Osteochondrosis and regular back pain affect 60–80% of the population over 30 years of age. Untreated osteochondrosis reduces the quality of life and can lead to disability and disability, so it is important to recognize it in the initial stages of development and seek help from a doctor.
In the article we will talk about osteochondrosis, its symptoms and diagnostic methods, as well as how to distinguish osteochondrosis from other diseases that manifest as back pain and what to do if signs of spinal osteochondrosis appear.
What is spinal osteochondrosis?
Osteochondrosis is a chronic disease in which the core of the intervertebral disc is gradually destroyed. Over time, damage to the intervertebral disc involves other structures of the spine in the pathological process and leads to disorders of the musculoskeletal system and nervous system. Osteochondrosis is also characterized as premature aging of the articular system or as a pathology resulting from damage to the vertebrae, for example, after injury.
The development of osteochondrosis is influenced by many factors, so researchers have systematized the reasons that explain the origin of the disease:
- involutive - inflammatory processes and other damage to the spine lead to premature aging of cartilage, for example, as a result of a sedentary lifestyle;
- degenerative – disorders in the intervertebral discs occur as a result of a failure of metabolic processes, for example, as a result of an unbalanced diet and alcohol abuse;
- dysmetabolic - osteochondrosis occurs due to malnutrition in the intervertebral cartilage due to the fact that with age the number of blood vessels that supply blood with nutrients decreases.
The development of osteochondrosis is a cascade in which one pathological process triggers another. For example, due to age-related changes and a decrease in the number of vessels in the disc, nutrition is disrupted, which leads to a malfunction in biochemical processes and damage to the intervertebral disc.
As degenerative and dystrophic changes develop in the spine, muscle tone and the functioning of the nerve roots that exit the spinal cord through natural openings in the vertebrae are disrupted. This leads to consequences on the nervous and musculoskeletal systems.
Question answer:
What types of massages are there for thoracic osteochondrosis?
Therapeutic massage is divided into subtypes: acupressure, vacuum, lymphatic drainage.
Such massages promote microcirculation, improve tissue nutrition, normalize muscle tone, relieve swelling, relieve pain, and have a generally beneficial effect on the musculoskeletal system as a whole. But please note that massage should only be performed by an experienced specialist; do not use the services of amateurs.
Why is a paravertebral block needed?
This is a highly effective procedure that instantly relieves pain. An injection containing a steroid and analgesic is given to the point where the nerve root exits the spine. Thanks to this, a rapid analgesic effect is achieved. The number of repeated procedures depends on the quality of the manipulation performed.
Symptoms of spinal osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis is a chronic disease with periodic exacerbations that are provoked by injuries, a sedentary lifestyle, heavy lifting, hypothermia and psycho-emotional stress. The most common and characteristic symptom for dystrophic disorders in the core of the intervertebral discs is regular aching back pain in different segments: in the neck, chest and lower back.
There are two types of symptoms of osteochondrosis: reflex and compression. Reflex symptoms develop due to irritation of the spinal cord roots. They manifest themselves in the form of spasm or vasodilation, muscle twitching, and weakening of muscle strength. Compression symptoms develop due to compression (usually caused by a herniated disc) of the nerves and manifest as loss of sensation in the affected segment (neck, arms or lower back).
The following symptoms are also characteristic of osteochondrosis:
- tension and soreness in the muscles of the neck and back;
- curvature of the spine to the side, back or forward;
- disturbance of sensitivity and nervous regulation: there is a feeling of goosebumps crawling on the skin, changes in heat and cold on the skin of the back and limbs, numbness in the arms or legs;
- weakening of the muscle strength of the limbs;
- frequent urination – up to 10–12 times a day.
Where can osteochondrosis lead to?
Pain due to osteochondrosis is localized not only in the back. They spread to the upper and lower extremities. To your feet:
- buttocks;
- back and sides of the thighs;
- lower leg and inner ankle;
- back of the feet;
- toes;
- heels.
Pain can also spread into the arms to:
- deltoid muscle;
- the outer edge of the hand, down to the fingers;
- back of the hand;
- three middle fingers;
- ring finger and little finger (rare).
