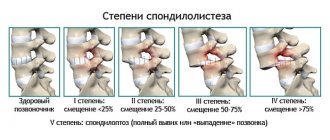
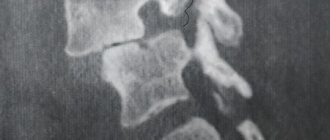
Myelodysplasia is a congenital disease characterized by pathological changes in the spinal column and spinal cord. The pathology has many varieties and can occur in a mild degree without significant symptoms, but severe degrees of the disorder lead to serious health problems and disability. It can affect any part of the spinal column, but in 85% of cases it develops in the final part. How to recognize spinal-sacral myelodysplasia and can the disease be cured?
Myelodysplasia of the lumbosacral spine
Myelodysplasia - what is it?
The term “myelodysplasia” refers to several pathologies of the musculoskeletal and nervous systems, each of which has its own signs and characteristics of the clinical course.
Spina Bifida is one of the lifelong spinal defects that primarily affects motor ability.
Table. Pathologies of the musculoskeletal and nervous system.
| Pathology | Features of the clinical course |
| Spina bifida | Pathological changes in which spina bifida or non-fusion of the vertebral arches is observed. |
| Spina bifida | Protrusion of various elements of the spinal cord (nerve endings, white matter, spinal membranes) through a hole formed in hard tissues due to pathological changes in its structure. |
| Syringomyelia | The formation of cavities in the spinal substance and associated disorders of the nervous system. |
| Rachishisis | A pathology in which spina bifida occurs, the spinal canal remains open, and the spinal cord is not protected by bone tissue and gapes outward. |
| Benign neoplasms | As a rule, benign tumors in myelodysplasia are represented by cysts; other forms of neoplasms are less common. |
| Osteophytes | Formations that are formed from bone tissue at the edges of the spinal column. |
Osteophytes on bones
Myelodysplasia of the spine can be accompanied by several pathologies - for example, spina bifida in combination with rachischisis, and if the disease is represented by one disorder, then it is usually spina bifida.
Attention! The term "myelodysplasia" can refer not only to the nervous system and musculoskeletal system, but also to hematopoiesis. Myelodysplasia of the blood is an oncohematological pathology, and has nothing in common with myelodysplasia of the spine.
Myelodysplasia
Deformation and other developmental anomalies of the sacrum
The sacrum is the part of the spine located between the lower back and the tailbone. Unlike the rest of its parts located above, it is completely motionless, looks like a massive triangular bone formed by five fused large vertebrae. The structure of the sacrum in women and men has some differences: the female sacrum is wider and less curved than the male one. This segment of the spinal column bears a large load when moving and in a sitting position, therefore, if there are any anomalies of the sacrum, pain occurs in this area. In some cases, such defects do not manifest themselves with any external symptoms.
Causes and risk factors
The exact reasons for the development of lumbar myelodysplasia are unknown - doctors believe that the pathology may be associated with malfunctions that occur in the fetus during the development of the nervous system and spine:
- genetic mutations of the germ cells of the mother or father can be either spontaneous or hereditary (occurs in 20-25% of patients);
- the negative impact of various factors on the body of the expectant mother and child in the first trimester of pregnancy, during which the formation of most organs occurs.
Genetic mutations are one of the possible causes
Sometimes genetic mutations are accompanied by an adverse effect on the body of the expectant mother, as a result of which the child develops myelodysplasia and other serious disorders. At risk are children of women with chronic diseases, mothers over 30 years of age, as well as pregnant women who live in regions with poor ecology.
An alarming sign for future parents may be an aggravated pregnancy - according to statistics, problems with bearing a child, especially in the first trimester, are observed in 70% of cases of myelodysplasia. The greatest danger is posed by intrauterine infections, vitamin deficiency, and exposure to drugs with teratogenic effects .
Intrauterine infections
What kind of disease is spondylodysplasia?
Spondylodysplasia, or Scheuermann-Mau disease, also called juvenile kyphosis, is a progressive disease, the main symptom of which is kyphotic curvature of the spine. It most often occurs in adolescents during puberty, but can also be diagnosed in children.
Initially, the symptoms are hidden, and only over time the first symptoms begin to appear - pain and stoop, which in severe cases leads to the development of a hump. Neurological complications may also be present.
