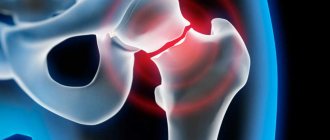
Endoprosthesis replacement is an operation that must be performed when there is significant wear and tear on the hip joint. After such surgery, the damaged joints are replaced with artificial ones. Motor function is restored, and the patient can live a normal, full life!
Operation stages
It’s not for nothing that children are sent for routine examinations to specialist doctors every month.
Sometimes in the maternity hospital they do not notice, and sometimes such a problem as physiological immaturity of the joints simply does not manifest itself. Parents are very afraid of the diagnosis, but with timely detection and taking certain measures, everything will go back to normal without any difficulties. All types of hip replacement surgeries are performed by qualified surgeons in specialized centers equipped with the necessary equipment. It is also advisable to spend the recovery period in a special rehabilitation center.
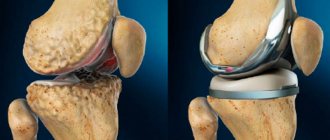
Total (complete) hip replacement is the most radical method. The volume of intervention is maximum, which carries certain risks. At the same time, this technique allows you to achieve the greatest results.
Stages of total hip replacement.
- Preparing for surgery. The patient is examined in an outpatient setting. Indications and contraindications for hip replacement are identified, and the scope of intervention is determined. Next, the patient is admitted to a specialized hospital. On the eve of the operation, the anesthesiologist decides on the type of anesthesia and carries out preoperative preparation (tranquilizers). The patient is given a cleansing enema.
- Anesthesia. On the day of the intervention, the patient enters the operating room on an empty stomach. The anesthesiologist performs pain relief. The most commonly used is conduction anesthesia (epidural, spinal). In some cases, endotracheal anesthesia is preferred.
- Fixing the patient on the operating table using special supports. The side position is used.
- Treatment of the surgical field.
- A surgical incision is made in the skin and underlying tissue above the hip joint parallel to the axis of the limb. The doctor sequentially cuts layers of skin, subcutaneous fat, and muscle tissue.
- Hip rotation. Using stops, the limb is fixed in a bent position after external rotation.
- Dislocation of the femoral head. The head of the femur is removed from the joint into the surgical incision.
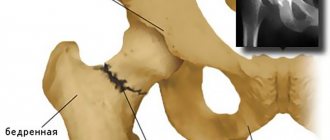
- Removal of the femoral head. A cut is made at the level of the femoral neck with a flat surgical saw.
- Treatment of the acetabulum. The acetabulum is sequentially reamed to a larger diameter.
- Installation of the femoral endoprosthesis. An implant (metal or ceramic) is placed on the femur and secured with a long pin along the axis of the bone.
- Installation of the pelvic part of the implant in place of the acetabulum. Using bone cement or screws, a titanium cup corresponding to the shape of the femoral prosthesis is installed.
- Comparison of implant parts. The hip is internally rotated. The femoral part of the implant is inserted into the acetabular implant.
- Installation of drainage tubes around the joint.
- Consistent restoration of the muscle layer, underlying tissues and skin.
Types of hip replacement
Contrary to popular belief, prosthetics is not always a complete replacement of a joint with an artificial one. There are partial replacements of natural body tissues. Differences in the design of prostheses also affect surgical technology.
Implant installation operations are divided into the following categories:
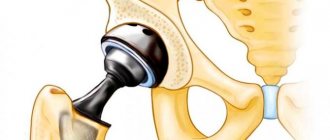
- Total. As the name suggests, the hip joint is completely replaced with an artificial one. A prosthesis made of the selected material is inserted into the femoral canal, and a metal cup coated on the inside with ceramics or polyethylene is inserted into the acetabulum.
- Superficial. This surgery is also known as arthroplasty. Damaged tissue is removed from the head of the femur and, after the necessary treatment, a special cap made of metal is put on. This operation has been abandoned in a number of countries or is performed as rarely as possible. This is due to the fact that when the cap and the head of the bone come into contact, its surface oxidizes.
- Single pole. With this type of prosthetics, only the head of the femur is replaced. The acetabulum is not exposed, so the prosthesis and cartilage tissue are in direct contact during its operation.
- Bipolar. Here artificial prostheses with 2 degrees of mobility are used. The head of the prosthesis moves in the acetabulum and can rotate on the stem. This design completely eliminates postoperative dislocations, which often occur with traditional prosthetics.
Possible complications
Hip replacement surgery has been performed for over 30 years. Hundreds of thousands of patients undergo this intervention every year. Serious complications of the operation are recorded in less than 2% of patients.
Preoperative examination and preparation for surgery can reduce the risk to the patient's health.
The most severe complications of hip replacement include:
- Infectious complications in the surgical area (0.5-2%);
- Pulmonary embolism (0.05%);
- Massive blood loss;
- Postoperative pneumonia.
Infectious processes in the area of the endoprosthesis are a consequence of decreased immunity and impaired surgical technique. The body's own defenses are weakened in patients receiving treatment with glucocorticosteroids (rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, etc.).
Hip replacement is accompanied by massive antibiotic therapy to prevent infectious complications. The drugs begin to be used a few days before surgery and continue throughout the early postoperative period.
Pulmonary embolism can lead to the death of the patient. Currently, this complication is extremely rare, since there are highly effective preventive agents - anticoagulants. The drugs are prescribed for several weeks after surgery.
Quite rare complications of hip replacement include:
- Implant fracture;
- Osteolysis;
- Implant displacement;
- Allergic reactions to implant materials;
- Cardiovascular complications (myocardial infarction, cerebrovascular accidents and strokes).
Rare complications of hip replacement are associated both with the individual reaction of the body to the intervention, and with violations in the surgical technique and postoperative regimen.
