Many people face the problem of pain in the lumbar region. It is not always possible to immediately understand whether the pain is in the lower back or the kidneys.
The lower back can hurt for many reasons: radiculitis, osteochondrosis, cholelithiasis, aortic aneurysm, pancreatitis, stomach or duodenal ulcer, kidney disease, inflammatory processes in the pelvic cavity. Pain in the lumbar region can be a symptom of many diseases, of which 90 percent are problems with the spine and back muscles, about six percent are kidney diseases, and only the remaining four percent are diseases of other internal organs.
How do the spine and back muscles hurt?
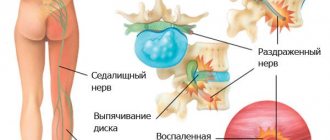
The pain can be nagging or sharp, “shooting”, when it is impossible to even straighten your back. With problems with the spine, pain is often localized in the middle of the lower back. It can radiate to the lower extremities.
Pain with osteochondrosis and radiculitis usually intensifies during movement. Mobility in the lumbar region is limited due to muscle spasm. Pain sensations decrease after rubbing warming and anti-inflammatory ointments or gels into the lower back. Back pain can also be relieved by wearing a warming or special orthopedic belt.
Symptoms of kidney diseases
Lethargy, drowsiness, fatigue, weakness; increased blood pressure and, as a result, headache; the appearance of swelling on the face and legs, which is usually noticeable in the morning and smooths out in the evening; increased body temperature, chills, sweating; nausea, loss of appetite, vomiting; frequent or painful urination; the intensity of pain does not depend on body position.
Urine may also change: it becomes rich in color or, conversely, colorless, contains blood, mucus or sediment.
The location of the pain is very important. Many people do not know where the kidneys hurt and what the characteristics of the pain are. With kidney diseases, pain occurs more often on one side - to the left or right of the spine. It is localized just below the ribs and can radiate to the lateral surface of the abdomen and groin, along the ureter, to the external genitalia, and inner thighs.
Causes of pain
There are two main groups of causes that lead to pain in the kidney area:
- primary – caused by problems with the spinal column;
- secondary – are a symptom of somatic pathology.
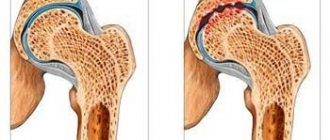
Primary causes include: osteochondrosis (most often), intervertebral hernia, protrusion of intervertebral discs, spondyloarthrosis, curvature of the spinal column, spinal injuries. Secondary causes: tumor processes, infectious inflammation of the vertebrae, kidney diseases, pelvic organs, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, rheumatoid arthritis and others.
The pain can be acute or chronic (long-term).
Acute pain syndrome occurs in the following cases:
- sprains of the spine (pain sensations are localized on the left and right, do not radiate anywhere, and mobility is limited);
- injuries to the lumbar vertebrae, which lead to sharp acute pain (first the back hurts while walking, then when you lie or sit);
- displacement of the intervertebral discs (pain appears on the right or left side, the person takes a forced position, possible loss of sensitivity);
- arthrosis of the intervertebral joints (back pain in the kidney area on one side, where there is also a decrease in sensitivity).
The pain can be localized on both the right and left sides
Pain becomes chronic in a number of diseases:
- spondyloarthrosis deformans: the so-called intermittent claudication, nagging, aching pain, weakness in the limbs and decreased sensitivity;
- ankylosing spondylosis: pain is more often diagnosed in young people, with lower back pain, stiffness after sleep in the morning, in parallel, poor posture is observed, discomfort may appear in the thoracic region;
- tumor formations;
- osteomyelitis (infectious inflammation of the bones);
- tumor formations;
- multiple myeloma.
No ads 1
Unilateral pain in the kidney area
Unilateral localization of pain, in addition to diseases of the musculoskeletal system, can be associated directly with the organ of the urinary system. Pain on the right side is accompanied by the following conditions:
- acute pyelonephritis or exacerbation of a chronic process: pain from the inflamed kidney is observed, dysuric disorders occur, and the temperature rises;
- nephroptosis (or prolapse of the kidney): the pain is dull, long-lasting, mild, and intensifies with prolonged standing or sitting.
This also includes urolithiasis, a complication of which is renal colic: the pain is acute, intense on the affected side, radiates along the ureter to the groin area, the patient rushes about, cannot take a forced position. We are also talking about tumors in the kidney of various types.
Some patients have back pain in the area of the kidneys on the right with diseases of the gallbladder, gynecological problems, gastrointestinal diseases, appendicitis, which is not so common. If pain at the level of the kidneys bothers you on the left side of the back, it means that the pathological process concerns the left kidney (prolapse of the kidney, acute pyelonephritis, movement of stones from the left kidney, etc.). By the way, nephroptosis, as a rule, most often affects the right kidney.
It should be noted that with a kidney disease such as glomerulonephritis, the pain is always bilateral.
Often the pain radiates to the groin area
Characteristics of pain in kidney pathology
Renal colic is characterized by acute paroxysmal pain. Painful sensations from urolithiasis are associated with blockage of the urinary tract by a calculus and a violation of the outflow of urine. Increased peristalsis and spasm of the ureters occur, in addition, a stone with sharp edges injures and irritates the nerve endings in the wall of the urinary tract. These changes are the cause of pain.
