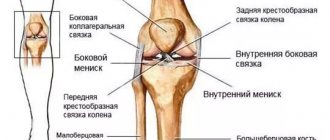
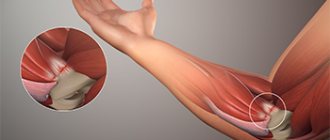
What is radiculitis, symptoms
Radiculitis affects the peripheral nervous system. It occurs due to pinching of the nerve roots of the spinal cord. At the same time, the latter are subject to an inflammatory process and can even be damaged due to serious pinching. This disease is characterized by periods of exacerbation and remission .
During periods of exacerbation, severe pain occurs in the affected area of the spinal column.
Below are the causes of sciatica
The cause of exacerbations of radiculitis can be:
- stressful situations;
- hypothermia;
- passive lifestyle;
- playing sports;
- progressive osteochondrosis;
- hard physical labor;
- tumors of the spinal column;
- expanding osteophytes;
- deposited salts.
Depending on the location, the following types of radiculitis are distinguished::
| Cervical | Soreness appears in the neck and occipital region. The pain increases significantly with coughing and head movements. |
| Cervicobrachial | Pain occurs in the neck, shoulders and upper extremities. |
| Chest | Manifests itself as girdling pain in the sternum area. |
| Lumbosacral | It is characterized by pain in the lumbar region, which can radiate to one of the lower extremities. |
Radiculitis. Treatment, prevention
Radiculitis is a fairly common disease of the peripheral nervous system. The disease is based on damage to bundles of nerve fibers, the so-called nerve roots extending from the spinal cord. Any damage or inflammation is radiculitis.
Causes of radiculitis
The main reliably established reasons are:
- disc herniation in one of the parts of the spine - narrowing of the spinal canal - narrowing of the canal where the nerve root is located - trauma - tumor - degeneration of the vertebral discs - osteophytes (a bone spur, a growth that is not normal for a healthy skeleton, is a full-fledged bone mass that is formed in as a result of the protective reaction of the spine to overload) An attack of radiculitis can be triggered by metabolic disorders, infections, heavy lifting, sleeping in an uncomfortable position, or awkward movement. Those at risk of developing radiculitis include professional athletes, people engaged in heavy physical labor, summer residents, as well as people leading a sedentary lifestyle.
Types of radiculitis
Most often, the disease develops acutely and for the most part becomes chronic with temporary exacerbations. Depending on the location, radiculitis is divided into four types.
• Lumbosacral radiculitis, characterized by damage to the roots of the sacral spine. In this case, pain occurs and intensifies with movement, bending, and walking. This is the case when you bend down to tie your shoelaces, but you can no longer straighten up, because it causes severe pain. This case of radiculitis is most often encountered in medical practice.
• Cervicobrachial, characterized by pain in the neck, shoulders, and arms. The pain intensifies when moving the arms or head, and also when coughing.
• Cervical sciatica will make you suffer from pain in the neck and back of the head. Head movements increase the pain.
• Thoracic radiculitis. Of all the types of radiculitis, this is the rarest. Accompanied by pain in the intercostal spaces.
Still, the common and main symptom of radiculitis for any part of the spine is shooting pain (as from an electric shock) at the site of the lesion along the nerve.
Later, numbness and tingling may appear at the site of the lesion. Pain and temperature sensitivity may decrease or be completely absent. Muscle weakness and vascular disorders are observed.
Treatment methods for radiculitis
Treatment for sciatica depends on the severity of symptoms. In the acute period, strict bed rest (preferably on a hard bed) and the use of anti-inflammatory and painkillers are necessary.
It is better to treat radiculitis comprehensively, combining traditional medicine and medical practices with folk remedies. In general, the treatment process is carried out with the help of medications, physiotherapy, manual therapy, acupuncture, exercise therapy and folk remedies.
In especially severe cases, with a pronounced clinical picture or in the presence of persistent pain, surgical intervention is required.
Treatment of radiculitis with medication
The essence of treating radiculitis with medications is to relieve muscle spasms and eliminate pain. Unfortunately, drug treatment for radiculitis is temporary. To consolidate the results of treatment, it is necessary to undergo a course of exercise therapy and take advantage of the possibilities of physiotherapy, manual therapy or acupuncture.
