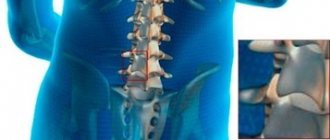
Spondyloarthrosis (osteoarthritis) is a common pathology of the lumbar spine. Spondyloarthritis of the lumbosacral spine is more common in older people, but it can also develop in people who do heavy physical work, are obese, or in anyone who has had a previous spinal injury.
Osteoarthritis of the lumbar spine develops in the joints that connect the segments of the spine. Each vertebra is connected to another vertebra in three places. In front of the spinal cord, the vertebrae are separated by the spinal disc. Behind the spinal cord, the vertebrae are connected by two small joints called facet joints. These joints, along with the intervertebral disc, allow the spine to move and perform movements such as bending and extension or rotation of the back.
Treatment of spondyloarthrosis of the lumbar-sacral spine can be either conservative or surgical, and the choice of treatment tactics depends mainly on the clinical picture.
Causes
Common causes of osteoarthritis of the facet joints of the lumbar spine are:
- Degenerative changes in joints and wear and tear of joints over time.
- Disc degeneration can cause the distance between vertebrae to decrease, which will increase stress on the facet joints, accelerating wear and tear on these joints.
- Backward movements of the trunk (extensions) can put pressure on the facet joints, which can lead to degenerative changes.
- A sudden fall or injury, such as a car accident, can damage the facet joints, increasing and accelerating wear and tear on the joints.
- Genetic factors may influence your likelihood of developing degenerative joint disease.
- Repetitive stress injuries, such as lifting or carrying heavy objects, can cause joint irritation and degeneration.
What is included in the examination
The diagnosis is made based on physical examination and X-ray, MRI and/or CT data. To detect inflammation of the facet joints, a radioisotope scan of the spine is performed. In order to exclude the development of vertebral artery syndrome in cervical spondyloarthrosis, an MRI or CT scan of the brain vessels is performed, as well as a duplex ultrasound scan of the arteries of the head and neck. In some cases, diagnostic blockades with Novocaine and steroids are performed. Reduction or disappearance of pain after the procedure clearly indicates the presence of spondyloarthrosis.
Symptoms
Symptoms of spondyloarthrosis of the lumbar spine will depend on which motor segment is most damaged and the degree of impact on nearby nerve structures.
Symptoms can range from mild to severe and can mimic those of disc disease:
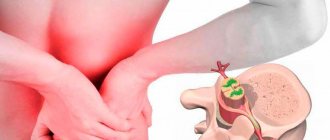
- Back pain or radicular pain radiating into the buttock, into the leg and extending down to the back of the knee, less commonly to the front of the leg or foot.
- Pain and tenderness are localized at the level of the facet joint involved in the pathological process.
- Muscle spasm and forced changes in posture.
- Loss of movement, such as the inability to straighten, bend the body to the side, or maintain an upright position for long periods of time.
- There may be disturbances in walking and standing in cases of severe pathological process
- Sitting is usually more comfortable.
- Change in normal lumbar curvature or lordosis.
- Development of stenosis-like symptoms.
- Stiffness in the joints after a period of rest.
- Pain after excessive activity and pain relief after rest.
- There may be some swelling at the level of the pathologically changed facet joints.
- Muscle weakness in the lower extremities or symptoms of cauda equina syndrome due to the development of spinal stenosis
Medicinal properties
Due to the wide range of substances contained in sainfoin honey, it has the following healing properties:
- heals wounds, cuts, regenerates tissue;
- helps increase mental and physical activity;
- relieves inflammation;
- cleanses the body;
- normalizes hormonal levels;
- corrects the functioning of the digestive tract.
In addition, the unique properties of sainfoin honey are used for ulcers and gastritis. It is useful to take it after illnesses or operations. The bee product has a beneficial effect on the nervous system and regulates metabolic processes.
Diagnostics
A patient who has been experiencing back pain or stiffness for more than two weeks should see a doctor for a physical examination.
Disease history
The physician must evaluate the patient's medical history, examine symptoms, pain characteristics, and joint function, how and when symptoms began, and how they have changed over time.
The doctor also needs to find out the presence of concomitant pathology, previous treatment, family history and bad habits (for example, alcohol consumption, smoking, etc.),
Physical examination. The doctor will need to perform a physical examination to evaluate the patient's general health, muscle and bone condition, nerve conduction, reflexes, and spinal joint mobility.
