Electrophoresis is a type of physiotherapeutic procedure that is used to treat various diseases. During electrophoresis, the human body is exposed to a direct electric current generated by a special apparatus. Using electrophoresis, a medicinal substance is introduced into the body through the skin and mucous membranes. Electrophoresis is prescribed by the attending physician after a thorough examination and exclusion of contraindications. The procedure is performed in a medical facility in compliance with all rules and regulations. There are devices for home use, however, they should also be used after consultation with a doctor and strict adherence to instructions and safety measures. It is better to entrust the performance of physiotherapy to professionals.
At the Yusupov Hospital you can take a full course of electrophoresis in the comfortable conditions of a rehabilitation center. Specialists perform this physical procedure with high quality, which contributes to the patient’s speedy recovery.
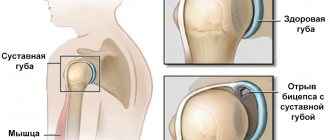
Principle of action and therapeutic properties
The drug penetrates the joint internally through:
- glands,
- hair follicles,
- between epidermal cells.
Electrophoresis is prescribed by the attending physician (usually an orthopedist) and performed by a qualified nurse. Before applying the electrodes, she must ensure that the skin is intact and that there are no pustules or moles.
During the procedure, the child feels a slight tingling sensation, “goosebumps”. Depending on age and disease, the current strength and duration of the session are adjusted.
In case of dysplasia, the number of repetitions can be increased to 20. After the course, the doctor prescribes a break and, if necessary, prescribes a repetition of electrophoresis for the hip joints. The session takes up to 10 minutes, depending on the specific case.
The intensity of the procedure is affected by:
- dosage,
- patient's age,
- greater or lesser force on the joint.
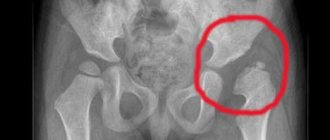
Hip dysplasia in newborns treatment
Hip dysplasia affects approximately 7% of infants, and the problem is often detected immediately after birth. This pathology is a violation in the formation of a healthy hip joint, so early detection and timely treatment are the key to successful recovery.
Diagnosis of hip dysplasia in newborns
Already during the first examination of the child at birth, the doctor pays attention to the presence of signs of dysplasia. These include:
- pronounced difference in the length of the legs;
- mismatch of femoral, inguinal and gluteal skin folds;
- asymmetrical and incomplete spread of legs bent at the knees;
- clicking sound when hip abducts.
These same signs are also informative during routine monthly examinations of the baby. If necessary, the child is prescribed a consultation with an orthopedist and additional tests - up to 3 months of age this is an ultrasound, and for older children - an x-ray of the pelvis and joints
Particular attention is paid to children at risk. It is included in the presence of threatening factors:
- birth weight less than 2 kg and more than 3.5 kg;
- twins;
- prematurity;
- breech presentation;
- toxicosis or hormonal characteristics in the mother;
- first or late pregnancy;
- deficiency of vitamin D and calcium during pregnancy;
- hereditary predisposition;
- female gender of the child.
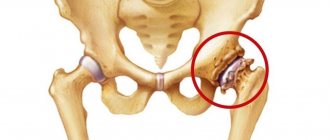
Stages of hip dysplasia
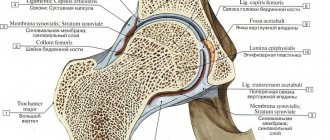
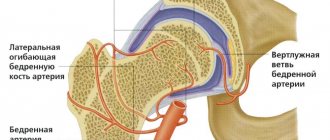
At the time of birth, the baby's hip joint is not yet mature enough. The acetabulum is not fully formed, the ligaments are very elastic, and the head of the femur is fixed in place by the capsule surrounding the joint on the outside. With dysplasia in the joint, anatomical changes are observed, the severity of which determines the degree of violation:
- preluxation;
- subluxation;
- hip dislocation.
Pre-luxation is a borderline condition between a normal newborn joint and obvious dysplasia. At this stage, the acetabulum is flatter and shallower, but the head of the femur remains in place.
httpv://www.youtube.com/watch?v=embed/kFwYoC2OhQ8
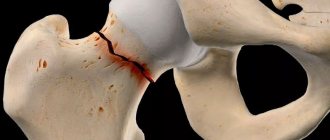
With subluxation, the femoral head is shifted relative to the axis of the joint, the ligaments are greatly stretched. The cartilaginous plate of the acetabulum does not prevent the displacement of the head, which, under load, can extend beyond the boundaries of the cavity. Subluxation is hip dysplasia in the narrow sense.
The most severe form is hip dislocation. It can be diagnosed either immediately after birth (congenital) or as a result of untreated mild forms of dysplasia. When dislocated, the femoral head is significantly displaced relative to the acetabulum, the articular surface of which is greatly smoothed.
Treatment of hip dysplasia
Treatment of dysplasia is a long process, taking 6-9 months, since it takes time to restore the joint. Treatment tactics are selected based on the degree of dysplasia and the age of the baby. Orthopedic and physiotherapeutic methods, exercise therapy, and massage are used. In severe advanced cases, they resort to surgery.
Orthopedic treatment methods
Orthopedic treatment is the basis for the treatment of dysplasia, since the child’s legs must be fixed in a divorced state for a long time. For infants under 3 months of age, products are recommended that provide soft fixation without restricting mobility. They use wide swaddling with half-bent legs apart (“frog” pose), Pavlik stirrups, soft elastic splints, and a Freik pillow.
From the age of three months, along with Pavlik stirrups, rigid fixation is also used. A plaster cast is used to hold the legs apart and bent at right angles, Volkov and Vilensky splints.
