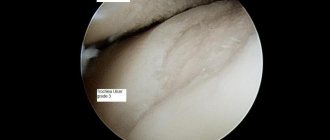
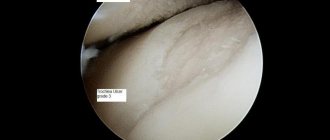
- Ligaments
- Muscles
The articular surfaces of all three bones that form the knee joint are covered with cartilage, which is a hard, elastic material that acts as a shock absorber for the joint. Also, this function is performed by two C-shaped rollers, which also have a cartilaginous structure - the medial (inner) and lateral (outer) menisci. They lie between the femur and tibia, performing a shock-absorbing function and ensuring congruence of the articular surfaces.
Classification of knee joint diseases
As a rule, all diseases of the knee joint are classified according to their etiology. Thus, the pathology can be inflammatory in nature (and the inflammatory process can be of both an infectious and non-infectious nature), as well as dystrophic (in case of metabolic disorders in certain tissues) or traumatic. In addition, according to the nature of the pathological process, it is either acute or chronic.
Diseases of the knee joint most often refer to either arthrosis
(degenerative-dystrophic pathologies), or to
arthritis
(various inflammations of joint tissues). Other diseases are much less common, for example:
- meniscopathy,
- luxation of the patella,
- dysplasia of the femoral condyles,
- bursitis,
- tendinitis,
- chondromatosis,
- Becker cyst,
- Koenig's disease
- Osgood-Schlatter disease, etc.
Palpable anatomical landmarks[edit | edit code]
Medial surface
- Tibial collateral ligament
- Medial joint line
- Medial meniscus
Lateral surface
- Peroneal collateral ligament
- Lateral line of the joint
- Lateral meniscus
Front surface
- Quadriceps tendon
- Patella
- Patellar ligament
Rear surface
- Popliteal fossa
- Biceps femoris tendon
- Semitendinosus tendon
- Semimembranosus tendon
Symptoms of knee joint pathologies
Most knee diseases have a number of common symptoms. First of all, it is a prolonged pain, which, as a rule, intensifies when the affected limb is flexed at the knee joint. Symptomatic treatment of knee pathologies involves the primary relief of severe pain
.
Other common symptoms that indicate the need for knee treatment include:
- the appearance of discomfort when putting weight on the sore leg;
- clicking sound when bending the knee;
- deformation of the limb in the area of the affected knee, swelling.
Inflammatory diseases are usually accompanied by significant swelling. There may also be an increase in temperature (of the whole body or just the area of the affected joint). All this indicates the acute nature of the pathology.
Dystrophic deviations, on the contrary, develop slowly and become chronic with acute periods and remissions. They are usually associated with heredity or congenital changes, as well as increased stress on the joint. In rare cases, this kind of problem becomes a consequence of metabolic disorders. It should be noted that such pathologies require long-term and constant treatment, strict compliance with all doctor’s instructions. Post-traumatic pathologies
There are both acute and chronic.
Indications for replacement
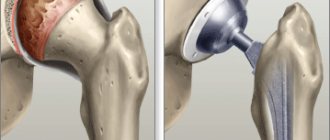
Look at the x-ray, you can see the extent to which, with advanced gonarthrosis, the hyaline cartilage, which ensures smooth gliding of the articular surfaces, is worn out. The end sections of the bones are grossly deformed, disrupting the functions of flexion and extension of the limb, causing intense pain.
Comparison of a healthy and affected joint.
Diagnosis of the knee joint
Since different diseases can have similar symptoms, a comprehensive diagnosis must be carried out as soon as possible to effectively treat them. To cure the knee joint, you should eliminate the true cause of the disease, and not deal with negative symptoms.
To examine patients complaining of problems with knee joints, modern highly effective diagnostic methods are used in Israel:
- magnetic resonance imaging;
- computed tomography;
- ultrasonography;
- radiography;
- arthroscopy;
- joint puncture with examination of synovial fluid
; - biopsy of joint tissue with study of biopsy material, etc.
