors of the spine can be represented by:
- hemangioma;
- osteochondroma;
- osteoid osteoma;
- osteoblastoma;
- eosinophilic granuloma;
- aneurysmal bone cysts.
In addition, other benign tumors that are not related to the spine can form on the back. These can be atheromas or lipomas, i.e. tumors of subcutaneous fat.
Hemangioma
Spinal hemangioma is a vascular tumor, which in most cases is congenital and much less likely to form during life. It is one of the least dangerous neoplasms and is formed from endothelial cells in the thickness of the cancellous bone of the vertebra.
Hemangiomas account for 10-12.5% of all spinal tumors.
Most often, hemangiomas are found in the thoracic spine, somewhat less frequently in the lumbar spine, and extremely rarely in the cervical spine. As a rule, the tumor behaves calmly and does not require treatment, especially if its size does not exceed 1 cm, but it definitely needs dynamic monitoring. If during the examination it is discovered that the hemangioma has reached a large size, surgical intervention is recommended, as this is associated with the risk of a vertebral compression fracture. In general, hemangiomas have a positive prognosis, especially with timely surgery.
Osteochondroma
Osteochondroma is a nodular neoplasm that forms on the surface of bone tissue, with areas of calcified cartilaginous tissue. Its anterior surface is covered with smooth cartilage. Osteochondroma usually affects the spinous processes of the vertebrae and occurs in children around the age of 10 years. The tumor grows over 15-16 years and can be detected and removed at any stage of development. The prognosis is favorable.
Osteochondroma is the most common tumor of the spine. This is what is diagnosed in 36% of cases of detection of tumors in the spine.
Osteoid osteoma
Osteoid osteoma is a round tumor formed from osteoclasts and affecting bone tissue. Most often it is found in the lumbar spine and affects the articular processes of the vertebrae, involving the posterior structures of the vertebra, in particular the arch, in the pathological process. The tumor can be removed and has a favorable prognosis.
Osteoid osteoma is diagnosed in 10-12% of cases of detection of spinal tumors.
Osteoblastoma
Osteoblastoma or giant cell tumor is similar in many ways to osteoid osteoma, but is much larger in size. Such neoplasms are very rare and are diagnosed in only 1% of patients with spinal tumors, and most often this occurs in patients under 30 years of age, mostly men. Osteoblastoma is characterized by a sensation of the presence of a foreign body in the spine. Treatment is surgical, prognosis is favorable.
Eosinophilic granuloma
This type of benign tumor of the spine is an infiltrate, saturated with macrophages and affecting the bone tissue of the vertebrae. It is a rare phenomenon and has extremely mild symptoms. Initially, eosinophilic granuloma causes increased fatigue, limited movement in the affected area and mild pain during physical activity. But the formation of a tumor can also be completely asymptomatic, which is its main danger.
If persisted for a long time, eosinophilic granuloma of the spine can provoke spinal deformities, cause hypertonicity of the back muscles, and lead to severe pain and gait disturbances. Depending on the complexity of the situation, treatment can be conservative or surgical.
Aneurysmal bone cysts
Bone cysts are benign tumors filled with blood and located within the hard structures of the spine. They most often form in the cervical region at the back of the vertebrae or just inside the vertebral body. Aneurysmal bone cysts can act as a consequence of spinal injury. Treatment is surgical, the prognosis is favorable.
Complications and consequences of the disease
The cervical region is the narrowest part of the spinal system, in which the largest arteriovascular highway passes. The department includes the largest arteries - the left, right vertebral and basilar, each of which forms up to 6 groups of vascular branches.
In the back of the neck there is also an important cervical nerve bundle (node), which consists of the hypoglossal, lesser occipital, greater auditory, transverse, and supraclavicular nerves.
Thus, even slight deformations of the disc, displacement of the vertebrae in an overly narrow area, densely penetrated by nerves and blood vessels, can cause a real catastrophe:
- clamping of arteries and nerve roots, constant severe pain;
- blocking the circulation of blood and cerebrospinal fluid between the spinal cord and brain with severe cerebro-vertebral signs;
- neurotic nature of auditory and visual disturbances, frequent loss of consciousness, coordination disorders;
- serious dysfunctions of the gastrointestinal tract (nausea, vomiting, fecal incontinence), urinary system (uncontrolled urination) and genital organs (impotence, frigidity, infertility);
- muscle weakness of the arms, including complete or partial paralysis;
- depression of respiratory functions due to severe damage to the spinal substance and nerve nodes, up to the cessation of breathing;
- insufficient blood supply to the brain, which can lead to cerebral ischemia and stroke.