In 30% of all patients with this disease, it is combined with scoliosis. Moreover, this is a fairly common pathology, which is detected in 1% of all children 8–12 years of age and older.
Symptoms
In complex cases, myelodysplasia can be diagnosed immediately after birth or in utero using ultrasound, but sometimes it goes undetected until the patient develops certain signs and abnormalities. Symptoms of the pathology include:
- impairment of motor activity of the lower extremities, partial or complete (paresis, paralysis);
- sensitivity disorders of the skin and soft tissues over the affected area of the spinal column - lack of response to high or low temperatures and other irritating factors;
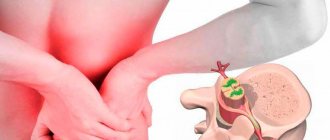
- pain in the lumbosacral region;
Lower back pain
- muscle hypotonicity, which manifests itself as fatigue and weakness;
- decreased reflexes - depending on the form of the pathology, patients may lack different reflexes;
- curvature of the spinal column – scoliosis, kyphosis, lordosis;
- gait disturbances, including clubfoot, lameness, etc.;
- dysfunction of the urinary system and digestive tract - most often enuresis or fecal incontinence, less often a tendency to constipation and increased gas formation;
- delays in physical and mental development;
- the appearance of trophic ulcers on the legs or back, which can fester, become inflamed and not heal for a long time.
Rachiocampsis
The severity of symptoms and the patient’s well-being depend on the characteristics of the clinical course of the disease. Mild forms can occur almost unnoticed by the child and his loved ones, and in some cases a person can live to adulthood without knowing that he is sick - the pathology is detected during routine examinations.
The disease can occur in an open or closed form. In the first case, patients are diagnosed with spinal cord cysts, which are not accompanied by other changes and are quite easily removed surgically. The closed form, as a rule, has unexpressed symptoms, so it is quite difficult to identify it, especially in the first stages.
Spinal cord cyst
Attention! If internal organs are involved in the pathological process of myelodysplasia (their innervation is disrupted or compression occurs by altered structures of the spine), the symptoms of the disease can be completely different. For example, with kidney damage, patients experience urinary and digestive tract disorders, swelling, and headaches.
Cervical spine dysplasia
Primary dysplasia of the cervical spine is the result of traumatic impact on the spinal column.
Most often, it forms after a compression fracture of the vertebral body or a crack in its spinous process. Secondary cervical dysplasia is a common complication of the degenerative dystrophic process in the cartilaginous tissues of the intervertebral discs. If a person develops osteochondrosis, then the height of the intervertebral discs gradually decreases. When moving, the vertebral bodies begin to touch each other. Keystone osteophytes form on their surface. They tend to merge with each other. This is the process of spinal dysplasia in the cervical region. As a result of the fusion of adjacent vertebrae, the neck loses its usual flexibility and mobility. It becomes difficult to tilt your head or turn it in one direction or another. Dysplasia of the cervical spine in children is almost always the result of congenital genetic disorders or birth trauma. When the cervical vertebrae are displaced during the passage of the birth canal, weakness of the baby's neck muscles occurs. If you do not actively massage this area during the first month of life, instability of the cervical vertebrae may persist. This is fraught with the fact that the process of assimilation of the first cervical vertebra (atlas) by the occipital bone may begin.
Also, spinal dysplasia in children may be associated with metabolic disorders. In the first place is vitamin D deficiency. In this case, rickets develops. This disease leads to the destruction and softening of bone tissue throughout the body. The lower extremities are the first to be affected. Following them, the spinal column bends. The process of dysplasia of the vertebral bodies and intervertebral discs begins.
There are also types of dysplasia associated with negative heredity. In their presence, the baby lags significantly behind his peers in growth and physical development.
Dysplasia of the cervical spine in adults can develop when exposed to the following unfavorable factors:
- constant static muscle tension in the neck and collar area;
- incorrect posture and growth of the “widow’s mound” in the area of the 6-7 cervical vertebrae;
- neck injuries;
- cervical myositis ossificans;
- osteochondrosis of the cervical spine and its complications, such as hernia, protrusion and extrusion of the disc.
If signs of cervical spine dysplasia appear, you should seek medical help as soon as possible.