Pain caused by kidney inflammation is of a different nature. Inflamed kidneys increase in volume, their tissue swells. As a result, the renal capsule, which contains many nerve endings, stretches. When the membrane is stretched, these endings are irritated, which leads to painful sensations.
The region's first endosurgery center opened at the Kaluga Clinical Emergency Hospital
Pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis are characterized by dull aching sensations in the right or left lumbar region. With these diseases, the pain is not very pronounced, unlike urolithiasis and diseases of the spine.
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
If symptoms of acute nephritis or renal colic occur, the patient is immediately sent for hospital treatment. For mild to moderate cases, outpatient therapy is possible. Until the cause of the pain syndrome is identified, therapeutic measures include organizing a gentle regimen, selecting a diet with limited salt. To alleviate a person’s condition, symptomatic therapy is carried out.
Conservative therapy
The patient management plan is determined by the clinical form of the disease and the etiological factor. For all types of pathology, strict monitoring of the amount of fluid consumed and the volume of diuresis is indicated in order to monitor the excretory and concentration function of the kidneys. Some nephrological diseases require limiting protein intake. Drug therapy includes a number of drugs:
- Diuretics
. Allows you to normalize diuresis and reduce swelling. Loop, thiazide and potassium-sparing diuretics are used depending on the electrolyte composition of the blood. Diuretics are recommended only if the urinary tract is normal. - Corticosteroids
. The drugs quickly stop inflammation and have an immunosuppressive effect. They affect the cause of the disease, so kidney pain disappears quite quickly. Hormones are mainly used for glomerulonephritis and interstitial nephritis. - Antibiotic therapy
. Etiotropic antibacterial drugs are administered for pyelonephritis and other infectious kidney damage. Antibiotics from the group of cephalosporins and fluoroquinolones are predominantly prescribed. For mild forms of infection, uroseptics are effective. - Antihypertensive drugs
. Chronic kidney disease is accompanied by hypertension, for the treatment of which ACE inhibitors and angiotensin-II receptor blockers are selected. Calcium antagonists are also prescribed to normalize blood pressure. - Detoxification products
. Detoxification therapy is advisable for acute processes that are provoked by toxic influences. Specific antidotes are introduced, infusion therapy, and extracorporeal detoxification techniques are carried out.
If renal function is significantly impaired, replacement therapy is required - hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis. The criteria for starting treatment are pathological creatinine levels and insufficient glomerular filtration rate, changes in potassium levels in the blood, the presence of life-threatening complications, and renal failure.
Diagnostic tests
An experienced specialist knows which symptoms of kidney disease are most typical. To distinguish renal pathology from back pain, the doctor performs the following technique: he taps the lumbar region with the edge of his palm. In case of kidney disease, effleurage is accompanied by the appearance of dull internal pain. To identify the cause of the pain, an X-ray of the lumbar spine is taken (with osteochondrosis and radiculitis, there are characteristic changes in the spine - osteophytes, intervertebral hernias, etc.); general blood test (with diseases of the spine there are usually no changes, with kidney disease – leukocytosis, anemia, increased ESR); general urinalysis (increased or decreased relative density of urine, hematuria, leukocyturia, bacteriuria, increased salt content indicate kidney disease); Ultrasound of the kidneys and abdominal cavity (increase in the volume of the kidneys, the presence of stones in them).
Important:
If you find that lower back pain is accompanied by these symptoms, do not self-medicate and consult a doctor immediately. If you have kidney inflammation, you should not heat your lower back, so do not apply a heating pad or apply ointment until you consult a specialist.
Prepared by Tatiana PETROVA.
Diagnostics
When collecting anamnesis, the nephrologist takes into account the duration of symptoms and the events that preceded the manifestation of the disease. During a physical examination, Pasternatsky's symptom is checked and edema is searched for. Laboratory and instrumental research data are decisive for identifying the causes of pain in the kidneys. Diagnostics includes the following methods:
- Urine tests.
In kidney pathology, several specific changes are observed: the presence of protein, cellular elements (erythrocytes, leukocytes), cylinders. To assess the concentration function, a urine test is performed according to Zimnitsky, to confirm hematuria or leukocyturia - a study according to Nechiporenko. - Blood tests.
Leukocytosis and increased ESR in the hemogram indicate the inflammatory nature of the disease. In a biochemical blood test, attention is paid to the level of total protein, albumin, and lipid profile. Assess creatinine and urea levels. - Ultrasound of the kidneys.
Sonography examines the size, contours and thickness of the renal parenchyma. According to ultrasound data, dilation of the pyelocaliceal system is established, and stones are detected in the kidneys or urinary tract. Renal blood flow is assessed using Doppler ultrasound. - Excretory urography.
The technique provides detailed visualization of the structure of the kidneys and urinary tract. Based on the results of this method, changes in the size of the organ, its deformation are revealed, and the excretory function of the kidneys is assessed. Urography is supplemented with other X-ray studies - CT, scintigraphy. - Kidney biopsy.
Invasive research data are required for the differential diagnosis of chronic glomerulonephritis, autoimmune kidney damage, and neoplasms. When performing a cytological examination of biopsy specimens, attention is paid to infiltration with leukocytes, the presence of immune complexes, and atypical cells.