From this article you will learn:
- What are the basic principles of physical therapy for spinal hernia
- Who is contraindicated for physical therapy for spinal hernia?
- What exercises are most effective in the treatment of hernia of the cervical, thoracic, lumbar regions
- What are the methods of Dikul and Bubnovsky in the treatment of spinal hernia
- Does swimming help with a hernia of the lumbar spine?
Spinal hernia these days is a phenomenon that often occurs not only among older people, but also among young people. Treatment includes a complex of medicinal and non-medicinal measures. The first is nothing more than taking anti-inflammatory and painkillers. Non-drug treatment is aimed at strengthening the muscle corset. Physical therapy for spinal hernia is the safest method of treatment and prevention of relapses. We will talk about it in more detail in our article.
Basic principles of physical therapy for spinal hernia
Physical therapy for the occurrence of a herniated disc is one of the main methods of therapy. It relieves pain, helps strengthen the muscle corset, returns the spine to its natural position, and improves blood circulation. Such a complex, as a rule, consists of simple exercises such as flexion, extension and extension of the spine.
Before starting exercise therapy, you should consult your doctor. He will help you select the types of exercises and adjust the number of repetitions, taking into account the current condition of the patient and the characteristics of his illness.
At the initial stage, you should perform only those tasks in which the movements of the vertebrae are minimal. Try to avoid sharpness, do not bend deeply, protect your back from shocks and blows.
It is necessary to increase the intensity, quantity and duration of exercises gradually, as you feel better and strengthen your muscle corset. This takes time. It is impossible to restore muscle functionality in a few days. Prepare yourself for long work. The first positive changes should appear after a few weeks of regular exercise therapy.
Exercise therapy necessarily provides for preliminary preparation of the body, namely:
- Normalization of breathing.
- Warming up the muscles.
Allow at least half an hour for classes. It is best to distribute the set of exercises throughout the day so as not to overload the sore lower back.
Cervical physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic procedures also do not treat a hernia, but fight its symptom complex according to approximately the same principle as massage and exercise therapy. The goal of standard physiotherapy sessions (magnetic therapy, electrophoresis, laser and ultrasound therapy) is to reduce swelling around the affected intervertebral disc, promote blood flow to the weak area, and relieve muscle strain.
If this goal is fully achieved, the patient feels much better after a course of physical therapy, noting an increase in the range of motion in the neck, a persistent disappearance or reduction in pain and other previously disturbing signs. But, according to clinical studies, the effect of physiotherapy is noted by only 50% of patients with this diagnosis. In some cases (up to 40%, as a rule, with stage 3-4 pathology), on the contrary, after treatment with physiotherapy, a deterioration in well-being is observed.
Contraindications to physical therapy
There are cases when physical therapy is contraindicated. Among them are:
- oncological diseases;
- stroke;
- pre-infarction condition;
- diseases accompanied by elevated body temperature;
- exacerbation of intervertebral hernia;
- hypertensive crisis;
- if a little time has passed since surgery.
Effects of exercise
With regular training in the body, the patient notes:
- reduction in pain intensity;
- reduction in the severity of other symptoms of the disease (headache, tingling in the hands, tinnitus);
- restoration of normal muscle tone;
- increased flexibility of the spine;
- improved hand mobility;
- reduction in the frequency of pain attacks.
Therapeutic exercises help restore blood flow in the tissues of the neck and improve the condition of the organs located here.
Therapeutic exercise in the treatment of hernia of different parts of the spine
1. Therapeutic exercise for hernia of the cervical spine.
The neck is one of the most fragile structures in the body, and therefore a hernia of this part of the spine is often the culprit of causeless headaches. That is why the specifics of physical therapy for such localization of the problem are selected especially scrupulously. An incorrectly formed set of exercises can provoke pain, which in turn will lead to impaired cerebral circulation.
Physical therapy for a herniated cervical spine includes a standard set of tasks, which are most often performed in two positions: standing and sitting. Warm-up begins with slow turns of the head until it stops. Then bend your head forward until your chin touches your chest. Next, tilt your head back as if you were looking at the ceiling. Lock in this position for a couple of seconds and return to the starting position. Then tilt your head to the sides, as if laying it on your right or left shoulder.