In the treatment of radiculitis, narcotic analgesics are used medicinally - muscle relaxants (metacarbomal and cyclobenzaprine). Simple analgesics, such as paracetamol, panadol, aspirin, ifuprofen (nurofen), pentalgin, baralgin, will also help relieve pain.
Now, more about non-drug treatment of radiculitis. Physiotherapy helps improve blood circulation in tissues,
adjacent to the root, improve the conduction of nerve impulses along nerve fibers, and also reduce pain.
There are many techniques for treating sciatica using physical therapy, such as ultrasound, electrophoresis and dynamic current. Massage and manual therapy can relieve muscle spasms and blocks, which also helps reduce pain.
Acupuncture is designed to restore the process of conducting impulses along nerve fibers by influencing biologically active points of the body.
Exercise therapy is designed to help restore the natural biomechanics of the spine and normalize movements. Sometimes, with the help of exercises, by redistributing the load on the muscles, it is possible to relieve compression of the spine. Exercises help increase the elasticity of muscles and ligaments, and can also stop degenerative processes in the spine, which allows you to increase range of motion.
Regular exercise is a good prevention of relapses of radiculitis. Exercises on simulators give the greatest effect.
Aerotherapy is a complex effect of hardening, swimming, sun treatment and air exposure on the patient’s body. Aerotherapy gives good results in the treatment of radiculitis.
Air procedures are the simplest form of hardening. Air baths have a chemical, mechanical and temperature effect on the body. The sea and forest air are especially healing. For the greatest effect, it is better to take air baths undressed.
The beneficial effects of solar procedures will only occur if they are carried out correctly. The average course of treatment is 20 - 40 procedures, with a break every seventh day. It is recommended to sunbathe in the morning, in the shade of greenery, and no more than two hours a day.
If there is not enough sun, especially in the northern regions, you can drink a decoction of St. John's wort before the procedure, which will increase the effect of sunlight on the body. Sun therapy should be stopped if one of the symptoms appears: increased heart rate, dizziness, loss of appetite. In any case, you should not sunbathe until you get burns or sunstroke.
Contrast showers and bathing are considered useful procedures for radiculitis. Contrast shower stimulates skin cells, blood vessels and nerves
endings, which is important for patients with radiculitis. In addition, a contrast shower has a hardening effect.
Swimming will have the greatest effect in a natural body of water, where the same temperature of water and air is not maintained throughout the year. In addition to the strengthening effect on the back muscles from swimming, here you can also get all the benefits of hardening.
Diet for radiculitis
Everyone knows that food greatly affects the condition of the body. To prevent attacks of radiculitis, it is recommended to adhere to a diet. You need to eat little by little 4 - 5 times a day.
The diet should contain a lot of fiber, vegetables and fruits are healthy. Tomatoes, cucumbers, radishes, carrots, and cabbage are especially useful. As for fruits, you should often eat bananas, dried apricots, prunes, persimmons, pomegranates and citrus fruits.
Black elderberry is very useful for radiculitis. In addition, you need to give up fatty meat, strong meat broths, coffee, alcohol, carbonated drinks, salty, smoked, and spices.
It is unhealthy to eat flour and sweets. You need to eat fish 2-3 times a week. Porridges are healthy, especially oatmeal, rice and buckwheat. They recommend eating peas, beans, and corn.
Prevention of radiculitis
In order for painful attacks of radiculitis to be as rare as possible, it is necessary to engage in the prevention of radiculitis. After all, it is easier to prevent illness than to suffer from piercing pain.
Prevention of radiculitis consists of several important areas.
* Do not forget to prevent osteochondrosis
* Prevent pathologies of the spinal cord and spinal column
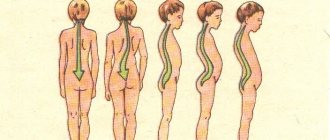
* Maintain posture (keep your back correct)
* Treat infectious and colds in a timely manner
* Avoid hypothermia.
* Avoid prolonged positions in uncomfortable positions, prolonged static loads, heavy lifting and very sudden movements.
* Avoid beds that are too soft, where the spine is in the wrong position all night and the back does not rest (it is best to have an orthopedic mattress, or at least any good hard mattress)
* Do not forget to do gymnastics, including therapeutic exercises. Correct physical activity is of great importance in preventing the disease and treating radiculitis. We must remember that moderate physical exercise relieves tension from the muscles, trains the muscular frame and strengthens the spine.