The doctor also needs to obtain information about the patient's muscle strength, flexibility, and ability to perform activities of daily living, such as walking, bending, and standing.
The patient may need to perform some movements so that the doctor can understand the range of motion and determine which movements increase symptoms.
Instrumental diagnostic methods
Radiography
- a doctor may order an x-ray to see if there is injury to the spinal joints and how extensive it is. X-rays can show cartilage loss, bone changes, and the location of possible bone growths (osteophytes).
Additional diagnostic methods that may be required to exclude other causes of pain or confirm the presence of spondyloarthrosis:
PAT.
A bone scan is used to rule out inflammation, cancer, infection or a small fracture.
CT scan
can be performed to more accurately measure the degree of narrowing of the spinal canal and morphological changes in surrounding structures.
MRI.
Magnetic resonance imaging is a method that can provide a very detailed morphological picture of the spinal cord, nerve roots, intervertebral discs, ligaments and surrounding tissues.
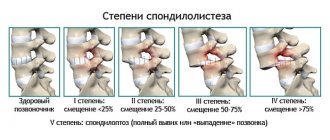
Stages and classification
Spondylosis and its variety - spondyloarthrosis, as well as osteochondrosis, can manifest themselves in different parts of the spine. These diseases are characterized by stages, so the clinical picture does not develop immediately, which interferes with the early diagnosis of diseases.
Table No. 1. Stages of diseases.
| Stage | Description |
| Stage 1 | On an x-ray you can see many bone growths that do not leave the vertebrae. Intervertebral discs are intact. Their height is unchanged. |
| Stage 2 | Osteophytes extend beyond the vertebrae and grow together. But at the second stage this process remains incomplete. |
| Stage 3 | Osteophytes are completely fused and form brackets. The affected part of the spine loses its mobility. Stenosis of the vertebral canal is observed. |
According to the rate of progression, spondylosis can be classified into:
- slow;
- moderate;
- fast;
- fulminant.
Fortunately, slow and moderate forms are statistically more common. Rapid and lightning-fast spondylosis is the result of concomitant pathologies of the spine that accelerate the process.
According to the nature of the pathogenesis of the disease, there can be the following forms.
- Ankylosing (Bechterew's disease) is a chronic systemic inflammatory disease that leads to curvature of the spine.
- Deforming is a pathology characterized by two things - protrusion of the fibrous rings of intervertebral cartilage and subsequent deformation of the vertebrae.
- Congenital - a consequence of abnormal intrauterine fusion of the vertebrae due to a lack of synthesis of collagen and other connective tissue structures.
Ankylosing spondylosis predominantly affects young males. In addition to the vertebral joints, the disease affects the joints of the limbs. The lack of necessary treatment inevitably and quickly leads to a poor outcome of the disease and disability.
Ankylosing spondylosis most often develops in young men
Deforming forms of diseases are more typical for older people. The pathogenesis is based on a decrease in the volume of intervertebral cartilage and compensatory filling of the remaining space. Spondylosis deformans and spondyloarthrosis can be perceived as a natural aging process. In addition, other causes may include exposure to radiation and hormonal imbalance.
Spondyloarthrosis predominantly develops in one specific area. Based on this, they distinguish:
- cervicoarthrosis (damage to the cervical spine);
- dorsarthrosis (damage to the thoracic region);
- lumbarthrosis (damage to the lumbar region).
At the same time, pathology develops in several departments very rarely.
Treatment
Treatment of spondyloarthrosis of the lumbosacral spine is aimed at both reducing symptoms and stopping the progression of pathological processes in the joints or bones.
Most doctors take a conservative approach in the initial phase of treatment, and only then consider invasive options, but only if symptoms do not respond to conservative therapy or severe neurological signs develop.
Some of the most common treatments for lumbar spondyloarthrosis are:
- Physical therapy (PT)
is used to strengthen the muscles of the lumbar spine. Stronger muscles support the spine better and thus reduce stress on the facet joints. - Losing weight
improves symptoms simply by reducing the stress on the lumbar spine. Although weight loss can be difficult for some patients, low-impact exercise (such as swimming) combined with a low-calorie diet can often achieve the results needed to relieve pain. - Drug treatment
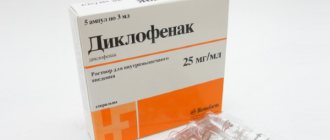
. Anti-inflammatory medications can reduce swelling and inflammation in the facet joint area. While over-the-counter medications such as Aleve (naproxen) or Advil (ibuprofen) can often provide sufficient symptom relief, stronger prescription medications such as Voltaren (diclofenac) and Arthrotec (diclofenac/misoprostol) are sometimes required. - The use of cold and heat
can also be effective in relieving pain in the lumbar spine. Heat can help loosen the spine before physical activity, while ice is best used after activity to reduce inflammation. - Manual therapy
. Manipulation is widely used to treat spinal diseases. Although manual therapy does not allow you to restore the full range of motion in the motor segments of the spine and restore the structure of the spine, nevertheless, manipulations can reduce pain and improve mobility. - Epidural injections
include: Injecting a steroid (cortisone or analogues) into the area of the pinched nerve. Cortisone may affect the immune system, thereby reducing localized inflammation and radicular pain.