Do 15 reps.
2. Exercises for the thoracic spine.
Hernial protrusions of the thoracic spine are rare, but this does not reduce their danger and does not reduce pain.
Physical therapy for this problem consists of the following exercises:
- Sit on a chair. Place your hands on the back of your head. Keep your spine straight and your back should fit snugly against the back of the chair. Make inclined movements, first in one direction, then in the other, each time returning to the starting position. Please note that the movements should be made in the spine, and not in the pelvis.
- Lie on the floor with a small cushion under your thoracic back. Hold the back of your head with your hands. After taking the starting position, arch your back as you exhale.
Perform all exercises of the treatment complex at a slow pace. Sudden movements without first warming up the muscles and ligaments are prohibited.
Recommended articles on the topic:
- Thermal detoxification: lightness of the body and clear skin
- Lipolytic therapy: indications, contraindications, stages of the procedure
- Weight correction: everything you need to know about the procedure
3. Exercises for the lower back.
Physical therapy for lumbar spinal hernia includes the following exercises:
- In a lying position, bend your legs and extend your arms along your body, tensing your abdominal muscles as much as possible and taking a deep breath. Count to four and exhale, then inhale again at the count of eight. In total you need to perform up to 15 such repetitions.
- Starting position – lying on your back. The legs must be placed on some object (for example, a chair) so that a right angle is formed at the knees. Now raise your torso to your knees and stay in this position for a few seconds. Do 15 reps. This exercise is similar to the classic ab pump, and it really strengthens the muscle corset in the front.
- Starting position – lying on your back. Bend your legs at the knees and perform cross movements with your hands: left to right, and right to left leg. At the same time, the hands pull the knees towards the head so as to achieve some resistance. In this position, the body is fixed for 10 seconds, and then there is a rest of 15 seconds. There should be at least 5-10 repetitions in total.
Physical therapy for a herniated sacral spine includes the following exercises:
- Walking on all fours. Trainers recommend this simple task because it creates normal mobility for this part of the body, without overstraining it, but providing the necessary feasible load. Thanks to it, the correct position of the vertebrae will be restored. You can perform this exercise as much as you have time and feel.
- Starting position – lying on your back. You need to reach your chin towards your chest, and at the same time, your toes should be pulled up. Do this for one to two minutes.
Read material on the topic:
Myostimulation of body muscles: indications, contraindications and features of the procedure
What is an intervertebral hernia, symptoms
A potential herniated disc is considered to be a protrusion or crack of the dense spinal capsule . Often the pain in this condition is not severe, and many people ignore the problem, which then leads to its rupture and loss of the jelly-like core with increased pain. This seriously complicates the functioning of numerous ligaments and vessels, especially if the cause of the disease is osteochondrosis.
Below you can see the symptoms of a herniated cervical spine.
An important symptom of a cervical hernia is pain; depending on the area where the disc is pinched, it projects (radiates) to different parts of the body:
- If the problem is located in the area of the fifth nerve root, then the shoulder hurts.
- With a hernia in the area of the sixth root, the biceps and wrist are affected, this is expressed by weakness, numbness, burning and tingling in them.
- Seventh root neurosis causes pain in the back of the shoulder, reaching the forearm and fingers.
- If the hernia has descended even lower, then the hand hurts and becomes numb to such an extent that the fingers cannot be clenched into a fist, and the burning sensation spreads from the shoulder to the little finger.
Due to disturbances in brain activity, which are inevitable with a cervical hernia, problems with hearing and vision appear, performance decreases, and can even lead to a stroke or other pathologies.
Other symptoms are possible:
- difficulty moving the neck and head;
- dizziness;
- insomnia;
- decreased attention;
- migraine.
Swimming with a hernia of the lumbar spine
Many doctors agree that swimming is one of the most effective and least traumatic types of physical activity. Classes affect the maximum number of organs and tissues. During swimming, an even load is created on all the muscles of the body. Regular exercises help get rid of the pain syndrome that occurs with spasms, as well as minimize the risk of relapses.
