Causes of discomfort in the sacral area
Aching, dull pain is caused by the following pathologies:
- lumbar radiculitis;
- lumbar osteochondrosis;
- irritable bowel syndrome;
- kidney diseases;
- pinched nerve between vertebrae;
- problems with cartilage tissue.
If the pain is acute and sudden, the following pathologies are possible:
- exacerbation of chronic osteochondrosis;
- lumbosacral hernia;
- inflammation of cartilage tissue.
The cause of pain in the sacrum in women in some cases may be premenstrual syndrome. In this case, discomfort is also felt in the lower abdomen.
Inflammatory process in the kidneys is another common cause of pain in the sacrum in women and men. In this case, problems with urination are also observed. In this case, exercise therapy may worsen the patient's condition.
Basic principles of performing therapeutic exercises
Exercises for the sacral spine should be performed adhering to the following rules:
- All movements are smooth and easy; jerking, jumping, and sudden lunges are prohibited.
- Stretching should be done as slowly as possible and not cause pain.
- If you are thirsty, you should not limit yourself to drinking clean water during training.
- The optimal time to eat is two hours before exercise and about three hours after.
- Before starting exercises for the sacral spine, you should do a warm-up, and then a cool-down.
- Monitor your breathing and do not hold air in your lungs, try to inhale diaphragmatically and exhale through the chest.
Warm up before exercise
Approximate execution algorithm.
- Starting position - feet shoulder-width apart. The back is straight, the head is located exactly in the middle relative to the body. Take a deep breath, stand on your toes, reach for the sky.
- Exhale, lower your arms as low as possible, trying to reach your feet with your fingertips.
- Tilts to the left and right - do it as carefully as possible. If pain occurs when bending, you should stop doing it.
- Rotating your head allows you to stretch your neck.
- Rotating the pelvis clockwise and then counter-clockwise allows you to stretch and stretch the lumbosacral spine.
Exercise sets
There are 3 main stages in which gymnastics for the lumbar spine with osteochondrosis is performed sequentially. The exercises for each stage are different.
Exercises for the acute period
During this period, bed rest must be observed. In this regard, exercises for osteochondrosis of the lumbosacral spine are of a general strengthening nature.
So, exercises in which you need to lie on your back (the starting position of all exercises in this block is as follows):
- We bend our legs at the knees and gather our fingers into a fist. Next, bend and straighten your legs, as well as your fingers in turn.
- Raise and stretch your arms up, then lower them behind your head.
- Move one leg to the side and return it back. Repeat for the other leg.
- Bend your knees and gradually pull them closer to your stomach. As you exhale, return to the starting position.
- Take turns moving your knees to the sides. Return to starting position.
- We bend our arms at the elbows and inhale, and then straighten them as we exhale.
Do each exercise 4-6 times depending on how you feel.
Exercises for the subacute period
Executed after the first block. Therapeutic gymnastics for osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine at the second stage is aimed at training the lower muscle group:
- Lying on your back, bend your knees, while inhaling, you need to raise your sacrum up a little, hold for a second, and lower as you exhale.
- We lie on our backs. As you exhale, you need to raise your head a little, while your abs should tense. As you inhale, lower your head.
- Lying on your back, legs and arms straight. Tighten your buttocks, holding them in this state for about 10 seconds. After this, breathe in and relax.
- On all fours on the bed. Slowly lower onto your heels. Return to starting position.
- On all fours, you need to relax your neck and press your chin to your chest. Next, inhale and bend at the lower back, then hold for a couple of seconds and exhale, returning to the starting position.
Exercises for the remission period
Exercise therapy exercises for osteochondrosis of the lumbar region during the period of remission consistently involve an increasing number of muscles:
- Lying on your back, cross your arms over your chest, bend your knees. Exhale, slightly raise your head and shoulders (your abs should be tense), inhale and return to the starting position.
- We lie on our back, as we exhale, we raise our legs and pull our knees to our chest; if necessary, you can help yourself with your hands. Hold for a few seconds, and then inhale and return to the starting position.
- On knees. Extend your leg back, maintaining your balance for a few seconds, and return to the starting position. Do the same with the other leg.
- Lie on the cushion with your stomach, with your arms spread to the sides. As you inhale, raise your shoulders a little (hold for a few seconds), as you exhale, lower to the starting position.
- We use a cushion and lie down on it with our stomach. The chin rests on the hands. Inhale - raise your legs and pelvis above the bed, hold for a couple of seconds, lower to the starting position, and then exhale.
