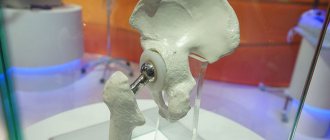
Back in the last century, hip replacement was called the most successful operation in orthopedics. Installation of implants is a chance for patients with severe damage to bone and cartilage tissue to live a full life without disability. The essence of the operation is to remove pathological areas and install an artificial prosthesis made of durable, biocompatible materials.
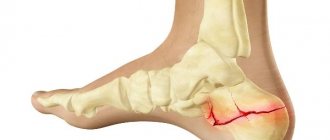
The hip joint is the largest and most massive in the human body. It works on the principle of a simple hinge, involving the head of the femur, which is like a ball, and a cup-shaped socket. Due to their connection, multi-axis movements of the hip are possible. The head of the femur and acetabulum are covered with thin, smooth hyaline cartilage, which allows the head to slide easily into the socket.
If pathological changes occur in one of these structures, the full functioning of the entire joint is disrupted. At first this manifests itself as discomfort and pain, which intensify over time and lead to a decrease in the amplitude of movements, and then to a limitation of mobility. The quality of life deteriorates significantly, a person has to give up active recreation, even walking a short distance becomes a problem.
The pain in the joint, which bothers you day and night, is exhausting. For many people, joint arthroplasty (joint replacement) is the only way to return to life without pain. This is a modern, high-tech operation, worked out to the smallest detail. The installed prostheses reproduce the anatomy of the joint as accurately as possible, completely restore its function, relieving pain.
Thanks to innovative technologies, complex structures can not be changed for 10-15 years. Even the most modern prostheses cannot last forever and work for a limited time; the need to replace them can be called a disadvantage of endoprosthetics. For this reason, the operation should not be too early; doctors try to delay it with muscle training, drug therapy, and physiotherapeutic procedures. But if pain and physical limitations increase, the issue of surgery is decided.
Indications for surgery
Joint replacement (endoprosthetics) has a larger list of indications. It is recommended if conservative therapy methods do not produce results and there is no other way to maintain the patient’s normal quality of life, that is, to relieve his pain and restrictions of movement. Most often, hip replacement is indicated for:
- femoral neck fracture;
- hip dysplasia of acquired or congenital origin;
- aseptic necrosis of the femoral head;
- deforming arthrosis or coxarthrosis of 3-4 degrees;
- neoplasms in the joint.
Many years ago, after fractures in the hip joint, patients were bedridden, where they lived their last years, since the arthroplasty technique had not yet been developed. With its advent, timely replacement of the affected parts of the joint with artificial and durable implants allows a person to live as before the injury.
Precautionary measures
You already know how long rehabilitation takes after hip replacement of the musculoskeletal system, and that in the early stages the musculoskeletal frame of the body is too weak. Therefore, to avoid displacement of the functional components of the endoprosthesis (dislocation) or instability in the places of attachment of the artificial hip joint, strictly follow the instructions below.
- Do not exceed the amplitude of hip flexion more than 90 degrees, especially with its internal rotation and adduction.
- You cannot apply a full axial load to the prosthetic segment. This is dangerous due to loosening of the implant.
- Do not sit on chairs, sofas, or beds with low surfaces. The corresponding furniture must be high enough.
- Avoid vigorous and forced movements in the joint both during self-care and during rehabilitation physical therapy. Forget about the “leg over leg” position, this position is strictly prohibited for at least 4 months!
- During classes aimed at restoring the hip joint after total hip replacement surgery, be careful to ensure that your legs do not come close to each other or cross each other.
- Do not take any medications that have an analgesic effect immediately before exercise therapy or during exercise. They powerfully suppress pain sensitivity, which is why you lose control over your own sensations during physical activity, which can greatly harm the operated leg.
- Do not lie on the problematic side either during sleep or during normal rest. Rest on your unaffected side using a bolster or small pad between your two limbs. They will protect you from sudden unsuccessful movement, which can disrupt the congruence of the joint elements of the endoprosthesis. It is preferable to sleep on your back at first, and do not forget to place a demarcation pillow between your legs.
