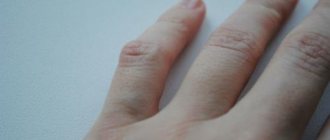
Often young women are perplexed: where did the strange lump appear on their hand?
?
Although painless, but quite large (from 0.5 to 6 cm in diameter), it cannot go unnoticed due to its location. So what is hygroma
- cancer or a purely aesthetic defect?
Although hygroma on the arm is a tumor-like formation, it, contrary to misconceptions, is not an oncological disease
, and also
never degenerates into cancer
. This disease is quite widespread (up to 50% of all neoplasms on the hands) and can be successfully treated. On the other hand, this subcutaneous formation can cause discomfort or even interfere with normal blood circulation in the hands.
Hygroma
(or, as it is also called,
ganglion
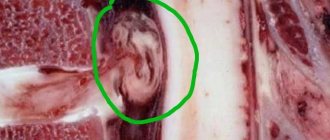
) is a capsule-bag that is dense to the touch, filled with a viscous and jelly-like protein liquid mixed with fibrin. The hygroma noticeably protrudes over the ligaments and tendons and practically does not move under the skin. Most often, synovial cysts are observed in women aged 20 to 30 years (⅔ of the total number of patients). Children are least likely to suffer from it.
In what cases should you worry about treating hygroma and can it be prevented?
Hygroma - formation in the form of a tumor
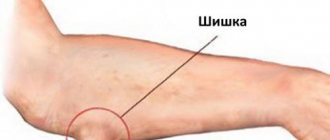
Reasons for the appearance of bumps on the hands under the skin
The reasons for the appearance of lumps under the skin on the hands are caused by degenerative changes in epithelial tissues, a consequence of their inflammation or injury.
The following factors and conditions are identified that cause the formation of foreign tumors under the skin of the upper extremities:
- diseases of the blood vessels associated with increased blood clotting, the formation of blood clots and disruption of the integrity of the venous walls;
- mechanical damage and trauma to bone, connective or soft tissues;
- internal hemorrhage of capillary or venous blood, which led to the appearance of a hematoma;
- inflammatory processes in soft tissues, as well as nodes of the lymphatic system;
- complications after surgery, when the wound surface became infected and fibrous tissue began to form;
- the appearance of benign or cancerous tumors located in the subcutaneous layer (as the foreign tumor grows, accompanying symptoms of the disease appear, the lump increases in size, becomes denser and more voluminous, rising above the general level of the epithelium);
- heavy physical labor associated with moving loads and constant emphasis on the same area of the surface of the upper limb;
- hereditary predisposition to the formation of lumps under the skin of the hands;
- muscle fiber ruptures.
The cause of the pathological condition of the epithelial tissues of the upper extremities is determined by a dermatologist or surgeon based on the results of a diagnostic examination. Determining the factors causing the disease is an important aspect in organizing an effective course of treatment.
Causes of hygroma
The exact causes of hygroma on the hand have not yet been established. It is believed that joint injuries can lead to the formation of small cavities, which are filled with serous fluid and then merge into one large or several small cysts. Doctors identify several factors that contribute to the onset of the disease and the growth of education:
- tenosynovitis
(inflammation of the tendon sheath) or bursitis (inflammation of the joint capsule) with a subacute course; - hand injury
(bruise, sprain, fracture, ligament rupture); - chronic trauma to articular and periarticular tissues
(ligaments, tendons, cartilage lining), for example, due to repetitive professional movements; - previous hand surgeries
; - diseases of the musculoskeletal system localized in the hands
; - the need to write or draw a lot by hand
(especially if the position or selection of stationery is incorrect); - congenital weakness of the tissues that form the joint capsule
(in cases where the tendency to hygromas is inherited between family members).
It has been established that athletes (tennis players, golfers and others), musicians (pianists, violinists and others), as well as people whose work involves stress on their hands (painters, turners, loaders, typists, bakers, etc.) are most often susceptible to hand hygroma. hobby). Sewing, embroidery, beadwork and similar hobbies can also increase the risk of developing a hygroma.
Types of diseases that cause bumps on the hands under the skin
There are certain types of diseases, the presence of which causes a symptom such as the formation of single or multiple lumps under the skin surface of the hands. Some of them are not dangerous to life and health, while others can lead to disability and even death.
