The hip joint is the largest structure in the human musculoskeletal system. There are different causes for the development of diseases of the hip joint; the symptoms of these pathologies are largely similar. For treatment to be effective and to shorten the rehabilitation period, it is necessary to consult a doctor as early as possible without ignoring the first symptoms. Effective treatment methods are medications and physiotherapeutic procedures. In advanced stages of the disease, surgery may be necessary, followed by long recovery. You can get rid of pain in the hip joint without surgery with the help of comprehensive treatment at ArthroMedCenter.
Anatomy of the hip joint area
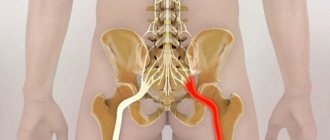
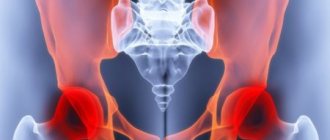
The hip joint is the largest joint in the human body. It connects the head of the femur to the acetabulum of the pelvis. The muscular and ligamentous apparatus, together with the joint, provides the motor function of the limb. Normally, the head of the hip bone is spherical in shape, with smooth cartilage tissue present on all surfaces of the joint.
The fluid inside a joint is called synovial fluid. It is located in the joint cavity, due to this, friction between the surfaces of the joint is reduced. Synovial fluid supplies cartilaginous structures with useful components, due to this there is depreciation and uniform load distribution.
There are such structures of the hip joint:
- femur - with its help a joint is formed;
- the hip joint is a kind of hinge, its surface is covered with a ball of smooth substance, thanks to which motor function occurs;
- femoral head;
- the acetabulum, which is bowl-shaped;
- cartilage - cushions the joint, allows smooth movement of bones, it is not visualized on radiographic images;
- The pelvis is a large, flattened bone. It has an irregular shape, narrows towards the center, widens upward and downward, the anterior surface of the parts is connected by the pubic symphysis, and the posterior surface is connected to the head of the femur.
Anatomical features and functions of the muscular frame
The musculature of the hip joint is represented by fibers of various types and functionality. This is primarily due to the varied trajectory of movement that the hip can perform. So, if we classify muscle fibers into groups according to function, in the anatomy of the hip joint we should highlight:
- The transverse, or frontal, muscle group, which is responsible for flexion and extension of the lower limb in the pelvic area. Among them are the flexor muscles (sartorius, iliopsoas, pectineus, rectus, tensor fascia lata) and hip extensor muscles (gluteus maximus, adductor magnus, semitendinosus, semimembranosus and biceps). Thanks to their coordinated work, a person can sit down and stand up, squat down and take a vertical position, pull his legs to his chest and straighten up.
- The anteroposterior, or sagittal, muscles regulate the adduction and abduction of the leg. This group includes adductors (major, short and long adductors, gracilis and pectineus) and abductors (obturator internus, tensor fascia lata, twin, piriformis, gluteus medius and minimus) muscle fibers.
- The longitudinal muscle group coordinates the rotation of the hip. Here the supinator muscles are distinguished (gemini, piriformis, iliopsoas, quadratus, sartorius, obturator, gluteus maximus and posterior groups of the middle and small gluteal fibers) and pronators (tensor fascia lata, semitendinosus, semimembranosus, anterior group of the middle and small gluteal fibers) .
Each of the muscles represented in the anatomy of the hip joint performs not only a motor function: powerful fibers take on part of the load during movements. And the more trained they are, the better they cope with pressure, thereby unloading the joint and performing a shock-absorbing function. Thanks to this, the likelihood of injury due to unsuccessful movements is also reduced, since the muscles are more mobile and extensible than the tissues of the joint.
What structures can become inflamed in the hip area?
In this area of the musculoskeletal system, an inflammatory process can develop, which affects specific structures or spreads to the entire pelvis.
With arthrosis of the hip joint or coxarthrosis, the inflammatory process directly affects the head of the joint. The development of the disease occurs over a long period of time. The reason is:
- overload;
- inflammation;
- injury;
- infectious process.
