Author, editor and medical expert – Yulia Yuryevna Muraeva.
Number of views: 189 735
Last updated date: 08/26/2021
Average reading time: 13 minutes
Back pain (synonymous with dorsalgia) is one of the most common reasons for visiting a doctor - second only to acute respiratory diseases1. Most often, such complaints come to a neurologist, therapist or general practitioner. According to international studies, from 19 to 43% of the adult population who were examined recently reported back pain during the last month, from 27 to 65% over the last year. Those who have experienced this at least once in their lives number 59-84%1. Almost every fifth adult on our planet may be experiencing severe back pain at this minute2. Their most common location is the lower back and lower back2.
Up to contents
Why do back and lower back pain occur?
Among the main causes of back pain are 2:
- Vertebrogenic causes – associated with spinal pathology:
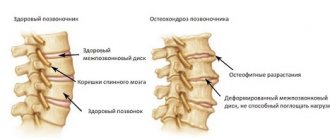
- pathology of intervertebral discs, including hernias;
- narrowing of the spinal canal;
- joint diseases;
- consequences of injuries;
- congenital defects and developmental anomalies;
- metabolic disorders;
- spondylitis – inflammatory processes in the intervertebral joints.
- Nonvertebrogenic - not associated with pathology of the spinal column:
- sprains and muscles associated with heavy loads;
- myofascial syndrome – chronic muscle pain;
- inflammation of muscle tissue - myositis;
- diseases of internal organs;
- pathology of large vessels, for example, aneurysm (sharp expansion) of the abdominal aorta;
- arthrosis of the hip joint is an inflammatory-dystrophic disease;
- mental disorders, etc.
Depending on the origin, the following types of pain are distinguished:
- Specific - associated with a specific disease that can be detected by standard examination methods. This type accounts for up to 3%1 of all cases. These could be compression fractures of the spine, tumors, infectious processes, diseases of the pelvic organs (especially with back pain in women).
At the same time, there are a number of specific symptoms, so-called “red flags”, which indicate serious illnesses and require in-depth examination. These include:
— rapid causeless loss of body weight and/or indication of oncological pathology in the past (tumors);
- weakness in the lower extremities, impaired sensitivity and function of the pelvic organs (cauda equina syndrome);
- use of antibiotic therapy, increase in body temperature (infectious processes);
- trauma or established diagnosis of osteoporosis in the past, age over 55 years (vertebral fracture);
- young age - up to 20 years;
- long-term persistence of painful sensations and their intensity, despite treatment.
- combined with general weakness or gait disturbance, worsens at night, does not change with changes in body position
- Radicular is the next most common (up to 27%). It develops as a result of pinching and/or inflammation of the spinal cord root, which exits through the openings of the spinal column. This type may be indicated by increased pain when coughing, sneezing, exercise, and other activities.
- Nonspecific - often acute; it can be difficult to immediately determine the specific cause of its development; it is usually the consequence of dystrophic changes in the bone and cartilage tissue of the spine, as well as the muscles and ligaments that make up the supporting apparatus of the back. In the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10) there is a special section for defining such syndromes - dorsopathies.
Such dorsalgia accounts for up to 85%1 of all cases and is mainly associated with disruption of the normal functioning of individual structures of the spine, any of which can become a source of pain impulses. The pain can be compression (from compression of the nerve roots) and reflex - from all other tissues, including spasmed muscles.
Another type of pain syndrome is described, which is not associated with any organic lesions of the spine and paravertebral tissues. This is the so-called dysfunctional pain3. It can be caused by psychological problems and chronic stress.
According to localization they distinguish:
| What is the name of | Where does it hurt |
| cervicalgia | pain in the neck |
| cervicocranilagia | neck+head |
| cervicobrachialgia | neck and gives it to the hand |
| thoracalgia | pain in the thoracic region of the back and chest, pain under the shoulder blades from the back |
| lumbodynia | lower back and lumbosacral region |
| sciatica | lower back+leg |
| sacralgia | sacrum |
| coccydynia | coccyx |
In addition to the reasons, we can identify factors that can provoke the development of pain4:
- severe physical overload, resulting in overstretching of muscles and ligaments;
- uncomfortable or static positions that a person holds for a long time;
- untrained muscles and their overload, lack of mobility;
- trauma and microtrauma;
- hypothermia;
- prolonged immobility, for example, bed rest;
- alcohol abuse;
- diseases of internal organs;
- joint pathology;
- overweight;
- individual characteristics: curvature of the spine, stoop;
- poor nutrition, diseases of the digestive system3, which may be accompanied by disturbances in the absorption of vitamins, mineral metabolism, and a significant intake of salts that affect the joints;
- occupational hazards: thermal effects, temperature fluctuations, vibration, working with heavy objects, etc.