Additional treatments include acupuncture, massage, magnetic therapy
, naturopathic remedies and other direct or indirect forms of posterior those. Although scientific evidence supporting these alternative treatments is largely lacking, most have few side effects and are reasonable options when used in conjunction with standard medical treatments.
Prevention
There are no preventive measures that would guarantee 100% prevention of the disease. The risk of developing spondyloarthrosis can be minimized by strengthening the muscular frame of the back and eliminating physical overload. It is also recommended to follow a diet to maintain normal weight, consume sufficient amounts of vitamins and microelements, and exercise therapy. Treatment of spinal spondyloarthrosis is successfully carried out in our center. Here you can undergo all the necessary procedures in accordance with your diagnosis. Consultations are carried out by high-level specialists, so during the visit patients feel as comfortable as possible. Modern equipment is at your service, allowing you to perform even complex manipulations.
Complications of spondyloarthrosis of the lumbosacral spine
Osteoarthritis rarely causes severe neurological dysfunction due to compression of nerve structures.
However, over time, degenerative changes can cause spinal stenosis, which means that narrowing of the spinal canal can cause compression of the spinal cord and nerve roots.
Spinal stenosis can be a complication of spondyloarthrosis.
Cauda equina syndrome is a disorder caused by compression of the nerves in the lower spinal cord by a tissue overgrowth or intervertebral disc, a rare complication of osteoarthritis that can cause serious neurological problems.
Costotransverse type of arthrosis
In the thoracic region there are costotransverse and costovertebral joints, which form the connections of the thoracic vertebrae with the ribs. These two types of formations are mechanically interconnected and therefore cannot work without each other. The costovertebral joint and the transverse costal joint perform the same function: raising and lowering the symmetrical arcuate bones that form the rib cage. This specificity of the articular apparatus of the spinal column is characteristic specifically of the thoracic region.
A little anatomy.
Each of the presented joints can suffer from degenerative-dystrophic pathogenesis. Although it is worth noting that articular lesions in this spinal region are very rare, since the thoracic segment is powerfully strengthened by the muscular-ligamentous complex. They develop more often in older people, mainly women.
As for clinical manifestations, in the previous paragraph we have already talked about the nature of the dorsal type of the disease. Let us recall one distinctive feature: pathological signs are predominantly concentrated in the region of the ribs and the upper part of the abdominal wall. If the disease is severely neglected, dangerous complications may follow: severe depression of the respiratory center and serious disorders of the functioning of the cardiovascular system.
Surgery
In cases of severe spondyloarthrosis that cannot be treated conservatively, surgery may be indicated.
Generally, surgery is considered if the patient experiences some of the following symptoms:
- Increased radicular pain
- Increased pain or nerve irritation
- Associated disk damage
- If degenerative changes in the facet joints lead to compression of the nerve roots, then radicular syndrome occurs. This causes radicular pain, weakness, and stenosis-like symptoms. In this case, surgery may be indicated to release the nerve root and remove excess degenerative tissue that is putting pressure on the root. One such procedure is called a foraminotomy. In addition, an operation such as vertebral fusion (spinal fusion) is used.
- Vertebral fusion is a surgical procedure used to eliminate movement between adjacent vertebrae. When all other treatments fail to provide relief, spinal fusion may be a reasonable option for treating severe spondyloarthritis.
Other conservative therapies
The third degree of deforming spondyloarthrosis requires special treatment methods. This is due to profound physiological changes in the joints plus the connective tissue corset. In order to eliminate constant pain of varying intensity, intra-articular injections of corticosteroid drugs (Prednisolone, Hydrocartisone or Kenalog) are performed. Injections are more effective than tablets; they do not affect the liver, kidneys, or other organs and systems. There are fewer side effects.