How is osteochondrosis diagnosed?
Diagnosis of osteochondrosis is based on a survey, physical examination and instrumental examination methods. Specific examination methods are determined during consultation.
The doctor begins the diagnosis by collecting an anamnesis: identifying the probable causes of back pain, establishing the location of the pain and its duration, identifying the presence of concomitant pathologies, for example, allergies, congenital diseases and drug intolerance. Next he moves on to inspection. The physical examination is performed standing or sitting. The doctor can identify the curvature of the spine, evaluate muscle strength and reflexes, and look at the color of the skin. To detail the picture of the disease, you need to consult with related specialists: a neurologist, neurosurgeon, oncologist, rheumatologist and phthisiatrician.
A neurologist makes a diagnosis of “osteochondrosis” if:
- regular aching back pain;
- increased pain when lifting weights, sneezing, coughing;
- numbness and a feeling of aching in the joints;
- decreased range of motion in joints;
- muscle spasm;
- damage to the nerve roots;
- changes on an x-ray of the spine.
Do you need an X-ray of the spine?
X-ray of the spine or spondylography is one of the mandatory examinations for osteochondrosis, with the help of which structural disorders of the spine can be identified. Spondylography allows you to find pathological changes, for example, thinning of the intervertebral disc. Typically, for the cervical, thoracic and lumbosacral spine, x-rays are taken in two (and sometimes three) projections for greater detail.
Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging make it possible to identify pathologies associated with osteochondrosis: disc herniation and reduction of the lumen of the spinal canal, protrusion of the intervertebral disc into the spinal canal and compression of the spinal cord.
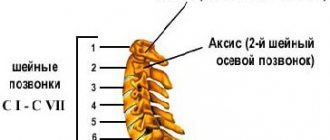
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
With cervical osteochondrosis of the spine, two main symptoms appear - cervicago and cervicalgia. Cervicago is an acute painful cervical lumbago that appears when moving the head and due to tension in the muscles of the cervical spine. Cervicalgia is aching and severe pain in the neck. Cervicalgia is accompanied by paresthesia - a disturbance of sensitivity in the form of numbness and a sensation of crawling on the skin.
If damage to the nuclei of the intervertebral discs of the neck progresses, cervical radiculitis appears - painful sensations in the back of the head. The pain is characterized by regularity; in addition, it intensifies occasionally, especially when moving the head.
This triad - cervicalgia, cervical radiculitis and cervicago - can be complicated by the syndrome of nocturnal hand dysesthesia, in which sensitivity is distorted. For example, a warm object may feel cold to your fingers, but if you shake your hands, sensitivity is restored.
Osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine
Osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine is most characterized by painful lumbago in the chest area (dorsalgia). Chest pain worsens with moving your arms, sneezing, coughing, and lifting heavy objects. Most often the pain is girdling. Paresthesia also often occurs in the chest. Sometimes damage to the nuclei of the intervertebral discs can be disguised as diseases of the internal organs, for example, gastritis or angina, since pain can be localized in the upper abdomen and in the heart area.
Degrees of the disease
Thoracic osteochondrosis, the treatment of which in women, men and children should be comprehensive, can be divided into the following stages:
- The first is that the pathology manifests itself as a local pain syndrome, the occurrence of which is caused by a weakening of muscle tissue, which in medicine is also known as thoracalgia. Gradually, spasm occurs in the paravertibral muscles, which leads to limited mobility.
- The second is characterized by a significant increase in pain in the back. Inflammation spreads to the pain endings, herniated intervertebral discs and protrusions appear.
- Third, the patient suffers from constant pain that occurs in the area of the nerve affected by the inflammatory process. Characteristic features of this stage of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine are numbness of the limbs, constant severe pain, difficulty breathing, headaches and heart rhythm disturbances. The risk of hernia rupture and its movement throughout the body increases, which in most cases leads to the need for surgical intervention.
- The fourth is the most complex degree of osteochondrosis, which leads to disruption of the basic functions of the intervertebral discs. The vertebral body gradually grows, which leads to their connection with each other, which leads to disruption of the blood supply to the brain. An advanced form of the disease without proper therapy can lead to disability.
