If a person says: “I have abdominal pain,” then it is important to understand: behind abdominal pain there may be problems with any organs of the abdominal cavity, retroperitoneal space, or small pelvis.
If a person says: “I have abdominal pain,” then it is important to understand: behind abdominal pain there may be problems with any organs of the abdominal cavity, retroperitoneal space, or small pelvis. The intestines (ileum, jejunum, colon, sigmoid, colon, transverse colon), appendix, stomach, liver, duodenum, spleen, ureters, kidneys, mesenteric (mesenteric) vessels of the intestine can cause painful sensations in the abdomen. Therefore, pathologies can be gastroenterological, surgical, gynecological, or urological in nature.
Types of pain
Abdominal pain can be very different:
- Acute and chronic . Acute pain occurs suddenly, chronic pain develops gradually, its intensity increases step by step - sometimes over several weeks. In this case, a special type is formed by chronically recurrent abdominal pain. They can suddenly make themselves felt, and then also suddenly pass and resume after a certain period of time.
- Tonic and clonic . With tonic pain, the muscles are very tense, compacted areas appear on the abdomen, and uncontrolled muscle contraction is observed. Tonic pain is accompanied by fairly rhythmic spastic spasms.
- Burning (cutting) and aching – reminiscent of hunger.
The localization of pain can be the abdominal cavity, hypochondrium, areas above or below them.
How to stop an attack at home
Every person should know what to do to relieve acute pain in the lower back that appears suddenly. To do this, follow these steps:
- Lie down on a flat, hard surface, take a position that eases the pain, and try to relax.
- After a couple of minutes, roll over onto your back and place your feet on a hill. Remain in this position until the pain decreases.
- Then carefully roll over onto your side, get on all fours, reach the support, grab it, smoothly straighten your back, but rise using the strength of your arms. Then carefully rise from your knees, trying not to move your body.
- Secure your lower back with a special corset, belt or regular scarf.
If there is a sudden attack of pain in the lower back, you need to lie down on a hard, flat surface.
To relieve severe pain, use NSAIDs, for example, Ibuprofen, Diclofenac.
When sleeping, it is better to lie in the fetal position and hold a pillow between your legs. If the patient is used to sleeping on his back, then a cushion should be placed under the knees to relieve the load on the lower back.
After an attack, avoid physical activity for 2 days. This is necessary to eliminate discomfort and reduce inflammation.
Symptoms
A person who complains of abdominal pain may have different symptoms. Most often it manifests itself in the form of spasms and colic.
- Colic is an attack of primarily stabbing (hence the name) pain. In case of colitis, a person has colitis in both sides, in case of appendicitis or inflammation of the ovaries - in the lower abdomen, in case of poisoning, the localization of colic can be in different parts of the abdomen and most often an additional symptom appears (vomiting, diarrhea).
- Spasms are pain that is accompanied by involuntary muscle contraction. At the same time, the skin turns pale. The pain may cause the person to lose consciousness. If the spasms are due to inflammatory diseases of the intestines or stomach, they are accompanied by fever. Gynecological problems are indicated by spasms accompanied by bleeding.
- Anginal pain is an unpleasant sensation with a strong burning sensation.
- Sharp pain in the area above the navel is a common occurrence with appendicitis.
- A feeling of “fullness” in the lower back may indicate problems with the colon
- Cyclic pain (either intensifies or subsides) is a characteristic symptom of diseases of the bladder and intestines.
- Pain accompanied by severe gas formation indicates improper functioning of the colon.
- Painful sensations accompanied by itching of the anus are symptoms of damage to the rectum.
- Unpleasant sensations in the abdomen , intensifying at rest and disappearing with movement, are the result of problems with blood circulation.
The most important
There are many reasons that provoke acute pain in the lower back, but they are not always associated with the spine. Therefore, do not try to make a diagnosis yourself, especially if the pain is very severe or neurological disorders are present (numbness of the lower body, involuntary urination, defecation). In the absence of competent therapy, the risk of complications, chronicity of the process, and disability increases. In most cases, conservative treatment (with timely diagnosis) is sufficient, which includes medication, physiotherapy, massage, manual methods, and exercise therapy. The operation is often prescribed for intervertebral hernia, which is accompanied by neurological disorders.