At first, discomfort appears, but later it develops into pain. As the disease progresses, the volume of synovial fluid decreases, gradual thinning and damage begins, and subsequently destruction of cartilage tissue. Movements are limited, joint deformation occurs, and osteophytes form.
With hip dysplasia, the acetabulum is affected. This pathology is congenital. Currently, this developmental anomaly can be diagnosed at an early age thanks to instrumental research methods. The consequence of untreated dysplasia is coxarthrosis and hip dislocation.
With aseptic or avascular necrosis of the head of the femur, blockage or compression of the vascular bundles that supply blood to the head occurs. Subsequently, calcium is washed out and cysts form. This is manifested by severe pain, fraught with complete immobilization and disability of a person.
The femoral neck most often suffers from a fracture. The provoking factor of this condition is osteoporosis, in which there is increased fragility of bones and thinning of tissues. Such an injury can occur even with a minor injury or fall from a small height. The fracture is accompanied by severe pain and deterioration in motor function.
Diseases that provoke pain in the hip joint
Before visiting a doctor and conducting a qualified diagnosis, you can independently navigate and understand what you should be prepared for, what to do, how to treat the pathology.
The likelihood of having a rapidly developing disease is high even when there are no external causes of pain in the hip joint, but only discomfort.
The table will help you independently diagnose a possible disease, the symptoms of which the patient is experiencing.
| No. | Disease | Characteristic |
| 1. | Arthritis (inflammation of the joint) | A particularly common problem affecting older people. Elderly people most often experience a full “set” of inflammatory processes of a degenerative, dystrophic nature occurring in the joints. The first place to suffer is the hip joint. The symptoms are as follows:
Some symptoms may manifest themselves strictly individually, since the provoking factors are different for each organism. |
| 2. | Coxarthrosis (deforming arthrosis) | The disease most often affects middle-aged people. Development may occur unnoticed, but early signs are noticeable even in the first stages:
|
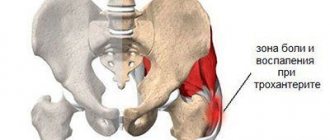
| 3. | Bursitis of the trochanteric bursa | Under the very protrusion of the femur bone is a fluid trochanteric bursa. It is in the case of its inflammation that repeated pain in the buttocks area, in their outer part, can occur. The usual position of lying on the side, which is most affected, causes increased pain. Most often it is the trochanteric bursa that suffers, but inflammatory processes occur in other fluid bursae of the hip joint, for example, in the ischial or iliopectineal bursa. |
| 4. | Tendinitis (inflammation of tendons) | This type of disease affects people who engage in active physical activity with systematic heavy loads. The most severe pain with tendinitis is the hip joint during active movement, during loading of the joint. A light load may be devoid of pain. |
Features of pain in the hip joint
Painful sensations that occur in the area of the hip joint can be different:
- aching;
- permanent or temporary, periodic, occurring after load;
- pulling;
- bursting;
- spasms;
- piercing;
- sharp or mildly expressed.
The pain can move to the groin, buttock, knee, lower back, ankle. It may be accompanied by a clicking or crunching sound, swelling, swelling, and hyperemia of tissue in the joint area. Local or general body temperature may also increase.
How to understand that you have coxarthrosis
At different stages of the disease, pain has different intensity. Initially, the patient periodically feels aching pain after exercise, which is more pronounced in the groin. In the second stage, it increases and does not stop at night. Movement is somewhat limited, and there is a characteristic swaying or limp in the gait. As a rule, at this stage the person already has a clearly defined diagnosis and is undergoing treatment.
If this does not happen, the joint becomes completely motionless, and the limb is significantly shortened. Conservative treatment rarely helps - surgery is necessary.
Most people understand that they have coxarthrosis only at stage 2
Main causes of hip pain
The causes and provoking factors for the appearance of an unpleasant symptom may be:
- arthritis – juvenile rheumatoid, osteoarthritis, psoriatic, rheumatoid, septic;
- injuries of various types - bursitis, dislocation, fracture, damage, bruise, tendinitis;
- pinching of nerve fibers or bundles - vertebrogenic Bernhardt-Roth meralgia paresthetica, sacroiliitis, sciatica, lumbago;
- oncological diseases - cancer with metastases, osteosarcoma, leukemia;
- development of avascular necrosis of the femoral head;
- Legg-Calvé-Perthes syndrome;
- development of osteomyelitis;
- development of osteoporosis;
- the presence of synovitis.
