Disturbance of spinal statics is a serious pathology that leads to dysfunction of all internal organs and systems, changes hemodynamics and microcirculation of lymphatic fluid. Any dysfunction of the spine entails a change in the functioning of the associated parts of the musculoskeletal system. Thus, if the posture of the spine is disturbed, the heads of the femoral bones in the acetabulum are displaced, followed by the development of deforming osteoarthritis. Then the knee and ankle joints are destroyed.
With the loss of static in the thoracic spine, it becomes deformed and the costal arches diverge. Spondyloarthrosis and arthrosis of the costovertebral joints quickly develop. The most serious health problems can arise when statics in the cervical spine are disturbed. The position of the cerebral blood vessels changes, resulting in insufficient blood supply to the brain. Problems also begin with the innervation of the sinus node of the heart muscle, pacemaker, and coronary circulatory system. This leads to the development of severe forms of angina, arrhythmia and ischemia.
In the early stages, spinal static disorders can be treated with conservative methods. Basic courses of kinesiotherapy and osteopathy are sufficient, followed by regular use of an individually developed course of therapeutic exercises. In addition to strengthening the muscular frame of the back, it is necessary to eliminate the effect of the negative factor - the reason why the static function is impaired.
If you have a static disorder, do not put off your visit to the doctor. In Moscow, you can make a free appointment with a vertebrologist in our manual therapy clinic. The doctor will conduct an examination, make an accurate diagnosis and develop an individual course of treatment. Call the administrator and make an appointment at any time convenient for you.
Functional disorder of the spine
In order to understand what the functional disorder of the spine is, it is necessary to find out exactly what functions this part of the musculoskeletal system performs. They include:
- supporting function – the spine creates a reliable frame for the whole body;
- shock-absorbing – due to physiological bends and cartilaginous intervertebral discs, physical load is evenly distributed during movement of the human body;
- ensuring upright walking - between the last lumbar and first sacral disc there is a conditional center of gravity of the human body, which allows you to walk on two legs;
- protective - inside each vertebra there is an oval hole that forms the walls of the spinal canal, it contains the spinal cord, which is responsible for the innervation of the entire body;
- motor – due to flexibility and mobility, the spinal column allows you to make various movements of the body (bending, turning, twisting, etc.).
Providing statistics, i.e. a certain limitation of movement and stability of the position of the vertebral bodies relative to each other - this is another important function, not of the spinal column, but of the muscular frame of the back, ligamentous and tendon apparatus located along it. If it is subjected to extreme physical stress, inflammation, stretching and other negative impacts, then the algorithm of its operation changes. The muscular frame of the back loses its ability to hold the spinal column in a certain position. When the ligaments of the spine are sprained and scar deformities occur in their structure, instability in the position of the vertebral bodies occurs. Most often, dysfunction of the spine is secondary in nature - it develops against the background of long-term diseases of a degenerative and deformative nature.
Treatment of static disorders without concomitant therapy for these diseases is impossible. Therefore, at the initial stage of diagnosis, it is important to establish all possible causes and conduct a full examination of the condition of not only the spinal column, but also the soft tissues surrounding it.
Circulatory disorders with static dysfunction of the spine
Any static disorders of the spine invariably lead to changes in the functionality of a number of systems:
- the movement of blood through the main blood vessels, which are located inside and outside the spine, is disrupted;
- the process of diffuse nutrition of the cartilage tissue of the intervertebral discs changes, due to which they become dehydrated and lose their functionality, and a spinal hernia develops;
- physiological posture is disturbed;
- the chest is deformed;
- the position of the heart, lungs, and abdominal organs changes;
- dysfunction of the intestines and bladder occurs (urinary and fecal incontinence may occur);
- congestion forms in the lymphatic system.
When the static function of the spine is disrupted, all organs and systems of the human body suffer without exception, since the spinal cord, located in the spinal canal, is responsible for the innervation of all areas. Any deformation of the spinal canal causes serious neurological problems.
The process of circulatory disorders in the spine depends on the degree of deformation. If the displacement of the vertebrae is insignificant, then the arteries inside the spinal canal are not infringed and continue to fully supply the structures of the spinal cord and the radicular nerves extending from it with blood. If poor posture and vertebral displacement are significant, then areas of ischemia may occur. A spinal stroke develops with paralysis of certain parts of the body and changes in the functioning of internal organs.