Causes
What are the causes of abdominal pain, dysfunction of the abdominal organs and retroperitoneal space?
The cause of colic can be appendicitis, inflammation of the ovaries (in these cases, colic in the lower abdomen), poisoning, or colitis. With colitis, a person has colitis in both sides. If the colic is cramping and is localized both in the abdomen and in the lower back, the pain is more intense, the cause is most often urolithiasis, kidney injuries or pyelonephritis. Colic in the navel area may be a response to irritants of the sensitive mesenteric plexus of the intestine.
Among the common causes of paroxysmal spasms are intestinal obstruction and gastroduodenitis. And uterine endometriosis is most often behind spasms during urination in women.
If abdominal pain is accompanied by increased gas formation and a frequent urge to defecate, then the cause will most often be associated with diseases of the colon.
If you have abdominal pain - anginal, and the patient is bothered by an expressive burning sensation - the cause is most often gastritis (inflammation of the stomach lining) or pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas). If pain and burning are accompanied by severe tension in the muscles of the abdominal wall, and a person complains of pressure in the chest, the cause may be associated with heart pathologies: in particular, such pain is typical for 60% of patients with myocardial infarction.
The cause of abdominal pain accompanied by low-grade fever (the temperature remains at 37.1–37.5 °C for a long time) is most often inflammatory bowel disease.
Did a sudden sharp pain take you by surprise? We'll help you get rid of it.
Often pain catches us at the most inopportune moment, sharp, acute, dull, aching... Sometimes attacks pass quickly, sometimes they drag on for a long time, developing into a chronic form.
This happens if a person does not pay attention to the first clues from his body and starts the process of disease progression without the necessary treatment. However, do you need these consequences? Why “pull” another sore onto yourself and suffer with it until the end of time...
What are the causes of these pains, what is their nature, where do they come from and how to deal with them?
Today we will talk about acute pain in the body. Let's go through its main parts and find out what caused the acute pain, what it talks to you about, what it's high time to pay attention to and what measures to take.
We read, analyze our condition, draw conclusions and, if the body requires it, take all measures to eliminate the cause.
Let's start our excursion with the neck.
Acute neck pain: cervicalgia.
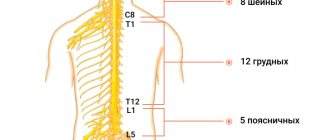
The scientific name for neck pain is cervicalgia. This is one of the most common diseases among the population. It is due to the fact that our neck, due to its structure, has increased vulnerability. It consists of seven formative vertebrae, which are much thinner than the thoracic or lumbar vertebrae.
At the same time, the cervical region is the most mobile of all parts of the spine. It provides various head movements and support. In all positions except the lying position, the neck experiences constant stress, which can result in pain.
Causes of acute neck pain.
The causes of neck pain can be associated with injuries, diseases of the spine, muscle tissue, nervous and cardiovascular systems.
What diseases can neck pain indicate?
- Cervical osteochondrosis
- Cervical radiculitis
- Cervical spondylosis
- Intervertebral hernia
- Subluxation and displacement of vertebrae
- Muscle spasms
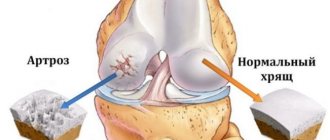
- Uncovertebral arthrosis
- Myositis
- Inflammation of the lymph nodes
- Occipital neuralgia
- Meningitis
This is not a complete list of diseases. However, as you can see, it is quite extensive. Acute pain is a consequence, a consequence of the development of the disease. The disease itself is also a consequence.
Factors that can affect this are, for example: a sedentary lifestyle, lack of physical education, incorrect posture, excessive physical activity, sedentary work, nutrition, obesity, stress, bad habits. All this can provoke and lead to neck pain.
For any effective treatment, it is important to correctly diagnose and determine the cause. By removing it, the consequences will also go away.