The table below lists the types of diseases in which lumps appear under the epithelial layer of the upper extremities.
| Type of disease | Clinical manifestations of pathology |
| Calcifying hematoma | Subcutaneous hemorrhage of capillary or venous blood with damage to soft tissues, which resulted in calcification of the hematoma. The process of resorption of a bruise can occur due to hypothermia of the tissues, their repeated damage, or improperly organized treatment. If a lump on the hand, which has signs of a hematoma, does not go away for more than 5 days, remains the same size, then you need to seek help from the clinic. It is possible that surgical removal of the subcutaneous lump will be required. |
| Lymphadenitis | Acute or chronic inflammation of the tissues of the lymphatic system. It is characterized by damage to nodes that perform the function of biological filters of lymph. If the appearance of lumps under the skin of the hands is associated with lymphadenitis, then in this case the neoplasms will be localized in the armpit or on the inside of the elbow joint. It is in this part of the arm that there are lymph nodes that may be in the affected area of lymphadenitis. The cone has a regular round shape. The skin above its surface has a redder tint, the area of the body is painful on palpation, and an increase in local temperature is felt. The etiology of the disease is associated with infection of the body by pathogens, prolonged hypothermia, and oncology of the lymphatic system. |
| Lipoma | A benign tumor, the structural basis of which is fat cells. Lipomas (wen) are non-dangerous formations that can form in the form of single subcutaneous lumps or multiple compactions. During palpation, the lipoma does not cause pain and is soft to the touch. In most cases, it appears on the areas of the arms where the largest number of sebaceous glands are concentrated (shoulders). The only effective method of treating the pathology is surgical removal of the foreign tumor, but at the same time there is a high probability of relapse of the disease. |
| Dermatofibroma | This is another type of benign tumor that is formed from a person’s own epithelial cells. It can be presented in a single quantity, or cover the entire surface of the hands. During palpation it does not cause pain, but causes an aesthetic defect. It extremely rarely degenerates into malignant tumors, but doctors still recommend removing such tumors. |
| Liposarcoma | It is a tumor of malignant etiology. It is formed from the tumor carrier’s own fat cells. Outwardly it resembles a round, medium-sized cone that rises above the general level of the epithelial cover. During palpation it is not painful, the color shade of the skin is not changed. A distinctive feature of this malignant tumor is that it does not spread metastases to the deeper layer of the epithelium and bone tissue. If you go to the hospital in a timely manner, the prognosis for full recovery is favorable. Patients undergo a course of chemotherapy drugs, as well as surgical removal of the tumor. |
| Fibrosarcoma | A malignant neoplasm under the skin of the hands, which is not formed from fatty tissue, but is formed in the thickness of the muscle fibers. Therefore, the localization of cones caused by this disease is the shoulders, forearm, and the area of the limb where the biceps and triceps muscles are located. Fibrosarcoma can develop rapidly, but it appears above the general surface of the skin in the form of a hard lump only when it has already reached a large size. Initially, its formation occurs deep in the muscles. It gradually grows until it penetrates the subcutaneous layer. Seeing a doctor should be done immediately, since this type of tumor can spread metastases, affecting other segments of the limb. |
| Atheroma | In dermatology it is also called an epidermal cyst. This is a benign neoplasm, which externally looks like a lump with sizes ranging from 2 to 5 cm in diameter. It is formed from a person’s own epithelial cells, as well as follicles. Does not cause pain or any other discomfort. In most cases, it affects the skin of young people from 20 to 35 years old. At risk are men and women who abuse sunbathing, solariums, and dry skin cleansing. Under the influence of negative factors, atheroma can degenerate into a cancerous tumor, spreading metastases throughout the body. |
A lipoma can cause a lump under the skin to appear on your hands.
Lumps on the hands under the skin, the causes of which are associated with mechanical injuries or tumor growths, can be successfully treated provided that medical help is sought in a timely manner. Determining the underlying disease that provoked the pathological symptom is a guarantee of preventing relapse of the disease.
Treatment of hygroma
Although sometimes a hygroma on the arm can be left without treatment, due to the risk of complications and aesthetic discomfort, doctors usually recommend its removal. Sometimes a synovial cyst can resolve spontaneously if the factor that provokes it (for example, occupational stress) is eliminated in a timely manner - then the synovial fluid will simply stop flowing into the capsule.
The indication for treatment of hygroma is its multi-chamber nature, rapid growth of formation, development of the inflammatory process, pain syndrome, and limited mobility in the joint.
The preferred treatment for hygroma is surgical removal.
, since puncture or aspiration of the tumor is usually ineffective or poses a risk of complications.
Thus, conservative treatment of wrist hygroma is characterized by recurrence of the disease in approximately 80-90% of cases
, while for surgical treatment the same figure is only
8-20%
.
Surgery
Doctors do not recommend delaying surgical treatment of hygroma, since a large, albeit benign, formation soon begins to displace blood vessels, muscles, ligaments and nerves. Their non-physiological position significantly complicates the operation and may have consequences for the patient
.