Under the influence of water, painless stretching occurs in the affected area of the spine, which eliminates various types of displacement, indentation, and pinching in the intervertebral area.
It is for this reason that many patients who choose swimming as exercise therapy easily reduce the daily dosage of medications (mainly painkillers). This type of activity improves the overall emotional background due to the release of endorphins.
Like any physical therapy exercise, swimming has its limitations, contraindications and recommendations:
- You should not swim during an exacerbation of the pain syndrome, as even careful movements can cause harm. You should start only after a long remission, after consultation with a specialist in the field of neurology and under the supervision of a qualified trainer.
- The training program should be developed together with the attending physician, since it is necessary to take into account many factors, for example, how strong the hernia is, how quickly it develops, and what other diseases the patient has. Regular sport swimming puts excessive stress on the spine, so its volume and type must be selected individually.
- Preference should be given to backstroke and freestyle swimming, as they are the most effective and safe. It is these styles that train the lower back muscles, but do not put pressure on the intervertebral discs.
- Do not forget that, first of all, you need to listen to your body and if the slightest pain or discomfort occurs, you should abandon the movements that cause them. If a pain attack occurs while swimming, you must stop immediately.
- Many pools have a special system that simulates a whirlpool. This massage has a good effect on the muscles, relaxes and tones them at the same time.
- Classes should be systematic, and one session should last about an hour.
- The water temperature in the pool should be comfortable, especially during the first sessions. The ideal value is around thirty degrees. In the future, it will be possible to gradually lower the temperature to +23 °C so as not to irritate the body.
- Proper breathing during therapeutic swimming has a beneficial effect on blood circulation. Inhale deeply and exhale quickly.
One of the prerequisites for the occurrence of a hernia of the lumbar or sacral spine is osteochondrosis. It is observed in the vast majority of patients with lumbar hernia. Therefore, the swimming style should be selected based on the characteristics of osteochondrosis and other pathological processes:
- If there is a flattened curve of the ridge in the sternum area, it is necessary to swim on your back. In this position, she regains her physiological forms. If you swim on your stomach with this pathology, the condition can only worsen.
- If the back is too arched back, swimming on the back is contraindicated. After all, it loads the muscles of the shoulder girdle, and as a result the spine is even more rounded. That's why we swim only on our chest.
- For patients with low immunity, in years, with weakened muscles, movements with a large amplitude, such as in the crawl, are contraindicated.
If, after a doctor’s examination, no pathologies are found, the patient is prescribed a treatment complex containing the following tasks:
- Take a swimming board, sit comfortably on it and repeat the dolphin style with your feet at a distance of 100 m.
- Lie on your back and swim 400 m while moving your arms.
- Stay in this position and swim 250 m, alternately moving your arms.
- Swim crawl 150 m.
- Finish with a gentle 100m breaststroke.
Read material on the topic:
Manual therapy of the cervical spine as a worthy replacement for alternative treatment
Contraindications
Therapeutic exercises are prohibited for acute pain syndrome that cannot be relieved by medications. At this time, doctors recommend completely eliminating physical activity and maintaining bed rest. Therapeutic exercises will do more harm than good to people suffering from epilepsy, infectious diseases, heart problems, or cancer. Therefore, before starting training, all patients are recommended to undergo a comprehensive examination.
A hernia in the cervical spine is a serious pathological condition. It develops as a result of a sedentary lifestyle. If detected, the doctor prescribes complex treatment, which includes special gymnastics. A correctly selected complex allows you to recover faster, eliminate compression of nerve endings and compression of the spinal cord, and get rid of discomfort. There are no universal exercises; they are selected based on the individual characteristics of the individual patient’s body.
Dikul exercises for spinal hernia
Dikul’s set of physical therapy exercises belongs to kinesitherapy, the founder of which is considered to be Doctor of Medical Sciences S. M. Bubnovsky. The program was developed, one might say, from our own experience. At the age of 15, Valentin Dikul received a severe spinal cord injury as a result of multiple local injuries and a compression fracture of the spine. Doctors did not give any positive prognosis or prospects for recovery. But thanks to his own technique, Dikul was able to completely restore all functions of the spinal cord and return to his normal life. Its complex makes it possible to get rid of pain and cure pathology.