Painful symptoms are quickly relieved by our specialists. Relief comes after the first session. Of course, first, the Tibetan doctor will examine you and conduct a diagnosis in order to, taking into account your physiological characteristics, the nature of the disease and its cause, prescribe an effective treatment that will help you cope with the pain in a short time.
Acute back pain.
The spine is the main energy pillar that supplies our body with energy. When, for certain reasons, the flow of energy is disrupted, diseases arise.
Acute back pain indicates that your spine needs treatment. If you do not pay due attention to this problem, then over time complications will arise and associated diseases will begin to develop.
In medical terminology, back pain sounds like dorsago - acute pain in the thoracic spine and lumbago - acute pain in the lower back.
Let's look at the main diseases that can cause acute back pain.
Causes of acute back pain.
One of the common causes of acute back pain is radiculitis. Moreover, the pain from this disease spreads to the chest, along the intercostal nerves and to the back of the thigh, as well as the lower leg. This disease is associated with inflammation and pinching of the spinal nerves.
Also, the cause of acute back pain can be diseases such as:
- Osteochondrosis of the lumbar region
- Protrusion or herniation of a spinal disc
- Sciatica
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- Arthrosis of the intervertebral joints
- Kidney diseases
Procedures such as Tibetan acupressure, acupuncture, and manual therapy help quickly relieve acute pain.
To prevent the recurrence of back pain, a Tibetan doctor conducts an individually selected course of complex treatment. Which, in addition to the indicated procedures, additionally includes warming up bioactive points with wormwood cigars, hirudotherapy, vacuum therapy and others.
Thanks to this approach, congestion in the back is eliminated, the processes of restoration of spinal tissue are stimulated, blood supply is improved, and metabolic processes in the back are normalized.
Acute pain in the abdomen.
Perhaps the most common pain is abdominal pain. Few have not experienced it. It appears suddenly and causes great discomfort. Without understanding the cause, a person begins to independently take various popular remedies to eliminate the symptoms. However, the reason can sit deep and threaten not only the health, but also the life of a person.
What can cause pain? From the point of view of Tibetan medicine, abdominal pain can occur due to an imbalance in the Bile and Mucus systems. In the first option, imbalance occurs due to excessive aggression, increased irritability, intolerance, and alcohol abuse.
Disharmony of “Mucus” can be caused by overeating, eating incompatible foods, a sedentary lifestyle, and parasites in the body.
Acute abdominal pain can be caused by inflammatory diseases of the abdominal organs, gastrointestinal diseases, abdominal injuries, etc. This includes diseases such as:
- Appendicitis
- Gastritis
- Stomach ulcer
- Pancreatitis
- Cholecystitis
- Various intoxications
- Diseases of the genitourinary system
- And others.
The list is quite impressive and the main thing is to consult a doctor in time. In medical terminology, there is such a thing as an acute abdomen.
What is an acute abdomen?
Acute abdomen refers to a range of symptoms that occur as a result of acute, life-threatening diseases or injuries to the abdominal organs. This term is used in emergency situations, before a detailed examination and identification of the cause of the pain.
Main symptoms of acute abdomen:
- Constant or cramping sharp pain in the abdominal area
- Nausea, vomiting
- Retention of stool, gas, loose stools
- Protective tension of the abdominal wall muscles, fetal position
- Increased breathing rate, temperature, rapid pulse
- Drop in blood pressure
- Painful shock, fainting
With such symptoms, the condition can sharply worsen, so the person must be hospitalized urgently.
The cause of an acute abdomen may be inflammatory diseases of the abdominal cavity, requiring emergency surgical intervention. These are diseases such as appendicitis, acute mechanical intestinal obstruction, acute destructive cholecystitis, abdominal abscess, peritonitis and others.
Also, “acute abdomen” can cause gynecological diseases, gastrointestinal diseases, gastrointestinal bleeding, trauma and penetrating wounds of the abdomen, etc. by the list.
Acute pain in the shoulder joint.