The mechanism of development of back and lower back pain is associated with a block of intervertebral joints, which can be caused by loads, both static and dynamic, microtraumas and non-physiological postures. As a result, in one place the muscles spasm and overstrain, and in another they are overstretched. All this leads to the development of muscle pain, changes in pain sensitivity and the formation of pathological pain impulses.
Also, muscle spasm can be a reflex reaction to pathology of the spine or diseases of the internal organs. In this case, it is seen as a defensive reaction, but at the same time, it starts a new circle of pain. In addition, if the spasm persists for a long time, the transmission of nerve impulses to the muscle fibers is disrupted, they become more excitable, calcium deficiency may occur, and circulatory disorders further aggravate the situation.
According to the duration of dorsalgia there can be 2:
— acute – lasting up to 6 weeks;
- subacute - from 6 to 12 weeks;
- chronic - lasting from 12 weeks or longer.
Up to contents
Pain in the left side behind in the area of the kidney and lower back
Pain in the left side behind in the area of the kidney and lower back
Any pain indicates that not everything is in order in the body. It is especially worth paying attention to frequently recurring or persistent pain. In this case, you should not postpone visiting a doctor, since only a specialist will be able to correctly identify the cause and prescribe appropriate treatment. Based on the location, intensity and nature of the pain syndrome, as well as accompanying symptoms, you can draw your own conclusions about which organ the problems started with. So, if the pain is localized in the left half of the back, namely the kidney area, then problems may be associated with the urinary system, spleen or intestines.
Probable Causes
Pain in the left side behind most often indicates heart disease. If it is localized just below the scapula, it may indicate the following diseases:
- pericarditis;
- angina pectoris;
- myocardial infarction.
Moreover, if the problem is related to a heart attack, then sharp, sharp pain sensations are usually localized in the chest area. But they can affect the left half of the body, namely the lower back, or under the shoulder blade. That is why it is very difficult to determine without diagnosis what causes such pain. However, the following accompanying symptoms may indicate that the problems are related to the heart and not the kidneys:
Important: if the accompanying symptoms listed above appear, you must urgently call an ambulance.
Pain in the kidney area
If the left side behind in the kidney area hurts, then this may be caused by ailments of the urinary system, namely:
An attack of so-called renal colic due to urolithiasis. As a rule, nagging, mild pain is accompanied by urolithiasis at the initial stage. If the stones have just begun to form, the person may feel a dull pain from time to time. If the stone begins to move along the urinary tract, severe pain will appear, which is called renal colic. Moreover, its intensity and localization do not depend on changes in body position. No less severe pain will occur if the urinary duct is blocked by a calculus. Associated symptoms:
- blood in urine;
- temperature increase;
- deterioration in general health;
- Problems with urine excretion often occur.
Most often, pain in the left side behind with kidney problems is caused by pyelonephritis. This inflammatory disease of the pelvis of the organ is caused by infections. In addition to pressing and aching pain, other characteristic symptoms are also noted:
- temperature increase;
- general malaise;
- nausea and vomiting;
- no appetite;
- swelling in the morning;
- pale skin;
- frequent urge to urinate;
- pain in the process of urination.
Glomerulonephritis. In this disease, the inflammatory process is localized in the area of the renal tubules and glomeruli. Often the cause of the disease is streptococcal infection. Most often, the problem is localized on both kidneys, but unilateral damage can also occur. There are other signs of this disease:
- fatigue, lethargy;
- pallor;
- severe swelling in the morning and weight gain of the patient;
- a sharp increase in blood pressure to high levels;
- decrease in daily urine volume (less than a liter);
- Due to the ingress of blood, the urine takes on the color of meat slop.
Pain in the left side may also be due to thrombosis of the arteries of the kidneys. In this case, the symptoms are very similar to hypertension. If a cholesterol plaque clogs the artery duct, then due to the disruption of blood flow, a disruption occurs in the process of urine formation. This causes aching pain and increases blood pressure. Thrombosis of the renal arteries. If a detached blood clot blocks the lumen of the artery, then severe pain occurs, radiating to other parts of the body. Associated symptoms:
- constipation, vomiting and nausea;
- increased blood pressure;
- heat;
- decrease in the amount of urine or its absence.
