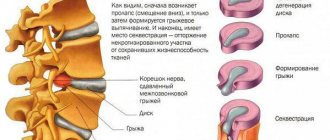
First, a little about what an “intervertebral disc” is. Our spine(s) are cushioned by pads of tissue called discs. They consist of an outer capsule or ring, the so-called annulus fibrosus. A tough annulus fibrosus surrounds the nucleus pulposus, which is a spongy center of jelly-like material.
The fibrous ring consists of many collagen and elastin fibers that, tightly intertwined, grow together with the vertebral bodies. In the middle of the ring is the nucleus pulposus, which consists of collagen, fibroblasts, and chondrocytes. In volume it is only 1-1.5 cm cubic.
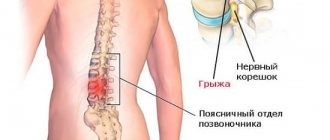
Healthy discs serve as shock absorbers for the spine, allowing it to be flexible. When they are damaged by age or disease, they begin to bulge and the annulus fibrosus may even rupture (the jelly-like material breaks through the tough outer layer). This disease is called intervertebral disc herniation .
A hernia can occur in any part of the spine, but most often appears in the lumbar region. A deformed disc can put significant pressure on both the spinal cord itself and the nerve roots that extend from it. A possible result of this pressure is pain or numbness in various parts of our body. However, many do not experience unpleasant symptoms from existing hernias. Most people who have them do not always require surgical intervention.
If a herniated disc has formed, its tissue can protrude both outward and inward.
The second case is the most dangerous.
In general, a hernia is dangerous not only because of the pain it causes, but also because of the complications it can lead to:
- stenosis (compression) of the spinal cord
- radicular radiculopathy (radiculitis)
- compression of blood vessels - vertebral veins and arteries
- paralysis and paresis
- headaches and dizziness
Treatment of hernias in our clinic
Various surgical and conservative treatment methods are used to treat herniated intervertebral discs. Surgical methods mainly involve mechanical “cutting” of the disc and it is clear that in this case the functions of the disc cannot be fully restored. Surgical methods are used when the hernia has already reached a large size, and conservative treatment has failed to produce positive results.
Treatment of hernias without surgery
In our clinic, for the treatment of intervertebral hernias, we successfully use only conservative methods that are highly effective - more than 90% and allow us to do without expensive operations.
What needs to be done to make hernias disappear?
Naturally, there is no universal answer that would be suitable for all patients. But the general principles of hernia treatment are well known to us, and the specific program is selected individually.
When treating hernias it is necessary:
- Relieve pain syndrome
- improve nutrition of the affected area
- relieve possible muscle spasms
- Strengthen the muscle corset
- improve metabolic processes
To achieve these goals, our clinic doctors have all the necessary equipment at their disposal:
- Shock wave therapy Zwave,
- Pulse currents, electrophoresis,
- Detensor - therapy (traction),
- Ultrasound Phonophoresis,
- Hiwamat deep massage,
- Acupuncture physiotherapy
- Laser therapy,
- Pressotherapy,
- Magnetotherapy,
- Bubnovsky simulator,
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is a method of treating a hernia aimed at stimulating the body to heal itself . The method is used in combination with medication, gymnastics, massage and other means of combating the disease. Physiotherapy helps prevent possible complications and improve the quality of basic therapy.
The procedures are based on the following influences:
- water flows;
- cool and warm air;
- ultrasound vibrations;
- magnetic field;
- laser radiation;
- electric current.
Physiotherapy improves blood circulation and metabolism of back tissues. Physiotherapy allows you to solve the following problems:
- improve the metabolism of affected tissues;
- accelerate vertebral regeneration;
- restore the functioning of internal organs;
- activate blood circulation;
- reduce inflammation and swelling;
- restore muscle tone;
- increase the mobility of the spine;
- reduce pain;
- get rid of muscle spasms;
- correct your posture.