Complex exercise therapy for osteochondrosis of the cervical spine (non-acute forms): 1. Warm-up Warm-up is a normal walk on the full foot, and then on the toes and heels. Moreover, it is necessary to walk until a feeling of warmth appears. 2. Relaxation of the cervical spine You need to stand up straight, with your arms hanging freely along your body. Then you need to tense your arms and hold the tension for 30 seconds, while you need to straighten your back and lower your shoulders and shoulder blades. Then the pressure should be released and the arms should be allowed to swing freely. 3. Swing your arms back You need to stand straight, while your body should be lowered parallel to the floor. Then you need to stretch your arms to the sides, but you don’t need to stretch your shoulders towards your ears, you should try to move the top of your head forward, while at the same time lowering your shoulder blades towards the spine. You have to imagine that your shoulder blades are your wings. Next, you should make a “swing” - forcefully pull the shoulder blades towards the spine, during this movement the straight arms move slightly back. You should not move your arms due to inertia, you should try to work with your back muscles. Exercise therapy complex for osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine: 1. Warm-up Warm-up for this exercise therapy complex is the same as for exercise therapy for cervical osteochondrosis. Exercise “Boat” To perform this exercise, you need to lie on your stomach, then lift your chest off the floor, and your arms should form perpendicular to your back. Then you need to try to move the shoulder blades one towards the other, with sharp angles reaching towards the spine. At the same time, you should try to move your hands back a little. It is necessary to feel the tension only in the muscles of the back, and not in the arms.
LH complex (therapeutic gymnastics) for osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine: 1. Warm-up The warm-up in this exercise therapy complex is similar to the warm-up in the previous complexes. 2. Tilting the pelvis You need to stand up straight, while your knees and hips should be relaxed, and your arms should not be strained. Next, you need to tighten your buttocks, as if tilting your pelvis inward. The goal of this exercise is a completely flat lower back in profile. This movement must be performed slowly, vertebra by vertebra. 3. Rotation of the pelvis It is necessary to perform movements that allow you to twist the pelvis to the right and left, while gradually pushing forward either the right or the left thigh. This movement is similar to an element from oriental dances. When performing this exercise, the upper body should be fixed in a stable position, the chest should swing, but you should not bend forward and backward at the waist. 4. Exercise “Cat-Cow” To perform this exercise, you need to get on all fours so that your thighs are strictly perpendicular to the floor and your palms are under your shoulders. Then you should relax your muscles and bend your lower back down, while stretching the neck area and moving your head back. In this position, you need to stretch for 20 seconds, and then perform the opposite movement, arching your lower back upward, and aim your thoracic spine towards your hips. All exercises of these exercise therapy complexes for osteochondrosis must be performed regularly, systematically, but before starting classes, you should consult a doctor.
Information provided based on publications of the NewsMedical website, Russia
Physiotherapist FTO Aleinikova N.E.
Traditional treatment of sciatica
Treatment of back pain is not complete without taking medications. Traditionally, sciatica is treated conservatively. The patient is prescribed:
- anti-inflammatory drugs (Diclofenac, Ortofen, Ibuprofen);
- painkillers (Ketonal, Movalis);
- novocaine blockades;
- muscle relaxants (“Mydocalm”, “Sirdalud”);
- warming ointments based on bee or snake venom;
- B vitamins.
Severe damage to the intervertebral discs may require surgical treatment..
In addition to drug and surgical treatment for radiculitis, physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed to relieve the inflammatory process, as well as to accelerate tissue regeneration and have a warming effect. Manual therapy and visits to a massage room and exercise therapy room are also recommended.
Video: “Exercises for acute back pain”
Find out more about traditional treatments for sciatica:
- You can find the names of gels and ointments for radiculitis on the page
- Effective injections for radiculitis, 3 ampoules each
- What medications are the most effective for radiculitis can be found out by going to the next article
Gymnastics in the treatment of thoracic radiculitis
A professional doctor or trainer should tell you what exercises to do for radiculitis, but an approximate training program may be as follows:
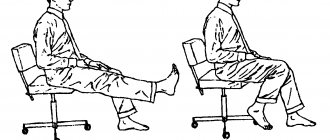
- The body is pressed to the floor, legs are bent at the knees, hands are on the chest. In this position, you need to take a deep breath and hold your breath for 5-7 seconds. Then such a deep breath must be repeated 5-7 times.