Pain syndrome can appear in the presence of pathologies or diseases of the muscular system. Each muscle has a specific effect on the functioning of the joint apparatus.
If hypertonicity or hypotonicity occurs, this makes it difficult to evenly distribute the load on the joint. The muscles of one group become too tense, and the other group become too relaxed. As a result of a malfunction in muscle tone, pain of a certain intensity may also appear in the thigh area. Usually it is short-lived and goes away on its own after changing body position or with rest.
There may also be radiating pain. It appears as a symptom of one of the diseases of the spinal column, groin (hernia). Systemic pathologies – myalgia, spondyloarthritis – can also cause pain in the hip joint.
Examination methods
During the first consultation, rheumatologists at the Yusupov Hospital conduct a comprehensive examination of the patient:
- Collection of complaints, clarification of the nature of pain in the hip joint;
- Obtaining information about the course of the disease, the onset of pain, the progression of pain, household and professional factors that, in the patient’s opinion, caused the pain;
- An external examination allows the doctor to determine visible deviations from the norm. To understand the nature of the pain and the area of its spread, the doctor asks the patient to perform various movements of the lower limb in the hip joint. The presence of pathology of the hip joint may be indicated by poor posture;
- Palpation (feeling). The doctor can find rheumatoid and rheumatic nodules, detect the exact location of pain during leg movements, determine the humidity and temperature of the skin in the hip joint area.
Next, the doctor conducts goniometry - an examination using a goniometer device.
It allows you to determine the range of joint mobility. Then the rheumatologist prescribes clinical and biological blood tests and a general urine test. Laboratory assistants at the Yusupov Hospital perform research using high-quality reagents and modern equipment, which allows them to obtain accurate test results. With inflammation of the hip joint, the number of leukocytes in the blood increases and the erythrocyte sedimentation rate increases. The inflammatory nature of the disease is indicated by an increase in the content of C-reactive protein in the blood serum.
An immunological blood test shows the presence of antinuclear antibodies in the blood in rheumatic inflammatory diseases. In patients suffering from arthritis, the concentration of uric acid in the blood serum increases sharply. The content of lysosomal enzymes (acid proteinase, acid phosphatase, cathepsins, deoxyribonuclease) in blood serum and synovial fluid changes in patients with rheumatism, psoriatic polyarthritis, rheumatism, and ankylosing spondylitis. In severe forms of hip joint pathology, significant deviations from the norm are observed in urine analysis.
Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital conduct x-ray examinations of patients with pain in the hip joints. It is indicated in the following cases:
- The presence of chronic or acute pain in the hip joint at rest and during movement;
- The occurrence of difficulties when moving the lower limb;
- The appearance of swelling and discoloration of the skin in the hip joint area.
Using computed tomography, doctors at the Yusupov Hospital evaluate the bones that participate in the formation of the hip joint.
On computed tomograms, the radiologist finds changes in the structure of bone tissue, cartilaginous growths, and osteophytes. Using magnetic resonance imaging, doctors evaluate the condition of the soft tissues that surround the hip joint.
Radionucleotide research methods make it possible to recognize pathology using radiopharmacological drugs.
Ultrasound examination of the hip joint is performed for injuries, inflammatory diseases, rheumatism and rheumatoid arthritis. The attending physician individually selects in each case the research methods necessary to determine the cause of pain in the hip joint.
Osteoarthritis of the hip joint
Arthrosis of the hip joint or coxarthrosis is a pathology of the musculoskeletal system. In an advanced stage, the disease leads to disability. The disease is accompanied by limitation or complete loss of motor function and joint deformation. The development of the disease involves thinning and destruction of cartilage tissue, as a result of which mobility deteriorates. This is a very common pathology.
The provoking factor is the person’s age. As the body ages, its tissues gradually wear out. The cartilage becomes thinner and begins to break down.