A cushion between the legs is a mandatory requirement for a month after surgery. Crossing your legs increases the risk of implant dislocation.
How long the early cycle rehabilitation will last after a hip replacement is decided only by the doctor on an individual basis. If all goals and objectives are achieved in full, well-being meets the deadlines, recovery is progressing according to plan, then the patient is transferred to the next stage - the longest and no less responsible.
At an angle of less than 90 degrees in the hip joint, this risk is also high.
Contraindications
Like any operation, endoprosthetics has a number of contraindications:
- severe forms of cardiovascular and respiratory failure;
- heart defects in the stage of decompensation;
- liver failure of 2-3 degrees;
- local inflammatory and infectious processes in the hip joint;
- absence of the medullary canal of the femur;
- thrombosis of the veins of the lower extremities;
- severe bleeding disorders;
- allergy to endoprosthesis material;
- uncontrolled diabetes mellitus;
- severe osteoporosis of bone tissue, neuromuscular disorders;
- drug addiction, alcoholism, dementia and other mental disorders;
- paralysis, paresis of a limb that is subject to surgery.
Relative contraindications include obesity of the 3rd degree, acute somatic pathologies, which increase the likelihood of complications after endoprosthetics. Each clinical case is considered individually in order to accurately determine the possibility of surgery, taking into account all the patient’s characteristics.
How does the consultation work?
Before starting to prepare for the operation itself, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive examination, collect anamnesis and select a prosthesis. The surgeon conducts an initial examination and interview of the patient to determine whether surgical treatment is possible in this case.
Next, a more in-depth examination is carried out, including x-rays, ultrasound, and examination by other doctors. When a complete picture of the patient’s health status is formed, in the absence of absolute contraindications, the optimal prosthesis option will be selected and the surgeon will set a date for the operation.
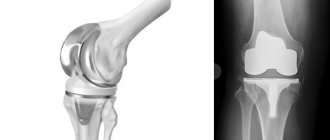
Types and elements of hip joint prosthesis
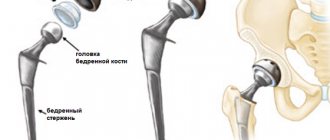
An artificial implant is a complex structure that completely imitates the hip joint. Withstands the same load as a natural joint and performs all its functions. Prostheses can be total - completely replacing the joint, and partial - replacing the head of the femur and acetabulum.
The endoprosthesis includes the following components:
- cup;
- liner;
- head;
- leg.
Considering fixation, endoprostheses come in two types: cemented and cementless. The first components of the joint are secured using special medical cement, which hardens very quickly, ensuring a durable installation. They are more often used in older people and those with osteoporosis.
Cementless prostheses are used most often. They have a rough surface, due to which they firmly fuse with bone tissue in about 3 months. Before installation, the surface of the bone is carefully processed with files to remove all damaged tissue. The leg of the prosthesis is carefully driven into the prepared bone canal to ensure primary fixation. Secondary consolidation will be achieved through further ingrowth of bone structures. To improve this process, a hydroxyapatite coating can be applied to the surface of the prosthesis.
Artificial joint elements are made from various materials:
- polyethylene;
- ceramics;
- metal alloys: steel, titanium, tantalum, cobalt, chromium.
The material can be treated with vitamin E to increase strength and can also be cross-linked. Endoprostheses made from the unique Oxinium alloy, which consists of zirconium and niobium with a durable ceramic surface, have high wear resistance and are not susceptible to splitting under load.
Well-known manufacturers produce lines with different sizes of prostheses, so that you can choose a design for any clinical case. Young patients are predominantly fitted with prostheses with a shortened stem, since in the future they may need to be replaced, and even more than once, due to the limited service life of any prosthesis.