- While lying on your back, you need to clasp your legs with your hands and stretch your head towards your knees. You need to fixate in this position for 5-10 seconds, then gradually return to the starting position.
- While lying on your back, you need to spread your arms to the sides, bend your knees and smoothly turn them from right to left and back.
- While lying on your back, place your hands behind your head and stretch with a deep sigh.
- While lying on your back, you need to place your arms along your body and raise your shoulders and chest.
All exercises are repeated 5-7 times.
The use of exercise therapy for radiculitis
Did you know that...
Next fact
Exercise therapy plays one of the most important roles in radiculitis . Therapeutic physical exercises are prescribed for any type of radiculitis. Only the set of exercises itself can differ.
Exercise therapy is aimed at strengthening the spinal column, increasing its functionality by strengthening the surrounding muscle corset, including the abdominal muscles, which play an important role in maintaining the lumbar region of the spine.
In addition, therapeutic exercises improve blood circulation, which has a positive effect on the condition of the spinal nerves , improving their nutrition and swelling of soft tissues, helping to eliminate existing swelling.
For radiculitis, all exercises should initially be performed in a gentle manner. Only gradually can you increase the intensity of physical activity. Exercises should be performed from simple to more complex.
It is forbidden to do any physical exercises or loads during exacerbation of radiculitis. Exercises that involve a lying position must be performed on a hard, flat surface. Ideally, use a specially designed mat during classes.
Physical therapy classes are not prescribed to patients:
- during the period of exacerbation of radiculitis (there is a high probability of only aggravating health problems);
- for cardiac pathologies;
- with intervertebral hernias, in which there is a possibility of damage to the spinal cord;
- with increased ESR;
- with an increase in body temperature.
Even if you do not fit into the category of patients for whom there are contraindications to exercise therapy, before starting exercises, it is still recommended to consult a specialist who must give his approval for this method of treating radiculitis. In addition, exercise therapy is an excellent prevention of this disease, and also helps to recover faster after surgical treatment.
Video: “Gymnastics for acute radiculitis”
Therapeutic exercise and gymnastics for cervical radiculitis
Radiculitis can be localized not only in the lower back, but also in the cervical spine. In this case, a set of exercise therapy exercises may be as follows:
- Starting position – standing. It is necessary to relax and smoothly bend your head forward so that your chin is pressed against your chest. In this position, you need to move your head from left to right and in the opposite direction.
- Tilts the head forward and backward. The spine should be straight, the shoulders should not move. Head movements should be smooth, without jerking.
- Smooth circular movements of the head.
- Turn the neck left and right as far as it will go.
- Head tilts left and right. Shoulders should not move.
All of the above exercises must be repeated 5-7 times. Gradually the number of repetitions can be increased to 10-15 times.
Exercise therapy for the treatment of radiculitis, technique
For cervical radiculitis, the following set of exercises is recommended::
- I.P. – standing, legs brought together . Bow your head towards your chest so that your chin touches the chest. In this position, make smooth movements of your head from left to right and vice versa, without lifting your chin from your chest. Repeat up to 15 times.
- I.P. – standing, legs together . Slowly move the back of your head back, almost touching it to your upper back. Stay in this position for at least 2 seconds and return to the starting position. Repeat 10-15 times.
- In a standing position, make circular movements with your head , avoiding strong deviations back (i.e., movements should be performed along a minor axis). Repeat at least 10 times.
- The fingers of both hands are clasped together at the back of the head . In this position, tilt your head forward, completely touching your chest. In the final position, completely relax and hold for about 10 seconds. Then return to the starting position. Repeat 15-20 head tilts.
- Standing with your feet shoulder-width apart, place your chin on your right hand, while clasping the back of your head with your left . In this position, make smooth movements with your head to the right side, holding at the end point for 20 seconds. Then return to the starting position. Repeat 15-20 times. Then change your hand and repeat the same manipulations, but only in the opposite direction.
For thoracic radiculitis, you can perform the following set of exercises in the starting position standing:
- Place your feet shoulder-width apart, bend both arms at the elbow joints at chest level . Raise your arms to the sides as you inhale, trying to bring your shoulder blades together and return to IP. on exhalation;
- Bend your arms at the elbow joints and place your hands on your shoulders . Alternately raise your left and right arms up so that they form a right angle with your shoulders and stay in this position for a few seconds. Then you can raise both hands together. It turns out: one lift - the left hand, the second lift - the right, the third lift - both hands together. Each position must be repeated at least 5 times;
- Bend both arms at the elbow joints . Raise your arms bent at the elbows up and back into IP, holding at the top point for 2-3 seconds;
- While lying on your stomach, alternately lift your left arm and left leg, and then your right arm and right leg. Lifting should be done while inhaling. There should be 8-10 lifts for each pair of limbs.