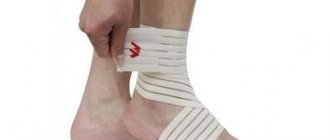
Removal of a hygroma on the arm is usually carried out under local anesthesia with a tourniquet and lasts no more than half an hour. The operation is performed using a scalpel or laser equipment. In advanced cases, large or unusual formations may require general anesthesia. When carrying out the procedure, it is important to remove all degenerative cells without exception (otherwise the altered tissue may again develop into a cyst), wash the capsule, and also bandage the so-called. the mouth of the hygroma, which is associated with the joint and feeds the lump with synovial fluid. The drainage tube for fluid drainage is removed 1-2 days after the procedure, and postoperative sutures after complete healing of the incision are removed on days 7-10. After this, it is recommended to immobilize the operated area with a splint and a pressure bandage for several weeks and avoid serious stress on it for 30-60 days.
.
Recently, surgeons have given preference to endoscopic removal of wrist hygroma, in which the capsule and its contents are removed through a small incision a couple of centimeters in size. Rehabilitation after such an intervention occurs much faster.
Conservative treatment of hygroma
As a conservative treatment for hygroma of the hand, crushing it (without penetration and formation of a wound) is occasionally used, followed by the application of a compressive bandage. This method should never be used on infected synovial cysts due to the risk of sepsis, but it can be used to treat sterile lumps. The main disadvantage of this approach is the rapid recurrence of the disease: as soon as the burst edges of the capsule grow together, it will again begin to fill with serous fluid.
A somewhat more successful technique is aspiration puncture of the formation, in which its contents are sucked out through a small puncture, and glucocorticoid solutions and sclerotization preparations are injected in its place. This allows the capsule to be filled with connective tissue instead of liquid. This method is also indicated for administering antibiotics and treating infected hygroma.
Conservative techniques do not eliminate degenerative cells
, which provoke the formation of hand hygroma and are therefore considered ineffective.
There are several methods for treating hygroma
Physiotherapy
A small cyst that does not grow, does not become inflamed and does not cause pain can often be treated conservatively using physiotherapeutic techniques. They help reduce the volume of formation and ensure the outflow of its contents, slow down cell growth. Although physiotherapy cannot completely cure hygroma, in combination with chondroprotectors
it helps keep the tumor under control without surgery.
Sometimes physiotherapy is the optimal solution for non-standard location of the lump
, in which excision can be a rather traumatic procedure.
This type of treatment helps relieve compression of nerve endings, eliminate pain and inflammation, improve tissue regeneration, and relax the muscles around the tumor.
In modern physiotherapy for hygroma of the wrist and other joints, the following is used:
- electrophoresis
; - ultra high frequency therapy
; - phonophoresis with hydrocortisone
; - magnetotherapy
; - paraffin applications
; - mud baths and wraps
; - UV therapy
.
During the entire course of physiotherapy, and also, as prescribed by the doctor, after it, a tight, compressive bandage is applied to the area affected by hygroma, which prevents further accumulation of fluid in the capsule.
If the tumor is too large or continues to grow, there are signs of inflammation, the attending physician, together with the patient, usually decides on surgical intervention.
Drug treatment
For the medicinal treatment of hygroma, a wide range of anti-inflammatory drugs are used, which are applied to the surface of the cone or injected directly into its cavity.
However, anti-inflammatory therapy provides only a temporary and symptomatic effect
,
and therefore used in combination with other techniques
.
In case of a purulent process inside the cyst, and also as a preventive measure before surgery to remove it, the attending physician selects a specialized antibiotic for the patient - usually in the form of injections.
But the most effective medicine for the treatment of tendon ganglion are chondroprotectors
.
They are helping:
- establish metabolic processes in the tissues adjacent to the hygroma, strengthen muscles and ligaments, prevent the destruction of synovial cartilage;
- improve the quality of synovial fluid - as a result, the joint begins to produce it in smaller volumes, and the nutrition of the hygroma is reduced;
- slow down further growth of tumor formation;
- relieve symptoms of inflammation in the area of hygroma;
- significantly reduce pain (many patients note a reduction in pain by 50-80%);
- cope with discomfort from the tendon ganglion, which cannot be operated on due to its small size.
Chondroprotectors do not allow the joint on which the hygroma occurred to “starve” due to poor supply of nutrients. They also relieve swelling and restore normal mobility in the fingers, hands and wrist joint. In addition, they have a systemic effect on the body, improving the condition of the musculoskeletal system and preventing the appearance of new hygromas, as well as the recurrence of old ones. Due to the almost complete absence of side effects, chondroprotectors can be taken to prevent synovial cysts even before they appear
,
during treatment of a neoplasm
, as well as
after surgery
.