Arthroscopy technique
To perform intra-articular manipulations, a special device is used - an arthroscope. It is inserted through a micro-incision into the cavity of the hip joint. Based on its operating principle, it belongs to endoscopic medical equipment. The arthroscope is inserted through a tube, which protects it from damage. A high-resolution video camera, a light source and a fiber-optic cable are attached to the main part of the device. These components are responsible for high-quality image transmission to monitors. The arthroscope also contains:
- channels for introducing various surgical instruments;
- an irrigation and aspiration system that allows the supply and removal of fluid from the joint cavity during arthroscopic operations.
When performing arthroscopy of the hip joint, aseptic conditions are required. Therefore, the manipulation is performed in the operating room. The procedure is performed under general anesthesia, which is most often administered endotracheally.
The position of the patient's body during manipulation is lying on the healthy side. This provides access to the affected hip joint. With the help of special stretchers, the joint is given a position in which the joint space is maximum. The entire preparatory process is controlled by radiography. Achieving an optimal position of the hip joint makes its cavity completely accessible for inspection during arthroscopy.
Before the manipulation, the doctor marks the boundaries of the articulation, the projection of the great vessels and the location of large nerve trunks on the patient’s skin. After which the safest access points to the joint cavity are selected.
Algorithm for hip arthroscopy:
1. Adrenaline, diluted to the required concentration with saline, is injected into the joint cavity. This allows you to increase the joint space to its maximum size.
2. Through a skin incision, a trocar is inserted into the cavity of the hip joint - a surgical instrument, through the tube of which it is used for safe insertion of the arthroscope. As a rule, the doctor makes 3 full accesses to the joint, which makes it possible to examine the condition of the articular structures in three planes.
At the end of both diagnostic and therapeutic arthroscopy, an antiseptic solution is injected into the joint cavity to prevent purulent complications. Anesthetics are used for pain relief. After removing the arthroscopes, the wound is sutured and sterile dressings are applied.
Progress of the operation
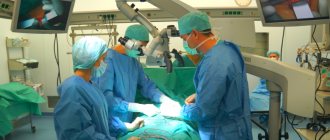
Taking into account the degree of damage to the hip joint, the patient may be shown total prosthetics with complete joint replacement or partial replacement with the replacement of the femoral head with an implant. The operation may take 1-3 hours. Stages of implementation:
- administration of anesthesia;
- performing a longitudinal oblique incision along the intertrochanteric line;
- gaining access to the joint, removing the head of the femur from the acetabulum;
- resection, removal of the femoral neck, cleaning of the acetabulum to the cancellous bone, insertion of a press-fit cup, liner (for total prosthetics);
- a channel is formed in the femur for the leg of the prosthesis;
- the leg is mounted into the femur;
- install the head of the prosthesis, set it into the preserved or artificial acetabulum;
- the wound is washed with antiseptic solutions, all tissues, ligaments, muscles are sutured in layers, the wound is covered with a sterile bandage.
After surgery, the patient is sent to the intensive care unit for observation.
Why is research needed?
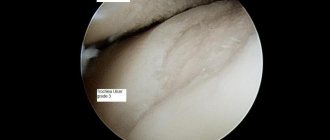
During hip arthroscopy, the doctor conducts a thorough examination of all its structures. The main goal is to identify lesions. Manipulation allows you to detect even minor pathological changes. The doctor examines:
- articular cavity (there must be a sufficient amount of synovial fluid in the cavity);
- femoral head;
- acetabulum;
- cartilage tissue;
- ·ligamentous apparatus of the joint.
Multiple access to the hip joint allows for a thorough examination of the structures from all sides.
Arthroscopy also makes it possible to carry out therapeutic procedures:
- remove bone fragments or a foreign body that has entered the joint cavity;
- excise pathologically altered cartilage tissue;
- remove adhesions;
- compare damaged areas of bone;
- restore the integrity of the ligamentous apparatus.
Preparing for surgery
The patient undergoes a comprehensive examination. Instrumental studies include: radiography, MRI or CT of the hip joint, ultrasound of the abdominal organs. Standard preparation before surgical treatment includes:
- general, biochemical blood test;
- coagulogram;
- blood type, Rh factor;
- blood for HIV, hepatitis, syphilis;
- general urine analysis;
- FGDS;
- ECG;
- X-ray of the lungs;
- consultation with a therapist.