Having noticed signs of osteochondrosis of the thoracic region, the treatment of which is possible with folk remedies or under the supervision of specialists, you should undergo a thorough diagnosis. Having determined the stage of the pathology, the doctor will be able to recommend the most effective methods of therapy.
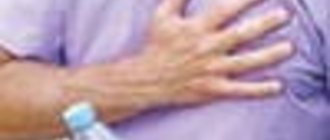
How to distinguish between heart pain or osteochondrosis?
Pectalgic syndrome is pain in the anterior chest wall, which may resemble pain in the heart. Pectalgia can be a sign of both osteochondrosis and heart problems.
However, pain during angina and heart attack differs from pectalgic syndrome due to osteochondrosis. The peculiarity of pain during angina pectoris and myocardial infarction is that it is of a compressive nature and spreads to the left shoulder blade, arm and jaw.
Pectalgic syndrome in osteochondrosis does not spread beyond the boundaries of the anterior chest wall, does not radiate to the arm and shoulder blade, and is not accompanied by fear of death. However, these are only subjective feelings. Therefore, to rule out cardiac pathology, you need to see a doctor and have an electrocardiogram done, which will reveal rhythm disturbances or signs of myocardial infarction.
If the pain begins to spread to the left shoulder blade, arm, jaw, is accompanied by a feeling of fear, is not eliminated by taking nitroglycerin and lasts more than 10–15 minutes, you need to call an ambulance.
Characteristic signs and possible complications
Osteochondrosis is accompanied by painful sensations spreading along the thoracic spine and between the shoulder blades. Loads and sudden movements lead to increased pain. If sympathetic nerve fibers are involved in the process, the internal organs for whose work they are responsible begin to ache.
In accordance with the characteristics of the manifestation, painful sensations can be classified into 2 main groups. About them in the table.
Table. Types of painful sensations
| Types of pain | Description |
| Dorsalgia | Characterized by long duration. Unpleasant sensations are localized at the location of the damaged elements. In combination with painful and uncomfortable sensations, there is a pronounced limitation of mobility - this mainly occurs in the chest area, but the neck and lumbar region can also be involved in the process. The immediate pain that accompanies this condition is relatively dull and weak. |
| Dorsago | It is characterized by extremely severe acute pain, predominantly of the paroxysmal type. Respiratory dysfunction and limited mobility may be observed. |
The width of the spinal canal in its thoracic region is relatively small. When hernias and other complications of osteochondrosis appear, even if they have insignificant dimensions, a pathological condition such as compression of the spinal cord may form. This is fraught with many problems with the most important internal organs.
Otherwise, the key symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis can be given in the form of the following list.
- Painful sensations localized between the shoulder blades and under them. They also often occur in the area of the ribs. Unpleasant sensations become more pronounced during inhalation and performing various active actions.
- Painful sensations localized in the left side of the chest. Has many similar properties to ischemia. To check for the presence of such, a patient with osteochondrosis must undergo an electrocardiographic examination.
- Limitation of mobility. The situation is complicated by the fact that the same symptom is characteristic of many other pathological processes. To obtain a reliable picture, the patient is prescribed radiography.
- Painful sensations that have a girdling character and intensify during movements and even when breathing.
- Feeling numb.
- Dysfunction of other internal organs and systems.
If left unattended, the disease can result in the following complications:
- vertrebrogenic radiculopathy;
- intercostal neuralgia;
- chronic pain;
- protrusion of intervertebral discs;
- hernias;
- cardialgia, etc.
Why is lumbar osteochondrosis dangerous?
With osteochondrosis of the lumbar region, lumbago or lumbodynia most often occur - regular lumbago and aching pain in the lumbar region. Due to constant pain, movements are limited: a person cannot bend down, do exercises or lift a heavy object.
Lumbago can go away on its own. However, they are prone to exacerbations, and each exacerbation indicates additional displacement of the intervertebral disc into the spinal canal. If the destruction of the intervertebral disc progresses, lumbosacral radiculitis is formed, accompanied by lower back pain that radiates to the buttocks and thighs.
Preventive recommendations
- Try to avoid unnecessary loads.