You need to finish the exercises with a few minutes of diaphragmatic breathing.
Pushups
This exercise allows you to safely pump up the muscles of the upper body for pain in the sacral spine.
Men can do push-ups with only their toes and toes touching the floor. The average amount is ten to fifteen times. The total number of approaches is three to four.
Women, as a rule, do not have proper physical fitness. They can do push-ups against a wall, vertically. Or on my knees.
Exercise "Frog"
This is an effective and popular exercise therapy exercise. In case of a hernia of the lumbosacral spine, it allows you to reduce the intensity of pain and slightly stretch the spinal column.
Starting position: get on all fours. Spread your knees as wide as possible and try to lower yourself onto them. Execution largely depends on the flexibility of the hip joints. If you can’t spread your legs wide, it doesn’t matter, you need to do it at the distance that is available. You need to raise and lower your pelvis - this is what doing exercises for the lower back at home is all about.
The total number of repetitions is no less than ten and no more than twenty. If an exercise provokes sharp pain in the lower back, sacrum or tailbone, you should delete it from the program.
If the mobility of the hip joints and lumbar region does not allow you to perform the exercise, you should try to perform it gradually, increasing the depth of the legs by several millimeters every day. Exercise therapy exercises for a hernia of the lumbosacral spine imply a standard level of flexibility, and it should be developed.
Lumbosacral osteochondrosis
Lumbosacral osteochondrosis is a disease in which degenerative processes develop in the joints of the spine, affecting the vertebrae and intervertebral discs of the lumbar and sacral regions. Patients with this diagnosis usually complain of pain in the lower back, sacrum, limited movements in the lower back, and there may be complaints of “lumbago” in the leg from the hip to the toes.
Often, a patient who comes to an appointment with back pain considers himself to be completely healthy, and the pain is a random temporary phenomenon, explaining it by lifting something heavy, bending over sharply, or turning unsuccessfully.
As a rule, the appearance of back pain is not accidental. Chronic diseases of the spine and joints are the consequences of their improper use or improper lifestyle. For example, physical inactivity.
To maintain health and body functions, physical hygiene is necessary - that is, muscle work that allows you to maintain good health and physical fitness of the body.
With a sedentary lifestyle or work, when a person is forced to be tense, in a monotonous static position, the superficial muscles of the back are little used, atrophy, and lose their volume.
At the same time, the deep back muscles have to cope with excessive axial loads. Unprepared muscles spasm, blood vessels suffer, microcirculation in tissues, adequate blood supply, and nutrition of joints and organs are disrupted.
Against the background of these pathological processes, dystrophic changes in the spine and surrounding tissues occur. The intervertebral discs suffer the most. Due to negative processes, they become thinner, their shock-absorbing properties are lost, and they can become deformed and tear. In places of “stress”, swelling, inflammation and, as a result, pain occur.
Painkillers are not helpful in this case. By influencing the symptoms, they only smooth out the clinical picture, do not allow a correct diagnosis, do not treat the disease, but only dull the pain for a while. A person has the illusion that he is feeling better, real treatment is postponed, and meanwhile the disease can become chronic and require a serious approach.
At the Dr. Bubnovsky Center, spinal diseases are successfully treated without drugs or surgeries using the author’s kinesitherapy technique, which eliminates the cause of the disease and its possible consequences.
Bubnovsky’s gymnastics is the treatment of the musculoskeletal system, the restoration of impaired health using correct movement.
Kinesiotherapists create an individual program of the most effective exercises for each patient. To do this, during the initial examination, myofascial diagnostics is performed, which allows one to analyze the range of movements in the joints and the condition of the musculoskeletal system. If necessary, the Center’s specialists can refer you for additional X-ray examination or MRI.
The doctor of the center draws up a personal movement program for the patient, consisting of a meaningful sequence of exercises with individually selected loads.
Classes are held in the kinesitherapy room using rehabilitation simulators and multifunctional simulators developed by Dr. Bubnovsky (MTB). Their unique design and block system allows you to perform exercises safely, without discomfort and traumatic axial load.
An individual set of exercises, affecting muscles and ligaments, restores them in a dynamic mode, enhancing tissue microcirculation and normalizing local and general biomechanics. All exercises are performed under the supervision of instructors and kinesiotherapists.
To achieve a more pronounced effect in a short time, massage, sauna, cold douches, and hardware cryotherapy may be recommended. Cold, as an anti-inflammatory factor, helps eliminate tissue swelling and relieve pain.