If there are foci of chronic infection, sanitation is carried out to eliminate them. The patient should prepare to return home after surgery. All objects in the house should be located in accessible places so that there is no need to stretch or squat. You need to make room for walking on crutches, remove wires from the floor, move furniture away so as not to get caught.
Equip the bathroom and toilet rooms with comfortable handrails. It is important to prepare a high chair or armchair and raise the level of the bed. Before surgery, you need to learn how to walk on crutches, learn the rules for performing exercise therapy exercises, in order to immediately begin treatment sessions.
Physical mode
From the first day the following activities are recommended:
- breathing diaphragmatic exercises;
- training a healthy limb through active exercises, as well as flexion/extension of the ankle of the endoprosthetic leg until a feeling of slight fatigue in the lower leg muscles;
- strengthening the gluteal, thigh and calf muscles using isometric tension in the corresponding zones;
- raising the pelvic region, resting on the elbows and foot of a healthy lower limb, in order to prevent bleeding and necrosis of the skin due to their compression due to a long stay in bed;
- from 2-3 days, individualized passive-active training on the leg with a replaced joint is included up to 6 times a day for 15 minutes (raising an even limb, sliding the feet on the bed with pulling the legs towards oneself, bending the knee joint area less than 90 degrees;
- special strengthening exercises for the adductor and abductor muscles, as well as the hip extensor muscles (Hula-Hula, Thomas test, etc.).
After approximately 2 days, the patient is allowed to sit down (sit for no more than 15-20 minutes), while the doctor will prescribe additional exercises performed in a “sitting” position, for example, straightening the leg at the knee joint, holding it in the extension position for 5 seconds (10 sets each). 5-6 times/day). Also, from the third day, the patient begins to get up, stand and walk a little on crutches, not yet transferring body weight to the problem side. The duration of the walk at first is 5 minutes, but the time is gradually added, and by the end of this period you need to walk three times a day for approximately 30 minutes.
A separate area of rehabilitation is occupational therapy, when the patient is taught to care for himself safely: get up and lie down on the bed, put on socks and shoes, other clothes, lift things from the floor, use crutches, etc.
Support on the leg is added very carefully, starting from a small touch of the foot with the floor surface, gradually increasing the percentage of the support load. Having mastered the “standing” position well, the patient, under the guidance of a methodologist, will learn to:
- abduction in the lateral and posterior direction of the straightened leg, holding on to the headboard of the bed, chair or walker, avoiding painful sensations;
- bending the knee while pulling the heel towards the buttocks, straining the gluteal part;
- controlled transfer of weight from one leg to another, from side to side, etc.
Anesthesia
Taking into account the amount of work during hip replacement, the patient’s health condition and a number of other points, general, spinal, epidural anesthesia or a combination of the last two can be performed. General is used extremely rarely; almost 90% of patients undergo spinal or epidural anesthesia in combination with intravenous sedation to reduce stress.
Both methods are not accompanied by a loss of consciousness of the patient. In spinal spinal surgery, an anesthetic is injected into the subarachnoid space of the spine through a thin needle into the cerebrospinal fluid, which blocks the transmission of nerve impulses. With epidural anesthesia is given through a thin catheter into the epidural space of the spinal column, which also leads to loss of pain sensitivity in the required area.
After anesthesia, a person does not feel the lower limbs for 4-8 hours, so he will be able to stand up only after sensation in the legs is restored. The patient has a urinary catheter installed because he cannot control his bladder for a certain period of time. As soon as sensitivity returns, it is removed. To reduce blood loss and improve visualization of the surgical area, the anesthesiologist maintains low pressure during the operation, which is called controlled hypotension.
Late stage recovery system
About 3 weeks have passed since the hip replacement was performed, rehabilitation is becoming more varied, longer in time and intensity. The specialist adds to the established physiotherapeutic treatment, namely electrical myostimulation and ultrasound, more procedures for musculocutaneous microcirculation and optimization of osteoreparation processes:
- medicinal calcium electrophoresis, possibly bischofite;
- infrared laser therapy;
- balneological treatment;
- acupuncture;
- paraffin therapy and ozokerite applications;
- massage of the lumbosacral spine and healthy leg.