The development of coxarthrosis can be caused by:
- injuries of various types - fractures, bruises, dislocations;
- genetic predisposition;
- diseases of the spine;
- overweight, obesity;
- disturbances in the endocrine system, hormonal imbalances;
- maintaining a sedentary lifestyle;
- deterioration of blood microcirculation in tissues;
- infectious diseases.
All these provoking factors lead to the fact that the cartilaginous structures are worn out and the articular surfaces begin to rub against each other. The bones become damaged and begin to deform. Movement is constrained and may be completely limited in the future.
This pathology can be primary or secondary. According to most doctors, primary coxarthrosis occurs when blood microcirculation in the joint area is disrupted. In the first two stages, the disease can be successfully treated with conservative methods. In the second two stages, a person needs surgery.
The key manifestation of this disease is severe pain that appears in the thigh and groin area. At first, this symptom appears only after physical exertion, after prolonged standing or walking. In the future, the pain becomes more pronounced and persists constantly, even after rest.
It is very important to see a doctor in the early stages of the disease. This will stop further progression of the pathological process. If hip arthrosis is not treated, the severity of the disease will progress. The pain radiates to other areas - lower back, groin, spine, knee, lower leg.
Painful sensations are accompanied by:
- discomfort;
- feeling of fullness;
- crunch;
- clicks during movements.
At the initial stages of the disease, stiffness appears after waking up in the morning. In the future, mobility is limited, and gradually it becomes difficult for a person to move without a cane. At an advanced stage, the ability to move is completely lost.
The presence of this disease can be determined using radiography, computer or magnetic resonance imaging, and ultrasound. Treatment in the early stages involves the use of conservative therapy. In the later stages, radical intervention can help.
Consequences
If the disease is not treated in a timely manner, it can develop to the most serious consequences in the form of a complete loss of working capacity, the inability to maintain an active lifestyle, and disability.
Moreover, it should be understood that if the affected joint is not treated, then ultimately the sick person simply will not be able to get out of bed, even to a sitting position. And this is already becoming a dangerous situation for the functioning of the entire organism as a whole. Needless to say, arthrosis without medical care in old age significantly shortens a person’s life span.
Diagnosis of the causes of pain in the hip joint
To diagnose and determine the cause of an unpleasant symptom, doctors prescribe the following types of examinations:
- radiography - it can be used to determine the condition of the bones, joints, and how narrowed the joint space is;
- computer and magnetic resonance imaging - using these methods, it is possible to establish in more detail the condition of bone and joint structures, determine the condition of cartilage tissue, ligamentous and muscular apparatus;
- laboratory blood tests, study of biochemical blood parameters;
- ultrasonography.
Joint condition assessment
You can independently navigate and prepare for diagnosis using the following methods:
- Lie down and examine the lower limb; its normal state is parallel to the median axis of the body. The leg is in a forced position when it is fractured or dislocated.
- Determine how intense the pain is in the joint and where it comes from.
- Actively move and rotate the joint, and then evaluate the sensations.
- Notice if there is a clicking or popping sound in the joint during passive movements.
- If you find it very difficult to perform any activity due to pain, you are dealing with a dislocation or fracture.
Treatment of arthrosis of the hip joint
Conservative therapy involves the use of:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- painkillers;
- muscle relaxants;
- chondroprotectors;
- drugs to improve blood circulation.
After it is possible to stop the acute inflammatory process and reduce the severity of pain, physiotherapy and massage are prescribed. But therapeutic exercises cannot be performed. With this disease, it is necessary to limit the load on the diseased joint and use a cane when walking.
To restore full joint mobility and compensate for the deficiency of cartilage tissue, chondroprotectors are injected into the joint. To reduce pain and stop the inflammatory process, injections of hormonal drugs and painkillers are used.
Effective auxiliary treatment methods are:
- phonophoresis;
- ultrasound;
- kinesiotherapy;
- electrical stimulation;
- magnetic therapy;
- laser therapy;
- cryotherapy;
- massage;
- UHF;
- ozokerite;
- shock wave therapy;
- mud and radon baths;
- balneotherapy.
How to get rid of pain?