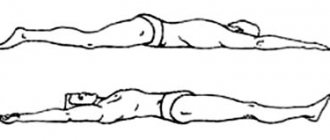
Exercise "Birch"
It came to us from hatha yoga. “Beryozka” is familiar to everyone from school. When performed correctly, it promotes blood flow from the lower body. This relieves pain in diseases of the lumbosacral spine. You can remain in the position of the static exercise “Birch” for up to one minute. If your level of physical fitness is low, you can limit yourself to five seconds.
The starting position of the exercise is lying on your back. The shoulder blades, head, and lower back are pressed to the surface. It is necessary to lift your straight legs off the floor, and without bending them at the knees, lift them above your head, then lift your lower back off the floor and stretch out straight in a “string”, holding your body on your shoulder blades, you can support yourself with your hands and lean on your elbows. The more vertical the body is, the better. You should stay in this position for at least five seconds, but no more than one minute.
“Birch” is one of the best exercises for the lower back at home. If you perform it daily, you can achieve remission and forget about pain and discomfort in the sacral area for a long time. An exception is if the disease is advanced to the point where medical intervention is necessary. For example, with a hernia or osteochondrosis of the lumbosacral spine, exercises may be powerless - manual therapy is necessary.
Eliminate lower back pain with exercise
The importance of physical therapy exercises
Exercise therapy helps not only to get rid of pain symptoms, but also to eliminate disorders that have arisen in the spine. The exercises that need to be performed in such cases are not difficult, but are always accompanied by a positive effect.
You can do the exercises at home; no equipment is required. If you feel discomfort, you must stop doing the exercise.
It is better to entrust the selection of a set of exercises to a doctor, who does this after conducting an appropriate examination. He will also advise how to perform the exercises correctly, and will also monitor the patient’s condition.
Strengthening the spine with exercise therapy
To do the steps below, lie down on a hard floor.
- Putting your hand on your knee, bend your leg, bringing it as close to your face as possible. The arm and leg alternate left and right, and then vice versa. The hand should provide resistance to the leg. You have 10 seconds to complete this exercise. After taking a short break, during which you should relax your limbs and torso. In total, you need to perform five exercises from each type.
- Pressing your feet to the floor, raise your upper body as much as possible and fix it for ten to fifteen seconds. Slowly lower, and after a short rest, repeat. The minimum number of exercises is ten to fifteen, but you can do more if discomfort does not occur.
- The arms are placed along the body, the legs are bent. Tighten your abdominal muscles, trying to harden them. During the exercise, the spine will slightly bend upward. The recommended number of exercises is ten to fifteen.
Exercises for the lumbosacral spine
The proposed exercises are effective when treating the lumbar spine, especially in its acute and chronic forms. Exercises help strengthen your back muscles and improve spinal flexibility.
- Get on all fours. Arch your back upward, hold for five seconds, and return to the starting position. Repeat – five to ten times.
- The starting position is the same as in the previous exercise, but you need to place a chair in front of you, on which to place your hands and head. The back should be arched to the right and left. The number of repetitions is five to ten.
- Lie on your back, bend your legs, extend your arms along your body. Turn your legs closed at the knees to the left, and the entire upper part, including your head, in the opposite direction. In this case, not only the torso, but also the spine is twisted in the form of a spiral, which is especially beneficial for the work of the lumbar vertebrae. Then do the mirror image exercise. A total of five times in each direction.
Exercises against acute pain in the lumbar region
With the help of these exercises, the spine is stretched and tissue pinching is eliminated. To perform this you need a horizontal bar or crossbar.
- Having assumed a hanging position with your legs extended, make slow turns alternately to the left and right. The neck and back are relaxed. The exercise is performed for three minutes. Three to four approaches are done per day.
- Take a hanging position for a minute on outstretched arms with bent legs. Do two or three approaches a day, with at least a 10-minute break between them.
Exercises for the treatment of chronic spinal diseases
- Sitting on the floor, bend one leg and tilt it to the side, the other leg is extended. Bend towards the outstretched leg, reaching with your hands to the tips of the leg. Change the position of your legs and perform a similar exercise. Repeat – 10 times for each leg.
- Standing at the table, lean your hand on it. Take a step and bend your knees. Tilt your torso back 10 times. Then take a step with the other foot and repeat 10 more times.
- Lie on your back, legs spread, arms along your body. Leg for 5-10 seconds. raise up and then lower. Repeat five to ten times, then change legs.