Acute pain in the shoulder joint is typical for diseases such as:
- Shoulder arthritis
- Arthrosis
- Inflammation of the brachial nerve (neuritis)
- Tendinitis or inflammation of the periarticular muscle corset
- Osteoporosis
- Tendobursitis, tendinitis
- Kasulite
- Shoulder sprain
And other diseases. You can learn more about the possible causes of shoulder pain, as well as treatment and prevention methods, in our article here.
Sharp pain under the shoulder blade.
Let's continue our acquaintance with the body and the causes of acute pain in it.
Acute pain under the shoulder blades can also be caused by a variety of diseases. For example, pain under the right shoulder blade may indicate hepatic colic due to cholelithiasis.
With urolithiasis, renal colic may occur, in which the pain is sharp, cutting and can radiate to the lower back and under the shoulder blade.
In addition, acute pain under the scapula may indicate protrusion, which is the initial form of intervertebral hernia. Acute pain occurs due to the interaction of displaced discs on the spinal roots and spinal cord.
Other factors and diseases that cause pain under the shoulder blades are:
- Scapula injuries
- Osteomyelitis
- Tumor of the scapula
- Pinched nerve
- Heart pathologies
- Lung diseases
- Damage to the gastrointestinal tract
- And others.
Understanding the cause of acute pain helps to quickly and effectively cope with the developing disease. Don't underestimate the possible consequences of inaction.
Sharp pain in the hands.
Pain in the arms can be muscular, joint and neuropathic. And it can be difficult to figure out the true cause of its occurrence on your own. You should not self-medicate without knowing the cause, as this is fraught with serious consequences and lost time.
An example for understanding. Pain in the left arm can be caused by diseases of the cardiovascular system. In particular, myocardial infarction. In this case, measures not taken in time will lead to serious consequences.
Often acute pain in the hands can occur due to various types of injuries, such as sprains, fractures, and bruises. Joint diseases, cervical osteochondrosis, protrusion and intervertebral hernia are also a common cause of pain.
Another list of diseases:
- Tendinitis
- Styloiditis
- Arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis
- Arthrosis
- Bursitis
- Chondrocalcinosis
- Ulnar nerve neuritis
Diagnostics at the “Tibetan Doctor” will allow us to accurately determine the cause of your pain in your hands and quickly eliminate it. You shouldn’t endure and suffer, you shouldn’t wait for the next attack of acute pain. After completing the course of treatment, you will get rid of pain in your hands and the diseases that caused it.
Acute pain in the legs.
Legs are our support. Thanks to them we walk, run, jump. Our legs are under constant load from our body weight. Therefore, excess weight negatively affects their health and contributes to the development of diseases such as arthrosis.
Acute pain in the legs can occur due to lumbosacral radiculitis; pinched and inflamed spinal nerves can cause acute pain in the back of the thigh and lower leg.
The weak point of the legs is the blood vessels, because the blood rises through them from bottom to top. Improper nutrition can cause a disease such as atherosclerosis, as a result of which the lumen of blood vessels decreases and varicose veins occur. Varicose veins can also cause leg pain.
Acute pain in the legs can be caused by injuries such as dislocations in the hip, knee, ankle, ligament damage, knee meniscus damage, popliteal cyst rupture, Achilles tendon damage, ankle ligament damage.
The list of diseases that can cause acute pain is also long. I will list some of them:
- Arthritis
- Arthrosis
- Ligament inflammation
- Diseases of the spine, especially its lower part
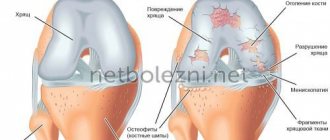
- Osteophytes
- Chondrocalcinosis
- Hemophilia
- Bursitis
- Diffuse fasciitis
- Myalgia, myositis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Gout
- Diabetes
And other diseases. Diseases that cause pain can be completely diverse, and their localization may not be related to the place where pain occurs. Therefore, it is important to correctly determine the cause and prescribe treatment.
Tibetan medicine has proven, effective methods of treating the diseases mentioned in this article. An integrated approach allows you not only to quickly relieve pain and get relief, but also to eliminate the root cause of the disease, which eliminates associated sores.
Finally.