When is electrophoresis needed?
The method affects the human body as follows:
- relaxes muscles
- relieves spasms,
- reduces inflammatory processes,
- relieves pain in the joints.
Therefore, electrophoresis using drugs for the lower extremities of infants is prescribed if:
- lesions of the musculoskeletal system, pelvic joint dysplasia,
- unpleasant sensations accompanying a particular disease,
- neuralgia of the legs: hyper- and hypotonicity, birth injuries.
Electrophoresis with drugs
The solution is prepared immediately before starting. The doctor determines the required concentration based on the diagnosis and specific indications.
To obtain the required percentage of the active substance, use distilled water, alcohol or dimexide.
According to Ratner
The method developed by the scientist involves the simultaneous use of 2 drugs:
- Eufillin,
- Papaverine.
Danger for babies
Electrophoresis is applicable as a treatment method even for infants. If there are no serious diseases and specific indications, doctors prefer it over drug therapy. But, as with any external influence on the body (especially infants), there are a number of contraindications:
- electrophoresis is strictly prohibited if the baby has purulent skin infections or dermatitis, since the procedure itself is associated with a direct effect on the external integument,
- at elevated body temperature, an electrical discharge will aggravate the problem,
- bronchial asthma with relapses is also a contraindication,
- renal and heart failure force specialists to abandon this relatively safe method of treatment,
- allergies to additional medications and intolerance to current discharges make electrophoresis impossible.
During the procedure, it is normal if at first the baby feels a little uncomfortable with cold wipes soaked in medicinal liquid, and if he feels a slight tingling in the affected areas.
Contraindications
Patients with an implanted electronic device (eg, pacemaker) should not be treated with iontophoresis. Pregnant women are also not recommended to use the device.
Patients with defective body parts that cannot be covered with Vaseline or films should not use electrophoresis. Concomitant treatment of the skin with aluminum chloride may reduce the effectiveness of iontophoresis. Physiotherapy with electrophoresis is strictly not recommended for infants. The baby may react unpredictably to the action of current or paraffin, which in some cases can lead to bad consequences.
Paraffin
httpv://www.youtube.com/watch?v=embed/C7U_MFuFQvs
Joint diseases are quite serious ailments that, if not treated promptly, can lead to disability. To prevent this from happening, you should consult a doctor in a timely manner. The specialist will conduct a full examination and diagnose the pathology at an early stage, while the cartilage tissue is not yet destroyed. At the same time, drug therapy remains the main method of treatment, and physiotherapy, in particular electrophoresis for joints, can enhance the effect of medications, reduce their dosage and eliminate some adverse reactions.
How is electrophoresis performed?
There are many models of apparatus for the procedure. The “Potok” device is popular in domestic medicine. Modern equipment is equipped with additional indicators to monitor the current level.
To administer the medication, a special pad or gauze is impregnated with the medication in a liquid state, which is then placed directly on the electrode. Under the influence of current, electrolysis occurs, facilitating the penetration of active substances into the joint. A larger percentage of them locally affects a given area, and the rest of the mass of particles is carried throughout the circulatory system and lymph.
Treatment options at different stages
It is very important to start treatment for arthrosis of the hip joint on time; the symptoms of the disease are severe. Experts distinguish several stages of the disease, their treatment will be different.
I degree
It is characterized by slight pain in the area of the disease, which most often occurs after physical activity. Movements are not impaired. For first-degree arthrosis of the hip joint, treatment is the simplest.
Only a qualified doctor can make an accurate diagnosis, and only he can recommend treatment with folk remedies for coxarthrosis of the hip joint. Moreover, most often they are an addition to the main methods. At this stage, drug treatment is used, and sometimes physiotherapeutic procedures and special sets of exercises are prescribed.
Special sets of exercises will help overcome the disease
II degree
The pain becomes stronger, the joint becomes less mobile. The patient experiences discomfort in the groin and knees. Due to the unclear location of pain, there is a risk of making an erroneous diagnosis and, as a result, prescribing incorrect treatment for second-degree arthrosis of the hip joint. To avoid such a mistake, the patient needs to be comprehensively examined.
Note that at this stage it is still possible to treat coxarthrosis without surgery. To combat the disease, a set of exercises, medications, physiotherapy and a number of non-traditional methods are used: acupuncture, apitherapy and the like.
Medications and alternative methods are effective in the fight against coxarthrosis
III degree
At this stage, the patient’s muscles are already greatly atrophied. The pain becomes stronger, due to which the person cannot sleep peacefully, and the deformation of the pelvis is visually noticeable.
After a thorough examination, the doctor determines how to treat arthrosis of the hip joint. Most often, injections, ointments, and physiotherapeutic techniques are prescribed. In this case, the duration of treatment will increase compared to grade 2 arthrosis. Most often, it cannot be done without surgical intervention.
Injections into the joint are quite effective in the treatment of coxarthrosis
IV stage
Note that not all experts distinguish the fourth degree of the disease. It is characterized by severe pain, the person practically cannot walk normally, it is difficult for him to sit and move.
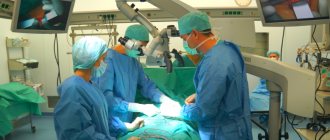
Therefore, most often doctors prescribe surgical intervention to the patient, followed by a long course of rehabilitation.
After endoprosthetics surgery, a long course of rehabilitation follows
Let us note that the professionalism of the doctor plays a vital role in diagnosis, because it is extremely important to establish a diagnosis in time and begin treatment for osteoarthritis of the hip joint