For the most part, the treatment process is directly dependent on the causes of pain, however, in all pathological conditions, the use of anti-inflammatory drugs (Movalis, Diclofenac Sodium, Ibuprofen, Nimesil) is possible.
The analgesic effect is ensured, and at the same time the level of inflammation decreases. Different pathological conditions are treated in their own way:
- Surgeries are required for malignant process in the hip joint. The tumor must be removed followed by chemotherapy.
- Repositioning of the bone, its realignment and immobilization for months.
- Drainage of the bone cavity and opening are carried out in case of purulent inflammation. This is followed by antibacterial therapy (Cefoperazone, Cefazolin, Ceftriaxone, Erythromycin, Clarithromycin, Levofloxacin, Ciprofloxacin, Moxifloxacin).
- Regeneration drugs that improve blood circulation, for example, Pentoxifylline, restore bone tissue.
- Tivortin is the best medication for normalizing blood flow in the limb; in combination with physiotherapy it gives good results.
The use of all painkillers is completely justified and relevant after surgery, joint replacement or metal osteosynthesis.
Arthritis treatment
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are appropriate for severe pain to relieve inflammation and reduce the pain effect:
- Xefocam;
- Nise;
- Ibuprofen;
- Ortofen.
Additionally, antibiotics, drugs to improve immunity, antiallergic drugs, and drugs that improve metabolism are prescribed.
It is forbidden to work on the problem joint; the affected limb must be at rest.
The effectiveness of treatment is predetermined by a correctly identified cause of hip arthritis.
Treatment of coxarthrosis
To treat this pathology, surgery is required, but in the early stages you can start with conservative treatment.
- to eliminate inflammatory processes and relieve pain symptoms, muscle relaxants, steroidal and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used;
- plasma lifting should be done to stimulate regenerative processes;
- chondroprotectors and vasodilators to restore cartilage tissue and activate blood supply in the problem area.
Kinesitherapy and physiotherapy are used as additional therapeutic measures. Diet correction is required.
Treatment of bursitis of the trochanteric bursa
Conservative treatment involves the following measures:
- restriction of physical activity;
- local anesthetics in combination with hormonal drugs;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- physical therapy, gymnastics, ultrasound and electrophoresis;
Compresses with calendula, sage, pine buds and plantain will not only relieve the inflammatory process, but also prevent the chronic development of pathology. These herbs have anti-edematous and anti-inflammatory effects. In rare cases, doctors resort to surgery if inflammation and pain persist even after long-term conservative treatment. Removing the bursa is the only option, while the hip joint will still function fully.
Treatment of arthrosis of the hip joint at ArthroMedCenter
At ArthroMedCenter, patients are prescribed the following procedures to effectively treat symptoms of pain due to arthrosis of the hip joint:
- SMT therapy. The procedure triggers the body's regenerative powers, improves tissue tone, and restores active blood circulation.
- Hivamat therapy. The procedure relieves pain and activates restoration processes in tissues.
- Electrophoresis. Medicinal substances are administered using current. This promotes effective pain relief and rapid recovery.
With the help of such procedures it is possible to stop further progression of the pathological process. It is very important to consult a doctor promptly when the first symptoms appear. This will quickly relieve pain in the hip joint and cure arthrosis.
Treatment with exercise therapy
The use of rehabilitation techniques in the treatment of the hip joint allows you to maintain its mobility, improve blood circulation in the joint, and accelerate the restoration of cartilage tissue. Specialists at the rehabilitation department select a set of physical therapy exercises taking into account the patient’s joint disease. Rehabilitation classes are conducted daily under the supervision of an instructor. For rehabilitation therapy, special simulators are used, and physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed in combination with physical education.
Features of the treatment of pain of different types
Treatment methods are selected depending on the established diagnosis. To temporarily relieve pain, you can take a painkiller. It will only act for a short time. Since the cause is not eliminated, the unpleasant sensations return again.
Most often, for diseases of the articular system, doctors prescribe conservative therapy. Medications are prescribed - steroidal or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, vasodilators, chondroprotectors, vitamin complexes. Additionally, physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed.