The doctor evaluates the functionality and stability of the joint and studies the dynamic behavior of the joint. The periarticular tissues - the skin, muscles, nerves and blood vessels - will tell a competent specialist a lot about the condition of the knee joint.
Surgical process
Knee replacement is performed under epidural anesthesia. An anesthetic drug is injected into the epidural space of the spine, which causes complete blocking of pain sensitivity in the lower extremities, while the patient remains conscious.
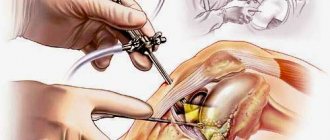
How the surgeon sees the joint during surgery.
Stages of the classic operation:
- First, a broad antiseptic treatment of the skin of the problematic leg is performed, after which the limb is covered with a film.
- Next, the surgeon makes an incision into the soft tissue on the front side of the knee, carefully exposing the affected joint.
- After opening the joint, pathological growths and free osteochondral fragments are removed.
- The bone units are aligned along the axis, the surface layers are removed from the femur and tibia, then the sawn-off components are polished.
- A small channel is created in the tibia, into which the posterior sleeve of the prosthesis is immersed. This flat metal or ceramic plate follows the geometry of the marginal bone area, with an elastic polymer insert.
- A part of the endoprosthesis is fixed onto the treated femur, which in shape imitates the natural roundness of the lower part of the femur bone.
- At the end of the procedure, the wound is washed generously, hemostasis is performed, a drainage system is installed, and the incision is sutured in layers using the interrupted suture technique. The surgical process is completed by applying a tight sterile bandage to the limb.
The surgical process lasts on average 2 hours. When the knee replacement surgery is completed, the patient is transferred to the intensive care unit for several hours. In the intensive care unit, medical staff closely monitor all life cycles of the body. Then the operated person is transferred to a regular ward, where they begin to implement a comprehensive rehabilitation program specially designed for a particular patient.
The most common diseases of the knee joint
Commonly diagnosed pathologies of the knee joint include the following diseases:
Arthrosis and arthritis
Treatment of arthrosis directly depends on the stage of the disease and the degree of tissue damage. Considering that this disease usually takes a chronic course, the doctor’s main task is to achieve long-term remission using means that minimally harm the patient’s healthy organs and tissues. The specialist must relieve severe pain, take measures to restore the integrity of the cartilage tissue, and ensure a normal range of motion in the joint.
To treat the knee joint for arthrosis and arthritis, various medications, massage and manual therapy, physical therapy and, if other treatment methods have not helped, surgery are used.
Anti-inflammatory drugs, hormones and acetylsalicylic acid help eliminate arthritis. Antibiotics and ointments may be prescribed. For arthrosis, chondroprotectors are used to slow down or even stop the destruction of articular cartilage
.
Severe cases of arthrosis require surgical treatment, the most effective option of which is joint replacement. Currently, joint replacement surgeries in Israel are very popular among patients from other countries, including Russia. Most often, endoprosthetics of the hip and knee joints are performed in Israeli clinics.
Tendinitis and bursitis
Inflammatory phenomena in the area of ligaments and tendons in Israel are eliminated using various anti-inflammatory drugs and providing rest to the affected limb. Using punctures
Excess fluid is removed and antibiotics are administered.
Severe cases of these pathologies require surgical treatment. For example, surgery will be required if calcium deposits are detected in the joint. Sometimes it is necessary to remove the joint capsule.
Chondropathy, meniscopathy, tendinopathy
This group of pathologies includes diseases of a non-inflammatory nature that are caused by injuries or chronic degenerative processes. The danger of this kind of disease is that its initial stages are not accompanied by characteristic, clear symptoms, so people often consult a doctor already in the last stages of the pathology. These diseases have a fairly narrow “specialization” - they develop only in the area of the meniscus
, cartilage or tendon and are most common in those who are seriously involved in sports.