- Exercise, watch your posture, avoid colds and do everything you can to strengthen your muscles.
- Avoid too wet and cold places, local and general hypothermia.
- If, due to work responsibilities or any other circumstances, you spend a lot of time in one position, be sure to take breaks. At least every 1-1.5 hours, get up from your chair to walk and stretch.
- Be a physically active person. Moderate loads will bring great benefits. As basic exercises, we can recommend, for example, the following. Lie down on a flat surface (the floor will do), on your stomach. Support yourself with your hands and carefully arch your back. Stay in this state for a few seconds, then lower yourself. Repeat several times throughout the day.
Thus, thoracic osteochondrosis is a serious illness that requires timely diagnosis and competent treatment. Now you know how this disease manifests itself.
Contact your doctor immediately if you notice any adverse changes in your condition and follow professional advice.
Be healthy!
What is the difference between osteochondrosis and osteoarthritis?
Osteochondrosis and osteoarthrosis (spondylogenic osteoarthritis) belong to the class of diseases of the musculoskeletal system. However, there is a key difference between them: with osteochondrosis, the core of the intervertebral disc is affected, and with osteoarthritis, the intervertebral joints are affected. This makes the difference in symptoms and treatment.
With osteochondrosis, back pain is regular and aching, manifests itself at rest and intensifies with movement, and with spondyloarthrosis, the appearance of pain is associated with extension and flexion of the spine. Typically, the pain syndrome with osteoarthritis of the spine is one-sided and has a cramping nature. Also, spondylogenic osteoarthritis is characterized by morning stiffness, which lasts from 30 to 60 minutes.
VSD or cervical osteochondrosis?
Vegetovascular dystonia is a syndrome in which the functioning of the autonomic nervous system is disrupted. VSD is a functional disorder in which there are no structural changes either in the spinal column or in the nuclei of the intervertebral discs.
Vegetative-vascular dystonia has a mental origin - it is a neurosis that is associated with intrapersonal conflicts or childhood traumas. Externally, VSD and osteochondrosis can be similar to each other: headaches, dizziness, pain in the anterior chest wall.
To distinguish diseases, it is necessary to carry out instrumental diagnostics - x-rays of the cervical spine and other parts, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. As a result of diagnosis, there will be no organic changes in VSD, unlike osteochondrosis.
Treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis at the Yusupov Hospital
At the first symptoms of osteochondrosis, you should seek qualified medical help. At the Yusupov Hospital you can make an appointment for a consultation around the clock. Diagnosis and treatment of osteochondrosis in most cases is carried out on an outpatient basis. Patients with suspected osteochondrosis are required to be examined by a neurologist, take an anamnesis, and x-ray examination of the spine (thoracic region). Magnetic resonance or computed tomography is also sometimes prescribed.
The Yusupov Hospital provides comprehensive treatment for osteochondrosis of the chest. If this treatment does not bring positive dynamics, the patient is offered surgical treatment. Patients have access to convenient, comfortable hospital rooms and round-the-clock assistance from medical staff. You can make an appointment with a specialist by calling the Yusupov Hospital.
Treatment of vegetative-vascular dystonia
Vegetative-vascular dystonia is treated with medications, psychotherapy and lifestyle correction. Patients are prescribed symptomatic treatment: sedatives, anti-anxiety drugs, sleeping pills, restoratives, and vitamins. The goal of psychotherapy for VSD is to teach the patient to regulate negative emotions and increase stress resistance. The lifestyle is also adjusted: you need to balance work and rest, exercise and adhere to a balanced diet.
How to treat osteochondrosis at home?
It is not recommended to treat osteochondrosis at home. There are several reasons for this:
- at home it is impossible to accurately diagnose “osteochondrosis”, since back pain has different origins: neurogenic, vascular, viscerogenic (due to diseases of the internal organs) and psychogenic. That is, a person is treating osteochondrosis, but in fact, back pain arose, for example, due to kidney diseases;
- it is impossible to objectively assess the effectiveness of treatment without control diagnostics;
- the patient cannot adequately select treatment for himself, and folk remedies do not have an evidence base, and therefore, most likely, they are ineffective and may have side effects.