Chondroprotectors stimulate tissue repair after surgery and prevent the re-formation of modified cells. The standard course lasts from 3 to 6 months per year. Compared to other drugs in this series, Artracam
, the course of which lasts 1.5 months, and then can be repeated after 2 months if necessary. It is made exclusively from natural ingredients - seafood.
Drug Artracam
is one of the most effective chondroprotectors for hygroma of the wrist and hand.
Diagnosis of lumps on the hands under the skin
After contacting a dermatologist or general surgeon with signs of subcutaneous lumps on the hands, the patient undergoes an initial examination by a specialist.
The doctor listens to the current symptoms that are bothering the patient, and then prescribes the following types of tests:
- taking blood from a vein to determine the possible presence of infectious microorganisms that provoke lymphadenitis, as well as cancer cells;
- a smear from the surface of the wound, if the lump has signs of inflammation, an abscess has formed and purulent or sanguineous discharge is observed;
- X-ray of the upper limb, the tissue of which is affected by lumps of unknown etiology (performed to exclude the factor of tumor germination into the bone of the arm);
- biopsy of a piece of tissue from a foreign tumor and sending it for histological analysis to establish the benign or malignant etiology of the tumor;
- examination of the deeper layers of the skin using a dermatoscope;
- donation of capillary blood and morning urine for clinical analysis.
Lumps on the hands under the skin, the causes of which are associated with the uncontrolled division of one’s own epithelial cells or an inflammatory process in the lymphatic system, are a dangerous symptom that requires a comprehensive diagnosis.
After receiving the above examination results, the attending physician has comprehensive information about the type of lump, as well as the diseases that caused their formation.
Diagnosis of hygroma
To make an accurate diagnosis, you need to visit a doctor - an orthopedist, surgeon or rheumatologist. Diagnosis of hygroma requires a comprehensive study of the clinical picture, taking into account localization, external signs, and also, if necessary, the results of laboratory or instrumental studies. Typically, a patient examination begins with palpation of the neoplasm, examination and questioning of the patient, as well as checking joint mobility. In some cases, this is enough, and sometimes additional examination of the lump is required to exclude lipoma, fibroma, atheroma or traumatic cyst. If the hygroma is in the palm area, tumor formations in the bone or cartilage tissue should be excluded
To exclude a malignant origin of the formation, the doctor may prescribe a puncture (fluid sampling) from the cyst for histological and/or cytological examination, which is carried out using a syringe.
In the case of an atypical location of the lump, an X-ray examination or ultrasound is performed to make a diagnosis. Ultrasound examination of the cyst helps determine the density of its contents, the presence of veins and other vessels nearby that it can compress, as well as the uniformity of the lump or the presence of several nodules. In some cases, the patient may be recommended an MRI (to determine the structure of the walls, the presence of vessels in the hygroma, and the consistency and composition of the filling of the cyst).
It is important to diagnose hygroma in the early stages
When to see a doctor
An appeal to a surgeon, oncologist, and also a dermatologist should take place in the first 1-2 days after a person discovers foreign tumors in the form of lumps on his hands. Regardless of whether they are single or multiple formations, they differ in pain syndrome or are completely painless.
Delay in diagnosis and initiation of treatment is fraught with the development of complications, the appearance of polycystic formations, the development of cancerous tumors and the degeneration of benign neoplasms. The average cost of diagnostics in a private clinic is 3000-5000 rubles. In government institutions, medical services are provided free of charge.
Prevention of bumps on the hands under the skin
Lumps on the hands under the skin, the causes of which are associated with inflammatory and tumor diseases of muscle, lymphatic, adipose, and connective tissue, can be prevented.
To do this, you must follow the following prevention rules every day:
- stop drinking alcohol, smoking, drugs, and lead a healthy lifestyle;
- avoid injuring the upper extremities, and if your arm is injured, immediately seek medical help;
- every 12 months undergo periodic medical examination by a dermatologist and surgeon if the family has close relatives with bumps on their hands of unknown etiology;
- promptly treat chronic infectious diseases that disrupt the functioning of the lymphatic system;
- eat right, eating only food products of biological value (cereals, fresh fruits, herbs, juices, lean meat, fish, chicken eggs, stewed vegetables);
- avoid gaining excess body weight with large amounts of adipose tissue in the upper extremities.
Men and women who follow the above recommendations are 3 times less likely to experience the formation of lumps under the skin of their hands. In addition, preventive measures are mandatory after undergoing surgery to remove foreign tumors.