Nephroptosis can cause pain in the left side behind. Nephroptosis is called prolapse of the kidney. This condition can be caused by various reasons. When the artery prolapses, the kidneys can be compressed, which causes poor circulation in the organ and pain. Also, pain can occur due to kinking of the ureter and disruption of the outflow of urine. The main feature of this condition is increased pain in an upright position and the ineffectiveness of using analgesics. Kidney cysts can cause nagging pain from the affected organ. These pathological neoplasms can be acquired or congenital. Associated symptoms: increased blood pressure, blood in the urine, frequent infections of the urinary system. But more often they exist asymptomatically, and pain occurs in the following cases:
- if a large cyst puts pressure on surrounding tissues and organs;
- overstretching of the kidney capsule;
- disturbance of urine outflow.
behind can be present for a long time with kidney cancer
Malignant and benign neoplasms of the organ. In the initial stages, these pathologies do not produce any symptoms. The first sign of trouble may be heaviness in the kidney area. Dull pain in the left side behind can be present for a long time with kidney cancer. In this case, at first the pain is very mild, but as the disease progresses, its intensity increases. With kidney cancer, there are accompanying signs of the disease:
- lack of appetite;
- drowsiness;
- increased fatigue;
- the patient loses weight;
- general malaise;
- anemia;
- pale skin;
- blood in urine;
- constant low-grade fever;
- high pressure.
Hydronephrosis. With this disease, urine stagnates in the renal pelvis and causes overstretching of the renal pelvis. There are different causes of hydronephrosis. In this case, painful sensations can radiate to other parts of the body and legs. Very often the symptoms of the disease are confused with problems of the digestive tract. Frequent infections of the urinary system may indirectly indicate the presence of this pathology. Children experience bloating, nausea, vomiting and digestive disorders. Often severe and long-lasting hydronephrosis causes developmental delays in children. Kidney tuberculosis at a later stage can cause stabbing pain in the area of the affected organ. At the initial stage, there is no pain, there is only a feeling of general weakness, lethargy and increased fatigue. If pain appears, then in terms of intensity and spontaneity it can be compared with renal colic. In addition, there are accompanying signs of the disease:
- blood and pus in the urine;
- cloudy urine.
Pain on the left just above the lower back
If pain occurs in the left side behind in the lumbar region, or rather, in the upper part, then they may not necessarily be associated with the kidneys. In this case, aching pain may indicate the following diseases:
- osteochondrosis;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- gastritis and ulcers;
- pneumonia;
- various ailments of the digestive system;
- spinal injuries;
- physiological conditions during pregnancy;
- after previously suffering from tuberculosis.
Pain in the hypochondrium when inhaling
If pain is localized under the lower ribs on the left and intensifies when inhaling, then they can be associated with heart disease, pneumonia, hernia, rupture of the spleen, diseases of the esophagus, and muscle pathologies. In this case, the cause of the painful syndrome can often be identified by the nature of the pain:
- Severe, sharp pain often appears unexpectedly. It may indicate life-threatening conditions and diseases such as rupture of the renal pelvis or spleen. Since these conditions threaten the patient’s life, you should immediately call an ambulance.
- Prolonged dull pain may indicate the presence of a chronic disease. They can be due to chronic kidney problems, gastritis or pancreatitis.
- Pulsating, incessant pain indicates the presence of a chronic inflammatory process in any organ. More often this is associated with chronic pyelonephritis, colitis, and peptic ulcer. If such pain occurs frequently, it may indicate a pre-infarction condition.
Aching pain in the lower back
Pain syndrome with such localization can be acute or dull in intensity. Moreover, it most often indicates problems with the spine, especially if there are no other symptoms characteristic of kidney diseases.
Lower back pain can be caused by the following diseases and conditions:
- osteochondrosis;
- excessive physical activity;
- prolonged sitting;
- intervertebral hernia;
- stenosis;
- spondylolisthesis;
- spinal arthritis;
- spine fracture;
- tumors of the spinal column;
- osteomyelitis.
Symptoms
Symptoms of dorsalgia depend on the cause, mechanism of development and the presence of concomitant diseases.
Nonspecific pain is characterized by the following symptoms:
- aching or nagging pain, sometimes tightening,
- increases with load or movements of the spine, as well as in certain poses,
- may decrease with kneading or rubbing the muscles, as well as after resting in a comfortable position;
- possible pain in the sides of the back or pain in the back,
- upon palpation, compaction, changes in contours, and tension are determined, but there are no disturbances in sensitivity in the painful area, a decrease in muscle strength, and reflexes do not change.
When a nerve root is compressed (radiculopathy), the pain varies in intensity, can be shooting, and often radiates to the leg, and in the limb it can be stronger than in the back. Upon examination, symptoms of damage to a specific nerve root are observed - muscle weakness, loss of sensitivity in a certain area.
Up to contents
Diseases of the spine and intercostal nerves
With thoracic osteochondrosis and intercostal neuralgia, pain is sometimes localized in the upper abdomen on the right. Even an experienced doctor cannot always immediately figure out why a patient has pain under the right rib. There are atypical cases; during an examination, the doctor can make one diagnosis, but the examination shows that the source of the problem is in a completely different organ.