A second option with high potential for treating stage three is antirheumatic drugs, or DMARDs. A certain dose (it is selected individually for each patient) eliminates symptoms to a minimum, that is, it stops the process of destruction-deformation, removes swelling and partially or completely returns mobility. Cartilage tissue begins to renew itself through chondroprotectors. Antirheumatic medications, physiotherapy, exercise therapy, and massage encourage the regeneration of connective tissue.
Self help
- Self-medication is important for pain caused by spondyloarthritis because pain may increase or decrease over several days.
- Experts have found that even if there is pain, staying in bed for a long time is not advisable. Therefore, it is recommended to continue normal physical activity.
- However, you should avoid anything that could aggravate the condition, such as lifting heavy loads.
- Some people benefit from applying heat or ice to treat back pain.
- Sleeping with a pillow between your legs can be beneficial for lower back pain. An orthopedic mattress can also provide good support.
Useful properties and applications
The properties of sainfoin honey make it possible to use it for the treatment of many diseases as an adjuvant. It has the following effects on the body:
- Heals wounds thanks to antimicrobial properties.
- Tones and strengthens.
- Calms the nervous system.
- Stimulates immunity.
- Resists the formation of tumors.
- Diuretic and diaphoretic.
Thanks to its anti-inflammatory effect, taking honey promotes the healing of internal wounds such as ulcers and gastritis. It has the same effect on inflamed gums. With the help of honey rinsing you can get rid of stomatitis and gingivitis. As part of complex treatment, it helps well with periodontal disease.
Sainfoin honey increases mental and muscle activity and performance. It strengthens the immune system and promotes rapid recovery from viral and colds.
High iron and copper content helps improve blood composition. By consuming sainfoin honey daily, you can cleanse the body of toxins, help the liver function, and speed up metabolic processes. Thanks to the enzymes contained in the product, its consumption improves intestinal microflora and promotes normal digestion.
If you eat a small amount of honey before bed, you can normalize your sleep. It reduces the toxic effect of nicotine, strengthens the walls of blood vessels, making them more elastic.
Cosmetologists love to use sainfoin honey as part of face masks. It nourishes and moisturizes the skin well, giving it elasticity. If you constantly use it as a cosmetic product in its pure form or as part of masks with different ingredients, you can maintain young skin and a beautiful complexion for a long time.
In cosmetic masks, it goes well with lemon, egg yolk, glycerin, cottage cheese and oatmeal. Massages and wraps with sainfoin honey provide a good anti-cellulite effect.
Even just eating a small amount of honey every day will improve the condition of your bones, skin, hair and nails.
Training complex for thoracic localization
Exercise therapy warm-ups will allow you to strengthen this part of the spinal column, increase and maintain its mobility, forget for a long time about excruciating pain in the shoulder blades, sternum and ribs, and restore the functionality of the internal organs.
- Stand straight, feet together. As you inhale, raise your arms up and slowly bend back; as you exhale, lower your arms and at the same time bend forward, rounding your back. Repeat 10 times.
- Sit on a chair, cross your arms behind your head. Inhaling, bend your back backwards, spreading your elbows as far apart as possible. As you exhale, we return back, relaxing our elbows (8 repetitions).
- Kneel down, rest on the palms of your straightened arms. Arch your back downwards, opening your chest as much as possible, and hold in this position for 3 seconds. Then bend your back upward, holding for the same amount of time. Perform alternate bending-bending 7 times for each task.
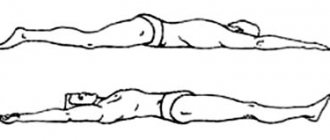
- Lie on your stomach, arms bent, palms at shoulder level. Straightening your upper limbs, raise your body. Standing on straight arms, smoothly arch the spine, pulling your chest forward (5-7 times).
- Starting position – lying on your stomach, upper limbs located along the body. We tear our shoulders off the surface, raise them to such a distance from the floor as your physical fitness allows (5-7 repetitions).
Massage
It is possible to improve the trophism of muscles, skin and joint components only through the use of massage, using a variety of gels with healing components in the form of chondroprotectors, analgesics and B vitamins. If there are no allergies to these drugs, and there are no skin diseases, then massage will help relieve pain , spasms, swelling of the affected back joints. Massage increases blood supply, improving the innervation of the vertebral joints, thus helping to increase metabolism, helping in the fight against pathogenic agents, pushing the regeneration mechanism of cartilage and connective tissue of joints to renewal.