There is nothing better than a swimming pool for recovery, but do not forget that the seam must heal before that!
Physical therapy consists largely of dynamic exercises, resistance training and weight training. The patient, under the supervision of a methodologist, performs a varied complex of exercise therapy on special simulators, as well as using sports equipment, for example, a rubber band, light weights, a step platform, and block equipment.
Suspension work is a great way to engage your deepest muscles.
Possible complications
Any surgical intervention is traumatic for the body and carries a certain risk of complications, even with the installation of an expensive endoprosthesis. They can occur both during and after surgery. These include:
- fracture of the femoral diaphysis;
- failure of prosthetic components;
- bleeding;
- fat embolism;
- vein thrombosis;
- inflammatory and infectious processes.
Prosthetic operations are so well developed that the likelihood of complications is extremely low. Negative reactions after anesthesia have also been significantly reduced, as more and more interventions are performed without general anesthesia.
Advantages of the technique
Hip arthroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure. It allows you to avoid significant tissue trauma and reduce the overall burden on the body compared to traditional surgical interventions. Thanks to high-quality optics, the doctor is able to see the condition of the articular components no worse than with open access.
Endoscopic access allows to reduce the duration of the recovery period. Already on the second day after the manipulation, the patient can stand up with support. Unpleasant sensations after such surgery are rarely severe. In most cases, the pain is moderate. The pain goes away within a few days and does not require long-term use of anesthetics.
Rehabilitation after surgery, hip replacement
Even an operation performed at a high level will not give good results without comprehensive and high-quality rehabilitation. The success of the operation and the patient’s quality of life depend on the conscientious implementation of all the doctor’s recommendations. For each patient, a set of restorative procedures is selected, taking into account the scope of the operation, the person’s condition, age and other nuances. Rehabilitation is aimed at:
- elimination of pain and inflammation in the operating area;
- restoration of the full functioning of the muscular-ligamentous complex, which is responsible for the coordinated movements of the femur and pelvic bones;
- reducing the risk of negative events;
- high-quality and reliable fusion of the prosthesis with the bones.
The rehabilitation period begins from the first day after surgery. On average, recovery takes about 3 months.
A gradual impact on the operated hip joint helps to quickly get rid of pain, swelling, and develop the limb as quickly as possible. During rehabilitation, discomfort and pain cannot be avoided, but if you follow all the doctor’s recommendations, these negative aspects will quickly pass.
In the early recovery period, the patient is constantly monitored, drug therapy is immediately prescribed, and exercise therapy is started. The latter consists only of breathing exercises to prevent congestion and passive movements in the joints.
If there are no complications, a day later the patient is transferred from the intensive care ward to the general room. Here, for 2-3 weeks, medical staff monitors the patient and helps him recover as much as possible after the operation. After discharge, the late stage of rehabilitation begins; it can be completed independently or under the supervision of a doctor.
Drug therapy
From the first day, patients are prescribed drug therapy, most often it includes:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to reduce pain and inflammation;
- anticoagulants – reduce the likelihood of thrombosis;
- broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs to reduce the risk of infectious complications;
- products containing calcium to strengthen bone tissue.
Groups of drugs, their dosage and duration are selected individually.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
All patients are prescribed courses of physiotherapeutic procedures:
- electrophoresis with drugs;
- electromyostimulation;
- UHF;
- laser therapy;
- magnetic therapy;
- ultrasound therapy;
- mud therapy;
- laser therapy and others.
Physiotherapeutic procedures improve blood circulation in the affected area, eliminate muscle spasms, reduce pain, inflammation, and have an anti-edematous effect. They have a positive effect on the speed of recovery, improving metabolic processes and tissue regeneration.