How to recognize myelodysplasia in the early stages
Diagnosing myelodysplasia in newborns and infants is quite difficult, especially if there are no obvious signs. Parents need to pay attention to any changes in the child’s condition, and if there are any alarming symptoms, immediately consult a doctor. A characteristic sign of myelodysplasia of the lumbosacral region, which is observed in almost 100% of patients, is fecal and urinary incontinence, and less often a tendency to constipation and severe gas formation. If uncontrolled bowel and bladder emptying is observed in a child who, by age, should already be able to independently control the body’s excretory functions, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Urinary incontinence is one of the characteristic symptoms
Features of dysplasia
Dysplasia is a congenital deviation of the vertebrae from the normal structure, type and, in some cases, quantity. Pathology can spread to any part of the spine.
The first manifestations of the disease can be detected after birth or in adolescence. Dysplasia can be detected by a common factor - underdeveloped bones of the spine, which leads to disproportionate body sizes of the child. If you compare the torso and limbs, the latter look much longer.
Spinal dysplasia is any abnormality in the development of the spine.
Slow growth leads to:
- change in the location of the spine;
- pathologies of vital organs.
Using X-rays, the doctor can determine from the external data of the vertebra how much they have changed and whether the spinal column has become denser.
Diagnostic methods
At the first signs of lumbar myelodysplasia, patients are prescribed a comprehensive diagnosis, which includes several types of laboratory and instrumental studies.
- Magnetic resonance imaging. The most effective method for identifying abnormalities of the spinal cord and spinal column at any stage.
Magnetic resonance imaging - Radiography . Prescribed for the diagnosis of kyphosis, scoliosis and other pathologies that accompany lumbar myelodysplasia.
- Neurosonography . The method is based on ultrasound examination of the brain to exclude a common complication of spinal pathologies – hydrocephalus.
- Electroneuromyography . Allows you to assess the degree of damage to nerve and muscle structures by recording electrical impulses.
- Ultrasound of internal organs . Ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity and genitourinary system is carried out in case of disorders of excretory function, as well as to assess the condition of organs that may be involved in the pathological process.
Electroneuromyography
Important! Children with suspected lumbosacral myelodysplasia, regardless of the primary diagnosis, need to be diagnosed regularly - the disease can occur in a latent form (without visible changes), but at the same time progress rapidly.
Symptoms and diagnosis of lumbar myelopathy
Each type of disease has individual symptoms, but there is also a general clinical picture that indicates the presence of this somatic syndrome:
- Numbness of the legs, up to paralysis.
- The occurrence of lumbodynia or pain in certain places.
- Feeling of weakness and failures in thermoregulation.
- Irradiation of pain through internal organs.
- Disorders of the pelvic organs.
- Disturbances in the musculoskeletal system (changes in gait, lameness, etc.).
- Regular spasm of the muscular corset with limited range of motion of the lower back, etc.
The appearance of any symptoms indicates the possible development of the disease, so they cannot be ignored. The sooner treatment begins, the greater the likelihood of stopping the pathological process and restoring the body.
A simple examination is not enough to confirm the diagnosis. The patient needs to undergo a lot of tests and diagnostic studies. In a hospital setting, the inflammatory process is determined (blood tests for biochemistry). This will also show the presence of infectious diseases that could lead to pathology. After this, instrumental studies are carried out:
- Cardiogram;
- CT scan;
- Radiography;
- Determination of bone mineralization density;
- Fluorography;
- MRI.
If a specialist suspects the presence of neoplasms, then a biopsy or culture of cerebrospinal fluid is added to the studies.
Prognosis and complications of myelodysplasia
The success of treatment, quality and life expectancy of patients depend on the form of the disease and the characteristics of the clinical course. Mild disorders, as a rule, are not accompanied by severe symptoms and pathological changes, so people with this diagnosis are practically no different from healthy people. In severe cases, patients experience impaired motor activity, constant discomfort in the back, disorders of the internal organs, paralysis and paresis.
Paralysis is one of the possible complications
Some patients cannot move independently and are forced to use special devices, and are also unable to care for themselves - in such cases, the person is assigned a certain disability group.