If you have not received an answer to your question, call the number above or sign up for a free diagnostic in the form below. It won't take more than a minute.
During the diagnosis, you will receive answers, get to know your body again, learn its strengths and weaknesses, and receive recommendations on your health and treatment from a Tibetan doctor.
Health to you and your loved ones!
Diseases
Most often, abdominal pain is caused by diseases of the intestines, stomach, pancreas, problems with the gallbladder, as well as hernias.
Intestinal diseases
- Ulcerative colitis is a diffuse inflammation. The rectal mucosa is affected. In the initial forms of ulcerative colitis, inflammation affects only the proximal part (the entrance to the intestine); in advanced forms, the problems affect the entire colon. As the disease progresses and worsens, the patient feels a sharp deterioration in health, the body begins to become intoxicated, the pulse quickens, and in most cases blood appears in the stool. If the disease is not treated, the body can poison itself, and peritonitis can develop - damage to the abdominal cavity that poses a threat to life.
- Enteritis . The small intestine becomes inflamed. At first, the disease is “masked” as a disease, and often accompanies this problem. If the disease is not treated in a timely manner, the functions of the small intestine are disrupted. Food begins to be poorly absorbed by the intestinal walls. Digestion processes are disrupted.
- Crohn's disease . One or several areas of the intestine can become inflamed. But almost always the inflammation affects the junction of the large and small intestines. One of the most unpleasant aspects is that the inflammation affects the entire thickness of the wall, and a complication of the disease is intestinal obstruction syndrome, the treatment of which requires the adoption of a set of measures related to the simulation of motility and restoration of intestinal function.
- Dysbacteriosis is a disorder of the intestinal microflora. The number of beneficial bacteria in the intestines is reduced, and pathogenic microflora develops. As a result, gas formation occurs, a person cannot digest food, and bowel movements are disrupted. Very often, the development of dysbiosis is a consequence of incorrect antibiotic therapy or a reaction to stress.
Pancreatic diseases
- Pancreatitis . The most common disease affecting the pancreas is pancreatitis. When the pancreas is inflamed, a person feels severe discomfort in the upper abdomen, and it becomes difficult for the body to digest proteins and fats. Often in everyday life they say in this case: “There are not enough enzymes.” And this really reflects the real picture. In the affected pancreas, the production of lipase, chymotrypsin, and trypsin is significantly reduced.
- Cystic fibrosis is a disease that disrupts the functioning of the pancreas and respiratory system. It is a non-inflammatory pathology. The reason is hereditary factors. A complication of the disease may be the formation of a duodenal ulcer.
Stomach diseases
Some of the most common diseases that affect people of all ages are accompanied by abdominal pain - these are pathologies of the stomach, especially its mucous membrane. The leaders are gastritis, ulcers, gastroesophageal reflux disease.
- Gastritis . It is an inflammation of the gastric mucosa. The entire stomach or certain parts of it can become inflamed. With gastritis, pain with burning and spasms predominate. The patient is concerned about discomfort after eating, a feeling of a full stomach or, on the contrary, “sucking” and a constant feeling of hunger. Accompanying the disease in the acute stage are vomiting and nausea.
- Stomach ulcer . Pain occurs against the background of characteristic ulcerative damage to the gastric mucosa. Dyspeptic symptoms are pronounced: heaviness in the stomach, a feeling of oversaturation of the stomach, pain in the epigastric region.
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (popularly known as “reflux”). The disease is associated with a weakening of the valve between the stomach and esophagus. The result of this weakening is pain, accompanied by heartburn. Very often, gastroesophageal reflux disease appears in patients who have already experienced gastritis or a stomach ulcer.
Challenges and possibilities of therapy
The main objectives of treating these patients are: providing conditions for a full course of rehabilitation measures, pain relief, preventing chronic pain, and preventing relapse of exacerbations [2]. First of all, the patient must be explained the essence of the disease and the favorable prognosis for the restoration of motor activity, as well as jointly develop further treatment tactics. In our opinion, involving the patient in the treatment process and jointly discussing the treatment plan reduces the anxiety that arises, especially in patients with limitations in daily activities. It is necessary to encourage the patient to quickly return to daily routine, even if the patient requires bed rest for a while, especially if the pain is severe.