If the disease is at an advanced stage of development, conservative therapy may be ineffective. In such a situation, doctors consider the advisability of surgical intervention. For bursitis, removal of fluid from the periarticular bursa is indicated. For infectious diseases, in addition to basic therapy, antibacterial drugs are prescribed.
Types of pain
Painful sensations while walking can vary in intensity and type. This is due to the provoking factor in the development of diseases, the individual pain threshold, and the stage of development of the disease.
Painful sensations can be severe or moderate. The nature of the pain is aching, sharp, stabbing, dull, pulling. When visiting a doctor, it is very important to establish the nature of this symptom; this will help to make a more accurate diagnosis and begin timely treatment.
The main types of unpleasant symptoms are:
- Acute pain. It is intense but short-lived. It is most pronounced in the pathologically changed area. In this case, the leg and buttock hurt slightly. Such pain is easier to cope with.
- Aching pain. In this case, the unpleasant sensations spread evenly throughout the entire limb, especially in those areas that are in close proximity to the damaged area. The pain can be aching and pulling, in this case diagnosis is difficult.
- Chronic pain. It is long lasting and is present over a long period. It is very difficult to get rid of it.
Treatment of coxarthrosis
Therapy is prescribed individually and depends on the cause of the leg lesion, the stage of the disease, and the presence or absence of concomitant diseases. First, a complex of conservative therapy is prescribed. If this does not help and the disease progresses, accompanied by severe pain, surgical treatment is recommended.
At any stage of the disease, the main goals of treating arthrosis of the hip joint are:
- pain relief;
- suppression of disease progression;
- restoration of destroyed cartilage.
The complex of conservative therapy includes drug treatment and non-drug methods - diet, physiotherapy, therapeutic exercises, etc.
Drug treatment (pharmacotherapy) of coxarthrosis
All medications for the treatment of arthrosis of the hip joint are selected individually for each patient, taking into account the characteristics of his body.
To eliminate pain the following is prescribed:
- Paracetamol - tablets or rectal suppositories in a dosage of 500 mg are enough to relieve pain and minor inflammation (if any); can be repeated up to 4 times a day; the safest pain reliever;
- drugs from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs); Depending on the severity of the pain syndrome, they can be prescribed in the form of intramuscular (IM) injections, rectal suppositories, orally in the form of tablets and externally:
- diclofenac (trade names - Diclofenac, Voltaren) - an effective analgesic but often gives side effects from the stomach;
- ketorolac (Ketorol, Ketanov) is the most powerful pain reliever from the NSAID group, but also has side effects;
- ketoprofen (Ketonal) - less effective than Ketorol and Diclofenac, but there are fewer side effects;
- ibuprofen (Ibuprofen, Nurofen) - more suitable for relieving fever and inflammation, but also effective as a pain reliever; fewer side effects;
- nimesulide (Nimesulide, Nise) - belongs to a new generation of NSAIDs and almost does not irritate the stomach;
- Any ointment (cream, gel) based on NSAIDs is applied externally to the site of pain.
All NSAIDs have side effects, including irritating the gastric mucosa (risk of ulcers) and thinning the blood (risk of bleeding). In addition, they do not treat degenerative processes in the joints, but simply eliminate pain.
To eliminate muscle tension, muscle relaxants are prescribed. Tension of the muscles adjacent to the joint is a protective reaction of the body, but increases pain in the leg. To relax the leg muscles, tolperisone (Mydocalm) or tizanidine (Sirdalud) are prescribed.
To improve blood circulation and nutrition of the joint - pentoxifylline (Pentoxifylline, Trental) - dilates small blood vessels, improves blood circulation.
Drugs for the treatment of coxarthrosis
Chondroprotectors are used to restore cartilage tissue. This group of drugs includes chondroitin sulfate (CS) and glucosamine sulfate (GS):
- Dona (contains GS) is an effective remedy with a relatively short course of treatment;
- Structum (contains cholesterol) - you will have to be treated for at least six months;
- Teraflex (CS + GS) - course of treatment from 3 to 6 months;
- externally: Chondroitin (CS) ointment - 2 times a day for 3 weeks, Teraflex M (CS + GS) cream 2 - 3 times a day for a month; A small amount of ointment is applied to the skin and lightly rubbed.