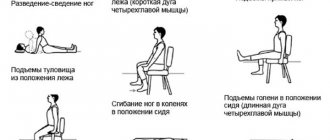
Exercise therapy (exercises)
Physical therapy is an integral part of rehabilitation, its basis. People who do not have problems with body weight and lead an active lifestyle within the limits of the permissible load recover much faster. But excessive activity and incorrect movements can negatively affect rehabilitation, so a set of exercises is developed for each patient and starts with minimal movements.
On the 2-3rd day after endoprosthetics, the patient switches to gentle activity. On the second day, you can get up and walk slowly, but only for short distances using crutches or a walker, under the supervision of a doctor. Isometric exercises aimed at contracting the leg muscles are shown, which are performed while lying on the bed. All movements are soft and smooth.
In the early stages, everything is supervised by an instructor so that the patient can learn the correct technique for performing the movements. Specialists teach the rules of sitting with an acceptable hip bend. At first, you can sit for about 15-20 minutes. In a lying position, a special anatomical cushion is placed under the legs to prevent the legs from being crossed, which negatively affects the condition of the hip joint. You can only sleep on your back, lie on your healthy side.
When walking, the main weight should be kept on the healthy limb so as not to load the operated one. Instructors teach how to stand, sit, and lie correctly, then move on to physical therapy. At the beginning of rehabilitation, all exercises are simple and easy. After about 2 weeks, the wound shrinks and heals; during this period, they switch to a lightly tonic regimen of physical activity - the load is gradually increased.
In the later stages of rehabilitation, patients can study at home independently according to a program developed by an instructor, but the best results are obtained from classes in special institutions that deal with the patient’s recovery after endoprosthetics. The centers are provided with the necessary exercise equipment so that people recover faster.
During late rehabilitation, you can gradually begin training on treadmills, an exercise bike, and block exercise machines. Performing them in gyms is highly discouraged, since local trainers do not have the proper qualifications to correctly determine the load and select exercises.
Massotherapy
Another mandatory component of recovery, like exercise therapy. Therapeutic massage sessions:
- reduce pain;
- eliminate swelling;
- activate blood flow not only in the operated joint, but throughout the whole body;
- improve muscle tone.
You can start the massage only after the acute pain has subsided. At the beginning of the procedure, the specialist prepares the muscles for more intense effects, thoroughly kneads the tissues, and always works the joints. But working with the operated area is possible only in the absence of inflammation.
Goals and objectives
The principles of recovery after surgery on the hip joints in the initial period are mainly based on the use of balanced kinesiotherapy, gentle static exercises, and myostimulating physiotherapy procedures. In addition, the patient receives competent medical care, including antibiotic therapy, administration of vascular drugs, and antiseptic wound treatment. Thanks to proportionate and targeted exercise therapy and adequate treatment with medications, the following is achieved:
- stimulation of blood circulation in the lower extremities;
- elimination of inflammation, swelling, painful syndrome;
- increasing muscle strength and range of motion in the problem area;
- correction of statics of the spinal sections;
- prevention of postoperative negative reactions (thrombosis, infections, etc.) and development of lasting immunity against all possible consequences.
Compression cuffs are a mandatory measure to prevent thrombosis in the first days after surgery.
Also, from the first day, such a device is used for passive expansion of the joint. Used for both knee and hip.
This period ensures the implementation of one of the most important goals - early activation of the operated patient. A rehabilitation doctor and exercise therapy instructor must teach a person all the norms of physical behavior and confident use of mobility aids; help develop the correct stereotype of walking and taking a sitting position, going up and down stairs. Also, their responsibilities include warning the patient about all types of physical activity that are strictly contraindicated at a given period of time.
results
With a high-quality operation, the correct selection of a prosthesis, and the patient’s conscientious implementation of all recommendations during the rehabilitation period, a normal standard of living and physical activity are restored. The designs of the latest models can last 10-15 years; after failure, a repeated replacement operation is required. To ensure that the prosthesis lasts as long as possible, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- exclude deep bends and squats;
- monitor your posture in any position;
- engage in therapeutic exercises even after full recovery;
- do not give up crutches before the recommended time;
- walk more, but at the same time avoid overwork;
- avoid too strenuous physical activity.