Prevention of hygroma and its complications
For standard prevention of hygroma of the wrist and other joints, you should:
- avoid injury and hypothermia;
- promptly treat arthritis, arthrosis and other connective tissue diseases;
- minimize the load on the joint, incl. monotonous (from time to time take a break from work or monotonous activities to warm up);
- pay attention to hereditary and metabolic diseases that can negatively affect the health of the musculoskeletal system (gout, diabetes);
- follow safety precautions and exercise rules when playing sports;
- Avoid self-medication for injuries and other lesions in the hands and wrists;
- Monitor your body weight and maintain a low-calorie diet rich in vitamins, minerals and amino acids.
If in your family or for your occupation there is a high predisposition to hygromas and other diseases of the musculoskeletal system, you should think about additional measures. Rheumatologists recommend an annual course of prophylaxis with chondroprotective drugs. They help strengthen connective tissue and improve its metabolism, preventing the development of degenerative cells. Artracam is ideal for this purpose.
- due to the high bioavailability of glucosamine sulfate, pleasant taste and convenient sachet form.
Take care of yourself!
Images designed by Freepik
Methods for treating lumps on the hands under the skin
The method of treating foreign tumors on the hands is selected based on the reasons that caused their appearance. Medicines or surgery may be used.
Medications
To eliminate lumps of inflammatory and malignant etiology, the following medications can be used:
- Erythromycin is an antibacterial agent that is effective for the treatment of bumps caused by lymphadenitis, prescribed 200-500 mg 2 times a day with a duration of therapy from 5 to 14 days (medicine price 67 rubles);
- Chemotherapy drugs - prescribed in courses in the form of intravenous drips, indicated for use when lumps are detected under the skin of the hands, which are cancerous tumors (the selection of a chemotherapy drug and the number of courses of treatment are determined individually);
- Azithromycin - the drug is prescribed for internal use, 1 capsule 2 times a day, 2 hours after meals, or 1 hour before eating (the duration of treatment for lumps of infectious or inflammatory etiology is 3-5 days, the cost of the medication is 105 rubles);
- Rescuer ointment - the drug is used for therapeutic purposes in the formation of subcutaneous lumps on the hands, which arose as a result of bruises, postoperative complications, calcification of hematomas (the ointment is applied to the surface of the tumor 2 times a day for 10-15 days, and the cost of a 30 g tube is 160 rub.).
The drug should be prescribed only by the attending dermatologist, oncologist or surgeon. Self-therapy can lead to deterioration of health.
Traditional methods
Lumps that form under the skin of the upper extremities due to the appearance of benign, cancerous tumors or acute inflammation of the lymph nodes can be symptoms of dangerous diseases.
Therefore, it is not recommended to use traditional medicine, since tinctures and decoctions of medicinal herbs will not have the desired therapeutic effect, but will transform the disease into a chronic or complicated form.
Other methods
Surgical therapy is used together with medications. Surgery is effective in cases where bumps on the hands are the consequences of lipoma, dermatofibroma, liposarcoma, fibrosarcoma or a complication of lymphadenitis.
The surgical operation is performed as follows:
- The patient is transferred to the surgical room.
- The anesthesiologist administers local or general anesthesia depending on the complexity of the clinical case.
- The surgeon dissects the epithelial and soft tissue in the area where the lump is located.
- The tumor is removed and the wound is treated with antiseptic.
- Suture material is applied.
The average duration of the operation is 30 minutes. up to 1 hour
The period for complete wound healing and rehabilitation lasts from 7 to 14 days. The cost of the operation varies from 2500 to 5000 rubles. depending on the pricing policy of the clinic management and the complexity of surgical procedures. In a public hospital, the operation is free.
Possible complications
In the event that a person who has discovered single or multiple lumps on his hands does not go to the hospital and does not treat the underlying disease, then the development of the following complications cannot be ruled out:
- degeneration of a benign cyst or tumor into a malignant neoplasm and its further growth with the transition to the final stages;
- the spread of cancer cells into the deeper layers of the dermis, damage to the bone tissue of the arm and muscle fibers, as well as the involvement of internal organs located in close proximity to the source of pathology in the oncological process;
- upper limb amputation;
- surgical removal of affected lymph nodes;
- inflammation of muscle fibers and temporary disability.
Regardless of what causes the appearance of lumps under the skin on the hands, the disease requires comprehensive treatment. In this case, you can count on a favorable prognosis and complete recovery of the patient without the risk of relapse.
Benign neoplasms are not dangerous to human health, but there is always a risk of their degeneration into a malignant tumor, which can lead to disability or, in the most severe cases, even death.