- The patient lies on his stomach, and the second person applies pressure to the muscles located along the spine. You should start from the neck, moving down.
Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr
Exercise "Butterfly"
Allows you to stretch the lumbosacral spine, helping to reduce the intensity of pain in this area. When performed daily, it can relieve pain for many years.
Get on all fours. Try to place your knees as far apart as possible, as in the “Frog” exercise. Only in this case should you not move your pelvis vertically. you need to lower your whole body as low as possible to the floor, while the pelvic area remains elevated above the floor level. This position allows you to maximally stretch the area of the sacrum and coccyx. After a few seconds, return to the starting position and repeat everything again. Each time try to press lower and lower to the floor.
This is one of the best exercises for osteochondrosis of the lumbosacral spine. The optimal number of repetitions is six to seven times. It should be performed smoothly, measuredly, monitor your breathing and avoid sudden movements.
What to do during exacerbations
Another mistake that leads to worsening of the back condition is incorrect treatment. For example, if you have an exacerbation, you should not use an ointment with a warming effect. It reflexively distracts from the pain, but then increases the swelling due to the fact that it warms and thereby increases the flow of fluids to the sore spot. The influx of fluid, accordingly, leads to even greater swelling, which will only intensify pain in the future. In the first days, it is better to use anti-inflammatory ointments; you also need to reduce active loads and use a corset. My course, Restoration of the lumbosacral spine in 10 minutes a day, has all the necessary recommendations: what to do on these days, and what exercises will help you quickly recover and return to your daily life.
Cool down after performing a set of therapeutic exercises
After doing the gymnastics, you can do swings with your arms and legs. It is also good to follow a standard light physical therapy program of light stretching.
- Sitting on your buttocks, stretch your legs straight and try to reach your heels with your fingertips. Slowly rocking forward in this position will help stretch the spinal column.
- Lying on your back, throw your legs behind your head as far as possible (excellently stretches the entire spinal column).
- Clasp your hands and try to move them as far behind your back as possible.
- Spread your legs as wide apart as possible and try to reach your left foot with your left hand and vice versa.
- Try to touch your left earlobe to your left shoulder and vice versa. This will stretch areas of the cervical spine.
- Lying on your stomach, lift yourself up onto your arms and arch your back. This will stretch the thoracic spine and the muscle tissue around it.
Strengthening the muscles of the lumbar region
Basic recommendations
Even if you have been involved in some kind of sport in the past, do not be deceived. All exercises must be coordinated with a qualified doctor and only then begin to perform them. The surest approach that will give the maximum result if you follow all the prescribed recommendations is to consult a specialist, undergo appropriate diagnostics and receive an individual rehabilitation program. A competent specialist will not only select the most suitable set of exercises for pumping up the muscles in the lumbar region, but also, like an experienced trainer, will tell you how, with what strength and amplitude you can exercise so as not to get injured. And the recommendations for almost any type of rehabilitation are as follows:
- slowly
- smoothly
- gradually
In this case, your enemies are sudden movements and an excessive increase in load, which the lower back muscles are not yet ready to receive. Doing the wrong exercises or performing them incorrectly can only make the situation worse. Strengthening the lower back muscles is a rather long and painstaking process. So be patient and calmly, evenly move along the road to achieving results.
Please note that even if you follow all the recommendations and slightly increase the load on the muscles, at some stage you may suddenly feel pain. This can happen, since each organism is individual. If such a situation arises, you should immediately stop doing the exercise and start exercising again only after consulting your doctor again.
Bridge exercise
As a child, everyone loved to stand on the bridge. But an adult, most likely, will not be able to perform this seemingly simple exercise without prior preparation. But, with regular training, your lower back muscles will not only begin to strengthen, but also placing on a bridge will help align the spinal column.
Leg raises while lying on your stomach
To perform this exercise, there is no need to visit gyms or purchase special equipment, just have a small free space on the floor. Let's get started: lie face down on the floor, stretch your arms along your body. Without lifting your upper body from the floor, raise your legs straight and hold them in this position for up to thirty seconds. Please note: the legs should not be bent at the knee joint, and the height of the lift from the floor is enough to be up to 20 centimeters. We finish by smoothly lowering the legs back to floor level. So, do eight to ten repetitions, but don't rush. Remember, there is no rush in this matter; you can start with five repetitions, doing everything calmly and as slowly as possible. When you feel that it has become easy to perform the exercise, add the following movement - when your legs are raised for 30 seconds, slightly spread and bring your straightened legs together again. Do eight such approaches.