Biologically active food additives (dietary supplements) of targeted action used in the treatment of arthrosis of the hip joint:
- Boswellia extract (Now Foods, USA) is a herbal preparation that protects cartilage from destruction, has an anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect; course of 1 capsule three times a day for a month;
- Connect Ol (Naturas Pluse, USA) – contains CS, GS, bromelain, calcium, zinc, copper, vitamin C, alfalfa, Chinese sea cucumber; course of 1 – 2 tablets per day for a month;
- Joint Formula (Cevan Nutritionals, USA) – contains GS; course of 1 capsule per day for a month.
Non-drug treatment of coxarthrosis
This is an even more significant section of the conservative treatment of arthrosis of the hip joint than medication. It includes proper nutrition, exercise and massage, and physiotherapy.
Nutrition for coxarthrosis
There is no special diet for degenerative-dystrophic diseases of the leg joints. But many people with sore feet are overweight. Therefore, sweets, baked goods, and sweet carbonated drinks should be excluded from the diet. It is necessary to significantly reduce the consumption of high-calorie foods: fatty meat, fish caviar, sausage. Regular consumption of alcohol is harmful - blood circulation in the joint is impaired.
You can eat lean meat, fish, dairy products, cottage cheese, cheese, buckwheat and oatmeal, first courses with vegetable or non-concentrated meat broth, compotes, fruit drinks.
Exercise therapy for arthrosis of the hip joint
The most important thing is to perform the exercises correctly, gradually increasing the load and not ignoring the appearance of pain (if pain appears, gymnastics should be stopped). Training should take place regularly. The first classes should be conducted under the supervision of a physical therapy instructor. And only after a while you will be able to conduct them yourself at home. Swimming in the pool, smooth gymnastics in the style of Pilates or yoga are very useful.
Exercise therapy for arthrosis of the hip joint strengthens muscles, activates blood circulation and metabolism, and helps restore the function of leg joints. Exercises for arthrosis of the hip joint can be performed from the starting position lying or standing.
Several exercise therapy exercises for the treatment of arthrosis of the hip joint
Physiotherapy for coxarthrosis
Physiotherapy procedures are of auxiliary importance, since the BTS is located deep under the muscle layer. However, sometimes electrophoresis with painkillers is prescribed to eliminate pain, and laser and magnetic therapy is prescribed to improve blood circulation.
In the absence of inflammatory phenomena in the joint, sanatorium-resort treatment with courses of ball and mud therapy is recommended. The resorts of Caucasian Mineralnye Vody are suitable.
How to treat arthrosis of the hip joint using traditional methods
Folk remedies are often included in complex treatment to reduce drug load:
- warming the upper part of the leg with sea salt; sew a long linen bag (must match the length of the upper leg), fill it with hot sea salt; First put a towel on the joint area, and then a bag; when the salt has cooled slightly, remove the towel, hold the sea salt until it has cooled completely; relieves pain, stimulates cartilage restoration, improves joint movements;
- honey massage; Use liquid warm honey as a massage oil: apply to the upper part of the leg and rub into the skin of the leg with light circular movements, patting occasionally, for three minutes; then wrap your leg and hold it there for two hours; perfectly relieves pain and activates blood circulation.
Surgical operations for coxarthrosis
Surgical treatment of arthrosis of the hip joint is recommended only in cases where all possibilities of conservative therapy have been exhausted, and the disease continues to progress and is accompanied by severe pain.
To help the patient, the following types of surgical interventions are used:
- arthrodesis – strong fastening of joint bones in the desired position using various structures; over time, this leads to their complete fusion; the leg fully performs the supporting function, but does not move, therefore arthrodesis is performed only if there are contraindications to other surgical interventions;
- femoral osteotomy – dissection of the femur to create an artificial fracture and subsequent fastening in the desired position using various metal structures; not only the supporting, but also partially motor function of the leg is preserved, pain disappears;
- endoprosthetics is the replacement of a destroyed joint with an artificial one that fully performs all the functions of the removed one.