Before prescribing therapy, the patient is advised to undergo a health examination, based on which the doctor will select suitable procedures. Physiotherapy is carried out strictly in medical institutions under the supervision of a specialist. The effect of the sessions becomes noticeable after just a few visits.
At what stage is it prescribed?
Physiotherapy can be used at any stage of pathology development. Moreover, they can be prescribed as an auxiliary method during the main therapy to enhance its effect and to speed up rehabilitation after treatment.
The doctor makes a decision on the appointment of physiotherapy sessions, their dosage and duration of exposure, based on the course of the disease and the individual characteristics of the patient.
Contraindications
Contraindications to physiotherapeutic procedures for spinal hernia are::
- pregnancy period;
- skin diseases;
- respiratory system disorders;
- dysfunction of the liver and kidneys;
- pathologies of the nervous system;
- malignant formations;
- serious illnesses;
- serious disorders of the cardiovascular system.
Want to know more about using physical therapy to treat your spine? Read the following articles:
- What physiotherapy procedures are used to treat osteochondrosis in the neck are described here
- Who can and cannot use a magnetic posture corrector?
- You can find out whether it is possible to cure a spinal hernia with acupuncture at the link pozvonochnik/drugie-zabolevaniya/mezhpozvonochnaya-gryzha/iglorefleksoterapiya-pri-gryzhe-pozvonochnika.html
PRICES FOR OUR PROCEDURES
(select the section you are interested in)
Shock wave therapy
Prices
UVT prices
Before starting the procedures, consultation with a specialist is required!!!
SHOCK WAVE THERAPY PRICE
| Name of procedure | Price, rub. |
| Name of procedure | Price, rub. |
| Shock wave therapy (SWT) procedure using the enPuls Zimmer device for the treatment of heel spurs | 800 |
| Shock wave therapy (SWT) procedure with enPuls Zimmer device for one anatomical zone | 1200 |
Areas of procedures for medical UVT treatment: Hand - 1 zone Forearm - 1 zone Shoulder - 1 zone Back - 2.5 zones Buttocks - 1 zone Thigh - 1 zone Lower leg - 1 zone Foot - 1 zone
Zones for cosmetic UVT procedures: Hand -1.5 zones Forearm -1.5 zones Shoulder -1.5 zones Back -3.5 zones Buttocks -1.5 zones Thigh -1.5 zones Lower leg -1.5 zones Foot -1.5 zones
Laser therapy, ILBI
Prices Laser Vlock
Prices Laser therapy ILBI
Before starting the procedures, consultation with a specialist is required!!!
| Name of procedure | Price, rub. |
| Laser therapy device "Mustang -2000+" one field | 500 |
| Laser therapy device "Mustang -2000+" two fields | 700 |
| Intravenous laser blood irradiation (ILBI) 1 procedure | 1000 |
| Intravenous laser blood irradiation (ILBI) 6 procedures | 5000 |
| Intravenous laser blood irradiation (ILBI) 10 procedures | 8000 |
Magnetotherapy
Prices Magnetotherapy
Prices Magnetotherapy
Before starting the procedures, consultation with a specialist is required!!!
| Name of procedure | Price, rub. |
| Vortex magnetotherapy apparatus “Magnetoturbotron” EOL | 1000 |
| Running magnetic therapy device "Almag-02" | 500 |
Ultrasound, Electrotherapy
Ultrasound Electrotherapy
Prices Ultrasound Electrotherapy
Before starting the procedures, consultation with a specialist is required!!!