Don't self-diagnose. It’s better to play it safe and see a doctor on time than to miss a serious illness and lead to serious complications. Make an appointment with a specialist and undergo a comprehensive examination at the international clinic Medica24: +7 (495) 230-00-01.
Diagnostics
The diagnostic algorithm for acute and chronic dorsalgia is somewhat different.
Acute pain5
In order to decide on treatment tactics, the doctor must, if possible, determine the cause of the pain syndrome: pinched nerves or their roots, trauma, tumors, inflammation, infections, osteoporosis, diseases of internal organs, etc. As a rule, these types of pain have quite clear and specific clinical manifestations. After examination and palpation, patients are referred to appropriate specialists or for further examination, for example:
- X-ray examination;
- MRI and CT of the spine;
- scintigraphy is a visualization method using a contrast agent;
- densitometry – determination of bone tissue density;
- laboratory tests to determine tumor markers, rheumatic tests, biochemical blood tests, etc.
Patients with nonspecific acute pain usually do not require additional testing3.
Chronic pain
Since the mechanisms of its development have not yet been sufficiently studied, identifying the source can be problematic, especially if it is a dysfunctional type that reflects the pathology of other organs. It may be a manifestation of diseases such as irritable bowel syndrome, chronic cystitis, chronic pyelonephritis and others5. In any case, a thorough interview and examination of the patient is carried out to decide on further treatment tactics.
For pain syndrome that occurs against the background of degenerative changes in the joints, after any mechanical stress or under the influence of other factors, it is possible to use magnetic resonance imaging to monitor the dynamics of the condition of the spine.
Up to contents
How to deal with acute back pain
Doctors who adhere to the principles of evidence-based medicine use the following tactics for managing patients with acute dorsalgia5:
- inform the patient about the causes of pain,
- exclude bed rest and recommend maintaining usual activity,
- prescribe effective drug and non-drug treatment,
- monitor dynamics and adjust therapy.
When choosing a medication, pay attention to its analgesic effect, speed of action and safety. Nonspecific anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are prescribed first, as they have been proven effective for back pain5. One such drug is Motrin®.
Motrin® is available as tablets for oral administration and gel for external use. The drug is indicated as an analgesic for back pain associated with injury, overload, and inflammation. It also has anti-inflammatory and antipyretic effects, the effect can last up to 12 hours6,7. If you are unable to visit a doctor in the near future, and the pain causes significant discomfort, then you can take Motrin® as follows: 2 tablets as a starting dose and then 2 tablets every 12 hours or 1 tablet every 8 hours. The course of admission without consulting a doctor is no longer than 5 days6.
If the intensity of the pain remains, it is possible to prescribe other groups of painkillers and sedatives (sedatives).
Non-drug treatments include:
- warming;
- manual therapy;
- physiotherapy;
- massage;
- physiotherapy;
- acupuncture and other alternative methods.
Up to contents
Pain in the right hypochondrium associated with liver and gallbladder diseases
The most severe pain under the right rib occurs with biliary colic as a result of blocking the lumen of the bile ducts with a stone and their spasm.
Usually colic occurs after errors in the diet. Our expert in this field:
Allahverdyan Alexander Sergeevich
Surgeon-oncologist, professor, MD. Head of the ROH expert group. International expert
Call the doctor Reviews about the doctor
Dull pain in the right hypochondrium and in the pit of the stomach is characteristic of cholecystitis. They are usually provoked by errors in diet and last from several minutes to several days. Acute cholangitis - inflammation of the bile ducts - manifests itself in the form of acute pain under the right rib, reminiscent of biliary colic, increased body temperature, and jaundice. In chronic cholangitis, the pain is dull. Aching pain is characteristic of biliary dyskinesia.
Pain in combination with other symptoms may indicate hepatitis, cirrhosis, or liver cancer.
Pain in the right hypochondrium occurs after physical activity in untrained people - due to the fact that a lot of blood is deposited in the veins of the liver.
Treatment of chronic back pain
If the localization of pain and the source of pain impulses can be identified, then local therapy is used - blockades, intradiscal effects and other procedures. For other patients, such treatment for back and lower back pain is not used, so a different treatment regimen is used. Its main goal is to reduce the intensity of pain and maintain quality of life5.
Just as for acute pain, drugs from the NSAID group are prescribed, including Motrin®, other analgesics, muscle relaxants, and B3 vitamins. Antidepressants are recommended if necessary. Manual therapy should be carried out by a qualified specialist and exercise therapy should be prescribed. Psychotherapeutic and physiotherapeutic treatment methods are used.
Up to contents