Patients are not recommended to engage in intense sports that involve lifting weights, sudden jerks of the body, swinging legs, or jumping. It is better to prefer swimming, race walking and similar sports.
In recent decades, endoprostheses, the instruments for their installation, and the materials used have undergone significant changes, and their service life has also increased. Every year their quality only improves, which gives hope for the possibility of one-time prosthetics without the need for replacement throughout life.
Main goals of the later period
The fundamental goals at this stage are the physical development of the lower limb until full functionality is reproduced in it, work on gait and posture, and improvement of the ligamentous-muscular center. The basis of measures to implement the assigned tasks is again kinesitherapy. Physiotherapy is not canceled; after hip joint replacement, it is given an equally significant place in rehabilitation. So, now all treatment and rehabilitation measures are aimed at:
- the maximum possible expansion of the motor-support functions of the limb, achieving absolute stability of the hip joint and full range of movements;
- regulation of muscle tone to normal, increasing muscle endurance;
- practicing symmetrical musculoskeletal work of both legs;
- correction of opportunistic habits when moving, which the patient was forced to follow before and after surgery due to motor incompetence and fear of pain.
As before, the rehabilitation instructor works with the ward to adapt to a new lifestyle, to develop sustainable movement patterns that he will use during self-care, when doing housework, and also outside the home.
Nordic walking is good for its safety.
It is important to understand that the effect will not occur immediately and on its own after a complex operation on the musculoskeletal system. How rehabilitation will proceed and how long it will last after hip replacement will be significantly influenced, first of all, by the adequacy of the type, frequency, intensity and duration of daily physical activity given to the joint. The effectiveness and approach of recovery are influenced by the patient’s diligence in relation to medical instructions, overcoming his own laziness, weakness and fear.
Attention! It is important to understand that the hip joint has been replaced with an artificial organ. Yes, this is an analogue organ that coincides with the configuration and functional parameters of the anatomical and physiological unit, but in any case it is not a biologically native element. In order for the “new” part of the musculoskeletal system to become an inextricable link in a single locomotor chain, harmoniously coordinated with all anatomical structures, which is a rather complex process, it takes time and a therapeutically competent, targeted effect on the prosthetic leg.
Balance exercises of a later period are suitable for those who want to get the maximum from the treatment provided.
Walking is now increased in duration to 60 minutes, and in frequency - up to 4 times a day. After 1.5-2 months, perhaps a little earlier or later, the supervising doctor will stop using crutches, allowing you to use a cane when moving. The cane is used until complete restoration of the operated area is confirmed. Usually it is canceled and allowed to do without any support at all between 13 and 17 weeks.
Reviews from patients after surgery
Hello dear Ruben Vachaganovich. Your patient in the past 2021 and now living Andrey Aleksandrovich from Uralsk Kazakhstan writes to you with words of gratitude. Briefly about our upcoming meeting with you... I’m not a fan of going to doctors unnecessarily, in fact, I have an active lifestyle, in 2021, somehow without noticing, lameness appeared on my right leg and discomfort in the hip joint on the right side. Months have passed. Pain appeared. First I contacted our specialist rheumatologist and took a picture. They recommended going to the Seredavin clinic in Samara. There the doctor diagnosed coxarthrosis of the second degree. They prescribed injections, pills and throughout 2021 and until the fall of 2021 I was treated to use many medications. There was no result. The pain intensified. While walking I had to stop several times. A pandemic began and in this regard, many clinics in Russia went into quarantine. The choice was Kazan and Moscow. I looked through a bunch of sites on the Internet. I stopped at your clinic and don’t have an ounce of regret. There was a lot of advice from relatives, but the decision was mine and only. By the way, while analyzing the fact that provoked this illness, I remembered an accident in my car in the past. I think that's all it is. This is how we met you in your clinic, in your ward. I also met a lot of wonderful people and have no regrets. In the end, I wanted to thank you Ruben Vachaganovich for your work, your experience and your golden hands. Thank you universally. Yours Andrey