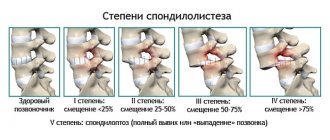
Types and degrees of dysfunction of the static function of the spine
The main types of spinal static disorders are determined by the localization of the pathological process. Most often, a violation of static function is diagnosed in the cervical and cervicothoracic spine. In second place in terms of development frequency is the lumbosacral region. It is extremely rare that statics are disturbed in the thoracic spine. The main reason for its appearance is a back injury during a fall from a height.
The following degrees of spinal dysfunction differ:
- the first is characterized by a slight weakening of the muscular frame of the back without displacement of the vertebral bodies;
- second – weakening of the muscles and longitudinal vertebral ligaments, slight displacement of the vertebral bodies;
- third – dystrophy of the muscular frame of the back, collar area and neck, significant displacement of the vertebral bodies, neurological clinic.
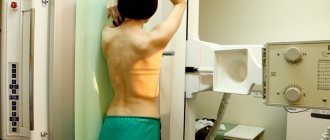
Diagnosis and determination of the type and degree of spinal static disorder is the responsibility of a vertebrologist. It is necessary to carry out a number of additional examinations, such as x-rays, MRI examinations, ultrasound, Doppler examination of blood vessels, etc.
Diagnosis of dorsopathy
A preliminary diagnosis is made during the initial examination of the patient. The examination is usually carried out by a neurologist in connection with the patient's complaints of local changes, which may manifest as pain, deformation or limited mobility. The spine is examined with the patient standing, sitting and lying, both at rest and in motion. The level of spinal damage is determined by counting the number of vertebrae from certain anatomical landmarks or according to a special scheme.
When examining the back, pay attention to posture, structural features of the body, note the line of the spinous processes (median groove of the back), the lower angles of the shoulder blades, the crests of the iliac bones, the lateral contours of the waist and neck, the position of the shoulder girdle, the deviation of the intergluteal groove from the vertical, and identify the protrusion of the spinous processes, pay attention to the relief of the muscles located next to the spine.
Feeling the spine allows you to supplement the examination data (presence or absence of deformation), determine the location, degree and nature of pain. When palpating, tension in the muscles located next to the spine is also noted, because Most injuries and diseases of the spine are accompanied by an increase in muscle tone.
Spinal flexion is used to determine the range of motion in various parts of the spine. The main role in the study of the spine is played by radiography, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging, with the help of which the level of damage is determined, the diagnosis is clarified and specified, and hidden pathologies are revealed. Diagnostic data allows the attending physician to determine treatment tactics and select the most effective treatment methods.
Disturbance of cervical spine statics
When the statics of any part of the spine is disturbed, a number of health problems arise. However, the most serious consequences are caused by a violation of the statics of the cervical spine, in which vertebral artery syndrome develops in the early stages and difficulties arise with the blood supply to the posterior lobes of the brain.
Severe dysfunction of the cervical spine leads to frequent headaches, dizziness, decreased mental performance, loss of memory and the ability to concentrate on solving a specific task.
A violation of the static function of the cervical spine develops due to the negative impact of the following factors:
- prolonged static tension of the muscles of the neck and collar area;
- degenerative dystrophic disease of the intervertebral discs (osteochondrosis) with a decrease in their height and the formation of conditions for excessive mobility of the vertebral bodies;
- spondylosis, spondyloarthrosis and ankylosing spondylitis;
- traumatic effects on the neck area;
- wearing excessively tight and constricting clothing;
- working on a computer;
- frequent injuries to muscles and ligaments in the collar area;
- changes in posture in the thoracic and lumbar regions.
Static disorders of the cervical spine lead to the development of a characteristic clinical picture. These are sharp pains in the neck, headaches (especially at the end of the working day), dizziness, insomnia, impaired performance of the upper free limbs, increased blood pressure, the development of arrhythmia and various types of VSD.
Development stages and stages
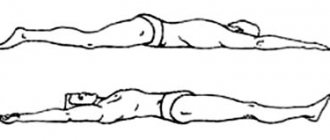
When bending forward, the following happens:
- People’s back muscles and ligaments are not always trained to lift weights, since they are designed only to perform some simple movements;
- Lifting weights overloads them and causes tendons to stretch;
- Repeating such unusual loads wears out the ligaments, so the weaker vertebrae “slip”;
- For some time, these microtraumas are restored, as they are replaced by scar tissue;
- Connective tissue is less strong, so it breaks again under stress;
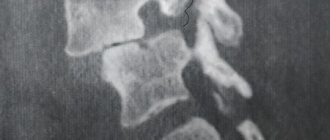
- Spondylolisthesis (a disease in which a weaker vertebra becomes displaced) appears asymptomatically;
- The destruction of adjacent intervertebral discs gradually continues due to curvature of the lumbar lordosis.