In order to save time on an explanatory conversation, patients may be offered information brochures, which is an addition to what the doctor said. The effectiveness of other forms of providing information to patients (videos, round tables, telephone communication, etc.) has been little studied [3]. Based on our experience, most patients make sufficient use of the Internet, read forums where patients share impressions, fears, and rumors, which in turn has an impact on impressionable, emotionally labile patients. In this regard, suggesting that all patients use additional sources of information is not correct and may only be acceptable for a certain category of patients.
Despite the general recommendation for the fastest return to daily activities, physical therapy, either guided or unguided, is ineffective during the acute period, so it is recommended that exercises begin after pain has subsided in 2-6 weeks. The effectiveness of other methods of therapy (massage, manual therapy, yoga, reflexology) is currently not fully studied. Treatment results are greatly influenced by the doctor’s experience and the techniques used [5, 9-11].
Studies have shown the effectiveness of analgesics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and muscle relaxants. One of the drugs for pain relief can be acetaminophen, which is inferior in severity to NSAIDs, but has a more favorable safety profile and price and can be used to treat pain both in the acute period and in chronic pain. At the same time, acetaminophen is characterized by an increase in aminotransferases at a daily dose of 4 g. Non-selective NSAIDs are more effective for pain relief than acetaminophen, but their use is associated with the development of gastrointerstitial and renovascular complications. In particular, one of the most common side effects of NSAIDs is gastropathy (from 15 to 30%), as a result of which more than 10% of patients stop taking medications. If it is necessary to use NSAIDs orally, preference is given to selective inhibitors of cyclooxygenase type 2 [2, 3].
The choice of a drug from the group of NSAIDs or cyclooxygenase inhibitors is based on an assessment of the risk of complications and possible ways to reduce it. The latter is achieved by prescribing lower effective doses of NSAIDs, as short a course as possible, or by concomitant use of proton pump inhibitors in patients at high risk of developing gastropathy [3]. Relief of pain and reduction of the dose of NSAIDs can be achieved by the combined use of NSAIDs with opioid analgesics, with benzodiazepine tranquilizers (increasing the analgesic effect of NSAIDs and reducing anxiety due to pain) or muscle relaxants. The combination of muscle relaxants with NSAIDs not only enhances the analgesic effect, but also reduces the dose of the latter by 2 times, thereby reducing the risk of developing gastropathy [2].
Hernias
Often abdominal pain is caused by peritoneal hernias. They can be umbilical, inguinal, diaphragmatic. Umbilical hernias are more often formed during pregnancy or in the postpartum period, inguinal hernias - with excessive stress, diaphragmatic hernias - defects of the abdominal wall that form as a reaction to improper bowel function, an incorrectly selected corset, or heavy lifting. The insidiousness of diaphragmatic hernias is that at the initial stage of the disease, a person believes that he has typical gastritis - with heartburn and belching, but traditional therapy does not provide treatment, and ultrasound shows that the cause is not inflammation of the stomach, but precisely the presence of a hernia. In toga, to combat pathology, it is not necessary to relieve inflammation or eliminate spasms, but to undergo surgical treatment, which is aimed at strengthening the abdominal wall.
Diseases of the gallbladder and bile ducts
A special group consists of diseases associated with the gallbladder and bile duct.
- Cholangitis . Inflammation of the bile ducts. The pain is unbearable. Mainly on the right side. It is complicated by the fact that it requires not only quick relief from the attack of pain itself, but also normalization of blood pressure.
- Cholecystitis . Acute pain due to eating fatty foods. Often the pain itself is followed by vomiting mixed with bile. Flatulence (gas formation) and vomiting may occur.
- Gallstone disease is the formation of hard structures – stones – in the bile. Pain in the disease is paroxysmal. Especially if the stones move through the gallbladder and ducts.
Contraindications
An incorrect diagnosis can lead to the fact that treatment will not only be useless, but will provoke serious complications. After all, many medications and physiotherapeutic techniques that are effective for some diseases accompanied by abdominal pain are strict contraindications for other diseases with similar symptoms.