In one case, you can be treated at home - only after consulting a doctor who will correctly diagnose, prescribe adequate treatment and periodically monitor the effectiveness of therapy using X-rays, CT or MRI.
Diagnostics
Faced with signs of thoracic osteochondrosis, most people wonder how the pathology is diagnosed and the degree of impairment is determined. Qualified specialists at the Ruzhansky sanatorium are ready to assess the patient’s general condition and prescribe appropriate therapy.
To prescribe a course of treatment, it is important to go through the following diagnostic stages:
- consultation with a qualified neurologist;
- examination by a doctor, palpation and medical history;
- laboratory examination;
- X-ray or MRI;
- additional examination;
- drawing up a course of complex therapy.
If you have been diagnosed with thoracic osteochondrosis, treatment at home may not give the expected effect. Therefore, it is best to undergo therapy under the supervision of qualified specialists and in appropriate conditions, which will minimize the risk of complications.
Lack of proper attention to the exacerbation of osteochondrosis of the thoracic region, a person may develop complications such as atherosclerosis, prostate dysfunction, pneumosclerosis and even infertility. The progression of the disease leads to the gradual destruction of the vertebrae, cartilage and ligaments.
Treatment of spinal osteochondrosis
Treatment of osteochondrosis can be conservative or surgical. Which method will be the main one depends on the stage of the disease and the neglect of the musculoskeletal system.
Conservative treatment includes medications, physical therapy and lifestyle adjustments. Medications are mainly prescribed anti-inflammatory drugs and muscle relaxants to relieve pain and normalize muscle tone. In physical therapy, one of the main conditions for recovery is early activation, that is, 1-3 days after pain is eliminated, you need to walk, run, exercise in the pool or ride a bike. It is also important to change your lifestyle to an active one, since sedentary behavior is one of the factors in the development of back pain and destruction of the nuclei of the intervertebral discs.
Surgical treatment is used in cases where conservative therapy has proven ineffective within 2–4 weeks, and in cases where there are pronounced structural changes in the spine. What kind of operation is needed will be determined by the surgeon after consultation with a neurologist and studying research data. For example, in the treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, methods are used that relieve the spinal cord from pressure from the vertebrae or hernia (discectomy and decompression).
If you experience back pain, which is accompanied by lumbago in the spine or neck, aching pain in the chest, weakened muscles in the arm or leg, unpleasant tactile sensations on the skin and numbness, consult a neurologist for advice.
0
0
0
Article rating:
5 out of 5 based on 1 rating
Author: Makeeva Marina Anatolyevna
Neuropathologist, reflexologist. Highest category. Candidate of Medical Sciences. Work experience 26 years.
Treatment Options
First of all, the patient will be assisted in eliminating painful sensations. For this purpose, appropriate medications can be prescribed in the format of tablets, injections and ointments.
The composition of therapy and the specifics of its implementation are determined exclusively by the attending physician. Additionally, actions will be taken to reduce the risk of exacerbations of the disease.
Physiotherapeutic methods are actively used, for example, magnetotherapy, electrophoresis, acupuncture, inductometry, etc.
First of all, they contribute to better absorption and increase the speed of action of the medications used, which makes it possible to count on a reduction in the duration of treatment and generally more positive results.
Along with this, it is important to understand that pills and painkiller injections do not eliminate the root cause of the disease, but only provide temporary relief. The therapy necessarily includes therapeutic exercises, consisting of special exercises, the main task of which is to strengthen the muscles and normalize the mobility of the spinal column.
Charging begins only at the stage of remission, after identifying and eliminating the causes that led to the appearance of osteochondrosis.
In rare cases, when conservative treatment methods do not have the desired effect, surgical intervention is resorted to.
Otherwise, they focus on conservative treatment. The specialist makes a diagnosis, prescribes bed rest if there is an exacerbation, recommends suitable painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs.
If necessary, medications are prescribed to normalize the function of the circulatory, genitourinary, muscular and other systems. In the presence of severe spinal cord damage, special paravertebral blockades can be used. This allows you to temporarily alleviate the patient’s condition during the period of primary treatment.