Violation of the statics of the thoracic spine
It is quite rare in the practice of a vertebrologist to encounter a violation of the statics of the thoracic spine in an isolated form. Most often, this condition accompanies the development of scoliosis and other types of postural disorders.
After a traumatic impact on the muscular frame of the back, an episodic or transient static disorder may occur, which quickly passes and the person completely restores the shock-absorbing capacity of the spinal column.
It is worth noting that with osteochondrosis of the upper intervertebral discs in the lumbar spine, a secondary static disorder may develop in the thoracic region. This is due to excess muscle tension in the lumbar region. If, during an exacerbation of lumbosacral osteochondrosis, you experience a feeling of excessive mobility in the thoracic region or, on the contrary, muscle tension, you should consult a vertebrologist. This is a characteristic clinical sign of a developing disorder of static function in the thoracic region.
Prevention
As you know, any disease is easier to prevent than to cure. Moreover, the displacement cannot be completely corrected, except to prevent the occurrence of other, more serious complications. Therefore, we recommend that you engage in the prevention of static disorders in all parts of the spine by changing your usual lifestyle to a healthy one. These tips and rules will be especially useful for those who engage in heavy physical labor.
- Change the way you interact with objects. For example, when lifting something, it is better to squat down and lift the load with a straight back without bending towards it;
- One of the most common preventive measures is wearing a hard or soft corset. This will strengthen the lumbar muscles, help maintain correct posture and lordosis of the lower back during any movements;
- Several courses of general back massage will not only help relieve tension at the end of the working day, but will also speed up the process of recovery of damaged ligaments;
- Engage in simultaneous strengthening of the longitudinal muscles of the back and abs. Swimming lessons in a pool can help with this.
Violation of the statics of the lumbar and lumbosacral spine
A sudden disturbance in the statics of the lumbar spine is in most cases a sign of a herniated intervertebral disc. When it falls out, the innervation of individual muscles of the lower back is disrupted and the patient experiences instability in this region. Sometimes excessive mobility of the vertebral bodies appears, which further aggravates the patient’s condition.
Violation of the statics of the lumbosacral spine can manifest itself in the form of the following clinical signs:
- pain in the lumbar region, spreading down the legs and radiating to the sacrum;
- numbness in the legs, in the anterior abdominal wall;
- paresthesia and tingling in the legs;
- inability to bend over and straighten up on your own;
- bladder and colon dysfunction.
For diagnosis, an examination by a vertebrologist is necessary. He may also order an X-ray or MRI examination of the lumbosacral spine. After diagnosis, treatment must be started immediately.
Treatment of spinal static disorders
Currently, treatment of spinal static disorders can be carried out using conservative methods. The main task facing the doctor is to restore the functionality of the ligamentous, tendon and muscular system. To do this, you need to restore normal microcirculation of blood and lymphatic fluid, strengthen the tone of muscle fibers, and eliminate the negative effects of the underlying disease.
Treatment at our manual therapy clinic begins with an examination and search for the potential cause of spinal imbalance. Then the patient receives comprehensive recommendations regarding correction of the daily routine, diet, arrangement of his sleeping and working space. An individual course of treatment is developed.
It may include laser correction of the condition of the structural tissues of the spine, electrical myostimulation, osteopathy, massage, and reflexology. The main emphasis in treatment is on kinesiotherapy and therapeutic exercises. They allow you to correct the condition of the muscular frame of the back, strengthen the tendon and ligament apparatus.
If you require treatment for a violation of the static function of the spinal column, you can make an appointment for a free appointment with a vertebrologist in our manual therapy clinic. The doctor will make a diagnosis and talk about the prospects for using manual therapy in treating your disease.
Treatment methods for pathological activity
Conservative
To relieve pain and stop the development of the inflammatory process, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are widely used. It is mandatory to wear a medical corset, which takes on the main load falling on the lumbosacral region. Physiotherapy procedures promote rapid penetration of medications directly to the site of inflammation. Therapeutic exercises are a mandatory element in the treatment of pathological activity. Exercises performed on a regular basis help improve blood supply to the vertebrae and maintain the elasticity of the ligaments.
The most effective conservative method of treating pathological mobility is non-load traction of the spine. After traction, the distance between the vertebrae is normalized, their structure is restored and nutrition improves.