Hip replacement
Endoprosthesis replacement is a surgical operation in which the patient's affected joint is removed and replaced with an artificial joint (endoprosthesis). The main indications for hip replacement are: • coxarthrosis; • femoral neck fracture; • arthritis; • necrosis (aseptic) of the femoral head; • tumors in the hip joint.
Methods of hip replacement
The methodology for performing hip replacement surgery at the State Institution "City Clinical Hospital No. 4" in Orenburg is individual in each case of the disease. If the damage is significant, causes severe pain to the patient and prevents him from moving, the doctor may decide on total endoprosthetics. It consists of completely replacing all parts of the diseased joint, including the acetabulum in the pelvic bone and the head of the femur. The implant for treatment is selected individually for each patient. Endoprostheses differ in the sizes of components and friction pairs: • metal/metal; • ceramics/ceramics; • ceramics/metal, etc. • The following modern methods of attaching implants for joint replacement have been adopted at the State Clinical Hospital No. 4 of Orenburg: • cementless: based on the natural fusion of bone tissue and a special coating of the endoprosthesis; • using special bone cement; • combined: combines the two above methods. Each fastening method corresponds to the patient’s age. Thus, for older people, doctors recommend using cemented fixation of the prosthesis when replacing a hip joint. Their activities are limited by age and they are not as physically active. And, conversely, for young people, in case of surgery, the doctor will suggest installing an endoprosthesis with cementless fastening. This technique involves damaging the integrity of the bones to a minimal extent, but careful adherence to all the recommendations of the orthopedist will be required during the recovery period after surgery.
Features of hip joint replacement Traumatologists and orthopedists of the State Institution "City Clinical Hospital No. 4" of Orenburg offer their patients only the latest minimally invasive methods for treating diseases of the musculoskeletal system, while using effective and high-quality implants from such companies as Mathys, Zimmer, Wright, Stryker and Smith&nephew .
Why these particular endoprostheses? It's all about their internal filling - durable, reliable material, similar in anatomy to natural joints. Consequently, the service life of such a prosthesis is long: up to 25 years. By the way, previously orthopedists could offer patients prostheses with a service life of only 15 years.
How the hip replacement procedure works Most of these operations are performed under a special anesthesia - spinal anesthesia combined with sedation, which ensures the patient sleeps peacefully without pain throughout the entire procedure. After administering anesthesia, the surgeon makes an incision on the patient's skin through which areas of bone tissue and cartilage are excised. Next comes work to prepare for the installation of the implant. The acetabulum is replaced with a cup-shaped metal element, which has a special coating on the outside that allows the endoprosthesis to fuse with the bone tissue. A metal-ceramic liner is placed inside this component.
Next, the surgeon inserts a metal leg of the endoprosthesis into the prepared canal of the femur, to which a round metal head is attached. After such installation of all components, the implant is set into place.
The operation lasts from one to two and a half hours. In the process, thanks to innovative methods, the doctor does not completely dissect the muscles and other tissues, but pushes them apart. This reduces surgical trauma, helps the joint recover faster and the patient recover. Full recovery will take 4-6 weeks.
What happens after surgery? The patient is allowed to get up the very next day after the surgical procedure. He can move independently with the help of a walker. The duration of hospitalization and primary rehabilitation measures at the State Autonomous Institution "City Clinical Hospital No. 4" in Orenburg is no more than 5 days.
After hospitalization ends, the patient is discharged. But his rehabilitation continues at home for several more weeks, and it consists of performing special exercises. And after a short time the person returns to his usual way of life.
Do you need advice or an accurate diagnosis of your illness? You can always make an appointment with specialists at 45-88-00:
Travkin Sergey Nikolaevich
Askov Sergey Petrovich
Kharitonov Igor Alexandrovich
Zhilyakov Vladimir Viktorovich
Matiyash Andrey Mikhailovich
Features of rehabilitation and recovery
Hip replacement allows patients to fully regain the functionality of the lower limb in 95% of cases. A properly designed rehabilitation program makes it possible to return to their normal lifestyle within six months.
- In the early postoperative period in the hospital, the patient receives infusion and anticoagulant therapy, systemic antibiotic therapy, immunotherapy, physiotherapeutic treatment, and massage.
- From 2-3 days after the operation, the patient performs physical therapy under the guidance of an instructor, learns to walk with the help of crutches with a dosed load on the operated leg. The modern approach to the postoperative period includes early activation of patients. A sufficiently large load on the operated leg is possible only two months after the operation.
- Postoperative sutures are removed 10-14 days after surgery. X-rays of the hip joint are performed multiple times (once every three months in the first year after surgery and then annually).
- The hip joint endoprosthesis is subject to wear. Intense physical activity and excess weight significantly reduce the service life of the prosthesis. If the regime is followed, the artificial joint can last quite a long time (15-20 years).
Signs of joint wear are determined clinically and during control radiography. If necessary, the patient undergoes a repeat arthroplasty operation.
How is hip replacement performed?
The operation is performed under anesthesia. After anesthesia, the skin and muscle tissue are cut. Once the joint is reached, the surgeon removes the top of the femur bone from the acetabulum. Further manipulations depend on the type of prosthetics chosen. The bone is adjusted to the shape of the endoprosthesis, which is fixed in it in various ways. The articular cartilage is removed from the acetabulum and the prosthesis cup is fixed in it. After completion of the prosthetics, the dissected tissues are sutured. Discharge from the wound will drain into a special suction drain, over which a bandage will be applied.
How long a hip replacement surgery will take depends on the individual characteristics of the patient’s body, the experience of the surgeon and the tactics he chooses. It usually lasts from 1.5 to 3.5 hours. In most cases, spinal anesthesia is used as it is the least harmful for elderly patients.