In the process of treating patients with intervertebral hernias, special simulators are used, personally developed by Valentin Ivanovich. The training program is selected individually for each patient. Before starting training, exercises are discussed with your doctor and possible contraindications are identified.
The complex for the lumbar spine, which Dikul proposed, helps solve several problems at once:
- strengthens the muscle corset, forms correct posture;
- reduces pain syndromes of paravertebral muscles and spinal cord nerves;
- eliminates muscle spasms and swelling;
- normalizes blood circulation and lymph movement in lymphatic vessels;
- works the deep-lying paravertebral muscles and restores normal muscle tension.
Valentin Dikul is sure: for classes to be effective, it is necessary to strictly follow the rules that he prepared for stable development of neurophysiological indicators and better adaptation of the body to new loads.
These rules read:
- Never change the sequence of exercises in the treatment complex on your own. This order must always be maintained.
- Classes should be regular, three to four times a week for 40–50 minutes. If training has stopped for any reason, then it is necessary to start it from the first stage, since muscle tissue very quickly adapts to the intensity of the current load.
- A set of exercises should be selected in consultation with a specialist.
- Gradually increase the load as the spinal muscles strengthen.
- Focus on your feelings during physical therapy exercises. If you experience discomfort, then you should stop training.
The duration of treatment depends on factors such as the condition of the muscles and the severity of the disease.
The Dikul training complex includes three stages:
- First, it is necessary to prepare for stress, especially for those patients who lead a sedentary lifestyle and have weakened muscles.
- The second stage is aimed at strengthening joints and ligaments.
- The third includes a therapeutic set of exercises to develop flexibility, mobility, and strengthen the spine.
The starting position for the main part of the exercises is lying on your back, on a hard surface. Some tasks may require additional equipment to complete. Physical therapy for lumbar spinal hernia includes exercises such as:
- Start with a warm-up to warm up your muscles (smooth stretches, turns, bends).
- Lie on your back. Cross your arms at the chest area. Take ten incremental steps, first to the left, then to the right. Make sure your legs and upper torso do not leave the floor.
- The starting position remains the same. Perform ten bends in each direction, sliding along the floor. The lower part of the body should remain motionless.
- The starting position is the same, bend your legs. Slowly draw your knees towards your sternum. Perform 7–10 times.
- Starting position – standing. Lower your hands, take a gymnastic stick. Keeping your back straight, bend down 7-10 times. For convenience, your legs need to be slightly bent.
- Take a rubber band in your left hand and secure the end of the projectile with your foot under your toe. Make five slow bends to the right. The patient must overcome the resistance of the elastic material. In this case, the right hand should be placed on the back of the head. Repeat to the left five times.
Read the material on the topic: MRI of the shoulder joint: indications and contraindications for its implementation
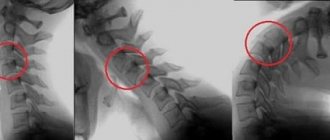
Diagnosis of the cervical spine
When a patient comes to the clinic, the neurologist first collects and analyzes the patient’s medical history. This is followed by testing of the spinal cord using special non-hardware tactics for examining the spine. Non-hardware diagnostics are based on neurological tests, which involve checking the problem area of the back using motor and palpation techniques, thereby establishing:
- presence and degree of neurological deficit;
- dependence and nature of the pain syndrome when performing certain movements of the neck, limbs, etc.;
- the consistency of the reflex response and the volume of amplitude of movements of the cervical level in various physiological directions;
- impaired sensitivity in areas of the body associated with SHO (hands, facial area, etc.).