Video - Myelodysplasia of the spine (Spina Bifida)
Leading spinal surgeons in Israel
| Dr. Zvi Lidar Neurosurgeon, orthopedist, leading Israeli specialist in the field of mini-invasive microsurgery of the spine (Ichilov) | Professor Reuven Gepstein Neurosurgeon, orthopedist, head of the department of spinal surgery (Meir) | Dr. Alon Friedlander Surgeon, orthopedist head of spine surgery (Sheba) | Dr. Nachshon Rand Surgeon, Leading Spinal Surgeon (Assuta) |
Click to see a doctor
Treatment of the disease
Therapy for myelodysplasia is aimed at improving motor activity and muscle tone, preventing possible complications, and, if necessary, social adaptation of the child and instilling self-care skills. For treatment, conservative or surgical techniques are used in combination with physiotherapy - the choice of treatment regimen and tactics depends on the clinical course of the pathology and the general condition of the patient.
Treatment of myelodysplasia
Conservative treatment with drugs
The following medications are used to treat lumbosacral myelodysplasia:
- medications to improve motor activity and the condition of peripheral muscles (“Neostigmine”, “Proserin”, “Physostigmine”);
- drugs to relieve muscle tension, which is observed with paresis of the lower extremities - “Baclofen”, “Cyclobenzaprine”;
"Baclofen" - neuroprotectors that promote the regeneration of damaged areas of the spinal cord (Citicoline, Cerebrolysin);
- B vitamins to activate metabolic processes in muscle tissue;
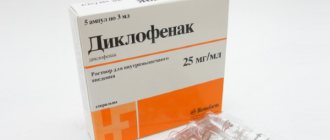
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, analgesics and antispasmodics - for pain;
- dehydration therapy with Diacarb and magnesium sulfate in combination with Asparkam is necessary in cases where myelodysplasia is accompanied by a deterioration in the outflow and accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid.
"Diakarb"
Attention! The regimen and dosage of drug treatment should be selected by the attending physician after a comprehensive diagnosis and assessment of the patient’s condition.
Conservative non-drug treatment
Non-drug therapy plays a key role in the fight against myelodysplasia and its complications. It improves muscle and nerve function, strengthens tissue, activates blood circulation and metabolic processes, reduces rehabilitation time after surgery, and in some cases literally puts the patient back on his feet.
- Physiotherapy . Electrophoresis, ultrasonic and magnetic effects, laser and ultrasound irradiation normalize microcirculation in the affected area, promote rapid tissue restoration, relieve pain and inflammation.
- Physiotherapy. The purpose of physical therapy exercises is to improve motor function and strengthen the muscle corset. A set of exercises is selected individually for each patient and is performed under the supervision of an experienced specialist. The basic rule of exercise therapy is to perform exercises regularly for a month or more.
Physiotherapy - Massage . Improves blood circulation in tissues, eliminates congestion, helps strengthen muscles and reduce hypertension.
Acupuncture and alternative treatments for myelodysplasia should be used with great caution, especially in young patients, otherwise serious deterioration of the condition may occur.
Surgical intervention
Surgical treatment of myelodysplasia of the lumbar spine is carried out in clinics specializing in neurosurgery. The most commonly used types of operations are:
- surgical stabilization of the spinal column (if there is a curvature of more than 30 degrees);
- plastic surgery of kyphosis and other congenital pathologies of the lumbosacral region, usually performed in the first weeks after the birth of the child;
- microsurgical procedures (removal of cysts and tumors);
- Emergency surgical treatment is performed for ruptures of the spinal membrane in the final stages of the hernia.
Surgical treatment of myelodysplasia of the lumbar spine
Surgical intervention eliminates compression of nerve endings, eliminates damage and improves the condition of the musculoskeletal system, but is associated with a risk of complications and is therefore prescribed only in severe cases.
Question answer
What kind of pain occurs with this type of osteochondrosis?
Osteochondrosis of the lumbar region is characterized by several types of pain. First of all, these are localized unpleasant sensations in the lumbar region, which continue over a long period of time and significantly intensify with an increase in a person’s motor activity and physical labor. This type of pain disappears if the body is placed in a horizontal position for at least 15–20 minutes.
If the disease worsens due to hypothermia, prolonged heavy physiological stress, or sudden “twisting” movements, then in addition to the above-mentioned background pain, a “shooting” effect also occurs, localized in the pelvic area and radiating to the lower extremities.
Is gymnastics useful for this osteochondrosis?