| Name of procedure | Price, rub. |
| Ultrasound therapy device “SoleoLine” (1 procedure) | 500 |
| Ultrasound therapy device “SoleoLine” (6 procedures) | 2500 |
| Ultrasound therapy device “SoleoLine” (10 procedures) | 4000 |
| Medicinal electrophoresis apparatus “SoleoLine” (1 procedure) | 700 |
| Medicinal electrophoresis apparatus “SoleoLine” (6 procedures) | 2500 |
| Medicinal electrophoresis apparatus “SoleoLine” (10 procedures) | 4000 |
| Pulse currents apparatus “SoleoLine” (1 procedure) | 500 |
| Pulse currents apparatus “SoleoLine” (6 procedures) | 2500 |
| Pulse currents apparatus “SoleoLine” (10 procedures) | 4000 |
Lymphatic drainage, Khivamat
Prices Lymphatic drainage hivamat
Prices Lymphatic drainage, Khivamat
LYMPH DRAINAGE
| Service | Prices / rub. |
| LYMPHODRAINAGE Morning Life Premium device: | |
| Lymphatic drainage of legs 30 min certified device (South Korea). | 800 |
| Hand lymphatic drainage 30 min certified device (South Korea). | 800 |
| Lymphatic drainage of the abdomen 30 min certified device (South Korea). | 800 |
| Lymphatic drainage of the thighs 30 min certified device (South Korea). | 800 |
| Procedures using the Hiwamat 200 device (Germany): | |
| Procedure apparatus Khivamat 200 one zone. | 1000 |
| Procedure apparatus Khivamat 200 two zones. | 1500 |
Others
Other prices
Prices Other
Before starting the procedures, consultation with a specialist is required!!!
| Name of procedure | Price, rub. |
| Vegetative resonance test (VRT) Parasites (40 min.) | 2000 |
| Vegetative resonance test (VRT) General (2 hours) | 4800 |
| Vegetative resonance test (VRT) Allergies (50 min.) | 2500 |
| Vegetative resonance test (VRT) Nutrition (40 min.) | 2500 |
| Vegetative resonance test (VRT) Drugs (50 min.) | 2800 |
| Initial appointment with a homeopath + selection + provision of a drug + bioresonance therapy session | 5000 |
| Repeated appointment with a homeopath + selection of a drug + provision of a drug + bioresonance therapy session | 3500 |
| Consultation with a homeopathic doctor regarding the possibility of using homeopathic treatment (without selecting medications) | 1500 |
| Bioresonance therapy, electropuncture (1 procedure) | 450 |
| Checking the compatibility of a drug using the ART method (1 drug) | 200 |
| Detensor therapy (1 procedure without instructor 45 min.) | 400 |
| Detensor therapy (1 procedure with instructor 75 min.) | 2200 |
| Khivamat medical massage for the back Khivamat medical massage for the lower back Khivamat medical massage for the collar area Khivamat medical massage for the extremities Khivamat anti-cellulite massage for the buttocks Khivamat anti-cellulite massage for the hips Khivamat anti-cellulite massage for the abdomen Anti-cellulite massage for the shoulders (arms) | 1500 1000 1000 1000 1000 1500 1000 1500 |
| Consultation with a physiotherapist, neurologist of the highest category (repeated consultation is free) | 900 |
FREE TREATMENTS
|
Intervertebral disc herniation: Causes of occurrence
Over many millennia, humans have anatomically adapted to the effects of gravity. Thus, the main power axis of our body, the spine, has acquired a shape reminiscent of a spring with a double S-shaped curvature. The elasticity and firmness of the spine is provided by the intervertebral discs. Thanks to their elastic properties (virtually non-compressible liquid), shocks and tremors experienced by the brain or spinal cord during any movement are significantly softened. But being very fragile, vulnerable formations, they unfortunately suffer from constant gravitational influence.
The appearance of a hernia is most often the result of gradual aging or wear of the intervertebral disc (degeneration). As we age, our spinal discs lose some of their water content. This makes them less flexible and more prone to tearing.
Loss of fluid is the main reason.
During the day, due to the resulting loads on the spinal column, fluid with waste products leaves the intervertebral disc, which leads to a decrease in its size. If loads prevail, then fluid consumption prevails over replenishment of its reserves. Thus, the disc loses water, increasing degeneration (degeneration, destruction) of its tissues develops, which is also accompanied by loosening of the fibrous part, the appearance of cracks (“dry soil”), and a decrease in height (it seems to “shrink”). This leads to a relative increase in the length of the intervertebral ligaments, and all together to an increase in the mobility of the vertebrae relative to each other. The next stage marks the exit of the inner part of the intervertebral disc beyond its limits, which can be facilitated by heavy lifting, unsuccessful turns of the torso, neck, etc. .