Gym on the couch
You can also strengthen your lower back muscles on the couch. To do this, lie across the sofa face down, grabbing the opposite edge with your hands. Straight legs hang down and rest your toes on the floor (like on tiptoes). Next, perform a leg lift similar to the previous exercise, only now the lift is performed to a horizontal level, that is, until the whole body assumes a “string” position. We perform the exercise eight times at a slow pace, each time holding for thirty seconds in a horizontal position.
You can also perform an exercise on the sofa, lifting your legs with your knees bent at 900. The principle of lifting is the same: slowly raise your bent legs until your body assumes a horizontal position. We linger at the top point for thirty seconds and slowly return the bent legs to their original position. Perform up to eight approaches in a smooth mode.
Side lying exercises
To begin the next exercise, you need to lie on the left side of your body.
Then we extend our left arm and place our head on it, the arm should be bent at the elbow. With your right hand, also bent at the elbow, we rest on the floor at chest level. The right leg is moved upward at a slow pace and remains in this position for about ten seconds, then lowers to its original position. Repeat 10 times. We do the same, turning over to the right side. To correctly perform exercises for the lumbar region, consult a specialist. Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr
List of prohibited exercises
The following weightlifting exercises are dangerous for the sacral spine:
- deadlift;
- Romanian deadlift;
- Bend over belly cravings;
- block pull behind the head;
- squats with a barbell or dumbbells;
- lunges with a barbell or dumbbells.
You should be as careful as possible when performing even those exercises that do not involve weights. It is forbidden to lift more than three kilograms if you have diseases of the sacral spine.
For exercises, it is worth assigning a role, first of all, to a therapeutic purpose. It is impossible to pump up muscles with chronic spinal diseases. When working with equipment, the pain will certainly worsen. Many young people with a hernia and osteochondrosis want to acquire beautiful muscles, but with such diagnoses, only therapeutic exercises for the lower back can be performed. Exercise machines and performing serious exercises can lead to injury and bring the matter to the operating table.
Features of exercise therapy for hernia
A herniated lumbar spine is a protrusion of a deformed intervertebral disc into the cavity of the spinal canal. The result is pressure on the spinal nerves. As a result, the patient is plagued by severe pain and discomfort. It becomes inoperable.
A hernia of the lumbar spine is the most dangerous type of intervertebral hernia. The lower back is an area of the body that is loaded both when standing and sitting. Therefore, patients with a sacral hernia need to lie down as much as possible. Even the exercises involve lying down on the floor.
Performing exercises for a hernia depends on the degree of damage. You should definitely consult with an orthopedist and surgeon about the advisability of performing any kind of gymnastics. In some cases, only surgery can help with a lumbosacral hernia.
Features of exercise therapy for osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis is a lesion of the cartilage tissue between the vertebrae. It is dangerous because it can not only cause pain, but also cause a malfunction in the functioning of internal organs.
Exercise therapy for osteochondrosis of the lumbosacral region is a real panacea. If you regularly perform therapeutic exercises, you can forget about the manifestations of osteochondrosis for a long time. Also, with this diagnosis, you can practice swimming, callanetics, and Pilates. Those sports that involve heavy lifting and sudden movements are prohibited. Jumping, running, and competitive sports with increased trauma are also prohibited.
Where do problems in the lumbar and sacral regions come from?
The lumbar region most often suffers from improper distribution of pressure on the vertebrae and intervertebral discs. And all this happens due to incorrect body position while sitting, walking or carrying heavy objects. The lumbosacral spine is often in a stagnant state also due to poor posture. And all this means that blood circulation and lymphatic drainage are disrupted in this place, and this, in turn, causes a disruption in the functioning of the pelvic organs, and the blood circulation of the lower extremities suffers.
Restoring back health is not only about strengthening the muscle corset. You need normally developed, relaxed and not over-pumped muscles, stretched and flexible ligaments. The vertebrae must “breathe” and be freely washed by internal fluids, so training should combine strengthening, stretching and relaxation of muscles and ligaments.
In my gymnastics complexes, I use the experience that I have gained in the recovery process of such patients. To strengthen the lumbar and sacral regions, I have developed a special video course: Restoring the lumbosacral spine in 10 minutes a day. It includes exercises for therapeutic exercises and exercises that are easy to do and easy to remember. The complexes combine strengthening, stretching and relaxation exercises, which allow you to get the desired result for the normal functioning of the spine.