An accurate diagnosis in the case of such problems can be difficult to make, so serious diagnostic studies are required: not only radiography, but also tomographic diagnostics (CT or MRI) or arthroscopy.
In the process of treating diseases of the knee joint, which are included in this group, the first step is to identify and eliminate the cause that caused the pathological process. Most often, conservative methods are not effective enough, so Israeli specialists usually use surgery as the main method of treating the knee joint for these pathologies.
Contraindications
Neither age nor high body weight are grounds for refusing surgery. The procedure is contraindicated if there are:
- uncontrolled diabetes mellitus and diabetes in the stage of decompensation;
- severe defects of the cardiovascular system;
- renal diseases characterized by impaired nitrogen excretion function of the kidneys (renal failure, etc.);
- liver and pulmonary failure grade 2-3;
- any chronic diseases in the acute phase;
- local and general infectious-inflammatory, purulent focus;
- serious conditions of immunodeficiency;
- paresis or paralysis of the limbs;
- severe forms of osteoporosis;
- severe blood clots in the veins of the lower extremities;
- severe neuropsychiatric disorders.
This is what a diabetic's wound might look like.
Treatment of the knee joint in Israel
The Ilyssa Medical Group medical center offers citizens of Russia, Ukraine, Belarus and other countries effective treatment for pathologies of the knee joints in the best conditions and at reasonable prices. We cooperate with such highly qualified and famous orthopedic surgeons as I. Kazansky, A. Kalganov, E. Atun. etc. By contacting our Israeli medical center, you can be sure that our specialists will do everything possible to ensure that your joints become healthy again.
Treatment of diseases of the hip joint Surgical treatment of atherosclerosis in Israel
Risks of surgery
The probability of complications, as we previously mentioned, does not exceed 2%. In Russia - 6%, this is:
- local infectious process;
- deep vein thrombosis of the legs and pulmonary thromboembolism;
- loosening and instability of the prosthesis;
- dislocations, subluxations, fracture of the endoprosthesis;
- periprosthetic bone fracture;
- persistent pain and contracture.
Infection is one of the most difficult complications to treat.
Why are all these negative reactions happening? They are mainly due to non-compliance with technological principles when installing an implant, incorrectly selected type of prosthesis, unsatisfactory conditions in the operating room, poor-quality rehabilitation, all kinds of limb injuries at any time after surgery and ignoring the rules regarding the physical regime.
Causes
The main causes of knee bursitis:
- Knee injuries range from severe (from falls, impacts) to microtraumas due to regular physical activity on the knees.
- Excessive physical activity due to obesity, carrying heavy objects, and playing strength sports.
- Diseases in which salts are deposited in the joint in the form of microcrystals.
- Arthritis of various natures (rheumatic, psoriatic and others).
- Spread of bacterial infections.
- Autoimmune diseases.
- Arthrosis of the knee joint (gonarthrosis).
- Malfunctions of the endocrine system.
Main symptoms of disorders
Tendon health problems can manifest in different ways, depending on the type of condition.
In general, the following symptoms of such pathologies can be identified:
- pain that increases with palpation;
- swelling;
- hyperemia of the soft tissues above the knee;
- creaking in the joint when moving;
- deterioration in limb mobility.
In case of ruptures, there is a retraction of the muscle to which the connection was broken. As a result, the normal functioning of the bone elements of the joint becomes impossible.
Prevention
To prevent the development of tendon pathologies, care must be taken to follow basic preventive measures.
These include:
- strengthening the immune system to resist infectious diseases;
- prevention of traumatic injuries to the knee joints and their overstrain;
- wearing comfortable shoes;
- timely treatment of any kind of disease;
- control of hormonal levels;
- treatment of spinal pathologies;
- use of vitamin supplements and chondroprotectors;
- doing daily exercises;
- promptly seek help from the hospital if suspicious symptoms occur.
For more information on the topic, watch the video in this article.