- Feet shoulder width apart . Swing alternately with each upper limb in the appropriate direction, i.e. left - to left, right - to right. Swings should not be sharp. Repeat 10-15 movements in each direction.
For lumbosacral radiculitis, the following exercises are recommended::
- In a standing position, spread your legs shoulder-width apart . Bend your arms at the elbows and place them on your lower back. Perform smooth bends alternately to the right and left, pausing at the bottom point for 3 seconds and returning to I.P. Repeat 10-15 times.
- Standing with your feet shoulder-width apart, smoothly tilt your body forward and backward , pausing at the bottom point for a few seconds. Your hands should be on your lower back. Repeat at least 10 times.
- Standing, feet shoulder-width apart, arms in a free position on both sides of the body, bend back and forth . The tilt should be while inhaling, and you should try to reach the floor with your hands. At the lowest point, freeze for 2-3 seconds. Repeat 5-10 bends in each direction.
- Lying on your stomach, place your arms loosely on either side of your body . As you inhale, leaning on your forearms, simultaneously lift your head and shoulders up, holding at the top point for 2 seconds, then return to IP. Repeat at least 5-7 lifts.
- Lying on your stomach, clasp your hands behind your back . As you inhale, lift your head up, while bending in the chest area. At the top point, pause for 2-3 seconds, and then exhale, return to the starting position.
A few more exercises for lower back pain
Special exercises for lumbar radiculitis
What exercises to do for lumbar radiculitis should be told to the patient by a neurologist
. This rule also applies to other types of radiculitis. Typically, a therapeutic course of physical education to eliminate lumbar radiculitis is based on the following exercises:
- Tilts of the torso from side to side, forward and backward from a standing position (hands on the belt).
- Feet shoulder-width apart, arms bent at the elbows and placed at the sides. You need to turn your body left and right, fixing your body for a few seconds while turning.
- Circular movements of the body left and right.
- Starting position: lying down, legs bent at the knees, arms along the body. You need to tighten your abs slightly. This exercise provokes a slight arch of the lower back.
- The body is pressed to the floor. You need to slightly raise both legs and “draw” scissors in the air. Perform such movements at least 3 times.
- The body is pressed to the floor. You need to raise your legs and imitate the movement, as when pedaling a bicycle.
- Lying on your back, you need to put your hands behind your head and bend them slightly. You need to try to lift the upper spine and stay in this position for 3-5 seconds. Then lie down straight and relax.
A separate group of exercises includes those that help eliminate pain or reduce it almost immediately. It must be remembered that if the lower back pain is severe and unbearable, you first need to take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (for example, ibuprofen). After the pain subsides, you can perform the following exercises:
- Starting position “lying on your back”. The leg (left or right - depending on where the pain is more localized) is bent at the knee and pulled towards the stomach with the hands. You need to hold in this position for 20-30 seconds. Then you need to return to the starting position, rest for a few seconds, and do this simple exercise again. The most important thing is not to overdo it, not to pull your leg to such an extent that it hurts and the muscles are severely stretched.
- Starting position “lying on your back”. Both legs are bent at the knees, pulled towards the stomach with the hands, and the body is transferred to the healthy side. The position needs to be fixed for 20-30 seconds, then rest and repeat again.
- Starting position “lying on your back”. One leg is bent at the knee, thrown over the other and pulled to the stomach with your hands. The position is fixed for 20-30 seconds, then rest and repeat.
To diversify the set of physical exercises and gymnastics performed for lumbar radiculitis and other diseases, you can watch a video on the Internet. Many professional doctors and trainers demonstrate interesting and effective exercises for different muscle groups. To make a correct diagnosis and prescribe effective exercise therapy, come to the specialists of the Energo clinic.
Diagnostics
As a rule, a physical examination of the patient makes it possible to make a diagnosis of lumbosacral radiculitis. The following methods are used to confirm it:
- electroneuromyography;
- X-ray of the spine in two projections;
- MRI;
- CT;
- lab tests.