But at the same time, there are also many other reasons leading to the appearance of intervertebral hernias, among them:
- general underdevelopment of the muscular corset of the spine,
- heavy physical activity,
- consequences of past injuries,
- incorrect posture,
- the presence of significant psycho-emotional overloads,
- hereditary factor, some others.
All these reasons affect the disruption of water-salt metabolism in the spine and can ultimately lead to the formation of hernias.
Physiology of the spine: age-related changes.
When forming the shock-absorbing and biomechanical properties of the intervertebral disc, the nature of water exchange is of particular importance, which is influenced by the so-called pump mechanism (for more details, see the section Detensor therapy ), as well as hormones of the pituitary gland, adrenal glands, thyroid gland, and individual characteristics of loads on the spine. At the age of 18 to 23 years, the tissue of the discs is most saturated with water and minerals and, as a result, they are strong and flexible. Over time, the content of mineral salts and water decreases, and, as a rule, this process occurs more intensively after 40 years, their depreciation function decreases. Under the influence of loads, they can even flatten, and sometimes the annulus fibrosus and nucleus pulposus protrude (without rupture of the annulus fibrosus) beyond the endplates, which is called protrusion. Over time, degenerative changes in the ring and core intensify and lead to the appearance of cracks and radial tears. With sudden movements: coughing, lifting heavy objects, sneezing, etc., rupture of the fibrous ring may occur. The contents of the intervertebral disc often protrude into the spinal canal in the form of a drop. A hernia can put pressure on a nerve root, causing irritation or compression.
Clinical picture of the cervical spine
>Intervertebral discs begin from the 3rd intervertebral space and provide flexion, extension of the neck and lateral bending with a significant amplitude. The posterior longitudinal ligament is wide, and the height of the intervertebral discs is relatively small. These anatomical and physiological features of the structure of the cervical spine make it very mobile. However, in the cervical region, the posterior longitudinal ligament is weaker, so disc protrusion can occur not only in the posterior, but also in the posterolateral direction. The transverse processes of the cervical vertebrae have openings. Located one above the other, they form a canal through which the vertebral artery, vein and sympathetic nerve pass, therefore, with a hernia of the cervical spine, cerebral circulation may be disrupted and vertebobasilar insufficiency (VBI) may occur.
This often leads to dizziness, headaches, hearing loss, memory loss, and uneven gait.
Read more about vertebobasilar insufficiency..
Autonomic disorders are also additional confirmation of the diagnosis
The following symptoms are also characteristic of a cervical hernia: pain in the neck, shoulder blade, shoulder or arm, numbness of the fingers, pressure surges.
Clinical picture of the lumbosacral region
Herniation of the intervertebral disc in this part of the spine is the most common. Its occurrence is facilitated primarily by the special operating conditions of the lumbar region - higher loads compared to other parts of the spine, since the discs of the lumbar region bear almost the entire weight of the body. The high incidence of hernias in this part of the spine is also associated with the anatomical features of the lower back, primarily with the significant height of the intervertebral discs. Also, in the formation of lumbar hernias, an important role is played by the weak and narrow longitudinal ligament; its width between the lower lumbar vertebrae is only 1-4 mm, so it cannot serve as sufficient resistance to hernial formation. Your spinal cord does not extend into the lower part of the spinal canal. At your waist, the spinal cord divides into a group of long nerve roots (cauda equina) that resemble a horse's tail. All these structural features of the lower lumbar spine make it especially vulnerable.
When a lumbar intervertebral disc herniation occurs, severe pain appears in the lower back. The patient loses the ability to move independently. Later, the pain in the lower back decreases, but shooting pain appears in the buttock, along the back or side of the leg, radiating to the toes.