Based on complaints and neurological tests, a specialist can make a preliminary diagnosis, and during the initial examination. But treatment will not be prescribed until suspicions of a hernia are confirmed by the results of hardware imaging. The generally established diagnostic standard for the purpose of detecting pathology and obtaining reliable detailed information about the clinic of hernial protrusion is magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Using volumetric layer-by-layer MRI images in different projections, as a rule, facts about:
- the development and degree of structural changes in the intervertebral discs at any stage;
- localization of the damaged fibrocartilaginous lining, and in the case of sequestration - the number and location of sequestration;
- the specifics of the growth of the bulge (direction vector);
- exact dimensions of the formation down to a millimeter;
- the presence and severity of pinching, compression of components of nerve nodes, arteries, spinal canal and spinal cord;
- intra- and paravertebral edema, inflammation, atrophy;
- condition of muscle tissue, ligaments, tendons, intervertebral joints;
- presence/absence of concomitant diseases on the examined part of the spinal column - stenosis, arthrosis, tumors, blood supply problems, etc.
X-ray does not fully reflect the clinical picture, since it visualizes only the outlines and position of the bone elements of the spine, the distance between the vertebrae, and osteophytes. X-rays do not show soft tissues, which include cervical discs, spinal cord, nerve plexuses, vascular and musculo-ligamentous structures. The slice-by-slice computed tomography method, although it involves the use of more advanced radioactive technologies than conventional x-rays, is also not informative enough in terms of the value of the obtained clinical signs in the diagnosis of this disease.
No conclusion is made about a cervical hernia based on X-ray or CT images alone; these are two auxiliary tactics, the advisability of which in each case is determined individually. Only MRI can thoroughly examine the problem area. Magnetic resonance imaging also has a significant advantage - it works on the phenomena of nuclear magnetic resonance and, unlike devices with ionizing radiation, does not have a negative effect on the human body.
Physical therapy for spinal hernia using Bubnovsky’s method
The main distinguishing feature of Bubnovsky’s exercises from conventional physical therapy is the load on the muscles through pain. In his opinion, it is necessary to fight pathology by overcoming the pain threshold, since it is this symptom that limits movement and causes muscle atrophy. Classes using the Bubnovsky system prevent the development of a hernia and reduce its size. This method is also called kinesitherapy.
The effectiveness of physical therapy according to the Bubnovsky system largely depends on the fulfillment of the following requirements. Necessary:
- Maintain proper breathing.
- Stretch your muscles and spine.
- Complete absence of drug treatment.
- Strengthen the muscle frame.
The impact should be on all muscles of the body, and especially on those that are subject to stress in everyday life.
The basic complex includes the following exercises:
- In yoga it is called “Cat”. Get on all fours, focusing on your palms and knees. Inhale and arch your back. Exhaling, bend in the opposite direction. Hold the pose for two to three seconds and return to the starting position. Repeat 10–20 times. Perform movements smoothly and slowly.
- Walking on your buttocks. Sit on the floor, keep your legs and back straight, arms at chest level. Walk forward using your butt muscles and come back. Perform 8–10 reps.
- "Bike". Starting position – lying on your back. Bend both legs at the knees and alternate your feet in a circle in the air (in other words, move as if you were riding a bicycle). Do the exercise for one minute.
- Side bends. Stand straight, feet shoulder-width apart, hands on your waist. As you inhale, bend to the right (do not bend your back), while exhaling, return to the starting position. Repeat the movement to the left. Perform the exercise ten times on each side.
- "Bridge". Lie on your back. Inhale deeply and, as you exhale, bend, rising on your arms and legs to the maximum possible height. Hold the pose for three to five seconds. Do five reps.
Nowadays, you no longer have to spend a lot of time performing complex and unpleasant procedures at home. It is much easier to seek help from real professionals - the Veronika Herba beauty and health center, equipped with effective and modern equipment.
Why clients choose Veronika Herba Beauty and Health Center:
- This is a beauty center where you can take care of yourself at a reasonable cost, while your face and/or body will be treated not by an ordinary cosmetologist, but by one of the best dermatologists in Moscow. This is a completely different, higher level of service!
- You can receive qualified help at any time convenient for you. The beauty center is open from 9:00 to 21:00, seven days a week. The main thing is to agree with your doctor in advance on the date and time of your appointment.
Sign up for a consultation with a specialist by phone +7 (495) 085-15-13
, and you will see for yourself!