Symptoms of lumbar radiculitis in women and men sometimes require differential diagnosis with diseases of the genitourinary system, metastatic lesions of the spine and intestinal diseases.
Treatment
The basis of treatment is to eliminate the pain attack. And also the treatment of lumbar radiculitis includes the fight against inflammation, compression and muscle-tonic disorders. In case of intense pain, paravertebral blockades of the lumbosacral region with analgesics and corticosteroids are performed.
Medication
Treatment of radiculitis of the lumbar and sacral spine includes the following groups of drugs:
- painkillers;
- muscle relaxants;
- B vitamins;
- means that normalize tissue trophism, restoring innervation and microcirculation;
- local ointments that relieve inflammation and stimulate blood circulation.
Outside of an exacerbation, chondroprotectors are used to restore the cartilaginous structures of the lumbosacral region of the spine. Concomitant pathologies are treated (spinal hernia, osteochondrosis, infectious diseases, etc.).
Folk remedies
Treatment of lumbar radiculitis at home can be carried out in the following ways:
- heating with salt (dry heat);
- use of medical cups;
- compresses with sea salt;
- mustard plasters, honey-based cakes;
- compresses, lotions and rubbing with infusions of medicinal herbs (chamomile, St. John's wort, sage, etc.);
- red pepper patches;
- applying horseradish leaves, grated garlic gruel, radish and other methods to the affected area.
Before using traditional recipes to eliminate lumbosacral radiculitis, you should obtain a doctor’s approval.
Conservative treatment
If a person has lumbosacral radiculitis, non-drug treatment will be as follows:
- wearing a corset;
- reflexology;
- physiotherapy (Ural irradiation, UHF, magnetic therapy, electrophoresis, grass therapy, etc.);
- manual and traction therapy;
- physiotherapy;
- myofascial massage of the lumbosacral region;
- water activities, swimming.
Massage and exercise therapy are indicated only outside of exacerbations. In case of stable remission, it is recommended to visit resorts, use mud applications on the lumbosacral area, and baths with radon and hydrogen sulfide.
Surgical intervention
If medication treatment for lumbar radiculitis does not produce results, they resort to surgical tactics. This usually happens in the presence of an intervertebral hernia, which injures the nerve roots and leads to permanent symptoms. Surgical treatment of lumbar radiculitis involves discectomy.
Causes
Lumbosacral radiculitis is predominantly associated with irrational loads on the spine. Most often the disease is diagnosed between the ages of 35 and 50 years. As a rule, the disease occurs as a result of degenerative-dystrophic changes in the vertebrae (osteochondrosis, spondylosis, spondyloarthrosis). The following factors contribute to the development of lumbosacral radiculitis:
- excessive load on the axial skeleton;
- physical inactivity;
- metabolic disorders in the body (diabetes mellitus, vitamin D deficiency, obesity, etc.);
- lumbosacral injuries;
- curvature of the spinal column;
- weakness of the lower back muscle corset;
- disruption of the innervation and blood supply to the spine.
The pathogenetic mechanism can be triggered and cause an exacerbation of lumbosacral radiculitis by hypothermia, a sharp tilt or rotation of the body, infection, intoxication, prolonged static or excessive dynamic load on the lumbar region.
What is lumbar radiculitis
Lumbar radiculitis is the radicular stage of lumbar osteochondrosis. With pathology, protrusions form inside the intervertebral discs. These formations can be protrusions or hernias. When a hernia puts pressure on a nerve root, sciatica occurs.
When intervertebral discs “fall out”, a sharp, sudden pain occurs. Patients suffering from prolonged lumbar pain previously (during the non-radicular stage of lumbar osteochondrosis) feel severe pain in the lower back, under the influence of provoking factors.
Diagnosis of radiculitis
To make a diagnosis, a medical examination and the following diagnostic procedures are performed:
- First, the doctor clarifies the symptoms, determines the intensity and nature of the pain, their duration, and determines sensitivity disorders.
- Next, a physical examination is performed to determine range of motion and muscle strength.
- A neurological examination checks the patient's reflex reactions and determines how sensitive and active different parts of the body are.
- X-ray shows where degenerative processes have occurred.
- MRI of the coccyx - accurately determines the degree of compression pressure on the nerve roots.
- EMG – allows you to visually understand how damaged the nerve fibers are.