For example, if a number of medications prescribed for pancreatitis are given to patients with hepatic colic, the reaction may be unpredictable. And treating a number of stomach diseases with antibiotics can cause serious dysbiosis.
And absolute contraindications for pain in the abdomen or stomach are self-medication - especially independent decision-making to take a painkiller or antispasmodic. If, for example, such drugs are used by a person whose appendix is inflamed, relief will follow for a while. But this will not be help, but false help to yourself. There are often cases when patients who did not get to the surgeon in a timely manner to remove appendicitis began to experience necrosis of the tissues of neighboring organs.
Under no circumstances should you resort to even seemingly “harmless” means to combat high acidity without making a diagnosis. What seems to be simply a release of excess hydrochloric acid and inflammation of the stomach may turn out to be a symptom of a completely different disease, such as a heart attack.
Also, for abdominal pain with an unclear diagnosis, you should not apply a heating pad with hot water. In a number of pathologies, heat only accelerates the inflammatory process and activates bleeding.
Causes of lower back pain
- Age-related degenerative-dystrophic changes in the structures of the spinal column and adjacent tissues;
- damage to nerve fibers and nerve nodules near the spinal column;
- inflammatory processes in cartilage and bone structures;
- adiculitis in the lumbar spine, lumbago, sciatica, intervertebral hernia and many other diseases of the musculoskeletal system;
- appendicitis, cholecystitis and other inflammatory lesions of internal organs;
- obesity of the fourth degree, causing a high load on the lumbar spine;
- benign and malignant tumors;
- infectious diseases, most often infectious lesions of bone tissue;
- in women - adnexitis, torsion of ovarian cysts, pregnancy or menopause;
- in men - prostatitis or epididymitis.
Surveys
An effective examination of a patient who is bothered by abdominal pain consists of an interview, palpation of the abdomen, and laboratory and functional diagnostics.
For a doctor to make a diagnosis, the smallest details are important. For example, even a basic assessment of stool can clarify a lot in the case of abdominal pain.
- Hard lumps (“sheep” feces) are a frequent companion to colitis, elongation of the sigmoid colon, and gastric ulcers.
- Watery stools often accompany poisoning and infectious diseases.
- With a parasitic disease (presence of worms in the intestines), dysbacteriosis, stool particles are usually very loose.
Also, to select a tool and diagnostic technology, an oral interview with the patient is important. The doctor asks the patient how long the pain lasts, whether there are attacks, what exactly causes the pain - physical movements, going to the toilet, eating, taking a certain position.
Diagnostics
The following types of research are especially valuable for identifying the cause of the disease and finding treatment methods for pathologies of the abdominal cavity:
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity. One of the most prompt measures in diagnosing diseases of the abdominal and pelvic organs and identifying the cause of abdominal pain is ultrasound diagnostics. Using ultrasound, you can identify pathologies of the liver, gall bladder, spleen, kidneys, uterus, and ovaries. Many people wonder whether the stomach and intestines are visible on an ultrasound. The stomach cannot be examined using ultrasound; the intestines cannot be examined partially. If the equipment has good resolution, for example, volumetric formations in this area are visible.
- FGDS (gastroscopy, probing, intestinal swallowing) is a diagnostic method that can be used to obtain an objective picture of the condition of the stomach, duodenum, and esophagus. If necessary, you can immediately conduct a rapid test for Helicobacter pylori (the cause of the development of ulcers), do cytology and biopsy to exclude the oncological nature of the disease, and determine “acidity”.
- X-ray. An old, but still practiced method of diagnosis. It can be used as an emergency measure to examine the stomach if for some reason an FGDS cannot be done. In addition, x-rays are informative in identifying diseases accompanied by symptoms of intestinal obstruction. Depending on the nature of the patient’s pain and complaints, traditional X-rays or contrast-enhanced X-rays (irrigoscopy) may be used.
- MRI is a progressive diagnostic method for abdominal injuries, liver enlargement, and an uninformative picture of the abdominal cavity on ultrasound (for example, due to severe flatulence).