Knee and Achilles reflexes decrease or disappear. In some cases, the symptoms of an intervertebral hernia are accompanied by a disorder in the pelvic organs in the form of delayed urination or stool. The patient is characterized by an antalgic posture; more often he prefers to stand rather than sit.
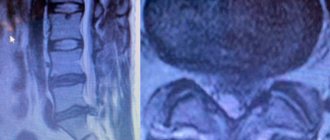
Intervertebral hernia: Diagnosis
Magnetic resonance imaging is used to diagnose intervertebral hernia. Due to the relative softness of the intervertebral disc, the most objective method of examination is magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the spine. For the same reason, many parts of it are not visible on an x-ray. After receiving an MRI, your doctor will ask you many questions during your appointment to make a correct diagnosis and develop a treatment plan. These questions will likely include the following:
- When did you start experiencing symptoms?
- Does pain prevent you from doing normal activities?
- Do you feel any pain, weakness or numbness in your arms or legs?
- Do you notice any changes when urinating or bowel movements?
- Does coughing, sneezing or straining to have a bowel movement worsen your leg pain?
- What, if anything, improves your symptoms?
- Is the pain related to sleep or work?
- What medications or nutritional supplements do you take?
To determine the true cause of the pain, the doctor will check your neurological status during the examination:
- Reflexes
- Muscle Strength
- Sensitivity (Ability to sense soft touch, pinpricks, or vibration)
Contraindications
There are a number of restrictions for the patient that can speed up the recovery process:
- At the early stage of rehabilitation, it is prohibited to play sports. You should also not use public transport, especially long trips, since the patient should not be in a sitting position for more than 15 minutes. You cannot wear a support corset for a long time (no more than 3-4 hours a day), however, it is also not recommended to completely neglect it. Doctors also prohibit giving the patient a massage, lifting a load weighing more than 2 kg and bending over it, taking medications on their own, drinking alcoholic beverages and smoking.
- During the late recovery period, you should not break your diet. If the body does not receive all the necessary vitamins and microelements, the healing process can be very delayed. Lying or sitting for a long time is not recommended, as is traveling long distances. Doctors advise not to be lazy and be sure to exercise regularly. The weights that the patient can lift should not weigh more than 8 kg. It is forbidden to wear clothing that leaves the affected area exposed or, conversely, contributes to its overheating. Also, the patient should not drive a car for at least three months. Neglecting the corset has a negative impact on the healing process. Even at this stage, it must be worn about 4 hours a day.
- During the deferred period there are not many restrictions. We must not forget about training, carry heavy weights, violate the prescribed diet and make jerks or sudden movements.
Throughout his life, a person is recommended to monitor his musculoskeletal system and not subject it to prolonged and severe stress. If the patient exhibits any symptoms of the disease again, he should immediately consult a doctor and undergo an examination.
Intervertebral disc herniation: Prevention and Recovery
- Strengthen the muscular corset of the spine. Strengthening your muscles will help stabilize and support your spinal column. Before engaging in exercise such as jogging or tennis, check with your doctor.
- Maintain good posture. Good posture reduces pressure on your spinal column and discs. Keep your back straight and level, especially when sitting. Remove heavy and uncomfortable shoes, or better use special orthopedic shoes. Remember, when walking, it is not your legs, but your back that does most of the work.
- Maintain a healthy weight. Excess weight puts more pressure on the spinal column and discs, making them more susceptible to the onset of many diseases.
- Avoid lying in bed for too long. This can lead to stiff joints and weak muscles, which can complicate your recovery. Instead, take a short walk or do light work that won't cause you pain. Try to avoid movements that increase pain.
Terms: intervertebral hernia, intervertebral hernia treatment, lumbar intervertebral hernia, intervertebral hernia with Zwave device, intervertebral hernia of the cervical spine, herniated disc treated with the UVT zimmer device, herniated disc treated with laser therapy Mustang 2000, herniated disc treated with enpuls device , Moscow, Khimki, Dolgoprudny , Mytishchi, Bibirevo, Timiryazevskaya, Otradnoe, Altufyevo.