Therapeutic exercise therapy allows you to consolidate the good effect of complex therapy for the disease, partially develop the intervertebral components of the joints, and also relax/train the muscles in the lumbar region. In addition, proper regular massages help get rid of the unpleasant pain that accompanies osteochondrosis.
A specific set and list of exercises, the number of approaches and frequency of exercises will be developed for you by your attending physician: he will take into account the current stage of the disease, a possible list of contraindications and restrictions, the patient’s condition and will recommend methods for using exercise therapy in practice.
{SOURCE}
Prevention of myelodysplasia
There is no specific prevention of lumbosacral myelodysplasia, therefore, to prevent the disease, it is necessary to adhere to general rules aimed at reducing the risk of developing congenital defects in the fetus during pregnancy:
- eat normally, eat foods containing vitamins and microelements;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- take special vitamin complexes for expectant mothers;
- do not use medications without consulting a doctor;
- attend antenatal clinics on time, take tests and follow medical recommendations;
- avoid factors that may contribute to impaired child development - ionizing radiation, exposure to heavy metals, infectious diseases.
You need to eat right during pregnancy
If one of the parents has hereditary diseases of the nervous system, you should consult a geneticist before planning a child.
Myelodysplasia is a serious disease that can significantly worsen a child’s quality of life, and in severe cases, turn him into a disabled person for the rest of his life. To prevent the development of pathology in a child, parents need to take a responsible approach to the planning and course of pregnancy, and carefully monitor the child’s health from the first days of his life.
Video - Improvement of the lumbosacral spine
Eliminating the symptoms of lumbosacral osteochondrosis with exercises
For more successful treatment of spinal pathology, it is necessary to strengthen the muscles of the back, buttocks and thighs. To do this you need to know and perform therapeutic exercises. Before performing exercise therapy, a person must visit a neurologist, who will correct the set of exercises. In some cases of osteochondrosis, exercise therapy is strictly prohibited. Sometimes you can only do certain exercises.
Therapeutic physical training complexes are divided into three groups:
- Exercises for the first stage of the acute phase, that is, with severe pain.
- Exercises for the second stage of acute pain, pain relief.
- Exercise during remission.
When performing exercise therapy, you cannot mix exercises from different groups; you must strictly follow the prescribed complex. The patient should not feel pain when moving: if there is pain, then it is necessary to abandon this exercise or reduce the range of motion.
Requirements for performing exercises for lumbosacral osteochondrosis:
- Exercise therapy should be performed every day;
- when performing exercises, you need to concentrate on the work of the muscles, do everything in a slow mode;
- monitor your breathing;
- consult a doctor.
By performing comprehensive treatment of spinal pathology, it is possible to minimize the occurrence of periods of exacerbation of the disease.
Other diseases - clinics in
Choose among the best clinics based on reviews and the best price and make an appointment
Family
Scoliosis Treatment Center named after K. Schroth
Moscow, st.
Azovskaya, 24, building 2 POM VI/KOM 5,6,7/ET 1 Sevastopolskaya
+7
- Consultation from 1500
- Exercise therapy from 2700
0 Write your review
Family
Oriental Medicine Clinic "Sagan Dali"
Moscow, prosp.
Mira, 79, building 1 Rizhskaya
+7
- Consultation from 1500
- Diagnostics from 0
- Reflexology from 1000
0 Write your review
Family
Center for Chinese Medicine "TAO"
Moscow, st.
Ostozhenka, 8 building 3, 1st floor Kropotkinskaya
+7
- Consultation from 1000
- Massage from 1500
- Reflexology from 1000
0 Write your review
Show all Moscow clinics
Other diseases - specialists in Moscow
Choose among the best specialists based on reviews and the best price and make an appointment
VertebrologistOrthopedist
Gromov Ilya Sergeevich
Moscow, st.
Azovskaya, 24, building 2 POM VI/KOM 5,6,7/ET 1 (Scoliosis Treatment Center named after K. Schroth) +7 Registration
0 Write your review
VertebrologistOrthopedist
Kudryakov Stepan Anatolievich
Moscow, st. Azovskaya, 24, building 2 POM VI/KOM 5,6,7/ET 1 (Scoliosis Treatment Center named after K. Schroth)
+7
Registry
0 Write your review
Orthopedist