- Colonoscopy. One of the most accurate methods for examining the intestines. This is done using a fiber colonoscope. Using the device, you can examine everything - even the most complex areas, including the inner surface of the colon.
- Cholescintigraphy . Isotopic study. It is carried out using a radiopharmacological drug. Informative for problems with the gallbladder and bile ducts.
- Blood, urine and canal analysis . In the blood test, special emphasis is placed on ESR (inflammation can be determined by the erythrocyte sedimentation rate), biochemical indicators, and in many types of examinations for abdominal pain, stool is examined for occult blood.
What to do?
So, the main thing for abdominal pain is not to self-medicate, and not to delay visiting a doctor and getting a diagnosis.
At the same time, in some cases, it is important not just to make an appointment at the clinic, but to immediately call an ambulance. In what cases is an ambulance required?
- Abdominal pain is very intense.
- Cold sweat appears.
- Severe vomiting of blood begins.
If the pain is not acute, there is no blood in the vomit, the temperature differs from that of a healthy person, but there is no fever, consultation with a therapist, gastroenterologist and diagnosis are recommended.
Timely diagnosis is a guarantee that the most gentle methods will be used to combat the disease. Even if we are talking about surgery.
- Laparoscopy is used to remove gallstones and appendicitis (if the situation is not advanced).
- Laparoscopic funduplication is used to treat gastroesophageal reflux disease.
- To effectively solve problems with hernias and strengthen the abdominal wall, surgical hernioplasty is used.
If there are no indications for surgical treatment, the therapeutic effect for many diseases of the intestines and stomach is provided by an integrated approach, which is based on diet therapy, physiotherapy and drug therapy - antibiotics, antiparasitic drugs, corticosteroids, prokinetics to improve intestinal motility.
Treatment
The key to success in the treatment of any spinal disease is an integrated approach. This is the only way to achieve a good and lasting effect. However, there is not and cannot be a single complex suitable for everyone. It all depends on the disease itself, its location and the characteristics of the body.
Methods successfully used in our clinic:
- Osteopathy;
- Manual therapy;
- Medical massage;
- Plasma therapy;
- Isometric kinesiotherapy;
- Kinesiotherapy using the Exart installation;
- Acupuncture;
- Tsubotherapy;
- Laser reflexology;
- Pharmacopuncture;
- Hirudotherapy;
- Kinesio taping;
- Ozone therapy;
- Physiotherapy;
- Physiotherapy with enzyme preparations;
- Therapeutic droppers;
- Botulinum therapy.
Where to go?
The doctors of the 5th Clinical Hospital have extensive experience in performing laparoscopic operations and hernioplasty in Minsk.
In addition to accepting patients who are citizens of Belarus, the 5th City Hospital of Minsk also accepts foreign citizens (on a paid basis). Each of them can undergo comprehensive diagnostics and treatment at the surgical and therapeutic departments.
The hospital has its own clinical diagnostic laboratory, X-ray department, X-ray CT and MRI rooms. The physiotherapy department has all the conditions for conducting rehabilitation programs.
Prevention
Doctors at the 5th Hospital will not only select the optimal diagnostic and treatment option for each patient, but will also advise on how to prevent relapses.
Diet occupies a special place among measures to prevent intestinal and stomach diseases. It is important to learn to maintain balance in nutrition. You should not overeat; you should chew food carefully and slowly. Water and willow tea https://teahelp.ru/tea/herbal-tea/ivan-chaj/ should be consumed in sufficient quantities; coffee is not recommended in this case. At the same time, when choosing a diet, experienced doctors take into account all factors:
- functional state of the intestines, liver, pancreas
- secretory function of the stomach,
- intestinal motility,
- the presence of other concomitant diseases.
In addition to your diet, it is important to reconsider how you store and process food. Do not leave food open in the sun. Avoid damp food storage areas. Otherwise, they may begin to mold and rot. Avoid contact between raw foods and cooked foods.
Exercise therapy is also of great importance in the complex of preventive measures. Instructors-methodologists select their own loads and exercises for each patient.